
Everything electric boats and boating


Electric Saildrive and Pod Boat Motors
Plugboats Guides Motors News Motors For Sale
Welcome to what we believe is the most complete guide to electric saildrive and pod boat motors. It provides top line details for more than 150 individual motors sorted by power range, style and usage. It has been assembled to provide a single place where someone interested in electric marine propulsion can find comparative information for motors made all over the world.
You may also be interested in our other guides »» Guide to Electric Outboards Under 5kW »» Guide to Electric Outboards Over 5kW »» Guide to Electric Inboards »» Guide to Electric Trolling Motors »» Guide to Electric Boat Batteries
»» Plugboats also has the world’s largest and most complete Directories of over 600 elect ric boats, motors, batteries, accessories, solar panels and rental/charter companies
Information on using this Plugboats Guide
The top of this web page is the Illustrated Guide with photos of the motors and specifications to the right.
Sortable/Searchable Table
At the bottom of the page is a table that can be searched if you know you are looking for a certain type of motor (i.e. pod or saildrive), a certain power range, or for a specific weight/length of boat. If you are going to use the table, the page is best viewed on a computer rather than mobile or tablet.
Illustrated Guide
The motors are organized in alphabetical order by manufacturer, then by style of motor, i.e. fixed pod, steerable pod, saildrive and then by power of motor within those listing. For many styles there are multiple powers of motor available and where that is the case we have made it as easy as possible to line up the motor with its specifications. i.e. if there are three power of motor with different weights, it will be noted as kW: 2kw, 2kw, 3kw • Weight: 10kg, 12kg, 15kg. For some manufacturers the variations are more complicated and we have done our best to make it simple and understandable.
There is a lot of variety in the way manufacturers detail the technical attributes of their products. We have tried to take the most common measurements and assemble an ‘apples to apples’ comparison. See the notes below in ‘Measurements’
The photographs and drawings are from the manufacturers’ websites and are not shown in any consistent scale.
kW • Voltage • Current • HP: Not all manufacturers list all of these specifications. We have included the specifications available and where not available have used the notation N/A.
kW is the kW rating provided by the manufacturer. Most websites do not indicate whether it is input or output kW. When it is indicated, we took the output.
Voltage is most often referred on the sites as ‘Voltage’. Some indicate nominal or peak, we have used nominal and indicated if peak is also referenced.
Current Is noted when the manufacturer supplies the information. Generally it is measured in amperes: A. In some cases the manufacturer uses Amp Hours: Ah and we have noted it where that is used.
HP : is ‘HorsePower equivalent’ so that you can get an idea of the power of the motor in comparison to a HP rating you might be more familiar with. Where available, these measurements come from the manufacturer’s website, and different manufacturers measure the HP in different ways. Some even use metric horsepower, which is slightly different from imperial horsepower. Again, we have tried to make it as apples to apples as possible. (For general guidance, 1kW is round one and a third HP 1kW=1.3HP, or the reverse is that 1HP is around three quarters of a kW: 1 HP = .75kW).
Static Thrust. Torque, Efficiency: This is probably the specification that has the most variability. We have simply given whatever information the manufacturer has published on their website, when available.
Range and Running Time : We have not included estimates of range or running time because it depends on too many factors: battery size (sometimes type also), water conditions, speed, etc. The exceptions are for the ePropulsion and Torqeedo models which have batteries from the manufacturers specifically matched to the motors and therefore provide estimates on their websites.
General : If a manufacturer publishes a specification, we have tried to include it here, even tough other manufacturers may not include the same type of measurement.
Information on this page updated February 4, 2024
You may also want to check our Directory of Electric Boat Motor manufacturers, dealers and distributors around the world, or the Plugboats Marketplace of electric boat motors for sale.

Manufacturers in this Buying Guide: Aquamot • Bellmarine • Combi • Electric Yacht • ELECTRINE • EP Technologies • ePropulsion • E-TECH • Fischer Panda • Gardenergy • Kräutler • Navigaflex • Oceanvolt • Piktronik • Rim Drive Technology • Seadrive • TEMA • Torqeedo
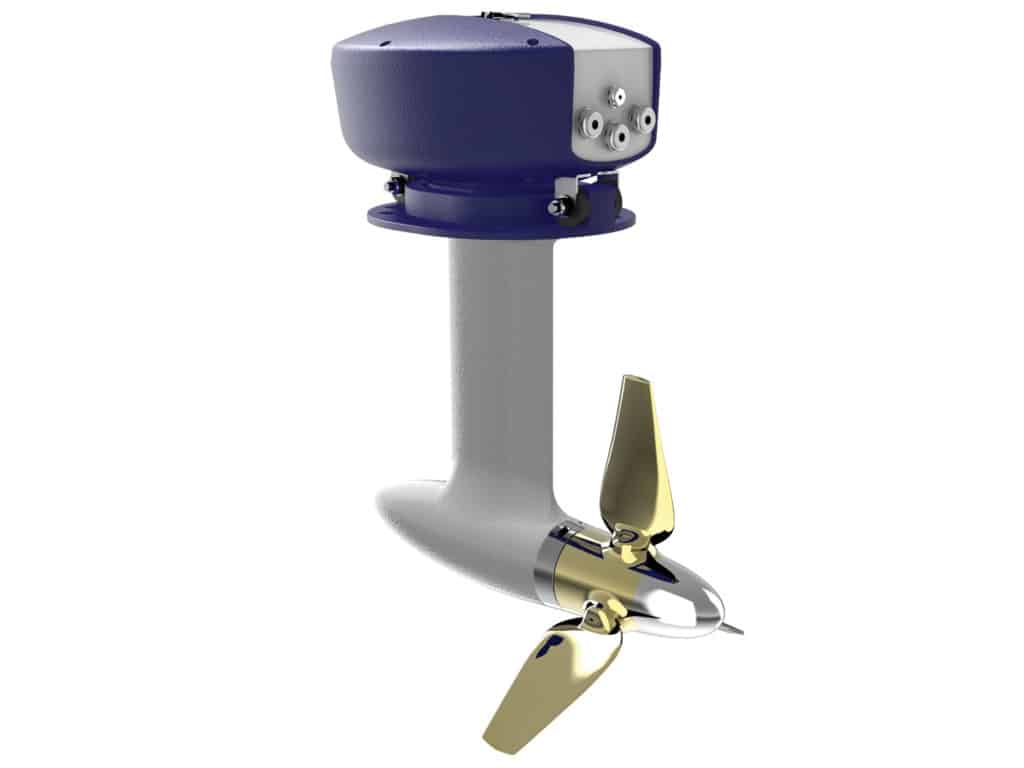
Aquamot was founded in 2003 by engineer Siegmund Hammerstrom and has grown to be a leading manufacturer of electric motors and accessories, including outboards inboards, chargers and batteries. They have two lines of fixed pod motors: Trend and Professional, as well as a line of steerable pods that line up with the power ranges of the Professional line.
Aquamot Trend Fixed Pod 1.1FM and 1.6FM

- Recommended Boat Size: <1.8 tons
- kW : 1.1 / 1.6 • Voltage : N/A • Current : N/A • HP : 3.5 / 5 • Static thrust : 89lbs
- Motor Type : Brushless AC asynchronous • Passive water cooled (motor underwater)
- Weight (kg) : 10.2 / 11.3
- Propeller/RPM : 3 blade fixed, folding optional • RPM : N/A
- Other : Includes: Integrated/removable lithium battery (0.64kWh), charger, display, emergency kill switch. Optional: spare battery, customized compensation wedge, folding propeller ($US 835). Warranty: 2 year limited
- Country of Manufacture : Austria
- Price (MSRP) : $US 2,200 / $2,600
Aquamot Trend Fixed Pod 2.2FM and 4.3FM
- Recommended Boat Size: <4 tons kW : 2.2 / 4.3 • Voltage : 24 / 48 • Current : N/A • HP : 6.4 / 11 • Static thrust : 124 lbs / 197 lbs
- Motor Type : Brushless AC asynchronous• Passive water cooled (motor underwater) Weight (kg) : 12.2 / 13.9
- Other : Includes: Controller, display, basic cables, emergency kill switch. Optional: customized compensation wedge, folding propeller ($US 835). Two year limited warranty.
- Price (MSRP) : $US 3,300 / $3,750
Aquamot Trend Fixed Pod 11.0FM to 25.0FM
- Recommended Boat Size: N/A
- kW : 11 – 25 • Voltage : 48 – 96 • Current : N/A • HP : 28 – 45 • Static thrust : n/a
- Motor Type : Brushless AC asynchronous• Passive water cooled (motor underwater)
- Weight (kg) : 44.3 – 48.9
- Propeller/RPM : 3 blade fixed • RPM : N/A
- Other : Includes: Controller, display, basic cables, emergency kill switch. Optional: customized compensation wedge. Warranty: 2 year limited
- Price (MSRP) : $US 7,150 / $9,915
Aquamot Professional Fixed Pod F10e to F250e

- kW : 1 – 25 • Voltage : 24 – 96 • Current : N/A • HP : 45 – 339 • Static thrust : n/a
- Motor Type : Sensor-less AC asynchronous • Passive water cooled (motor underwater) • Efficiency : 92%
- Weight (kg) : 12 – 50
- Propeller/RPM : 2 blade fixed, folding/feathering optional • RPM : N/A
- Other : Integrated anode, permanently usable for salt or fresh water, maintenance free. Operating efficiency 92%, Included: Custom-made compensation wedge, Controller, throttle, battery monitor, cables, Optional: display, folding/feathering propeller. Warranty: 2 year limited
- Price : N/A
Aquamot Trend Steerable Pod UF10e to UF250e

- Other : Optimized cavitation plate. Permanently usable for salt or fresh water, maintenance free. Operating efficiency 92%, Included: Custom-made compensation wedge, Controller, throttle, battery monitor, cables, Optional: display. Warranty: 2 year limited
»» Bellmarine website
Bellmarine is a very well established electric boat motor company with a history going back to 1999. Along the way they merged with a battery accessory manufacturer and have now been purchased by Transfluid, a large scale industrial motor manufacturer. Bellmarine offers a wide range of electric boat motor configurations, with their saildrive system consisting of their own motor combined with Yanmar drive mechanics. They range from 2kW to 20kW in power with either air or liquid cooling. They also offer a regeneration option. You may want to download the full Bellmarine catalogue
Bellmarine SailMaster Air Cooled Models 2A, 5A, 7A, 10A, 15A, 20A Download .pdf brochure

- kW : Bellmarine uses Nominal and Intermittent kW measurements. These are the intermittent figures: 2, 5, 7, 8, 10, 15, 20 • Voltage : 48V except for the 8A, 15A and 20A models which are 96V • Current : N/A • HP : 2.5, 6.5, 9, 10.5, 13, 20, 25
- Motor Type : Permanent Magnet AC • Air cooled
- Weight (kg) : N/A
- Propeller/RPM : propeller not supplied • RPM : Motor: 1500, Propeller 750 except for 20kW which is Motor 3000, Propeller 1500
- Other : Includes Yanmar SD25 Sail drive leg with 2:1 reduction, motor, controller, , stainless steel motor support brackets.
- Country of Manufacture : Netherlands
Bellmarine SailMaster Liquid Cooled Models 3W, 7W, 10W, 15W, 20W Download .pdf brochure

- kW : Bellmarine uses Nominal and Intermittent kW measurements. These are the intermittent figures: 3, 7, 10, 15, 20 • Voltage : 48V: for all models except 8A, 15A and 20A – 96V: Models 8A, 15A, 20A • Current : N/A • HP : 4, 9, 13, 20, 25
- Motor Type : Permanent Magnet AC • Liquid cooled
- RPM : 1500: Models 2A, 5A, 7A, 8A, 10A, 15A – 3000: Model 20A
»» Combi website
Combi Outboards was founded in 1979 in Giethoorn (‘the Dutch Venice’) to supply rental boats with clean electric power. It is now a leading international supplier of electric propulsion solutions for the maritime market. Combi manufactures inboards, pods, hybrids and outboards. There are six pods ranging in power from 1kW to 3.5 kW: 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3 and 3.5kW. They are available both as fixed pod or steerable pods.
Combi Nautic Fixed Pod/Saildrive Download .pdf brochure

- kW : 1.0 – 3.5 • Voltage : 24 (1.0kW + 1.5kW), 48 (2.0kW – 3.5kW) • Current : 42A – 73A • HP : 4 – 9
- Motor Type : Asynchronous AC • passive water cooled Weight (kg) : N/A
- Propeller/RPM : 3 blade fixed – 220mm or 230mm • RPM : 1050 (3.5kW 1300) Other : “Easy Connect” system delivered Plug & Play for owner installation.
Combi Nautic Steerable Pod Download .pdf brochure
The Steerable Pod Nautic models have the same specifications as the Saildrive models above.

- Motor Type : Asynchronous AC • passive water cooled
- Propeller/RPM : 3 blade fixed – 220mm or 230mm • RPM : 1050 (3.5kW 1300)
- Other : “Easy Connect” system delivered Plug & Play for owner installation.
Electric Yacht
Electric Yacht is one of the premier US suppliers of saildrives. They have developed a Plug-n-Play system that has been engineered for quick, simplified installation as well as long term durability. Their systems offer regenerative power while under the sail. 10 years of proven production with over 450 installs. 3 Year Warranty
Electric Yacht QuietTorque™ 10.0 Sail Drive

- Recommended Boat Size: <6 tons – 34’ (10m)
- kW : 10 • Voltage : 48 • Current : 200A • HP : 10.5
- Motor Type : Brushless PMAC
- Weight (kg) : 45
- Propeller/RPM : 2 or 3 blade, fixed or folding, 12” – 16” • RPM : N/A
- Other : Installs through 9” hole, Anodized aluminum frame and waterproof throttle,Digital Display of: State of Charge (SOC, Voltage, Current, Power, Motor RPM, time to discharge based on current power consumption, updated in real time, Programmable regeneration. 3 Year Warranty.
- Country of Manufacture : USA
- Price (MSRP): $US 11,995
Electric Yacht QuietTorque™ 20.0 Sail Drive
The Electric Yacht Quiet Torque 20 is essentially the 10.0 with twin motors

- Recommended Boat Size: <12 tons – 45’ (14m), catamarans 40’-46’ (12-15m)
- kW : 20 • Voltage : 48 • Current : 400A • HP : 21
- Motor Type : Brushless PMAC X 2
- Weight (kg) : 77 Propeller/RPM : 2 or 3 blade, fixed or folding, 12” – 18” • RPM : N/A
- Other : Installs through 9” hole, Anodized aluminum frame and waterproof throttle,Digital Display of: State of Charge (SOC, Voltage, Current, Power, Motor RPM, time to discharge based on current power consumption, updated in real time, Programmable regeneration. 3 Year
- Warranty.
- Price (MSRP): $US 14,695
Also: Electric Yacht QuietTorque™ 30.0 Sail Drive (boats <14 tons) Electric Yacht QuietTorque™ LC 45 Sail Drive (boats <17 tons) Electric Yacht QuietTorque™ LC 60.0 Sail Drive (boats <22 tons)

- Recommended Boat Size: 14 tons – 22 tons, 45’- 60′ (15-18m)
- kW : 30 – 60 • Voltage : 48 – 96 • Current : 300Ah – 600Ah • HP : 48 – 65
- Motor Type : Brushless PMAC X 2 • liquid cooled
- Weight (kg) : 100 – 106
- Propeller/RPM : N/A
- Other : Installs through 9” hole, Anodized aluminum frame and waterproof throttle, Digital Display of: State of Charge (SOC, Voltage, Current, Power, Motor RPM, time to discharge based on current power consumption, updated in real time, Programmable regeneration. 3 Year Warranty.
- Price (MSRP): $US 19,995 – 23,495
»» ELECTRINE website
ELECTRINE is a Korean manufacturer which has focused on maritime electrification since 2010, when the idea of electric mobility was still relatively uncommon. The company was known as LGM until 2020 and has had a consistent R&D effort for many years. They manufacture electric outboards, inboards and saildrives as well as accessories and Lithium-ion batteries using a Carbon Nano Tube heat exchanger technology. Ther are 6 motors in their eSaildrive line, ranging from 8 kW to 110 kW.
ELECTRINE eSaildrive line: S-8, S-16, S-25 (shown), S-40, S-80, S-110

- Recommended Boat Size: Daysailer / Racing / Monohull /Multihull
- kW : (Max) 8, 16, 25, 40, 90, 110 • Voltage (Vdc): 48, 48, 96, 96, 345.6, 345.6
- Motor Type : N/A
- Weight (kg) : 40.5, 46.5, 50.5, 172, 198, 218
- Other : Hydrogeneration on 8kW and 16kW models. ELECTRINE also makes batteries customized for the motors
- Country of Manufacture : Korea
- Price (MSRP): N/A
EP Technologies
»» ep technologies website.
EPTechnologies is a complete marine propulsion provider for electric and hybrid vessels. The company specializes in custom electric and hybrid systems, but also has ‘off the shelf’ motors, including a range of saildrives. Their Electric Turnable Saildrive offers 360-degree rotation, the key advantage being that no additional thruster is required behind the boat. Other saildrives (SD-25, SD-60, SD-15) have a fixed lower unit. All saildrives are include a complete system utilizing batteries designed and built by EP Technologies.
EP Technologies Turnable Saildrive

- kW : 25 – 60
- Voltage (VDC): 100 – 800
- RPM : 500 – 2000
- Other : 360° Rotatable, Electric servo motor, Joystick Control
- Country of Manufacture : Denmark
- Price : Contact EP Technologies
EP Technologies Saildrives: SD-25, SD-50, SD-15

- kW : SD-25: SD-60: 25, 39, 60, SD-15: 65, 95
- Voltage (VDC): SD-25: 48, SD-60: 100 – 800, SD-15: 400 – 800
- RPM : SD-25: 1000 – 2000, SD-60: 500 – 2000, SD-15: 500 – 2000
ePropulsion
»» epropulsion website.
ePropulsion was founded in 2012 by three engineers from the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST). The company continues to have a strong engineering culture where each engineer is individually responsible for creating as much value for users as possible. ePropulsion offer two pod models based on their outboards: the 1kW Spirit and 3kW Navy.
Click here to view motors from ePropulsion dealers in the Plugboats Marketplace
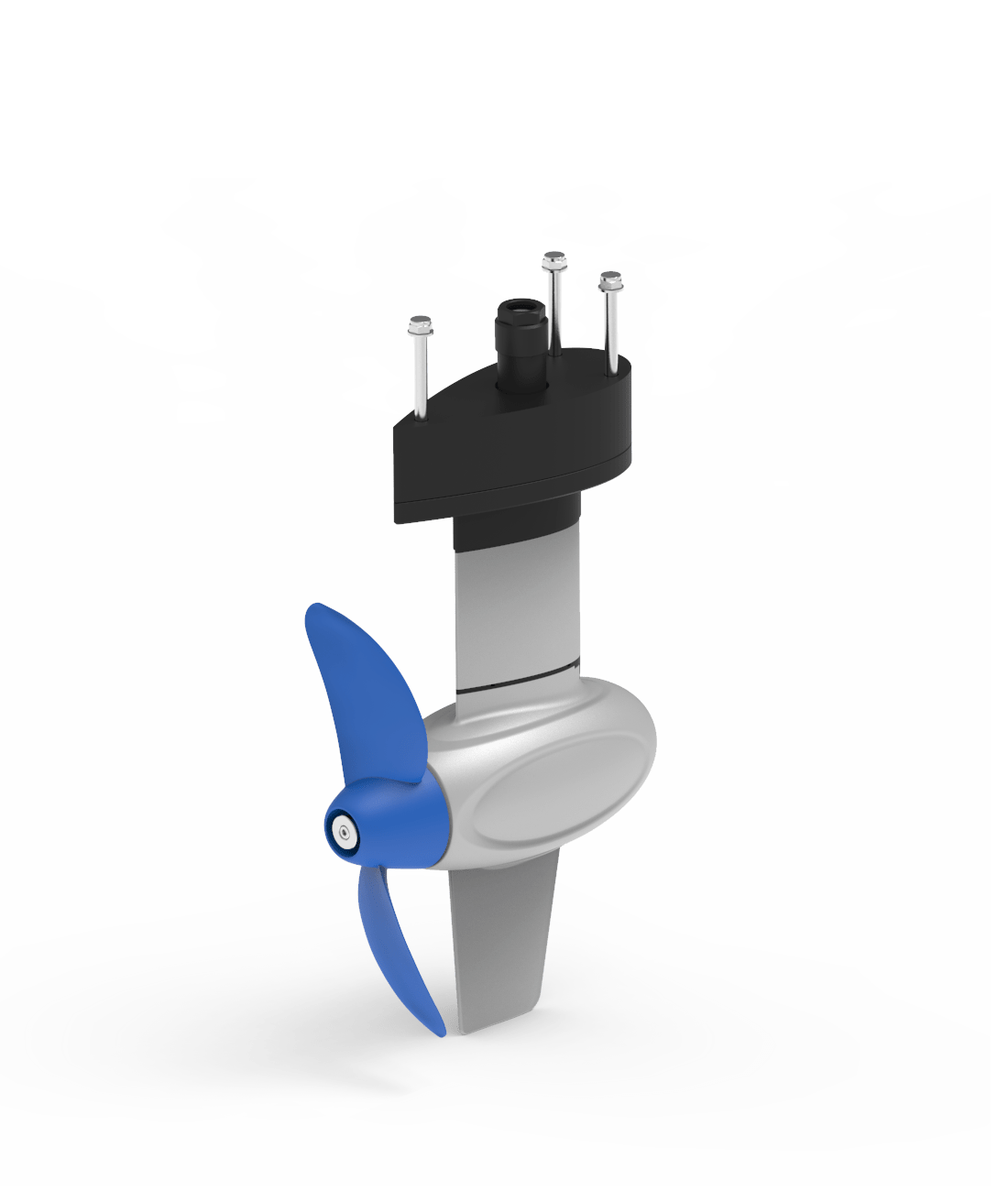
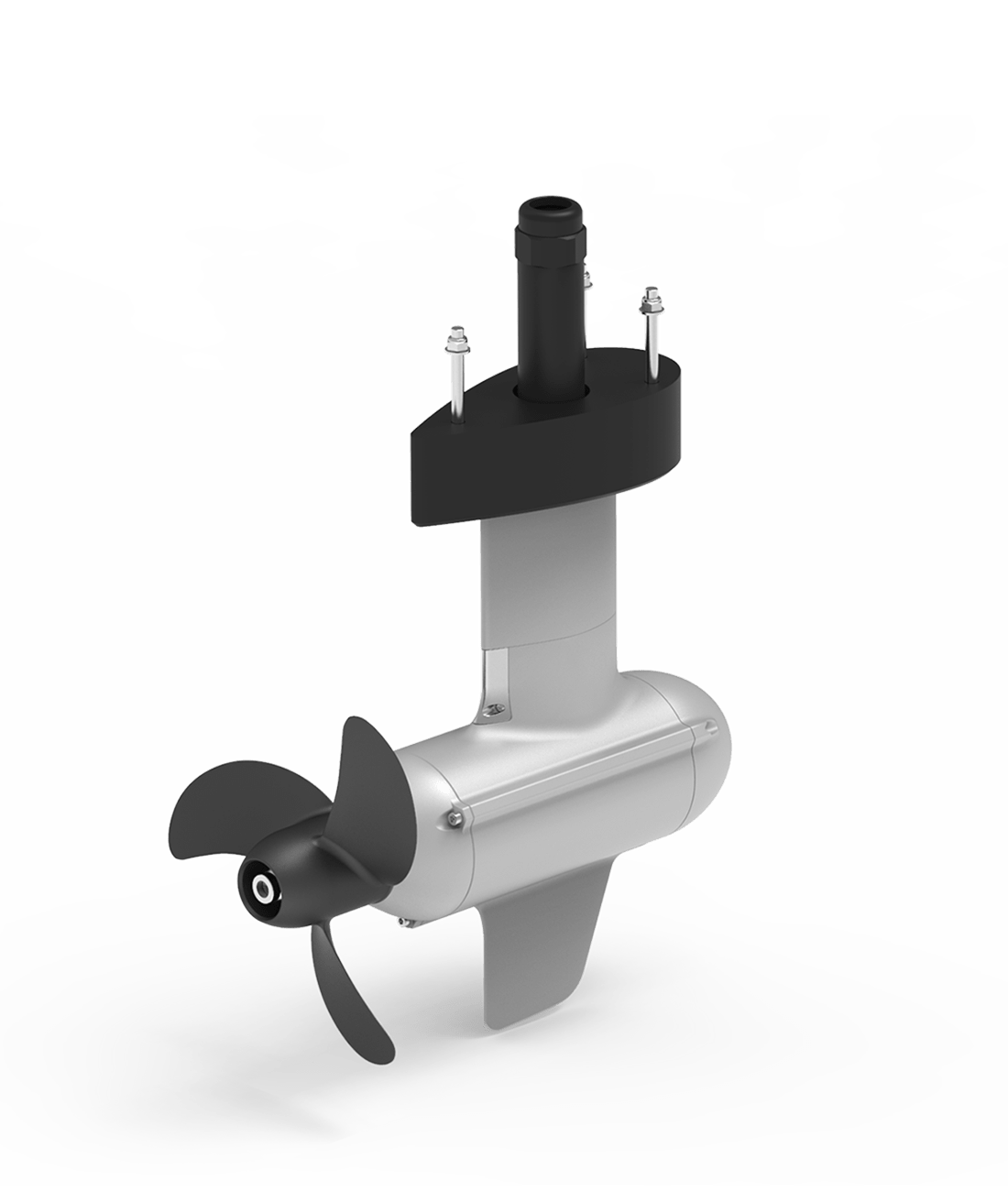
ePropulsion Pod Drive Evo 1.0 , 3.0, 6.0

- kW : 1, 3, 6 • Voltage : 40.7, 48 • Current : 25A, 62.5A • HP : 3, 6, 9.9 Static Thrust : 71, 132.6
- Weight (kg) : (Including integrated battery) 14.1, 15.6
- Propeller/RPM : Spirit: 2 blade, 28 × 14.7 cm (11′ × 5.8″), Navy: 2 blade, 26 × 17.1 cm (10.2″ × 6.7″), RPM: Spirit 1200, Navy 2300
- Other : Hydrogeneration, Includes battery and wireless remote controller (cable option also), Spirit has 1.1 kWh lithium battery, Navy has 3.0 kWh
- Country of Manufacture : Hong Kong/China
»» E-TECH website
E-TECH is a subsidiary of boatbuilder Starboats that was started in 2008 because they were dissatisfied with other electric motor offerings in the market at the time. The company has developed fixed pods, steerable pods and outboard motors that all utilize an in-water BLDC (BrushLess DC permanent magnet) pod motor in a watertight aluminum casing. There are 5 pod models available in both fixed pod and steerable pod configuration. All of these are equipped with the ruddershaft, tube and steering lever. There are also 4 models of high torque pods available only in fixed pod format.
Click here to view motors from E-TECH dealers in the Plugboats Marketplace
E-TECH 4 POD, 7 POD, 10 POD, 15 POD, 20 POD Link to Fixed Pod Motors • Link to Steerable Pod Motors Download .pdf brochure

- kW : 4.3, 7.5, 10.9, 16.6, 19.5 • Voltage : 48, 48, 48, 72, 96 • HP : ≈ 6, 10, 15, 22, 27 • RPM : 1350, 1350, 1470, 2240, 2200
- Motor Type : Brushless PMDC • water cooled
- Other : Includes controller, display with battery monitor, joystick (side- or top mounting), 2m steering cable, 5m connecting cables between controller and steering position (standard 5 meter).
- Country of Manufacture : Poland
The four High Torque E-TECH PODH engines are designed for those applications where a very high torque is needed.
E-Tech High Torque PODH: 13 POD, 18 POD, 23 POD, 35 POD Download .pdf brochure

- kW : 11.9, 16.7, 21.5, 33.7 • Voltage : 48, 72, 96, 144 • HP : ≈ 16, 23, 29, 45 • RPM : 760, 1140, 1520, 2500
Fischer Panda
»» Fischer Panda
Fischer Panda is one of the world’s best known manufacturers of marine generators but are also manufacturers of high quality electric boat motors, sometimes marketed under the ‘Whisperprop’ name. They have an “EasyBox” system that is intended to take the guesswork and complication out of purchasing electric boat motors.
Fischer Panda 48V Underwater Drive System (Easybox) Download .pdf brochure

- kW : 3.8 – 20.0 • Voltage : 48 • Current : N/A • HP : 5 – 25
- Motor Type : Brushless Permanent Magnet (PMAC)
- Weight (kg) : 18.7 – 120
- Propeller/RPM/Torque : Propeller not included • RPM : 600 – 2500 Torque (nM) : 28 – 320
- Other : Includes: Fischer Panda EasyBox control unit, control panel, throttle Options: Propeller, propeller protector, battery bank, charger, shore power connection.
- Country of Manufacture : Germany
Fischer Panda EasyBox HV High Voltage System Fischer Panda Download Centre

- Recommended Boat Size: <40 tons
- kW : 50, 80, 100 • Voltage : 360 – 420 • Current : N/A • HP : 65 – 125
- Weight (kg) : 42
- Propeller/RPM/Torque : 5 blade fixed • RPM : 1200 / 1900 Torque (nM) : 398 – 400
- Other : These motors are generally designed for use by small public transportation ferries, commercial working vessels and privately owned leisure yachts. Systems should be customized.
»» Gardenergyy website
Gardenergy is an Italian company established to offer ‘a simple and reliable product featuring cutting-edge technology’. They use the same motors in a variety of ways, cleverly configuring them for outboard, inboard shaft drives, and either fixed pods or steerable pods.
Gardenergy Pod
To see options and download .pdf brochures, go the Gardenergy site and click on ‘Links’. A pop up will appear with options. There is also an option for price list and a Configurator which can help with system assembly and pricing.
There are five Gardenergy pods with power input of: 2kW, 4.3 kw, 6kW, 8kw, 10kW. They are available as fixed or steerable pods.

- kW : 2, 4.3, 6, 8, 10 • Voltage : 48 except for 2kW which is 24V • Current : N/A • HP : 2.5, 5.5, 7.5, 10, 13
- Motor Type : PMAC
- Propeller/RPM/Torque : 3 blade fixed, folding available • RPM : 2kW: N/A, 4.3kW: 1450, 6kw: 1600, 8kW: 1750, 10kW: 1950
- Country of Manufacture : Italy
- Price (MSRP): Download MSRP Price List $US 3,975 – 6,625
»» Kräutler website
Kräutler is a long-established Austrian manufacturer of industrial electric motors. They began construction of electric boat motors in the 80’s mainly because they could not find a product that would live up to the standards of founder Oswald Kräutler. They make motors for industrial and ship use as well as recreational boats and probably offer the widest range of sailpods and saildrives on this page with everything from small .5kW steerable pods to electrically rotatable saildrives with power up to 30kW.
An explanation about the Kräutler section of this guide: The Kräutler fixed pods are available with AC motors (ACV) or DC motors (GPV). The AC are for smaller boats. They also come in two different configurations: fixed propeller and folding propeller. In the interests of making this page shorter, we have divided them in to the motor types for the written descriptions but have shown you the fixed and folding options in the images. In the table each of the motors has a separate listing. NOTE: The GPV motors are only suitable for short use in salt water.
Krautler Submersible Flange Motor Pods with D C motors Download .pdf brochure

- MOTOR TYPE: GPV
- Recommended Boat Size: <1.9 tons
- kW : 0.5, 0.8, 1.6, 2.2 • Voltage : 24 except for 2.2kW which is 36V • Current : 21, 34, 67, 61 • HP : 0.5, 1.0, 1.8, 2.5
- Motor Type : GPV: DC motor with permanent magnets, continuous control
- Weight (kg) : 14, 15, 20, 20
- Propeller/RPM/Torque : 3 blade fixed or folding (see intro note above) • RPM : N/A • Torque : N/A
- Other : ATTENTION: GP motors are only suitable for short use in salt water. Includes: Motor, bracket, electric regulation system, throttle, status display monitor, battery monitor, cables, battery master switcher & fuse, propeller, anode. Operating efficiency 85%
- Price (MSRP):
Krautler Submersible Flange Motor Pods with AC Motors Download .pdf brochure

- MOTOR TYPE: ACV
- Recommended Boat Size: <10 tons
- kW : 1.8, 2.0, 4, 8, 10 • Voltage : 24 (1.8, 2.0kW) 48 (4, 8, 10kw) • Current : 100, 107, 104, 202, 250 • HP : 2.3, 2.5, 5, 10, 13
- Motor Type : ACV: AC brushless three phase asynchronous motor
- Weight (kg) : 21, 29, 29, 40, 50
- Other : Includes: Motor, bracket, electric regulation system, throttle, status display monitor, battery monitor, cables, battery master switcher & fuse, propeller, anode. Operating efficiency 75% – 83%
Krautler Submersible Pod with Tiller Handle Download .pdf brochure

- MOTOR TYPE: ACV or GP
- Recommended Boat Size: Sailboat: <10 tons, Powerboat: <6 tons
- kW : 0.5 – 10 • Voltage : 24, 48 • Current : 21 – 250 • HP : 0.5 – 13
- Motor Type : ACV: AC brushless three phase asynchronous motor • GP: permanent magnet with continuous control
- Weight (kg) : 15 – 54
- Propeller/RPM/Torque : 3 blade fixed • RPM : N/A • Torque : N/A
- Other : Includes: Motor, bracket, electric regulation system, throttle, status display monitor, battery monitor, cables, battery master switcher & fuse, propeller, anode. Tubes/diaphragms available for installation. Standard shaft length: 450mm. Operating efficiency 75% – 85%
Krautler Saildrive Compact Download .pdf brochure

- Recommended Boat Size: <4 tons
- kW : 2.0, 3.0, 4.0 • Voltage : 24, 36, 48 • Current : 104, 100, 99 – 250 • HP : 0.5 – 13
- Motor Type : AC brushless three phase asynchronous motor with continuous control
- Weight (kg) : 42, 42, 42,
- Propeller/RPM/Torque : Propeller not included • RPM : N/A • Torque : N/A
- Other : ATTENTION: SDK drives are only suitable for short use in salt water. Includes: Motor, saildrive gear, base plate for lamination (depending on motor size), electric regulation system, throttle, status display monitor, battery monitor, cables, battery master switcher & fuse. Operating efficiency 80%, 83%, 84%
Krautler Saildrive Fixed Download .pdf brochure

- Recommended Boat Size: Sailboat: <30 tons, Powerboat <12 tons
- kW : 2.5 – 30.0 • Voltage : 24 – 144 • Current : 104 – 370 • HP : 3.5 – 40
- Motor Type : AC brushless three phase asynchronous motor with continuous control. MOTORS 15.0 – 30.0kW are water cooled.
- Weight (kg) : 45 – 91
- Other : ATTENTION: Water cooled drives are only useable in seawater with 2-circle water cooling. ATTENTION: SDK drives are only suitable for short use in salt water. Includes: Motor, saildrive gear, base plate for lamination (depending on motor size), electric regulation system, throttle, status display monitor, battery monitor, cables, battery master switcher & fuse. Operating efficiency 85% – 88%
Krautler Saildrive Mechanical Rotatable: 2 x 45° Download .pdf brochure

All of the Krautler motors with specs shown in the fixed saildrives above can be installed with a mechanical rotatable option shown here or electric rotatable option shown below. The Sail-Drive is supplied with a fiberglass foundation base, which can be laminated to the hull (depending on motor size). For existing Volvo and Yanmar foundations the Sail-Drive is equipped with an adapter plate and can be screwed directly on the existing foundation.
Krautler Saildrive Electric Rotable: 2 x 90° or 360° Download .pdf brochure

All of the Krautler motors with specs shown in the fixed saildrives above can be installed with an electric rotatable option shown here. The Sail-Drive is supplied with a fiberglass foundation base, which can be laminated to the hull (depending on motor size). For existing Volvo and Yanmar foundations the Sail-Drive is equipped with an adapter plate and can be screwed directly on the existing foundation. The electrical rotating mechanism includes an actuating drive with gearbox, electric regulation system for the drive, a steering lever and display.monitor indicating propeller position
»» Navigaflex website
The innovative Navigaflex motor has a Patent Pending design in which the motor itself retracts and pivots and can attached to the boat as an outboard or inboard motor. The motor is made with a minimum of parts, a light construction and is adaptable to all boat hulls. The standard motor can also be ordered with a “booster” to double the power for up to 2 minutes.
Navigaflex Motor

- Recommended Boat Size: 2 tons / 8m – 16 tons / 18m kW : 6kW, 8kW, 10kw, 15KW • Voltage : 48 (nominal) • HP : 8, 11, 13.5, 20
- Motor Type : Brushless Permanent Magnet (PMAC) • Water cooled (10kW and 15KW)
- Weight (kg) : 54 (4KW) – 68 (15KW)
- Propeller/RPM : 2 blade fixed • RPM : N/A
- Other : Retractable motor, Option to regenerate the current under sails, Digital motor controller with touch screen and mobile phone connected remotely.
- Country of Manufacture : Switzerland
- Price : $US 8,000 – 16,000
»» Oceanvolt website
Oceanvolt is one of the best known names in saildrives and its ServoProp regenerating system is regarded as one of the first and best. It is difficult to provide full information about their systems because their website encourages customers to provide information for customized solutions. These are some basics
Click »» here to see Oceanvolt motors for sale from vendors in the Plugboats Market
Oceanvolt SD Saildrive See more detailed information

- Recommended Boat Size: < 80 ft / 25m
- kW : 6, 8, 10, 15 • Voltage : 48 • HP : 8, 11, 13.5, 20
- Motor Type : Synchronous permanent magnet • Closed circulation liquid cooling provides cooling and lubrication
- Weight (kg) : 42.5, 42., 46.5, 46.5
- Propeller/RPM : Propeller not included • RPM : 2200 • Gear Reduction Ratio : 1.93: 1
- Other : Includes: Battery communication kit, hydrogeneration feature • Sold separately: Batteries, Charger, Propeller • Sail Drive with 1.93:1 reduction. Closed circulation liquid cooling provides cooling and lubrication. 10kW and 15kW systems include 15.2kWh Li-ion battery bank, charger
- Country of Manufacture : Finland
- Price : $US 13,500 – 45,000
Oceanvolt Servoprop Saildrive

The Oceanvolt ServoProp is a patented variable pitch sail drive that ‘combines a high efficiency sail drive with the most powerful hydro generator on the market’. Unique feature is the possibility to turn the propeller blades more than 180 degrees. The software controlled variable pitch sail drive adjusts the pitch of the propeller blades automatically so that the power generation and power output are optimal. The blades are designed to give the system maximum efficiency in forward, reverse and regeneration. With the blades set to the neutral sailing position, the propeller creates extremely low drag similar to the drag of a feathering propeller. ServoProp is capable of generating more than 1 kW at 7-8 knots & 3 kW at 11-12 knots.
»» Piktronik website
Piktronik is an Austrian-Slovenian company working on the research, development and production of components for electrical vehicles (EV) and boats. Their pods are available in a variety of configurations that vary by the power output. We have noted that below. They also sell motors as complete systems with batteries and chargers.
Piktronik UWM1 – UMW10 On arriving at the linked page, there are links for each motor to download more information

- kW : 1, 2, 5, 6.5, 10 • Voltage : 16, 17, 30, 30, 30 • Current : 50, 92, 120, 150, 200 • HP : 1.4, 2.7, 6.8, 8.8, 13.6
- Motor Type : PMSM (permanent-magnet synchronous)
- Weight (kg) : 18, 23, 25, 51, 95
- Propeller/RPM/Torque : 2 blade fixed – 4 blade fixed • RPM : 1100, 1200, 1850, 1200, 1000 • Torque (nM) : 7, 14, 27, 51, 95
- Other : Aside from the complete system detailed below the motors alone come in different configurations: 1kW and 2kW: steerable pod or fixed pod, 5kW: steerable pod, fixed pod, transom mount, 6.5kW: steerable pod or transom mount, 10kW: steerable pod or transom mount
- Country of Manufacture : Slovenia
Piktronik SYS Systems 1kW – 10kW On arriving at the linked page, there are links for each motor to download more information

Piktronic sells their motors in complete system kits for each of the motor sizes detailed above. Complete system includes: motor, motor controller, display monitor, cables, siwthces, fuses, battery charger, remote comtrol, steering arm, installation tube, tiller handle, propeller
Rim Drive Technology
Click here to view RIM Drive Technology motors for sale in the Plugboats Marketplace
»» Rim Drive Technology website
Rim Drive technology is a Netherlands company with a line of rim motors in which the propeller blades are affixed to a rim rather than a central hub. There are no wearing parts within the motor and much reduced chance of weeds or other debris snagging or clogging. The motors are available as outboards, pods, azimuths and thrusters. The company offers complete systems or standalone batteries, controllers, monitors and other accessories. The pods in the Guide are sorted as 24V, 48V and 48V+. All pods are available with extended shaft options to reduce hull effects on the rim drive water flow for quieter and smoother operation.
24V Pods POD 3.0, POD 5.0

- kW : 3.0, 5.0 • Voltage : 24 • HP : 6.5, 11.0 • Thrust (kg) : – 31, 62
- Battery : Sold separately, recommended LiFePO4 available from Rim Drive
- Running Time : Suggested 4-5 hours with recommended Rim Drive battery pack
- Shaft Length (cm) : N/A extended shaft length available
- Propeller Diameter (mm) : 86, 133
- Weight (motor only) (kg) : 3.5, 5.0
- Other : One year warranty for non-commercial use, Completely waterproof (IP68), Efficiency 90+, Includes 2m cable set
- Price : €3,340, €4,000
48V Pods: 5 motors POD 0.5, POD 3.0, POD 5.0, POD 11.0, POD 15.0
- kW : 0.5, 3.0, 5.0, 9, 11, 16 • Voltage : 48 • HP : 1, 6.5, 10, 20, 28 • Thrust (kg) : – 7, 31, 62, 156, 250
- Running Time : Up to 7 hours with suggested Rim Drive battery pack
- Propeller Diameter (mm) : 65, 86, 133, 212, 341
- Weight (motor only) (kg) : 2.5, 3.5, 5.0, 14.0, 70.0
- Price : €3,300, €3,400, €4,000, €6,850, €18,000
96V, 110V, 400V Pods POD 25.0, POD 30.0, POD 50.0

- kW : 25, 30, 50 • Voltage : 96, 110, 400 • HP : 42, 52, 74 • Thrust (kg) : – 380, 400, 750
- Running Time : Average 3 hours with suggested Rim Drive battery pack
- Propeller Diameter (mm) : 341, 341, 341
- Weight (motor only) (kg) : 70, 70, 75
- Price : €25,000, €25,000, €48,000
Steerable Pods (8 models) Steerable POD 3.0, 5.0, 8.0, 11.0, 15.0, 25.0, 30.0, 50.0
- kW : 3, 5, 8, 11, 15, 25, 30, 50 • Voltage : 48, 48, 48, 48, 48, 96, 110, 400-550 • HP : 42, 52 • Thrust (kg) : 31, 62, 120, 156, 195, 350, 400, 750
- Weight (kg) : 21.5, 23, 32, 32, 37, 110, 110, 110
- Other : Rotatable up to 200 degrees, Waterproof hull passthrough, Stainless steel or glass fibre seal available, Salt water resistant (IP68), Motor controller included, Joystick, steering wheel or CAN controlled
- Price : €7,350, €8,225, €12,075, €12,375, €14,900, €31,995, €31,995, €55,500
»» SeaDrive website
SeaDrive is a Norwegian manufacturer that has an innovative approach to pods, saildrives and all electric boat motors for which they received a nomination for a 2019 DAME Award. The concept is that the basic motors can be configured: fixed pods, steerable pod, a saildrive or lift-up azimuth side pod – also with the ability to have the propellers arranged for push propulsion or pull propulsion. There are also regenerative versions available. The pod motor systems come in three power ratings: 7.5, 15 and 30.
SeaDrive Modular Pods/Saildrives/Lift-Up Azimuths

- kW : 5-7.5, 10-15, 20-30 • Voltage : 48, 96, 144 • Current : NA • HP : 7.5, 15, 32 • Static Thrust: 90, 160, 300
- Weight (kg) : Motor Weight: Aluminum: 20, Bronze 23. Total Weight differs by configuration
- Propeller/RPM/Torque : Fixed or folding • RPM : N/A • Torque N/A
- Other : re-generative versions and TABLET/PC control.
- Country of Manufacture : Norway
»» TEMA website
TEMA is a Croatian company that makes highly regarded electric motors that can be purchased alone or in systems for marine, industrial and power generation applications. Their saildrive system uses their SPM132 series of very efficient compact permanent magnet motors. The motors operate on either DC or AC voltages and can be powered from battery systems (48 96Vdc) or generators.
TEMA SYS Systems 1kW – 10kW Download .pdf of Systems configuration Download .pdf of SPM Motors

- kW : For each of their models TEMA has dual figures – kW output at 1800/3600 RPM. The 5 models range in listed power from 12/19kW to 35/57kW • Voltage : There 48 and 96 Voltage availble for all models. • Current : 50, 92, 120, 150, 200 • HP : At 1800/3600 RPM they range from 25/39 to 47/76
- Motor Type : PMAC (Permanent Magnet AC), PMS (Permanent Magnet Synchronous) • Air cooled
- Weight (kg) : 73, 93, 110, 130, 148
- Propeller/RPM/Torque : Propeller not supplied • RPM : 1800/3600 across all motors • Torque (nM) : Maximum: 70, 111, 145, 178, 205
- Other : Includes all components: e-motor, motor controller, saildrive, marine throttle, display, plug and play wiring. Efficiency: 95%.
- Country of Manufacture : Croatia
»» Torqeedo website
Torqeedo is the world’s leading manufacturer of electric outboards. The company was founded in 2004 by Dr Christoph Ballin and Dr Friedrich Böbel when they decided they could build a better electric motor than the one on the boat Dr. Ballin had just purchased. The company offers trolling motors, inboards, outboards and pod motors and works with BMW’s battery division as well as partnering with many of the world’s premier boat designers and manufacturers. It may be useful to download the full Torqeedo Catalogue
Torqeedo Cruze FP Pod 2.0 – 4.0 Operating instruction .pdfs can be downloaded from link above

- kW : 2, 4 • Voltage : 2kW: 24, 4kW: 48 • Current : N/A • HP : 6, 9.9 • Static Thrust 155 lbs, 189 lbs
- Motor Type : Brushless External Rotor Motors with Rare-earth Magnets • Operating efficiency 56%.
- Weight (kg) : 15.4, 15.8 Propeller/RPM/Torque : 3 blade fixed or folding • RPM : 1300
- Other : GPS on-board computer & display: Real-time speed, input power. Operates with lithium or AGM/lead-gel batteries, exact battery status and remaining range available when using Torqeedo battery. Emergency magnetic kill switch.
- Price (MSRP): $US 4,549, 4,999
Torqeedo Cruze FP Pod 10.0 Operating instruction .pdfs can be downloaded from link above

- Recommended Boat Size: <10 tons kW : 10 • Voltage : 48 • Current : N/A • HP : 20 • Static Thrust ≤ 405 lbs
- Weight (kg) : 33.5
- Propeller/RPM/Torque : 5 blade fixed or folding • RPM : 1400
- Other : Includes: Remote throttle, integrated on-board computer with GPS-based range calculation, 70 mm² cable set (3 m) including fuse and main switch, plug connector. 2 year warranty.
- Price (MSRP): $8,999
Torqeedo Cruze FP Saildrive 10.0 Operating instruction .pdfs can be downloaded from link above

- kW : 10 • Voltage : 48 • Current : N/A • HP : 20 • Static Thrust ≤ 405 lbs
- Weight (kg) : 37
Torqeedo Deep Blue 25 Saildrive

- Recommended Boat Size: <50 tons
- kW : 25 continuous, 33 peak • Voltage : 345 • Current : N/A • HP : 40 • Static Thrust ≤ 405 lbs
- Motor Type : Brushless External Rotor Motors with Rare-earth Magnets • Operating efficiency 55%.
- Weight (kg) : 125, 314 total system including 1 battery
- Propeller/RPM : Propeller : not included • RPM : 1200
- Price (MSRP): On Request with requirements input
Table: Searchable and Sortable

Get all the latest electric boats and boating news delivered to your mailbox!
Sign up here for the plugboats newsletter..
IT’S FREE!
Email address:
No, thanks.
Terms and Conditions - Privacy Policy
- Spirit 1.0 Plus
- Spirit 1.0 Evo
- Pod Drive Evo
- E-Series Battery
- G102-100 Battery
Find a Dealer
Have a dealer contact me.
- Product Registration
- Support Center: FAQ & Guide
Video Tutorial
- Download Center
- Performance Bulletins
Electric Pod Drive
Space-saving and efficient. popular with sailboats and small watercrafts.
- Pod Drive 1.0 Evo

- Pod Drive 3.0 Evo
- Pod Drive 6.0 Evo
Introducing Pod Drives
ePropulsion pod drives are direc-drive and minimum maintenance electric motors for sailboats and small crafts. They’re space-saving and maximize your cabin space.You hear no noise onboard.
Hydrogeneration Empowers Sailboats
Build a pod drive system, choose your motor.

Choose Your Control
Choose Your Battery

E-Series Lithium Battery
We recommend you choosing ePropulsion original battery. 48V E-Series lithium iron phosphate battery is the perfect match for your Pod Drive.

Unit price is as low as $0.46 per watt-hour.
Incredible Range

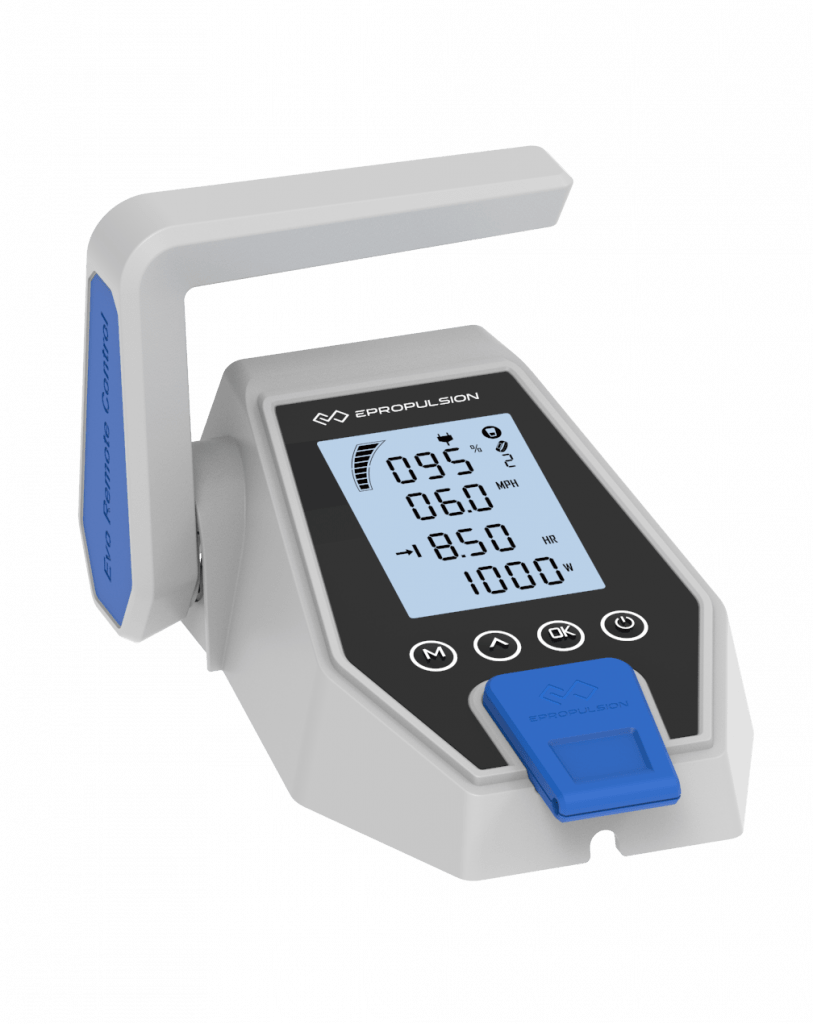
Three Evo Controls
With three controllers available, you can always find a controller that well satisfies your needs.
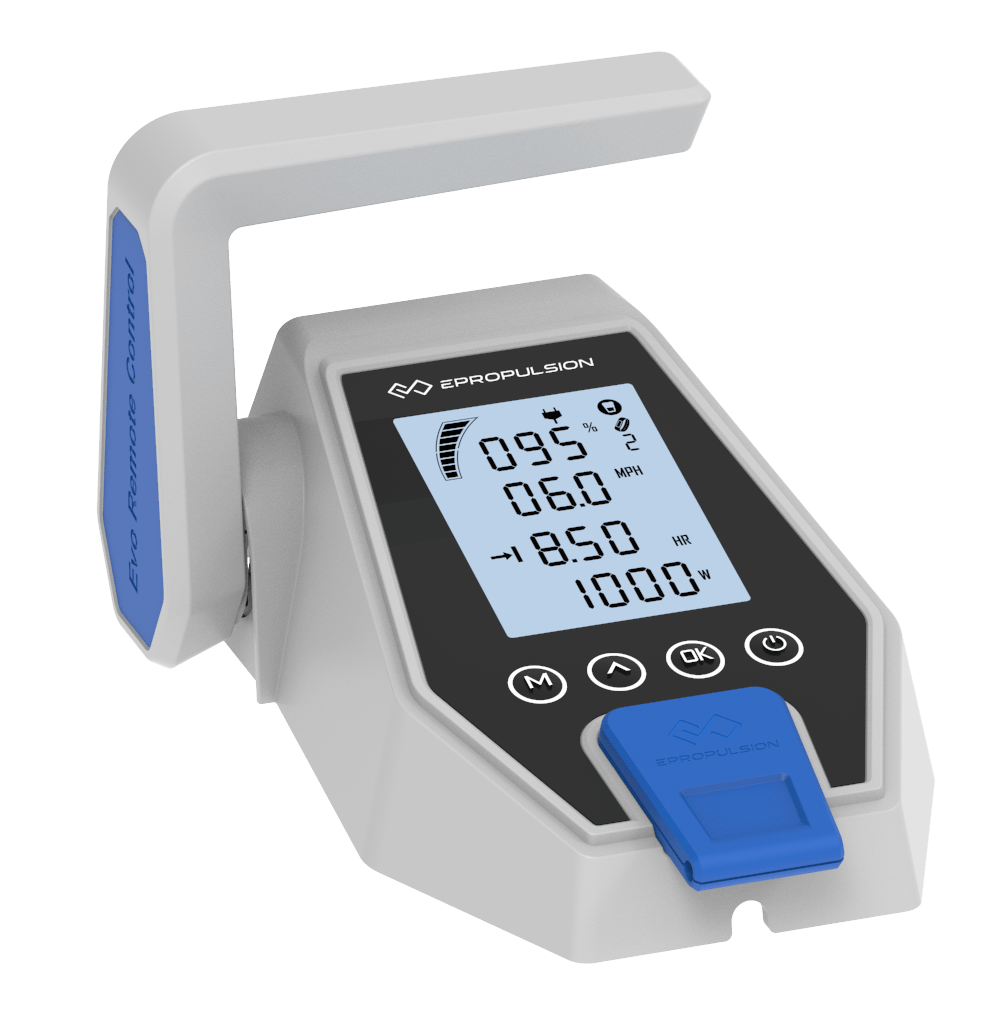

Digital Display
Offers real-time monitoring of the power, remaining runtime, battery level, voltage, etc.
Electric Start
Press the button and you’re ready to go. Saves your trouble pulling the cord to start.
Magnetic Kill Switch
Works as an emergency stop key for ePropulsion electric outboards. Keeps you safe on the boat.
Smooth Throttle Changing
Designed with excellent throttle response and clear throttle hand feel.
Adjustable Max Power Output
Adjustable full throttle power makes the ePropulsion electric boat motors kids-friendly and suitable for rental boats.
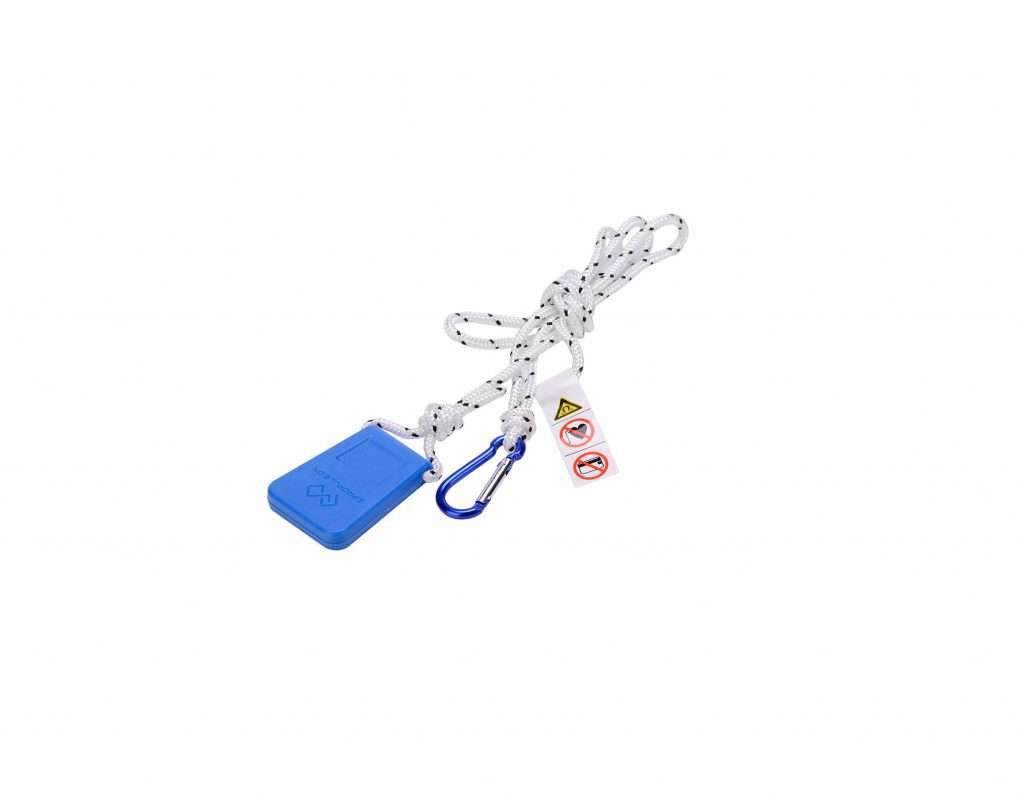
Safety Wristband
Easy-to-use and additional safety.
Man overboard protection
Wireless connection
Waterproof IP67
Max connection up to 8 wristbands per motor
Safety wristband works with Evo Tiller and Evo top mount control only, not compatible with Evo side mount control or Evo dual control.

What's in the Box

Accessories

Can I use E40 to power Pod Drive 3.0 Evo or E80 to power Pod Drive 6.0 Evo?
- Yes, but parallel connection is required. To power one Pod Drive 3.0 Evo with E40, you need two E40 batteries in parallel. To power one Pod Drive 6.0 Evo with E80, you need two E80 batteries in parallel.
- Officially, we recommend the E80 battery for Navy 3.0 Evo, and E175 battery for Navy 6.0 Evo. For more info, please check ePropulsion Tutorial: ePropulsion E-Series Battery | General Instructions
Can I use third-party batteries to power Pod Drive 1.0 / 3.0 / 6.0 Evo?
- First, our original E-Series battery has the best unit price on the market, as low as $0.46 per WattHour.
- Second, the E-Series battery weighs 70% less than the lead-acid battery with equivalent usable capacity, and costs 50% in five-year use.
- Third, because of incompatible communication protocol, when powered by third-party batteries, the ePropulsion motor cannot access real-time battery status and apply the best operation strategy.
- Despite all these, if you still prefer third party lithium or lead-acid batteries. The nominal battery voltage should be 48V. The continuous discharge current should be over 25A for Pod Drive 1.0 Evo, 62.5A for Pod Drive 3.0 Evo and 125A for Pod Drive 6.0 Evo.
Can Pod Drive motor work for saltwater use?
Yes, they’re all designed for extensive use in the saltwater. We choose high-quality aluminum alloy as the base material, and apply hard anodizing coating and teflon coating on top of it. For more info, please check ePropulsion Blog: How do we make an outboard corrosion-resistant?

This site uses cookies to personalize your experience and analyze site traffic. By clicking accept or continuing browsing the site, you are agreeing to our use of cookies. See our Privacy Policy here .
View the Serial Number
PowerFlow Marine
Experience the Power of Clean and Sustainable Propulsion
Upgrade your sailboat today and start enjoying the benefits of electric power on the water!
Electric Motors for Boats
Powerful Performance, Quiet operation, & Easy Installation

B15 (Liquid Cooled)
What our customers have to say about us.

Absolutely wonderful!
Error voluptate adipisci. Quas a delectus optio ut. Non consequatur voluptatem quia rerum cum similique enim.
Jack Nitzsche
Investor Group Coordinator
Electric Power Calculator
Simulate the performance of your vessel under electric propulsion

Don’t Miss Out
Get a free electrification report.
Our complimentary electrification report showcases the seamless integration of our electric motor system into your boat and outlines its impressive performance capabilities.
Passport 42
22kw direct-drive experience.
Sonya & Jack, a couple living on a boat in Mexico transform their Passport 42, Gemini into a fully electric vessel with the Powerflow Marine D22.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Quiet and vibration-free operation
- No exhaust fumes or fuel smell
- Seamless shifting between forwards and reverse
- Having only one moving part significantly reduces potential failure points compared to a diesel engine.
- Zero greenhouse emissions
- No pollution released into your local waterways
- Doesn’t scare away your local wildlife
- Option to be 100% renewable with solar and wind generation
- No more fuel and oil getting all over you and into your bilge
- No more need to carry combustible fuels on board
- Eliminate fuel costs
- Higher energy efficiency
- Charge from solar and wind
- Reduced maintenance cost
- Replacement components are relatively cheap
While sailing, our motor systems can harness wind power to recharge your batteries. Our display enables you to optimize energy capture by adjusting the braking level in real-time to match the sailing conditions. The amount of regeneration depends on various factors, with the propeller size being the primary determinant.
The motor size required for your boat depends on several factors, primarily the vessel’s size, weight, and operating conditions (such as currents, open sea, tides). User preference is also a consideration. As a rule of thumb, for displacement vessels, 1kW of electric power can replace approximately 3HP of diesel power. This may seem contradictory, but diesel motors are typically oversized to make up for their inefficiency and limited power delivery.
To assist you in motor sizing, we have developed an electric power calculator to simulate your vessel’s performance. Additionally, we provide a complimentary electrification report outlining the performance capabilities for your specific boat.
We have engineered our motor with retrofitting sailboats in mind, prioritizing ease of installation without compromising on durability or performance. Our free electrification report includes a 3D model illustrating how our motor system fits within the existing footprint of your diesel motor. We provide custom mounting brackets and shaft lengths to ensure a seamless installation.
Electric motors possess comparable power to diesel motors, while offering additional features that make them highly suitable for marine propulsion. They exhibit greater efficiency, typically 2 to 3 times more efficient than diesel motors, enabling an electric motor with one-third the size and weight to match the power output of a diesel motor. Moreover, electric motors can deliver torque across a broader range of speeds and provide full torque from 0 RPM.
Electric motors offer the advantage of seamless bidirectional operation, eliminating the need for a traditional gearbox with separate forward and reverse gears. While certain applications may still benefit from a gearbox, it would only require a single gear, effectively eliminating the inconvenient clunk often experienced when shifting between forward and reverse.
Customer Projects
July 9, 2023, june 15, 2023.
- BOAT OF THE YEAR
- Newsletters
- Sailboat Reviews
- Boating Safety
- Sailing Totem
- Charter Resources
- Destinations
- Galley Recipes
- Living Aboard
- Sails and Rigging
- Maintenance
- Best Marine Electronics & Technology
The Promises and Pitfalls of an All-Electric Yacht
- By Tim Murphy
- Updated: November 8, 2021
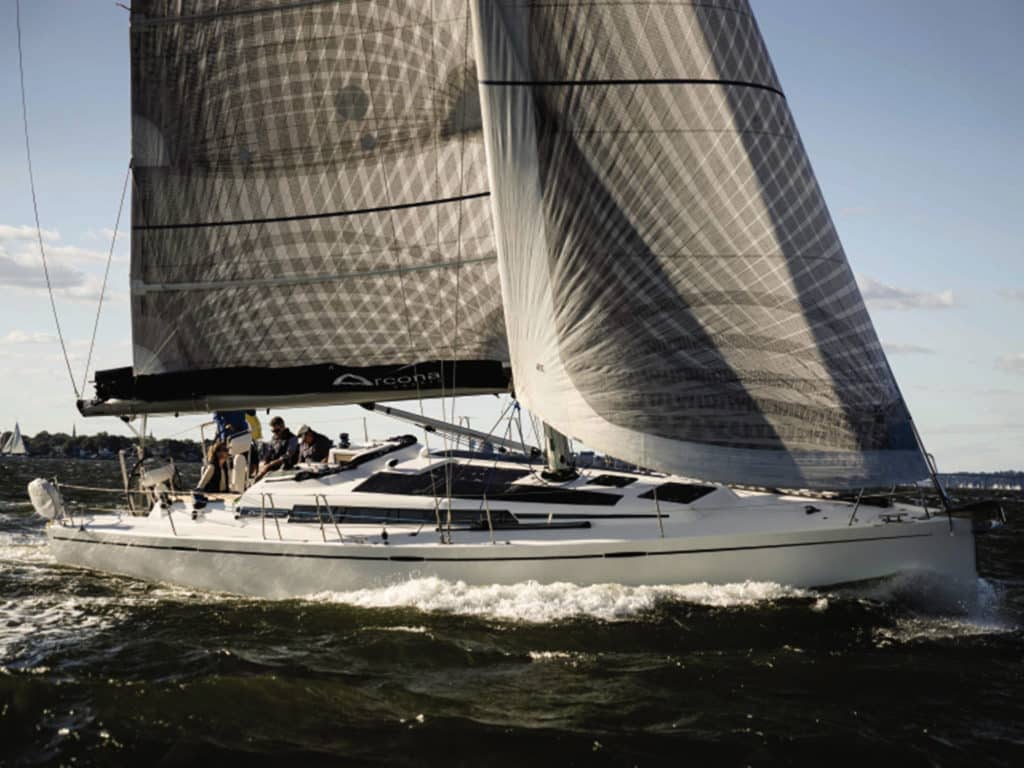

This past October, I saw one of the most interesting exhibits in more than 500 new cruising sailboats I’ve reviewed over two decades. It was the Arcona 435Z, built in Sweden and introduced by Graham Balch of Green Yachts in San Francisco. Balch describes his business as “a new brokerage dedicated to the electric revolution on the water,” and it was the “Z” in the boat’s name, which stands for “zero emissions,” that made this boat so interesting. This was the first electric propulsion system—not hybrid but all-electric —I’d ever seen on a cruising sailboat.
Electric propulsion isn’t new. Since 1879, electric motors have propelled boats; a fleet of some four-dozen electric launches transported visitors around the 1893 Colombian Exposition in Chicago. But cruising sailboats are not launches, and the open sea is not a protected canal. When we’re using cruising boats as they’re meant to be used, they seldom end their day plugged into a shore-power outlet. Cruising boats comprise many devices —stove, refrigerator, freezer, windlass, winches, autopilot, radar, lights—whose power typically comes from a tank of fossil fuel. And today’s cruising sailors are accustomed to using diesel auxiliary power to motor through lulls or punch into headwinds and seas.
Starting about 15 years ago, we saw a wave of diesel-electric and hybrid propulsion systems on production and custom cruising boats ( see “Perpetuated Motion,” CW , March 2005 ). Both of those systems ultimately start with an onboard internal-combustion engine. A diesel-electric propulsion system relies on a running genset to directly power the electric motor that turns the propeller. A hybrid system relies on batteries to power the electric motor, plus an internal-combustion genset to recharge the batteries. One of the promises of a hybrid system is the ability to regenerate electrical power. Regeneration means using boatspeed under sail to turn the propeller, whose spinning shaft sends electrons from the electric motor back through an electronic controller to recharge the batteries. In such a system, the boat’s propeller is both an electrical load (when running under power) and a charging source (when sailing in regeneration mode).
The Arcona 435Z was different from both of these systems: It incorporates no onboard fossil-fuel engine at all. Instead, it has a bank of lithium batteries, several solar panels, and a proprietary propulsion leg that looks like a saildrive. “This boat,” Balch said, “has the very first production unit in the world of Oceanvolt’s newest electric propulsion system, called the ServoProp.”

For our sea trial, Balch was joined by Derek Rupe, CEO of Oceanvolt USA. “If you can sail the boat and you have some solar, you can go anywhere in the world, and you can make all your power underway while you go,” Rupe said. When we spoke in October 2020, he touted three high-profile sailors who were using the Oceanvolt electric propulsion system: Alex Thomson, for his Hugo Boss Open 60 Vendée Globe program; Jimmy Cornell, for his Elcano 500 expedition; and Riley Whitelum and Elayna Carausu, who had been teasing their new boat for months on their popular Sailing La Vagabonde YouTube channel.
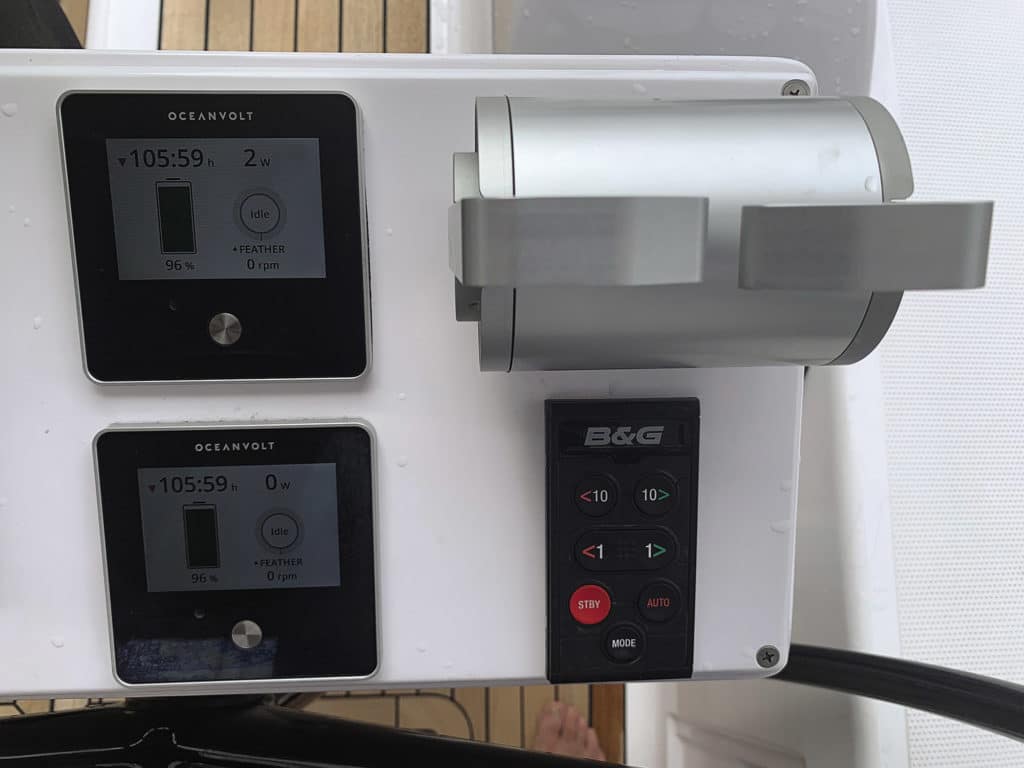
The efficiency of Oceanvolt’s ServoProp and the regeneration from it is the promised game-changer in each of these boats. The ServoProp is a leg with a feathering propeller that can be set for optimal pitch in three modes: forward, reverse and regeneration.
“You don’t need fuel,” Rupe said. “You don’t need to dock; you can go anywhere you want to go and always have the power for living and propulsion.”
That’s the promise. But are there also pitfalls?
Innovation and Risk
Marine electric propulsion is an emerging technology. Compared with the mature and settled technology of diesel engines and lead-acid batteries, electric-propulsion systems—with their electronic controllers and lithium batteries—are in a stage of development best described as adolescent. Every sailor has his or her own tolerance for technical innovation. For the promise of fewer seconds per mile, grand-prix-racing sailors willingly trade a high risk of expensive damage to the sails, rig or the boat’s structure itself; cruising sailors, by contrast, tend to favor yearslong reliability in their equipment as they seek miles per day.
Folks who identify as early adopters take special joy in the first-wave discoveries of a new technology; if they’re clear-eyed about supporting an ongoing experiment, they see themselves as partners with the developers, accepting failures as opportunities for learning. Sailors motivated primarily by changing the trajectory of climate change might be especially willing to modify their behavior to limit their own output of greenhouse gases. Investing in any emerging technology asks you to start with a clear assessment of your own risk tolerance. We’ll return to this theme with one or two real-life examples.

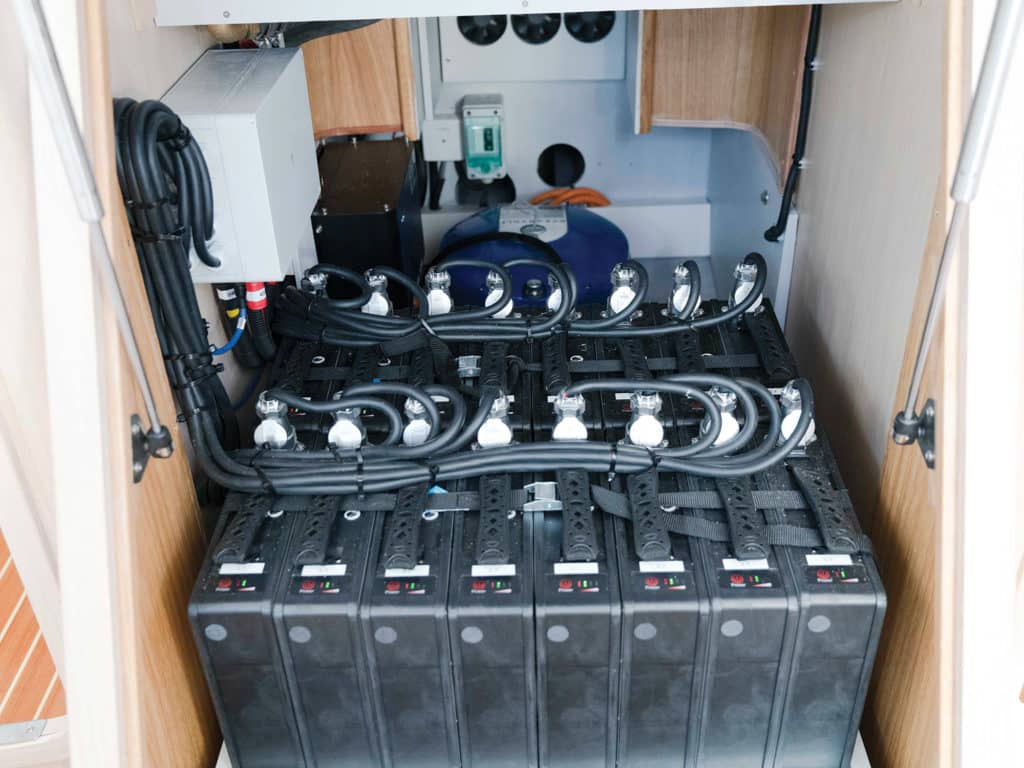
The American Boat and Yacht Council, founded in 1954, sets recommended standards for systems installed on recreational boats. For decades, ABYC has published standards related to installations of diesel and gasoline engines, as well as electrical systems based around lead-acid batteries. By contrast, it was only three years ago that ABYC came out with its first electric-propulsion standard (revised July 2021). And only last year it published its first technical-information report on lithium batteries (a technical-information report is an early step toward a future standard). The takeaway is that if you need help servicing your diesel engine or electrical system built around lead-acid batteries, you can pull into any reasonable-size port and find competent technicians to help you. With electric propulsion and lithium batteries, that pool of skilled talent is significantly scarcer.

To say that a technology is mature simply means that we’ve learned to live with it, warts and all, but that it holds few remaining surprises. Certainly, diesel-propulsion and lead-acid-battery technologies each leave plenty of room for improvement. When a charge of fuel ignites in the combustion chamber of a diesel engine, some three-quarters of the energy is lost in heat and the mechanical inefficiencies of converting reciprocating motion to rotation. Lead-acid batteries become damaged if we routinely discharge more than half of their capacity. During charging, they’re slow to take the electrons we could deliver.
Lithium batteries are comparatively full of promise. Their power density is far greater than that of lead-acid batteries, meaning they’re much lighter for a given capacity. They’re capable of being deeply discharged, which means you can use far more of the bank’s capacity, not merely the first half. And they accept a charge much more quickly; compare that to several hours a day running an engine to keep the beers iced down.

But the pitfalls? Let’s start with ABYC TE-13, Lithium Ion Batteries. Some of its language is bracing. “Lithium ion batteries are unlike lead-acid batteries in two important respects,” the report says. “1) The electrolyte within most lithium ion batteries is flammable. 2) Under certain fault conditions, lithium ion batteries can enter a condition known as thermal runaway, which results in rapid internal heating. Once initiated, it is a self-perpetuating and exothermic reaction that can be difficult to halt.”
Thermal runaway? Difficult to halt? Self-perpetuating?
“Typically, the best approach is to remove heat as fast as possible, which is most effectively done by flooding the battery with water,” TE-13 continues, “although this may have serious consequences for the boat’s electrical systems, machinery, buoyancy, etc.”
If you were following the news in January 2013, you might remember the story of Japan Airlines Flight 008. Shortly after landing at Boston’s Logan Airport, a mechanic opened the aft electronic equipment bay of the Boeing 787-8 to find smoke and flames billowing from the auxiliary-power unit. The fire extinguisher he used didn’t put out the flames. Eventually Boston firefighters put out the fire with Halotron, but when removing the still-hissing batteries from the plane, one of the firefighters was burned through his professional protective gear.
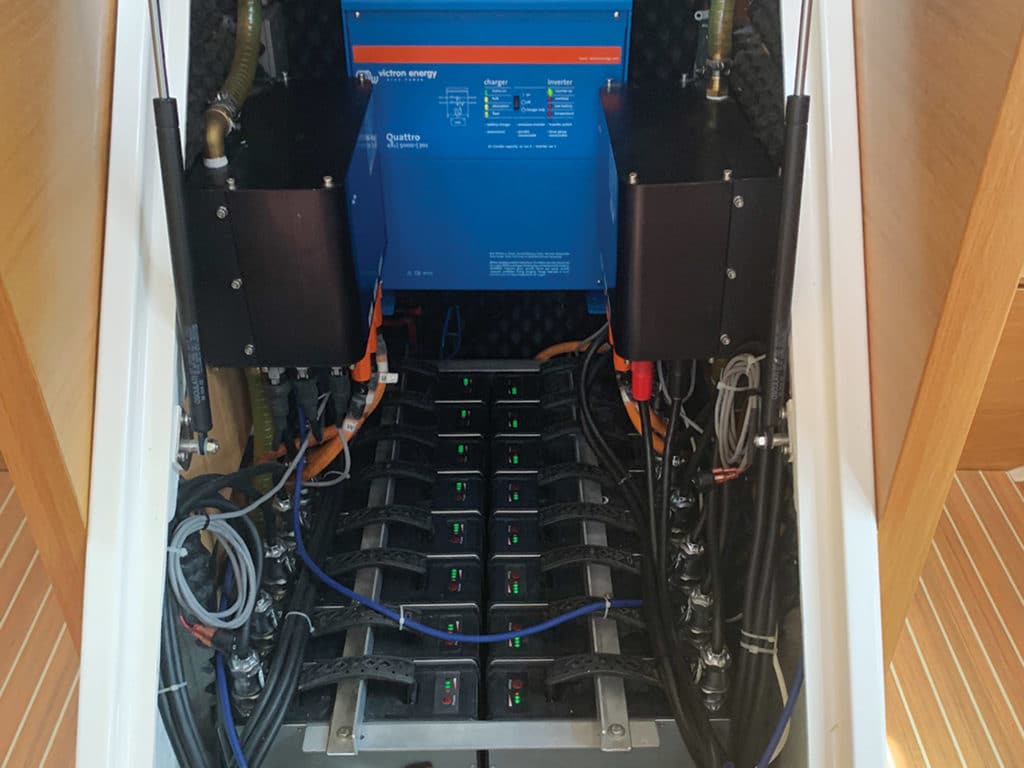

Samsung Galaxy cellphones, MacBook Pro laptops, powered skateboards—in the past decade, these and other devices have been recalled after their lithium batteries burned up. In that period, several high-end custom boats were declared a total loss following failures from lithium batteries. In March 2021, a 78-foot Norwegian hybrid-powered tour boat, built in 2019 with a 790 kW capacity battery bank, experienced thermal runaway that kept firefighters on watch for several days after the crew safely abandoned the ship.
Yes, experts are learning a lot about how to mitigate the risks around lithium batteries. But we’re still on the learning curve.
ABYC’s TE-13 “System Design” section starts, “All lithium-ion battery systems should have a battery management system (BMS) installed to prevent damage to the battery and provide for battery shutoff if potentially dangerous conditions exist.” It defines a bank’s “safe operating envelope” according to such parameters as high- and low-voltage limits, charging and discharging temperature limits, and charging and discharging current limits.
Graham Balch takes these safety recommendations a step further: “To our knowledge, the BMS has to monitor at the cell level. With most batteries, the BMS monitors at the module level.” The difference? “Let’s say you have 24 cells inside the battery module, and three of them stop working. Well, the other 21 have to work harder to compensate for those three. And that’s where thermal events occur.”
Balch followed the story of the Norwegian tour boat this past spring. He believes that the battery installation in that case didn’t meet waterproofing standards: “The hypothesis is that due to water intrusion, there was reverse polarity in one or more of the cells, which is worse than cells simply not working. It means that they’re actively working against the other cells. But if the BMS is monitoring only at the module level, you wouldn’t know it.”
On the Green Yachts website, Graham lists five battery manufacturers whose BMS regimes monitor at the cell level. “If I were sailing on an electric boat, whether it be commercial or recreational, I would feel comfortable with having batteries from these five companies and no other,” he said.
The broader takeaway for today’s sailors is that lithium batteries bring their own sets of problems and solutions, which are different from those of conventional propulsion and power-supply technologies. A reasonably skilled sailor could be expected to change fuel filters or bleed a diesel engine if it shuts down in rough conditions. With lithium-ion batteries aboard, an operator needs to understand the causes and remedies of thermal runaway, and be ready to respond if the BMS shuts down the boat’s power.
Real-World Electric Cruising Boats
When we met Oceanvolt’s Derek Rupe a year ago, he and his wife had taken their all-electric boat to the Bahamas and back the previous season. Before that, he’d been installing electric-propulsion packages for six years on new Alerion 41s and other refit projects. “My real passion is on the technical side of things—installations, really getting that right. That’s half the picture. The technology is there, but it needs to be installed correctly.”
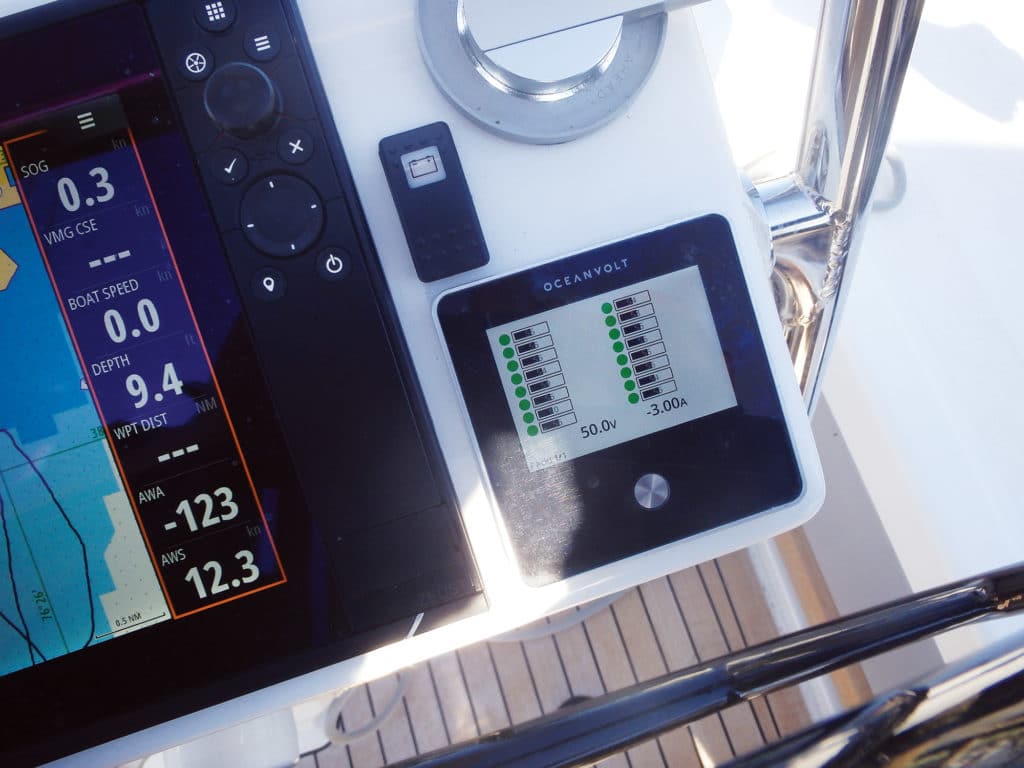
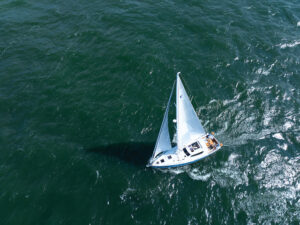
When talking to Rupe, I immediately encountered my first learning curve. I posed questions about the Oceanvolt system in amps and amp-hours; he responded in watts and kilowatt-hours. This was yet another example of the different mindset sailors of electric boats need to hold. Why? Because most cruising boats have just one or two electrical systems: DC and AC. The AC system might operate at 110 or 220 volts; the DC side might operate at 12 or 24 volts. On your own boat, that voltage is a given. From there we tend to think in terms of amps needed to power a load, and amp-hours of capacity in our battery banks. Going back to basics, the power formula tells us that power (watts) equals electrical potential (volts) times current (amps). If your boat’s electrical system is 12 volts and you know that your windlass is rated at 400 watts, it follows that the windlass is rated to draw 33 amps.
But an all-electric boat might comprise several systems at different voltages. A single battery bank might supply cabin lights at 12 volts DC; winches and windlasses at 24 volts DC; the propulsion motor at 48 volts DC; and an induction stove, microwave and television at 110 volts AC. A DC-to-DC power converter steps the voltage up or down, and an inverter changes DC to AC. Instead of translating through all those systems, the Oceanvolt monitor (and Derek Rupe) simply reports in watts coming in or going out of the bank.
“We keep all our thoughts in watts,” Rupe said. “Watts count in the AC induction. They count in the DC-to-DC converter. They count the solar in. They count the hydrogeneration in. And the power-management systems tracks it that way for shore-power in.
“On a boat like this, maybe I have 500 watts coming in the solar panels,” he continued. “So then I can think: ‘Well, my fridge is using 90 watts. My boat has an electric stove. When I cook a big meal, I can see that for every hour we cook, we lose about 10 to 12 minutes of our cruising range.’”
During his Bahamas cruising season, Rupe observed that on days that they were sailing, the combination of solar panels and hydroregeneration supplied all the power he and his wife needed. “When we weren’t sailing,” he said, “we found that we were losing 8 percent each day, in the difference from what the sun gave us to what we were using for the fridge, lights, charging our laptops, and all that stuff.”
Rupe’s solution? “Twice in Eleuthera and once outside Major’s, we went out and sailed laps for a couple of hours because the batteries were below 30 percent of capacity. It was good sailing, and the wind was coming over the shore, so we didn’t have any sea state. We did a couple of hot laps on nice beam reaches, and generated about 700 watts an hour.”
Of the three sailors Rupe touted in October 2020—Alex Thomson, Jimmy Cornell and the Sailing La Vagabonde couple—only Cornell can report back on his all-electric experiences with Oceanvolt. Alex Thomson ended his circumnavigation abruptly last November, just 20 days after the Vendée Globe start, when Hugo Boss collided with an object in the South Atlantic. And at press time in early fall 2021, Riley and Elayna had just recently announced the build of their new Rapido trimaran; keep an eye on their YouTube channel for more about their experiences with the Oceanvolt propulsion system.

As for Cornell—circumnavigator, World Cruising Routes author, creator of the transoceanic rally, and veteran of some 200,000 ocean miles—he suspended his planned Elcano 500 round-the-world expedition solely because of the Oceanvolt system in his new Outremer catamaran. His Aventura Zero Logs on the Cornell Sailing website, particularly the Electric Shock article posted on December 2, 2020, are essential reading for any sailor interested in sailing an electric boat. “Sailing around the world on an electric boat with zero emissions along the route of the first circumnavigation was such a tempting opportunity to do something meaningful and in tune with our concern for protecting the environment that my family agreed I should do it,” Cornell wrote. “What this passage has shown was that in spite of all our efforts to save energy, we were unable to regenerate sufficient electricity to cover consumption and top up the batteries.”
Cornell’s experience in that article is raw, and his tone in that moment bitterly disappointed. We recommend it as essential reading—not as a final rejection of the electric-boat concept or of Oceanvolt’s system, or even as an endorsement of Cornell’s own decision that the system didn’t work. I suspect that I may have arrived at the same conclusion. Yet given the same boat in the same conditions, one imagines that a new breed of sailor—a Graham Balch or a Derek Rupe—may have responded differently to the constraints imposed by an all-electric boat, as nearly every cruising sailor today habitually responds to the inconvenient constraints of diesel engines and lead-acid batteries.
“If you bring electric winches, electric heads and an induction stove, and then sail into a high-pressure system, you’ll set yourself up for failure,” Balch said. “You have to balance your power inputs and your power outputs.
“Sailing an electric boat is a return to the tradition of sailing that the crutch of a diesel engine has gotten us away from,” he added. “Magellan’s fleet got all the way around the world, and they didn’t have a diesel engine.”
Tim Murphy is a Cruising World editor-at-large and longtime Boat of the Year judge.
- More: Green Wakes , Hands-On Sailor , navigation , print nov 2021 , sailboat review , Sailboat Reviews
- More Sailboats

New to the Fleet: Pegasus Yachts 50

Balance 442 “Lasai” Set to Debut
Sailboat Review: Tartan 455

Meet the Bali 5.8

Cruising the Northwest Passage

A Legendary Sail

10 Best Sailing Movies of All Time
- Digital Edition
- Customer Service
- Privacy Policy
- Email Newsletters
- Cruising World
- Sailing World
- Salt Water Sportsman
- Sport Fishing
- Wakeboarding
Attainable Adventure Cruising
The Offshore Voyaging Reference Site
- When Electric Drive Works For a Cruising Sailboat
A few months ago several people wrote to me linking to an article by Jimmy Cornell in which he detailed the reasons for abandoning his Elcano Challenge , a project to sail around the world on an all-electric catamaran.

Many people will expect me to start crowing about Jimmy’s failure because I’m on record as being sceptical about both electric drive and electric cooking for offshore cruising boats… for most usage profiles .
Not a bit of it. In fact, I don’t regard Jimmy’s experience as a failure but rather, a real-world demonstration that going cruising with electric drive and sails as the only means of propulsion is practical, albeit at higher capital cost than most other options.
So let’s analyze Jimmy’s experience to figure out where he got it right (most of it) and what we could change to turn failure into success, without cheating by installing a generator .
Making It Work
You will notice that most anytime engineers like Matt Marsh and Eric Klem, who really understand this stuff, or even yours truly who rides on their coat tails, write about electric drive, the qualifier “ usage profile ” or some equivalent gets used—now you know why I put the term in bold above.
And that’s really all we need to know to make electric drive work:
We must change our usage profile to fit the limitations and strengths of the technology. End of article…
…OK, that’s not going to work, I can hear the howls from here.
So, first off, let’s dig in to understand what went wrong for Jimmy. To do that, I suggest you read Jimmy’s excellent and honest article, but here’s the key quote:
Our 1000-mile maiden voyage from La Grande Motte to Seville showed up some of the weaknesses of the regeneration system when it failed to keep up with the overall consumption on a proper voyage, not during a test in calm waters. The consumption included both the autopilot and instruments, and also domestic demands such as induction cooker, microwave oven, two fridges, etc. My doubts started after we had sailed 82 miles in a period of 10 hours at an average speed of 8.2 knots. The net gain was a disappointing 9.5% of our total battery capacity, equivalent to 5.32 kWh, or 532 Watts per hour. …I kept a detailed record over this entire passage, and the results were consistently and disappointingly the same… Jimmy Cornell (emphasis mine).
At first blush that seems like a deal breaker, but let’s not forget that Jimmy and his crew managed to sail the boat all the way from the south of France to the Canary Islands and back without burning a drop of diesel fuel, although, to be fair, I’m guessing they charged the batteries from shore power whenever they were in a marina. If so, some carbon was emitted, but a tiny amount. Whatever, an inspiring achievement.
Now, after that moment of optimism, I need to get realistic—electric drive fanboys will call it pessimistic—but don’t despair, my ending is all optimism, so stay with me.
Login to continue reading (scroll down)
Please Share a Link:
More Articles From Electric and Hybrid Diesel-Electric For Cruising Boats:
- Electric or Diesel-Electric Drives for Voyaging Boats
- Real Numbers For Electric And Diesel-Electric Drives
Hi John, You were speculating about 40-foot boat’s average speed on passage. On Alchemy, it is the 2 of us and we try not to press the boat at more than 75 or 80% of capacity (eaking out that last 20% is when damage to boat and/or crew is more likely to occur) and my impression is that we do much less motoring than most. I have been surprised by the consistency of 5.7kn average when we are on passage for more than 3-4 days. My best, Dick Stevenson, s/v Alchemy
Thanks, the real world report. That confirms that for a boat like yours electric, at least without shore power charging is simply impractical since regeneration would be effectively zero.
Hi Again, Dick,
I may have been wrong about regen not working. at all on a boat like yours. See Eric and Colin’s comments below. That said, I still think fast boats, probably cats, are the best option when thinking electric.
Oceanvolt writes about this too, as does Outremer: https://oceanvolt.com/oceanvolt-blog/facts-electric-shock/
Seems that they all agree that the real world tested the setup in ways that all the prework in the world did not.
The good news is that the companies (esp. Oceanvolt) are already studying what went wrong with the regeneration and how to fix that.
I guess somebody had to be a pioneer here too – much like those brave souls who built & flew the first aeroplanes 🙂
It will be interesting to see how a similar endeavour will go like in, say, five years. Perhaps, in addition to getting the regeneration working on the ocean, solar cells integrated in the sails are needed. That has already been done, and it works fine for day sailing and coastal hopping.
Well, it remains to be seen when we can eventually rid ourselves of the diesel engine on boats, but it’s not going to happen very soon.
Yes, I linked to that in Further Reading.
And yes, hopefully this will drive Oceanvolt and companies like them to stop publishing unrealistic claims and buckle down to actually make the gear meet their claims for it. That said, as I explained in the post above, the barriers to getting a lot more out of regeneration are formidable since, as Jimmy found out, they are running into basic physics here: drag balanced against regeneration and the need to sail efficiently.
As you say, none of this will get solved tomorrow.
Oceanvolt, at least, appears to be pretty honest with the numbers in their latest marketing materials update. The published figures for their AXC10 twin system (“replaces two 20-30 hp diesels” in a cat under 12 tonnes) claim that for €61730, you’ll expect 10 miles of range from 10.5 kWh, and should regen about 400 watts at 6 knots. That price includes a 10 kW DC generator, which can keep the drives running at half power for 325 miles or so on 100 L of fuel.
That’s honestly about the best we’ll be able to expect for a long while. Modern electric cars get their range by being incredibly slippery, coasting along at just a couple hundred watts per kilometre. There’s no nice shortcut to that kind of drag reduction on a boat.
Ah, how did I miss the further reading link.
Yeah, the regeneration seems like a tough nut to crack. What makes me wonder is the discrepancy between the tests and the real world. Is that due to the test setup being altogether unrealistic, or is it a question of what works in a small chop will not work in big waves. Oceanvolt seems to think that part of the problem is a lack of optimisation – perhaps that has to do with the ocean swell you often mention.
Drag will always be there, for sure.
I fear the 600% difference between “test data” and reality might have had a healthy dose of salesmanship applied, rather than any one technical problem.
Maybe have a lot of propane and two propane outboards, for emergencies only?
Hi Michael,
That would be one option, although I fear that “for emergencies only” becomes “whenever sailing is inconvenient” very quickly.
I suspect what constitutes inconvenience for the modern cruiser is a greater hurdle than the technology. The pioneers, like the Smeatons and the Hiscocks, were of the Primus stove and kerosene lamp generation, although electrical alternatives existed. Same with provisioning. Ice was for toffs ashore. Today few would find that level of simplicity appealing, so the question for those willing to confront further proof of the no-free-lunch problem is: where will you draw the line on conveniences? Particularly when the pure options are themselves complex and expensive?
All concerned in this project should be proud of what they have achieved and learnt to date. Far from being a failure, I think this is excellent work in trying to achieve ‘no diesel’ cruising and many of us will be grateful one day for near silent power sources. As others have said, the real world experience was far from the theoretical and calm water testing. Sadly it means I will re-power my, much smaller, catamaran with light weight modern diesels for now but keep looking forward to further developments.
Yes, I think we all owe Jimmy a dept of gratitude for lending his star power to this. That said, I think the industry would do a lot better if the were more realistic about the technology’s true capabilities and the limitations of basic physics. More on that in a coming article.
Still, it’s interesting you can dramatically lower your footprint. Most of your time is at anchor. With panels and a couple of D400s the genset need not go on. Even adding in an efficient watermaker like a spectra Cape Horn. One does see power moving to greater efficiency. The Arksen line and Greenline production boats are examples. Even the footprint of the Artnauticas is a marked improvement from a more traditional trawler. Think we shouldn’t let the excellent get in the way of the good.
I agree, and have long been a fan of incremental improvement that can make difference over a broad spectrum, rather than reaching for perfect and failing.
- New Sailboats
- Sailboats 21-30ft
- Sailboats 31-35ft
- Sailboats 36-40ft
- Sailboats Over 40ft
- Sailboats Under 21feet
- used_sailboats
- Apps and Computer Programs
- Communications
- Fishfinders
- Handheld Electronics
- Plotters MFDS Rradar
- Wind, Speed & Depth Instruments
- Anchoring Mooring
- Running Rigging
- Sails Canvas
- Standing Rigging
- Diesel Engines
- Off Grid Energy
- Cleaning Waxing
- DIY Projects
- Repair, Tools & Materials
- Spare Parts
- Tools & Gadgets
- Cabin Comfort
- Ventilation
- Footwear Apparel
- Foul Weather Gear
- Mailport & PS Advisor
- Inside Practical Sailor Blog
- Activate My Web Access
- Reset Password
- Pay My Bill
- Customer Service

- Free Newsletter
- Give a Gift

How to Sell Your Boat

Cal 2-46: A Venerable Lapworth Design Brought Up to Date

Rhumb Lines: Show Highlights from Annapolis

Open Transom Pros and Cons

Leaping Into Lithium

The Importance of Sea State in Weather Planning

Do-it-yourself Electrical System Survey and Inspection

Install a Standalone Sounder Without Drilling

When Should We Retire Dyneema Stays and Running Rigging?

Rethinking MOB Prevention

Top-notch Wind Indicators

The Everlasting Multihull Trampoline

Check Your Shorepower System for Hidden Dangers

How Dangerous is Your Shore Power?

DIY survey of boat solar and wind turbine systems

What’s Involved in Setting Up a Lithium Battery System?

The Scraper-only Approach to Bottom Paint Removal

Can You Recoat Dyneema?

Gonytia Hot Knife Proves its Mettle

How to Handle the Head

The Day Sailor’s First-Aid Kit

Choosing and Securing Seat Cushions

Cockpit Drains on Race Boats


Re-sealing the Seams on Waterproof Fabrics

Safer Sailing: Add Leg Loops to Your Harness

Waxing and Polishing Your Boat

Reducing Engine Room Noise

Tricks and Tips to Forming Do-it-yourself Rigging Terminals

Marine Toilet Maintenance Tips

Learning to Live with Plastic Boat Bits
- Systems & Propulsion
Electric and Hybrid Propulsion for Sailboats
Practical sailor looks at the players in the developing field of electric auxiliary engines.

How soon will electric auxiliary propulsion be available to everyman? That depends on whom you ask. Opinions differ widely not just on what type of drive system might surge to the forefront, but even on whether the concept itself is viable. While a handful of companies forge ahead, notably Glacier Bay and Electric Marine Propulsion on this side of the Atlantic, some expected participants are waiting on the sidelines.

Photos courtesy of Manufacturers
One of the big issues that divides promoters and detractors alike is whether the appropriate way to go in a sailboat is with a pure diesel-electric drive train, with a hybrid electric drive with a diesel generator as back-up, or as a pure electric drive with regeneration capability. We’ll take a look at these and other options later in this article. For now, the short answer is that no single approach suits every sailor all the time.
Simply put, in the diesel-electric system, the electric motor runs only when the diesel-driven generator is running. Such arrangements have long been employed in railway locomotives, submarines, and commercial vessels of many types. In the hybrid system, a large bank of batteries provides the energy for the electric motor and the diesel generator recharges the batteries. On the face of it, the hybrid system offers a certain degree of redundancy in that, assuming the batteries are kept well charged, the boat has a measure of emergency power should the generator fail at an inopportune moment. The hybrid also is capable of recharging its batteries when sailing: Driven by the turning propeller, the motor becomes a generator.
Each of these approaches has its strengths and weaknesses, and while we’ll leave it to their developers to work out the technical issues, we would like to urge anyone contemplating installing an electric drive, or purchasing a boat that has one, to first look very closely at how they expect to use the boat. There’s more entrained in the choice than in picking a flavor at Baskin-Robbins. More on this later.
Among the electric drives currently available in one form or another, or as components, the big variable is operating voltage. Motors are available that run on 24, 36, 48, 72, and 144 volts, and, in the case of Glacier Bay’s diesel-electric system with Ossa Powerlite technology, 240-volt DC. Each supplier will discourse at length on the merits of their voltage choice, but an inconvenient fact haunts the entire field: High-voltage DC is deadly, potentially more so in some circumstances than AC.
While neither form of high-voltage is “safe,” we have a lot more experience with AC aboard recreational vessels than with high-voltage DC. An extensive body of knowledge exists on which to base AC installations so as to make them safe as well as reliable. High-voltage DC is used in a variety of marine and non-marine commercial applications, but these installations are well protected from access by untrained operators.
What voltage constitutes high voltage? That, again, depends on whom you talk to. The American Boat & Yacht Council (ABYC), which sets voluntary standards for the marine industry, defines it as 50 volts and above. Prompted by rapid adoption of high-voltage services in small commercial craft and bigger yachts, though not specifically in propulsion systems, the ABYC is in the process of drawing up guidelines for voltages higher than the 48 volts covered by existing standards.
An absence of standards might not deter individuals from installing an electric drive, but it might impede widespread adoption of the technology. If a surveyor can’t state in an insurance survey that a boat is built according to ABYC standards, that could affect its insurability.
Jim Nolan, who manages the underwriting department for BoatUS, said the company has no clear cut guidance regarding insuring boats with electric propulsion. Each boat is dealt with on a case-by-case basis. A new boat with a factory-installed system would be a good deal easier to underwrite than a one-off or do-it-yourself project, especially in the absence of a standard practice. Lagoon Catamarans’ 72-volt-DC hybrid system, for instance, has qualified for the European standard (CE) certification on the strength of following industrial standards that apply to such applications as fork-lift trucks. Anyone contemplating an electric drive would be well advised to discuss it ahead of time with an insurer and even get a surveyor involved from the outset.
Because of the safety issues surrounding the voltages involved in electric propulsion, Fischer Panda has decided to limit its DC product line to boats weighing 10 tons or less. A company representative we spoke to said that while Fischer Panda currently sells DC generators up to 48 volts in the USA for marine use, it “won’t touch” high-voltage DC because it’s lethal.
A proposed collaboration with Catalina Yachts to fit a diesel-electric system in a Catalina-Morgan 440 never came to fruition due to budget constraints, according to Fischer Panda. But in Europe, Fischer Panda teamed up with Whisperprop to equip a Bavaria 49. (Beyond the fact that one of its boats was used, Bavaria Yachts was not involved in the project.) According to Fischer Panda, after evaluating the Bavaria project, the company decided that the diesel-electric AC system is a niche product that wouldn’t interest their prime market: original equipment builders.
“Although the AC system has some advantages in the improved response of the electric motors … and the quietness of the system, the desired fuel efficiency and weight savings were not evident,” Fischer Panda reported.
Fischer Panda considers the DC system to be more suitable for its North American customers. Although it’s limited in output due to its limited battery voltage of 48 volts, it is still able to power multihulls up to 10 tons.
Currently, much of the movement toward electric drives is taking place in the catamaran world. This makes sense when you consider that a single diesel generator can, in theory, provide all the boat’s electrical needs and also take the place of two diesel-propulsion engines. Taking the lead in the field, Lagoon Catamarans introduced in 2006 the Lagoon 420. Originally offered only as a hybrid, it now is also available in two diesel versions. Corsair Marine is building the Corsair 50 catamaran around the Glacier Bay diesel-electric drive, but the boat’s launch date—formerly set for this summer—has been postponed.
Dick Vermeulen, president of Maine Cat, tried the Glacier Bay system in a prototype power cat, but it failed to meet performance expectations, so production models will have conventional diesels. A number of other cat builders have announced hybrid or diesel-electric projects, but feedback on how they perform is scan’t.
So much for the mainstream—but backwater sailors will go their own way, as they always have. As more vendors and components enter the market, the options for do-it-yourselfers or custom-boat customers become broader and more attractive. However, before going ahead with an installation, make sure it’s appropriate to how you plan to use your boat, and even then be prepared to adapt the way you sail to take best advantage of the system’s characteristics. Here’s a rundown of the various types.
Electric Drive Only
Duffy Electric Boats has for years been building electric launches and lake boats that have the simple capability of puttering around in sheltered waters for a period of time determined by battery capacity and speed maintained. A battery charger powered by shore power charges the batteries overnight. Transferring that approach to a sailboat up to about 25 feet used for daysailing and kept near an electrical outlet shouldn’t be too difficult. It won’t offer the assurance of diesel when trying to get home against current or wind, but a proven 36- or 48-volt system will keep you out of uncharted standards territory.
For a bigger boat, more power, a greater range, or a combination of these requirements, it will be necessary to install a large battery bank and almost certainly will entail going to a higher voltage to keep the amps and the cabling needed to carry them manageable. The boat’s range under power will be limited by the weight of batteries, and while lighter lithium-based technology is on the horizon, for now the standard is lead/acid. The fast charging, but expensive pure lead thin plate (PLTP) Odyssey batteries have attracted particular interest among propulsion enthusiasts.
Electric Drive with Regeneration

The next level up in complexity is a “reversible” system. When the boat is sailing, the propeller turns the motor, which then becomes a generator. The electricity it makes is used to recharge the batteries. The capability to regenerate extends the boat’s potential range, but the drag on the propeller slows the boat measurably. One hour of regen will not restore the power consumed by one hour of motoring, but if sailing time sufficiently exceeds motoring time, this arrangement offers considerable range.
A regenerating system does have the potential to overcharge the batteries once they become fully charged and the boat continues to sail fast. The solution is, ironically, to give the motor some “throttle,” which reduces the drag on the propeller and consequently the power output. This phenomenon gives rise to a new technique, that of “electro-sailing” in which sails and an electric motor complement each other. At present, the “throttle” must be adjusted by hand, but developers are working on automatic controls. Field trials of existing regen motors such as the Solomon systems suggest that a small regen motor’s ability to match the output of a much higher-rated diesel have been overstated.
Hybrid Electric Drive
A hybrid system adds to the mix an onboard generator, which is used primarily to maintain charge in the batteries, both those for the propulsion motor and for the house services. This arrangement extends the boat’s capability to lie for long periods at anchor, independent of shore power for electricity and without the need to go sailing for the sole purpose of charging the batteries. A hybrid can motor constantly, as long as there is fuel, but it cannot sustain full speed for long periods. This is because the generator is usually rated at a far lower horsepower than that required to drive the boat at full speed.
Diesel-Electric Drive
In a pure diesel-electric, the electric propulsion motor runs only when the generator is running. Storage batteries are not needed for propulsion purposes, and the generator is the source for all onboard electrical power needs. The rationale behind diesel electric lies in the relationship between a diesel engine’s rate of fuel consumption and the load it’s working under. It burns fuel more efficiently when heavily loaded than when lightly loaded. When the diesel engine is disconnected from the propeller, it can be controlled so that it is working in the upper range of its efficiency regardless of how fast the propeller is turning. Nigel Calder’s series of articles in Professional Boatbuilder magazine (www.boatbuilder.com) beginning with the June/July issue delves deeply into the efficiency discussion surrounding these engines. Systems on large vessels are built around multiple generators that switch on or off according to the power demands of the moment. Translating those efficiencies into a smaller boat scenario has proven to be challenging.
Hype vs. Experience
Maine Cat’s Vermeulen, on the company’s website, describes the sea trials he performed in the Maine Cat 45, a power catamaran. He began with a Glacier Bay diesel-electric system with two 25-kW generators, each weighing about 550 pounds.
“With both generators putting out their full power of 25 kW each … our top speed was a disappointing 8.4 knots, and the assumption that electric horsepower was somehow more powerful than conventionally produced horsepower was in serious doubt.”
He replaced the propellers with a pair with less pitch, which allowed the electric motors to reach their full rating of 1,100 rpm, but that only increased the speed to 9.1 knots.
“These are about the same speeds and fuel burns we get on our Maine Cat 41 sailing cat … powered by twin 29-horsepower 3YM30 Yanmar diesels with saildrives and two-bladed, folding propellers.” At the time he installed them, the 25-kW generators were the highest power available from Glacier Bay.

Vermeulen replaced the diesel-electric system with twin 160-horsepower Volvo diesels. At 9.1 knots, they together burned 2.2 gallons per hour, considerably less than the 3 gallons per hour that the Glacier Bay system burned at the same speed. With the twin Volvos maxed out at 3,900 rpm, the boat made 24.5 knots.
Also among the unconvinced is Chris White, well-known designer of ocean-going catamarans. “To date, I’ve not seen any system that makes sense for a cruising boat,” he says, but he might change his mind, “if someone can show me by building one that delivers an advantage in performance, weight, or cost.”
White sees the current bubble of interest in diesel-electric drives as a fad. In the end, he says, you’re getting the horsepower the diesel creates at the crankshaft, which is basically the same whether it’s delivered to the prop via a conventional reduction gearbox or via a generator and an electric motor. Besides, he says, diesel engines and diesel fuel are understood and available anywhere in the world you might take a sailboat. Complex, electronically controlled electric motors are not.
White’s reservations notwithstanding, it’s in the world of catamarans that we’re seeing most of the applications. At first sight, it does seem logical that replacing three diesel engines—two propulsion and one generator—on a fully equipped cruising cat would result in fuel savings. Still, if the generator is big enough to drive the boat at cruising speed (which in a cat is expected to be in the vicinity of 10 knots) and run the air conditioning at the same time, it will be overkill for the times it’s only needed to operate the boat’s services. For this reason, commercial and military diesel-electric systems employ multiple generators that can be switched on and off according to the power demand of the moment.
Corsair Marine hopes that by installing a diesel-electric system in its 50-foot catamaran, it will be able to descend the weight spiral. Where a conventional installation would involve two 75-horsepower saildrives plus a 6-kW genset, it’s fitting a pair of 28-horsepower electric motors, one 25-kW generator, and a 40-amp, 230-volt battery bank. It expects to save about 700 pounds in equipment weight, some of it through the use of high-voltage, low-current systems, which will in turn reduce the rig requirement, thus the structural weight, and so on toward an estimated overall weight savings in the thousands of pounds.
Corsair’s David Renouf estimates that the boat will cruise at 8 knots and be capable of short bursts at 10. He admits that, until the first boat is launched, his information is “based on extrapolation, not proven numbers.” He says that some clients will add a second 25-kW genset to assure longer periods at 10 knots. Currently, the project is running behind schedule, with a launch scheduled before the end of the year.
Cost and Other Benefits
At the present time, there appears to be no reason to install any proprietary electric drive of any description in the expectation of bettering the economics of a standard diesel drive. The motors and their electronic controllers are sophisticated and expensive. A battery bank sufficient to provide a useful motoring range is a big investment in weight, space, and money. When you add a generator and its peripherals, the cost and weight take another upward leap.
Only the simplest system will begin to pay itself off in terms of fuel not burnt, and then only if the boat sees a great deal of use. A diesel-electric system designed to closely dovetail with the way you use the boat may prove to be more efficient over time than a conventional diesel installation, but until enough systems have been installed and used and data from that use compiled and compared, we can’t know that.
So why even consider going electric? Cleanliness and silence of operation are two qualities that make electric propulsion an attractive proposition for a sailboat, but in order to enjoy them, we have to accept the limitations they impose.
A hybrid or a diesel-electric system enables us to have a single fossil-fuel power source for both propulsion and onboard appliances, but whatever fuel we might save as a consequence of motoring more efficiently for a couple of hours will be inconsequential if we run the generator all night to power the air conditioning.
Conclusions
As we go to press, pickings are slim for sailors looking for an electric solution to the diesel problem. Suppliers of components are few, prices are high, and the feedback on long-term reliability is nonexistent. On top of all this is the elephant in the room: the unexplored safety ramifications that accompany high-voltage DC.
However, none of this should deter the dedicated tinkerer who has funds to match his curiosity and who can live within the parameters imposed by electric propulsion.
Practical Sailor encourages our readers to explore the technology, because ultimately, it is the experimenters who bring us the equipment we eventually come to take for granted.
- Pricing Electric Power for a 30-foot Sailboat
- Special Report
- Electric Engines
- Success in the Real World is a Matter of Perspective
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
I have gotten excited about repowering my Freedom 30 with an electric motor. A fellow Freedom 30 owner completed his refit about 8 months ago and is very happy with the result, although he wishes he had gone with larger Lipo batteries. He chose a motor from electricyacht.com which sells a 10KW package (quietTorque 10) including motor, performance display, throttle and shaft coupler for $6K. Batteries and charger are extra. The motor does does feature a regen capability. Figure a $10K investment. Big bucks for sure but equivalent to a yard installed diesel repower. I would do the install myself.
I am not a cruiser but have done some lengthy passages from San Francisco to Hawaii. Ideal conditions for regen. I expec between regen and a hundred watts of solar, I could have kept the bank topped up the whole way down despite AP loads, etc. The way back? Not so much. Realistically you would need a small generator and a good stock of gas if you wanted to do much motoring, Having said that, one of the boats that sailed down there with me came home with an outboard as his aux power. I think he had ten gallons of gas.
But I am not planning ocean passages in future, I will be sailing the SF Bay and coastal cruising. When I think about eliminating the engine noise, engine maintenance, fuel tank and tank maintenance, diesel hoses, diesel smell, diesel soot, diesel leaks, r=two boxes of hoses and spares. oil changes, coolant changes, transport and disposal of all the waste to the local recycling facility, lugging fuel jugs down to the boat, storing fuel, filling fuel, buying fuel, worrying about spilling fuel. I mean it just goes on and on.
Frankly, I can’t wait. In terms of range, well, I plan to get a hefty battery bank but I also intend to become a better sailor. I’ll slow down and do more sailing. Gee wiz, what a concept. I’ll be more mindful of time and tide, I’ll take advantage of favorable currents and I’ll be ready to anchor and chill when they are not favorable.
Meanwhile, Elon and his competitors are improving battery technology rapidly. Couple of years from now maybe I double range. But, by then, I won’t be worrying about it because I will be a real sailor.
I look forward to reading an update on the state of electric sailboat propulsion 13 years later…
Most of the time we leave the dock, motor for under half a nautical mile to get out of tiny Wilmette harbor and get the sails up, turn off our much abused Yanmar 3GMF, sail around, turn on the engine, lower the sails, and travel another half a nautical mile back to the dock. Almost all at a very low RPM. But, on occasion we motor or motor sail long distances for hours on end, so a battery only system would not work. But how nice it would be if we had electric propulsion for getting in and out of the harbor.
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Log in to leave a comment
Latest Videos

40-Footer Boat Tours – With Some Big Surprises! | Boat Tour

Electrical Do’s and Don’ts

Bahamas Travel Advisory: Cause for Concern?

Island Packet 370: What You Should Know | Boat Review
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell My Personal Information
- Online Account Activation
- Privacy Manager

- Select category
- Catamaran 10-30 passengers
- Large Group Tour
- Luxury 8-12 passengers
- Marriage Proposal
- Photography Tour
- Private Tours
- Sailboat 1-11 passengers
- Schooner 20-80 passengers
- Shared tours
- Small Group Tour
- Stag and Hen
- Sunset Tours
- Yacht Charter
- Stag and Hen Tours
- 2.5 Hour Sailing Tour
- 6 Hour Sailing Tour
- Catamaran Sailing Tour
- Photography boat tour Barcelona
- Sagrada Familia Sail Tour
- Yacht Charters
- Corporate Responsibility
- 5 step Electrical BLDC sailboat motor program
- Is electric sailing cheap or very expensive?
- Battery solution for electric sailboats
- Four options for electric drive propulsion sailboat
- Electric BLDC Sailboat Motor
- Best electric drive system for sailboats
- Marine biodegradable plastic in 2020
- Plastic ocean pollution during Sailing in Barcelona
- A guide for Single use biodegradable plastic in Restaurants
- Public awareness on plastic pollution in the Mediterranean
- Micro plastics in nature a full circle
- What have biodegradable plastic and Marlboro lights in common?
- Earth day event: Barcelona boat tour, plastic fishing
- Sailing Team building Events
- Online Team Building Events
- 10 best day activities in Barcelona
- Barcelona restaurants after sunset sail or day sail
- Best places to stay outside Barcelona
- Best things to do outside Barcelona
- Buying a boat in Spain in 2021
- Weather bulletins Barcelona
- 10 most important fish in the Mediterranean
- 6 most important mammals in the Mediterranean
- BarcelonaSail
- Our Good weather guarantee
- Our Sailboats
- BarcelonaSail Reviews
- Location Boats, Yachts and Catamarans
- Videos BarcelonaSail
- Sailing in Barcelona Frequently asked questions [FAQ]
- March 17, 2021
- Posted by Sailing Barcelona
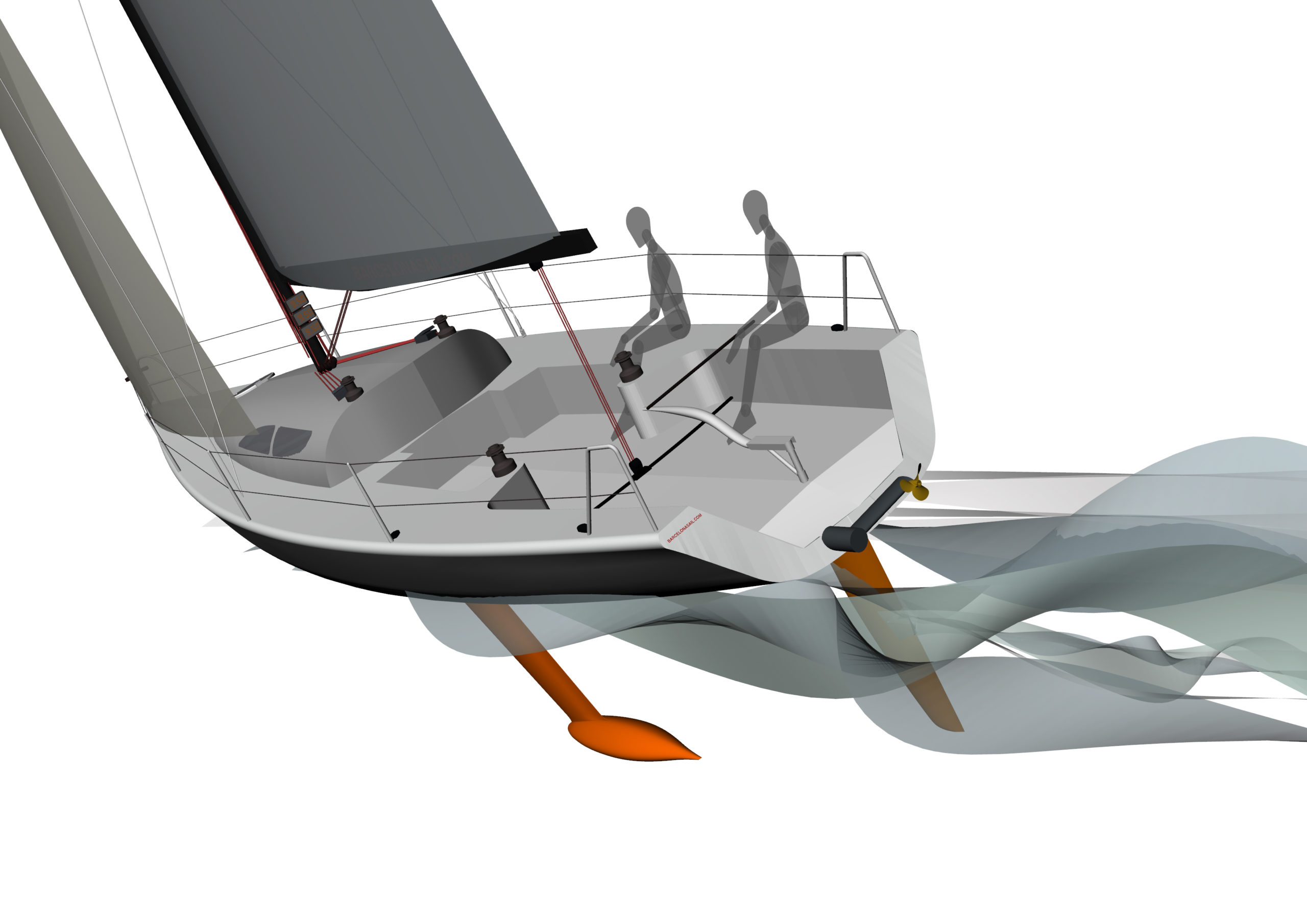

Criteria for best electric drive system for sailboats
In our first blog on electric sailboat conversion we described our initial criteria for an electrical drive system. First of all we want to reduce the drag. In addition we want to use the propeller for regeneration of the batteries. Regeneration of electricity under sail is the Holy Grail of electrical propulsion. However the problem is that the propeller must be small to minimize drag, and large for regenerating the batteries. Because it takes a lot force to make the electric motor rotate. Expensive three blade folding propellers alleviate this partially the regeneration performance of folding propellers is under debate.
Boat speed and autonomy are a function of the efficiency of the electrical BLDC motor (3W-7kW) and the battery package (Lithium Ion Phosphate LiFePO4). We set our minimum specifications for the electric motor and the batteries in a prior blog post .
Especially relevant is the fact that BarcelonaSail is a commercial sailboat tour operator. Therefor it is important to have easy access to the entire electrical drive system. Consequently we focus on an electric drive system for sailboats that allows access to all parts of the system. Furthermore we want the electric BLDC motor inside the boat, in other words, an inboard motor system.
In conclusion we believe that the best electric drive system for sailboats is an inboard motor system that eliminates hydrodynamic drag under sail, therefor solves drag versus regeneration and is easily accessible for maintenance. In addition we believe that the installation of electric BLDC motor should be possible without the need to create more holes in the boat and have a specialist involved.
Our solution can be best described as an electric propulsion system for sailboats with the reliability of an inboard motor, but the flexibility of an outboard motor. That means easy access for maintenance, flexibility, no additional drag and most noteworthy low costs. Let’s look how we designed it.
Drag vs Regeneration
Best electric drive system for sailboats solves the paradox between drag and regeneration problem, our solution does this via the rotation of the propeller section out of the water when regeneration is not required.
Easy access and no more holes in the boat
Best electric drive system for sailboats uses the existing transom exhaust opening, offering an easy low cost installation without making additional holes in the hull.
Existing transom exhaust opening is used to connect the inboard electrical motor with the carbon propeller shaft. Regenerating when under sail.
Very efficient simple electric drive system
Sail-drive, pod-drive, shaft-drives and outboard-drive propulsion systems loose mechanical efficiency with the use of traditional gearboxes, universal joints and bevel gears.
Best electric drive system for sailboats uses a direct drive with an elegant first-principles system of gearing to minimize mechanical losses in the transfer of power to the propeller.
How the electric drive system works
The design team uses the exhaust opening to connect the carbon propeller arm with the electric BLDC motor. Especially relevant is the fact that this specific design is under investigation for an IP. Rotating the carbon shaft 90 degrees to reduce drag is easy. The carbon shaft is very light and hollow. The inside space is used for gear reduction to increase the torque at the propeller.
This green and simple solution exists basically of two components: one, the propeller with the propeller arm outside, and two, the electric BLDC motor system inside. An IKEA ready package for boats between 7 and 13 meter will be available late 2017 according to the designers.
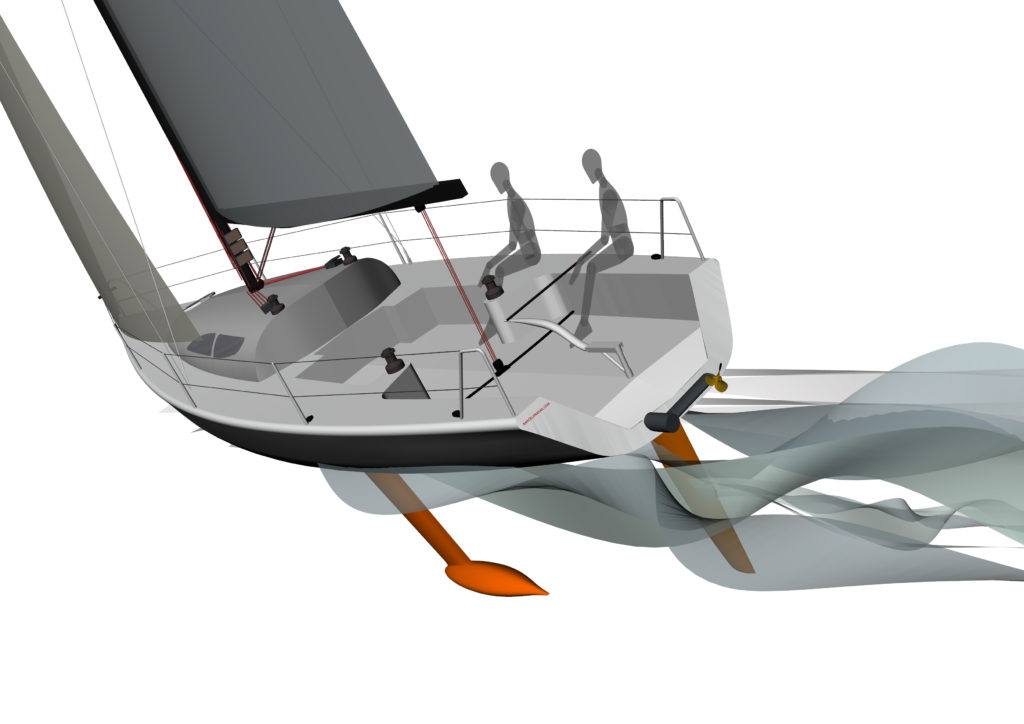

Remove propeller out of the water to minimize drag.
Benefits of this system
- No additional openings required in the hull.
- Simple rotating connection between the transom and the propeller arm using the existing exhaust outlet.
- In board motor with the ability to eliminate hydrodynamic drag that the electric sail-drive, pod-drive and shaft-drive propulsion systems cannot.
- No motor shaft issues.
- Minimal mechanical efficiency losses with direct gearing.
- Fast, easy and cheap maintenance.
- Easy and low cost installation .
- Flexible design fits all boats between 7 and 13 meters.
We believe that with this solution we can make the world of electric propulsion for sailboats more accessible to a wider range of boat owners.
Related Posts

Electric Sailing Barcelona
- March 12, 2021
Continue reading
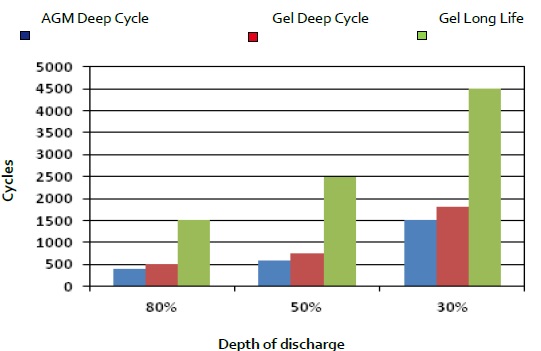

HYBRID AND ELECTRIC MARINE POWER AND PROPULSION SYSTEMS

Zero Emission
No environmental restrictions

No high voltage risk
Remote System Interface
State of the art Lithium Ion battery technology
Safe installation and operation

Instant power output for maneuverability
Zero to full torque in an instant
No waiting for engine rev to settle
No pre-start warning beep
Best quality components available

Patented Technology
Hydro power regeneration
Superior thrust efficiency and energy capture
Remote diagnostics
Low maintenance
System Solutions for a Range of Marine Activity

THE FACTS ABOUT ELECTRIC POWER, BATTERIES AND PROPULSION
Today's electric motor technology has already moved from
the open road to the open ocean.
Instant High Torque
Electric motors are in constant ‘stand by’ mode; you can engage the control lever at any time for instant forward or reverse propulsion.
Electric motors achieve instant torque with Electromotive Force while internal combustion engines need to build RPMs gradually by increasing piston firing frequency.
Hydro Generation
At sailing speeds over 6 knots Oceanvolt systems are able to generate significant power for recharging the battery bank by activating at the touch of a button.
Power regeneration increases exponentially with each additional knot of speed.
Lithium Ion batteries are superior to other battery storage technology; highest storage capacity, high effective current delivery, high charge capacity resiliency and wide temperature range performance. In today's digital age, where everything is just a click away, 1xbet mobile takes a significant chunk of the online casino services sector. Starting as an online casino service in 2007, 1xBet expanded its services in 2014 to include sports betting. Fast forward to 2018, and they marked their entry into the Indian market. Their app and website, designed in a calming blue and white hue, are not just a treat for the eyes but are also super intuitive. With a support interface that covers 50 languages, including Hindi, the platform ensures that language is no barrier to placing your bet.
Oceanvolt highly skilled technical team ensures proper installation and system-optimization. Only the highest quality Li-Ion batteries are used - to ensure performance and safety.
For those interested in a hybrid solution, generators are a highly efficient way to extend range while at sea.
DC generators have the advantage of rapid recharging capability.
AC generators are, generally, smaller and even portable which means that the generator can be aboard only in situations where longer motoring might be required.
Battery recharging is accomplished with shore connection, hydro generation (an integrated part of all Oceanvolt systems) and/or solar panels.
In Hybrid solutions , a generator (either AC or DC) can be used to recharge batteries / extend motoring range.
Integrated components
It is essential that all system components are properly selected and installed.
Our team of highly skilled technicians ensure that all components are compatible and that system management software is optimized.
Oceanvolt blog

For immediate release: Oceanvolt appoints Mikael Heikfolk as new CEO

Oceanvolt & Blue Marine showcase electric innovation at Seattle Boat Show 2024

Where to find Oceanvolt at BOOT 2024
Owner testimonials.

Traditional Mallorcan Llaut

Rapido 40 #7 “NullEins”

SQ46 Sailing Catamaran

Electric Motor
Please note:.
The following information is in regards to our initial set up. It has been almost 5 years since we wrote this. Many upgrades and improvements have been made since then. All can bee seen on our Youtube Channel. Updated wiring diagrams, specs and photos will be coming soon. In the meantime, much of the below information is still accurate and I’m sure you will find it useful. And the answer to our most asked question is YES, we still love our electric motor!
WHY ELECTRIC?

An electric motor . . .
Is not for everyone..
Lets first take a look back in time when “production” boats became popular in the late 60s early 70s, the intent was to make an inexpensive boat the average family could afford and handle with limited sailing experience and knowledge. As a result, one of their requirements was the ability to move the boat in difficult situations. This is where the “auxiliary engine” was coined. But, for many, it has become the primary means of maneuvering their boat. Yes, there are places in the world you can’t sail, like the Panama Canal. But, there are often alternatives where you CAN sail.
“We have yet to use our motor for more than 30 minutes at a time.”
As of today, November 2016, we have sailed over 3000 miles up the east coast of the United States and through the Bahamas to Haiti. We have yet to use our motor for more than 30 minutes at a time. The majority of use comes when we drop the mainsail and back down on our anchor to set it. Most of our sailing has been offshore. But, we have also sailed on the ICW and recently sailed 25 miles up the Cape Fear River to Wilmington, NC. We have sailed under many bridges, some on set schedules, others open on demand. In all cases, we sailed under. We have found that having a solid plan and the patience to wait for the right weather and tide is the key.After all, we own a sailboat. They are inherently slow. We are not in a rush. We love the idea of being self-sufficient. But, for those who sail with schedules, are short on time, lack the patience to sit out a wind hole, feel the need to power their boat to hull speed, enjoy maintaining a diesel engine, or are just set in their ways, then an electric motor probably isn’t the right choice.
Want to learn even MORE…?
Of course we would love for you to stick around and read this page all the way to the bottom, but, we have tucked in many distractions (i.e. links) along the way. Don’t feel bad if you digress, we know you’ll be back. If you want to just jump feet first into all things “electric sailboat” Electric Seas is a good place to start. It’s a great resources community and features several other electric sailboat stories for you to enjoy.

ANOTHER POTENTIALLY GREAT RESOURCES….
“My Electric Boats” by: Charles Mathys.
Although this book is currently on our Amazon wish list, we have not read it yet. But, it is the only one we could find on the subject and, for only $15, it looks promising. If you read it before we do, let us know what you think!
You don’t need a diesel . . .
For ocean passages..
Many people have written in and commented that an electric motor is only good for day sailors who weren’t going very far each day, and that you need a reliable diesel engine for long distance cruising. But we feel like the opposite is true. Since we don’t have a dock to tie up to and charge our batteries each night, we rely on sailing to recharge our system. The longer we sail and the more sun we get, the more power we make. Because we don’t have a 9-5 to return to at the end of a fun weekend out on the boat, we have no schedules requiring that we make it back to the dock on time, no matter what the wind is doing. So, we feel that an electric motor, depending on your sailing style, can be adapted to any boat. But, you have to be willing to work around the one major draw back, range.
“We have no schedules requiring that we make it back to the dock on time.”
Range is the one major downside to an electric motor. But, with a sailboat, and some adequate sailing skills, we have found we really don’t need a motor as much as we originally thought. For those who do have schedules, the possibility of a hybrid system may work well. It encompasses all the benefits of an electric system with the added back up of a diesel or gas genset rated to supply adequate power for extended motoring. Some companies even offer an electric motor, like this one, that can be installed in parallel to an existing diesel motor. So the majority of motoring is done with the traditional diesel, however for short periods of time, like moving around the marina, the electric drive can be used instead. This also incorporates the added benefit of capturing power from the spinning prop while sailing, often referred to as “regeneration” or “regen”.
Our conversion to electric . . .
Started with our motor..

We found the motor on ebay.com, knew it worked and that was about it. We chose this specific motor for three reasons:
- It was rated at 4.8kW at 36v which was adequate for our needs.
- It was overbuilt for an industrial application. This meant it had robust parts and easy to source replacement brushes.
- The motor cost us $125! Since this entire “Electro-Beke” project is just one big experiment, we tried at every corner to keep our expenses minimal.
Our motor weighs 110 pounds, which is quite a bit more than its brushless DC siblings like those used in the existing electric boat market. Although it is probably a little less efficient, its components are much more robust and durable. It is heavy duty, low cost and provides adequate power, with the added bonus of being simple and easy to find parts for. The only parts we will likely ever have to replace are the 8 carbon brushes that transfer electricity to the motor armature (the part that spins on the inside). Depending on use, they can last for many years without wearing out, and for about $80 we can buy a complete replacement set to have onboard. That’s it, virtually maintenance free, with only 1 moving part, the motor itself is relatively simple. On our boat, simplicity is often the defining factor for equipment selection.
This motor happens to be wired with separately excited field and armature (or SEPEX). It just means that we have a lot more control over the motors power output. We can tune it down to have more low end torque, or up to gain high end speed. This will allow us to customize the power output we need for our specific boat. A few other types of motors out there include, Series , and Permanent Magnet that only have one set of coils. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks. But we won’t get into any of that here. If you would like to know even more about DC motors, click HERE .
we didn’t buy new . . .
Because we received quotes from three different companies:.
- Here’s our quote from OceanVolt for their AX8 motor.
- Here’s our quote from Annapolis Hybrid Marine for a Thoosa 7000HT motor. Read their prediction for power consumption and battery drain.
- Click here to see some data and predictions from Electric Yacht for their Quite Torque 20 motor.
Our entire set up . . .
Cost us just $1,400..
As you can see by the above quotes, The motors and supplementary wiring are all in the $10,000 price range. That doesn’t include a battery bank. Our motor and wiring cost us just under $500. Many of our components were refurbished, used or salvaged from boats being demolished, including some of the wiring. The battery bank and additional tools, like wire crimpers and cutters were another $500. So, for about $1000, we installed our Electro-Beke system. Our charging system ended up costing us only $400 thanks to a few amazing companies who joined our Uma Angels Family and supplied the major components. Find out more about our charging system in the “Charging” section below.
That Breaks down to:
$500 _ for the motor, controller and supplementary wiring. $500 _ for the batteries. $400 _ for the solar charger, panels and bimini modifications.
Power required . . .
To push our boat and yours..
Our motor has an 8hp rating. For those accustomed to gas or diesel engines, this may not seem like much power. But, the rating systems used for gas engines and electric motors are so different that comparing the numbers is almost meaningless. It comes down to the way the two types of motors use their energy and torque curves, which is quite different. According to the research we have done, a 1 hp gas (or diesel) engine can push 500 pounds of displacement to hull speed in calm conditions. Now, the sources disagree a little here, but as a rule of thumb a 1hp electric motor can push about 3 to 3.5 times more displacement than its petrol equivalent. So a 1hp electric motor, drawing 750W, can push about 1500 pounds of displacement.
“Hull speed’ and ‘redundant power’ weren’t something we worried about in our system.”
Our boat displaces 13,500 pounds. so, 13,500 / 1500 = 9hp electric motor., now 1hp (of electric) draws about 750 watts. so, 9hp x 750w = 6.75kw electric motor..
At 48V, our motor should give us 6.3kW, which is slightly less than what we would need to push our boat to hull speed in calm conditions. But that is something we never intend to do. It takes a lot of power to push a displacement boat to hull speed. So the slower you go, the greater your range will be. However, it takes a long time to cover that distance. So, there is a sweet spot right around 4 kts (see graph to the right) where you make good headway, while being conservative with your power consumption. Of course, these are merely suggestions. Real world conditions are rarely perfect and adding 30% redundancy is often recommended by many motor companies.
We only use our motor for close quarter maneuvering where sailing isn’t an option, like a marina, or tight anchorage, so “hull speed” and “redundant power” weren’t something we worried about when designing our system. We often sail on and off the hook and choose places to anchor with few boats around.
Power | Speed | Range
Hover over any point to see exact data. For example, it is estimated that at 2.7 kts our motor will draw 600 watts (blue), giving us a range of 65 nautical miles (grey). This graph is based on a 14kW Lithium battery bank and a high end motor/controller combo.
Here are some great companies . . .
That install, sell, or can help answer your questions..
Thunderstruck-EV and EV-West are staffed by great people who would love to hear from you and help answer any questions you may have. They both offer DIY kits that will suit the needs of any boat. They can also help source adequate battery banks, help with solar and even find local experts to assist with installations as well.
If you’re looking for a more “plug and play” set up, check out the companies below. They represent the best in the industry and will gladly customize a set up for your specific needs and provide a detailed quote.

Elco Motors
elcomotoryachts.com
1 (877) 411-3526

Oceanvolt SEA
oceanvolt.com
+358 10 325 5281

clean-e-marine.com
+1 (410) 353-4348

Electric Yacht
electricyachtsocal.com
1 (855) 339-2248

Electroprop
electroprop.com
+1 (805) 455-8444
WANT TO LEARN EVEN MORE…?
Here is another great article about “How much electric power do you really need? !!! !!!
INSTALLATION
Getting down to the Nuts and Bolts
For the complete parts list and wiring diagram, scroll down..
There is a lot to talk about here. Hopefully you can follow along and not fall asleep. Like…I …….am…….right….nowwwww(yawn)www… SLAP !!! Ok! I’m awake. Where was I. Right, wiring.
With no degrees or formal training in electrical engineering (and no, they didn’t teach us this stuff in architecture school), we had a lot of learning to do. Here we were, with a big heavy electric motor we knew nothing about, a boat it could theoretically push and the dream it would all work in the end. Now all we had to do was figure out how to get the motor to spin the prop. Sounded simple enough…right?
“…all we had to do was figure out how to get the motor to spin the prop.”
This step, of course took the longest. Since all our components were used, refurbished or salvaged, we had to test everything. We then started wiring the system in pieces in the salon and testing those. We then modified, adjusted, replaced and fabricated new systems and tested those. In all, it took us 9 months from motor purchase, to moving boat. Granted, not all of that time was devoted to installing the motor. We did have a few other projects on the side.
There are four main sections to our electric motor installation:
- The motor controller
- The batteries
- The wires that connect it all together

The motor we talked about previously. In all honesty, the main concern when sourcing a motor, is that it has enough power (watts) to push your boat to the speed you would like. The second concern is that it will work with the voltage of the components you choose. 12/24/36/48/72/96V are all common. The general rule, is that the higher the voltage, the fewer amps need to be pushed through the system to attain the same wattage. With this in mind, we have found that 72/96V systems tend to be more expensive than similar 48V set ups and, pushing a boat requires much less power that pushing a car. So, we’re not worried about running hundreds of amps through the system. Although rated at 36V, we run our motor at 48V so we can utilize available golf cart components for the rest of our systems, which are also inexpensive and abundantly available. For our boat, we designed the system to handle 150 amps. This would give us a theoretical output of just over 7kW (48V x 150A = 7.2 kW). If you were paying attention earlier, you might notice that our motor is rated for only 4.8kW at 36V. That is a continuous rating however. It can handle more, but cannot sustain it for long periods of time without some external cooling system. But, because there are times when we need all the power we can get, like stopping or backing down on the anchor, we decided to run our system with a higher amperage rating to accommodate that need.
CHECK OUT THESE PHOTOS OF OUR FINAL INSTALLATION.
(As usual, click to enlarge)

The Motor Controller
This little box is the heart of an electrical conversion. Similar to the head of an ICE (internal combustion engine), it controls the speed at which the electric motor spins. It does this by breaking up the power stream coming in from the batteries into tiny little pulses. This is called Pulse Width Modulation or PWM. There are many different types of controllers out there. In general, if you found a motor with standard voltage range, there is a controller on the market that will work for it. Some are more complex than others. Some offer built in regen capabilities, while other require computer programing and digital displays.
Our controller is a Curtis 1209B. It is designed to run a series motor, but since we got it for such a good deal, we made it work with ours by only using it to power the armature. See the wiring diagram below for more details. This controller is not fancy. It is weather proof, simple and robust. If you haven’t figured it out by now, we love simple and robust.
The Batteries
We will explain more below in the “BATTERIES” section. But for now, as long as you can create a battery bank that can be wired to produce the required voltage for the rest of your system, then you’ll be fine. Also keep in mind how much space and weight the bank will require. Ours fit perfectly where our old fuel tank used to be and helped offset all the weight we lost by removing the tank and the old diesel motor. For typical lead acid banks, at 36V you will need 3 -12v or 6-6V batteries. A 48V bank will require 4 or 8 respectively and so on. Although you can purchase massive deep cycle batteries with equally large aH ratings, we don’t see the value of them since it is very difficult to maneuver them into tight spaces on a boat. Ideally, if you can afford them, a lithium bank would be the best for an electric motor conversion. We’ll talk more about them in the “WHAT”S NEXT” section below.
All our wires our tinned copper or “Marine Grade”, although, we despise that term since it often just means “more expensive.” The majority of which, we scrapped off of boats that were being demolished at the boatyard. What we couldn’t find for free, we purchased from a local discount marine store that sold surplus marine components. This allowed us to spend very little for all the wiring.
For the most part it is all oversized, but when it comes to wire, the bigger the better. There are many useful online calculators that can help give an idea of what size wire will be appropriate for a given application. If your wiring is undersized, the system will lose some efficiency. For the most part this is of no concern. However, in extreme circumstances it will heat the wire to the point of melting things. For example, we undersized the cables connecting the motor controller to the armature, after a 15min full power test at the dock, we melted off the heat shrink tubing on the terminal lugs. It was quickly replaced by something much more beefy and hasn’t been a problem since.
O yeah, One More Thing . . .
The motor mount. .
Oops, almost forgot. Somehow we had to keep the motor inline with the transmission and securely mounted to the boat. We built and re-built 6 different mounting brackets prior to the one we have now. Each being fabricated after hours of sketches and models were developed. We didn’t have to modify the motor any or the transmission itself. However, we did modify the original transmission adapter plate that was used to attach it to the back of our Westerbeke. We then securely attached the transmission to the hull of our boat. This allowed the motor to float in front of it, leaving the transmission to absorb any thrust from the prop.
We fabricated the brackets out of steal since it is easy to work with and weld. Once we settled on a final design, we epoxied and painted the brackets and motor with engine enamel. We’re quite pleased with the final outcome. All the exposed metal is protected from corrosion and it is very securely mounted to the old engine pan.
In tandem to our bracket iterations, were several attempts to connect the motor to the transmission. Our early versions were poorly aligned causing horrible vibrations that in turn produced noise. Noise was something we were trying to avoid by going electric. The final design paired two identical sprockets, connected inline by a #50 double roller chain. This seems to work quite well. It allows for small misalignments and produces the least amount of noise. There are of course many other options out there, and someday we may experiment with them. But, for now, this set up works for us.
Take a look through our Electro-Beke playlist on Youtube for video of the installation process.

WIRING DIAGRAM
Including complete parts list..
Here it is. The schematic you’ve all been requesting. You may notice that it is drawn for a direct drive system, where the motor is used to electronically shift from forward to reverse. We have since installed our motor in front of our old transmission and no longer need the Fwd/Rev circuit. However, since the majority of set ups out there use the motor to achieve Fwd/Rev, we wanted to show our diagram depicting a similar set up. If you end up with a Series or PM motor, you should be able to modify this diagram by excluding the 12V bank to motor connections. However, many of the components, like the contactors, require a 12V supply to operate their solenoids. So you will still need a 12V accessory bank. This is often the house bank of a boat, since many smaller boats run 12V house banks anyway.
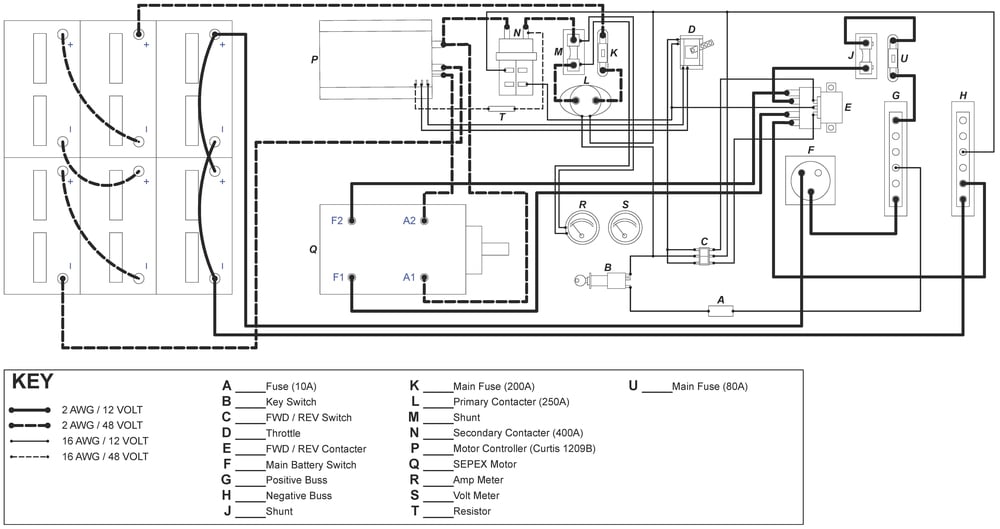
Below are the components we used, why we chose them, where to buy them and pictures of them installed in our boat. If you didn’t figure it out already, their letters correspond to the diagram above.
(A) – 10A FUSE

Buy one HERE .
This is a simple automotive fuse held in an inline fuse holder. It protects the ignition circuit wiring from drawing too much amperage in the event of a short.
(B) – Key Switch
Buy one here . .
The key switch is mainly for security. It can be replaced by a simple on/off switch, but taking the key out will slow down someone trying to leave with your boat, without your permission.
(C) – FWD/REV Switch
This switch is only needed if you are planning a direct drive system. We no longer have need for it, but also have yet to rewire our system after we installed the transmission. It is a basic rocker switch with an on/off/on rocker and 6 pins on the back. This allows both positive and negative wires to be switched. We also wired ours so that it will shut off the contactors if switched accidentally while the throttle was engaged. That way it wouldn’t cause any damage to the motor.
(D) – Throttle
The throttle tells the motor controller how much power to send the motor. We chose this one because it allowed us to keep our existing throttle lever and cable mounted on the steering pedestal. It also has a micro switch that we use to close the secondary contactor (N) on the 48V side and the Fwd/Rev contactor (E) on the 12V side when the throttle is pushed forward. This ensures no voltage is going through the system until the throttle is actually engaged.
(E) – FWD/REV Contactor
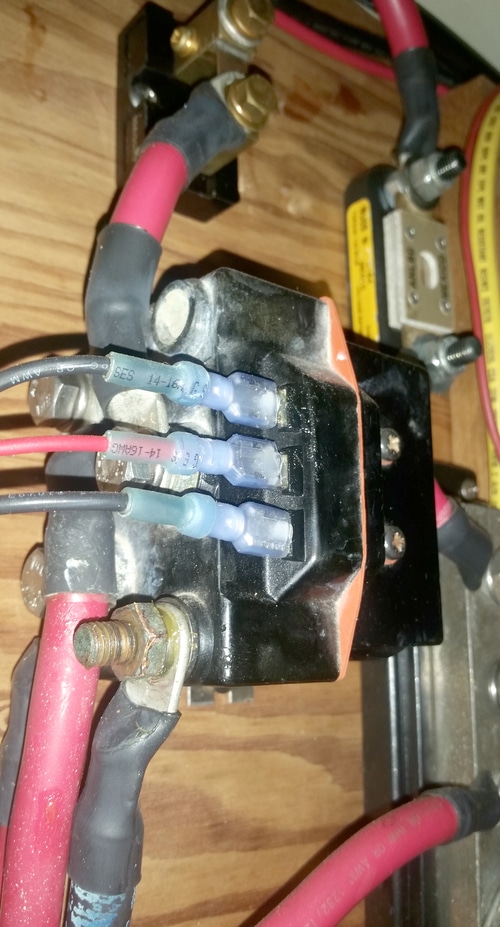

This, again, is not needed if you, like us, install the motor with a transmission that handles Fwd/Rev. However, if you are planning a direct drive set up, and the controller you chose doesn’t have a Fwd/Rev circuit, then this is a necessary evil. The one we used, we scrapped off an dead windlass. It works great for the 12V circuit and are easy to find.
(F) – Main Battery Switch
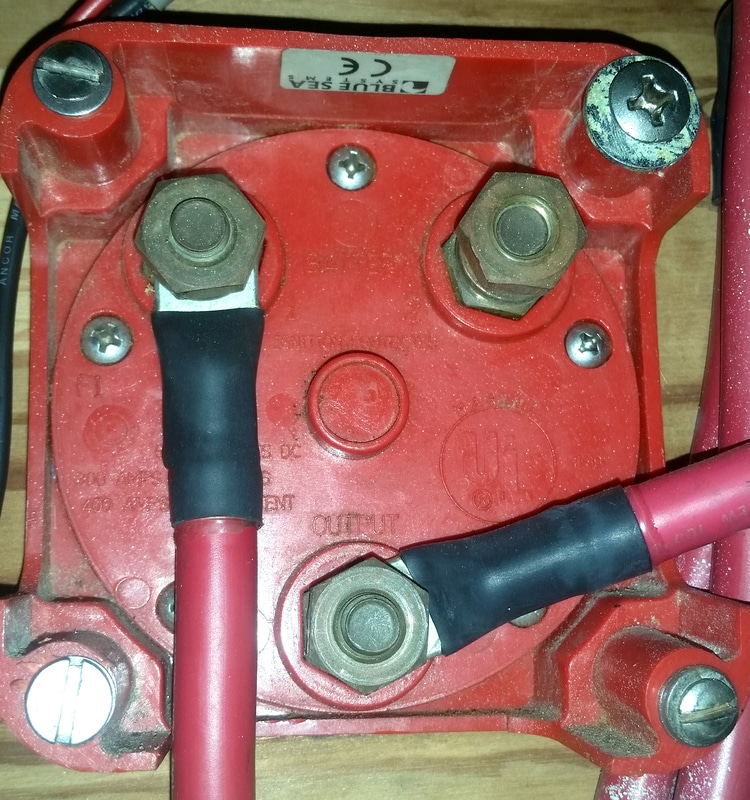

Our boat came with this switch installed already. We simply rewired it slightly to accommodate our systems. For now we only use the “Battery 1” and “off” settings. However, if we eventually install a DC-DC converter to bring our 48V bank down to 12V we could wire it to the “battery 2” position as a back up battery bank.
(G) – Positive Buss Bar
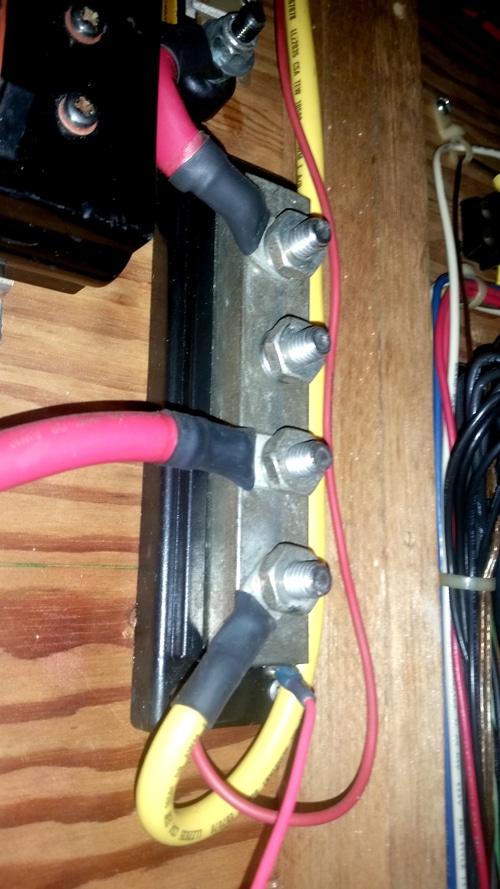

Pretty basic here. A buss bar is used to connect multiple leads to the same source. This one is beefy to handle high amperage on the positive side of the 12V circuit.
(H) – Negative Buss Bar
Same as the Positive buss bar above. However this one is tied into the 48V circuit.
(J & M) – Shunt
These are pretty standard. They are required to hook up an amp meter and measure how much amperage is running through your system. Often an amp meter will come with its own shunt. They sample the current so that not all 100+ amps are running through a meter. That would be very dangerous. Just make sure the shunt and meter are rated for the same mV, usually 50mV or 100mV.
(K & U) – Main Fuse
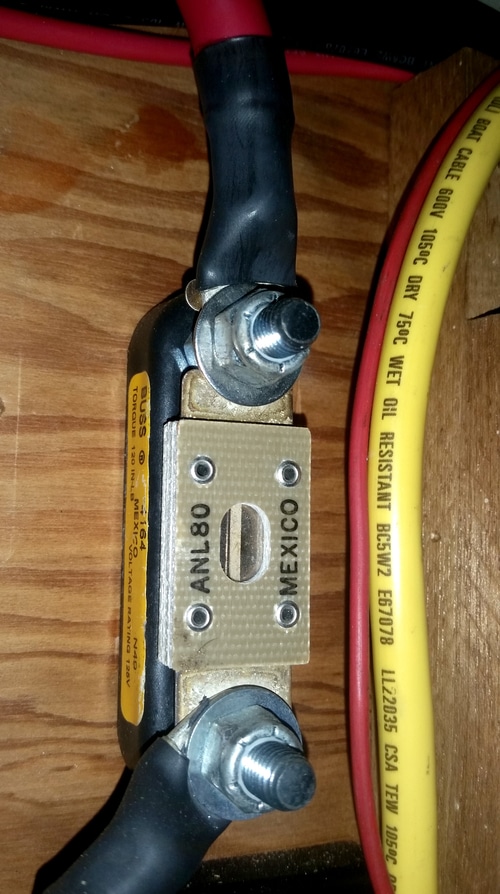

These fuses protect the wiring in the system. The closer to the battery bank the better. The fuse on the 48V side is rated for 200A and the 12V fuse is rated for 80A. These are rated for amperage only and can usually take a variety of voltages. Both fuses and holders are identical. They just have different ratings.
(L) – Primary Contactor
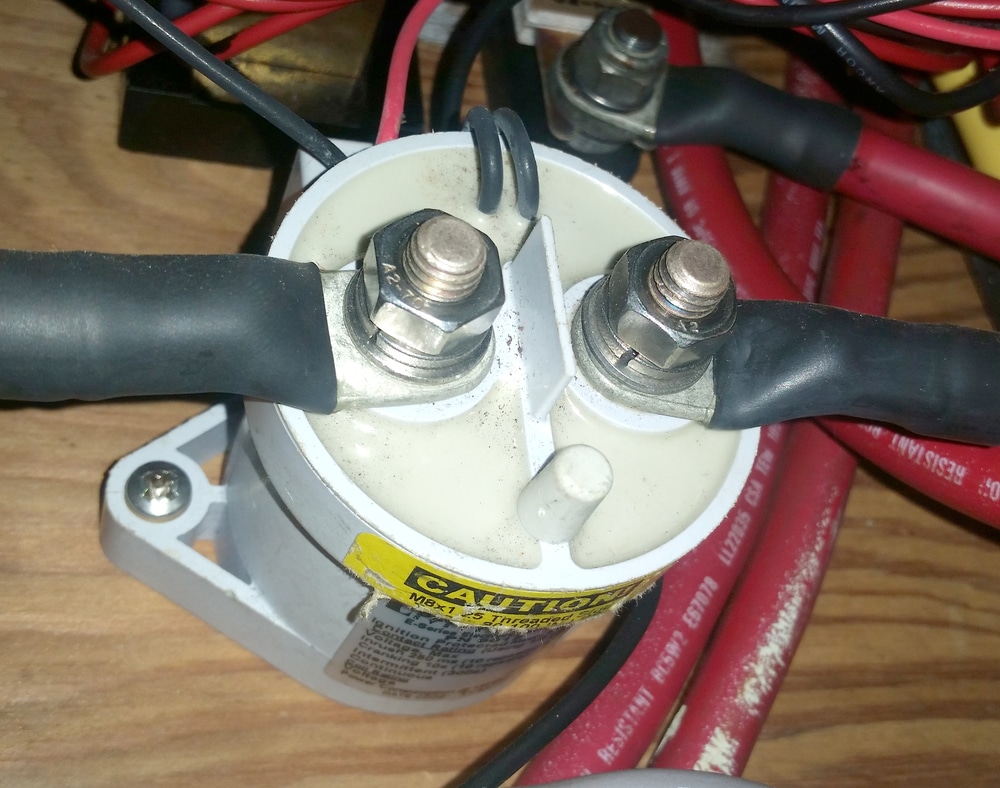

This contactor is wired to the main key switch. It is a bit redundant but shuts off any power from the controller, motor and gauges. It acts more like a battery shut off.
(N) – Secondary Contactor
This contactor supplies the motor controller with the power it needs to run the motor. It is also the one that is bypassed by (T) the pre-charge resistor. Contactors are just big remote activated switches. Like breakers, they activate very fast to eliminate high amperage arching.
(P) – Motor Controller
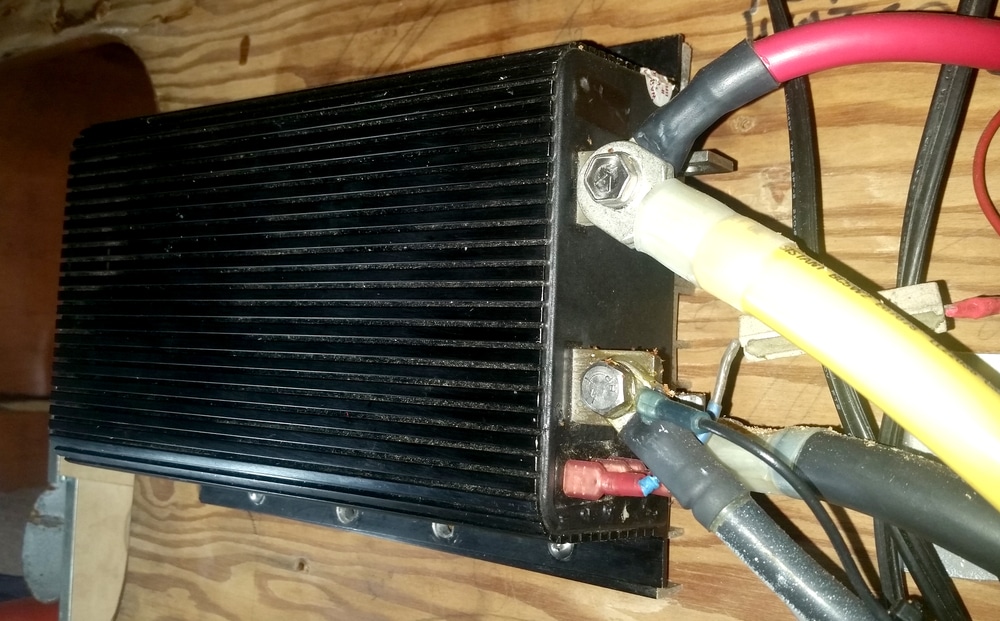

The motor controller we chose works for our application, but there are many out there to choose from. Do your own research here before deciding on what motor you will use. We happened to get a sweet deal on ours so we made it work with our motor. Our system would be less complicated if we used a controller designed for a SEPEX motor. The Curtis 1209B that we have is designed for a Series motor, but we make it work.
(Q) – DC Motor (SEPEX)
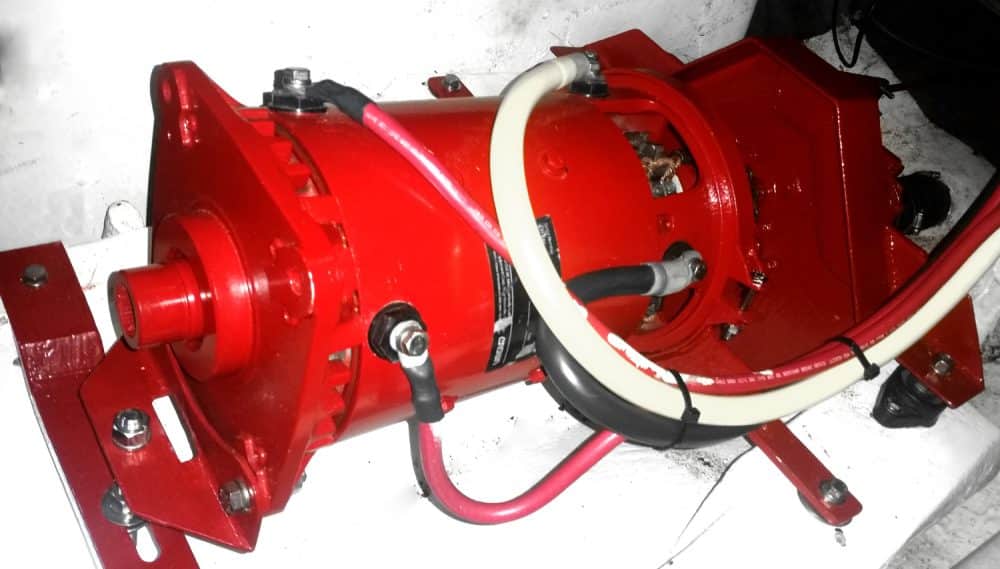

Sorry, you’ll have to find this one on your own.
Since another motor like ours has yet to show up again for sale online, we can’t really recommend the same one. However, the basic idea is finding a motor with the appropriate wattage to push your boat. Refer to our “Power Requirements” section to get an idea of what that might be. Then just make sure it will produce the desired power at a voltage that you would like to work with. We recommend 48V for most applications for reasons described previously.
(R) – Amp Meter
These attach to the shunt (J & M) and show you how many amps are running through the system. Depending on where it is placed it can either read the amps being drawn from the battery bank or the amps going to the motor. We decided to read the amps being drawn from our batteries.
(S) – Volt Meter
This meter does not require a shunt. As long as the negative lead makes its way back to the negative buss bar, the positive lead can be attached at any point along the circuit. We chose again to read the battery bank voltage with ours. However, it can also be place on the motor to read the voltage there instead.
(T) – Pre-charge Resistor
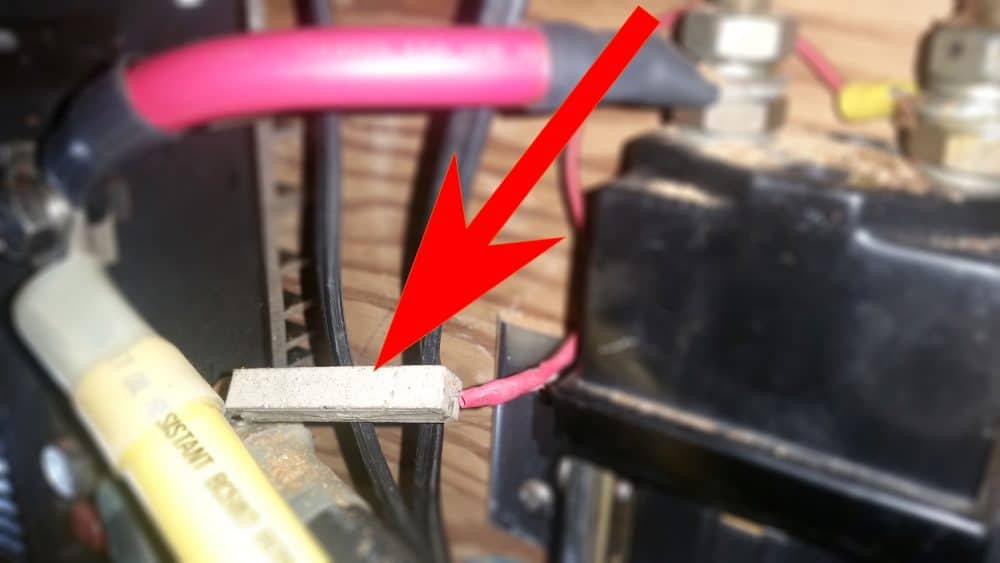

They look like THIS .
There is no specific item to show you here. Each controller and each set up is different. But, I can tell you that the pre-charge resistor is very important. It by-passes the main contactors and supplies the motor controller with the power it needs to pre-charge, so its ready when the main contactor is switched on and all that amperage comes rushing in.
Make sure you check out SV Bianka’s page for another detailed blog about his electric motor installation.For another great article about all the other stuff that goes into a motor installation,
you might want to read “Balance of System” . The article is for an electric motorcycle set up, but the basics are similar enough.

One thing we learned very early on was that . . .
Volts (v) x amps (a) = watts (w) or v x a = w.
At first we thought (please don’t laugh we were total newbies) that if we took 4 – 12V batteries with 125aH, and wired them in series, we would get a 48V bank with 500aH capacity. Obviously we forgot everything we learned in high school algebra. We soon resolved our mistake and learned that this formula is at the heart of everything electrical. As you can see, Watts are the thing you need to pay attention to. Remember high school physics? W=Work. Many appliances in your house, often things that produce heat, are rated in Watts, but marine stuff tends to rate things in Amps. Well, for our sake Watts are king. No matter what boat you have, it requires a certain amount of work (Watts) to push it through the water at any given speed. So, your job is to charge, store and supply to the motor a similar amount of wattage in order for your boat to move. The more watts you can store, the longer you can push your boat.
“The more watts you can store, the longer you can push your boat.”
As mentioned before, our motor is a SEPEX motor. This meant that the field and armature needed 2 separate voltages in order for the motor to spin. The way we solved this problem was with two separate battery banks. The field is powered by the house bank at 12V. This bank consists of two deep cycle batteries wired in parallel giving us about 250Ah at 12V. So far, it has held up great. It powers everything onboard including the inverter and laptops. We use about 30Ah on a slow day at anchor, and around 70Ah when sailing or when we’re both using our laptops all day at anchor. The nice part, is that even on a cloudy day, our 480W solar bank can replenish that before dinnertime. But we’ll talk more about that in the next section, “CHARGING” below.
The motor bank consists of 4 – 12V deep cycle batteries wired in series giving us about 125Ah @ 48V. This may not seem like much, but in the last month of sailing, we have logged over 1000 miles, including sailing 25 miles up the Cape Fear River, and have never depleted the motor bank more than 35%. That works out to drawing only 44Ah used. We’ll talk more about range and testing below in the “TESTING” section.
There are many types of lead acid batteries on the market. Don’t get too invested in brand. Most of the batteries on the market today are made by the same two companies. Trojan seems to be the brand of choice for many. We found batteries for sale locally and for $100 each, including delivery, we couldn’t pass them up. We also knew that the flooded lead acid bank we installed is only temporary. Like we’ve said before, this whole “Electro-Beke” thing is really one big experiment. We have plans to install a LiFePO4 bank soon enough. But we’ll tell you all about that in the “WHAT’S NEXT” section below.
There are many inefficiencies in electrical systems, like heat. However, don’t worry about them too much. If you budget 30% power redundancy into your system, it will more than cover any losses from heat, or mechanical friction and so on.
Check out www.batterystuff.com . They have useful calculators for battery banks and solar, along with great information on different types of batteries and what they are used for.

Our Solar System . . .
Also doesn’t include pluto..
We have 480 watts of solar. Broken down into 2 – 240W panels at 24v wired in series to give us a nominal voltage of 48V. Did you get all that? Great! Steven, from Solar EV Systems , gave us a great deal on them, landing him a spot in our Uma Angels Family . There are a several types of solar panels, but as far as we can tell, any modern panel is efficient and well made. None are much more efficient that others, it’s more about the size of your mounting space, and the size of your wallet. The ones we have are made by Trina, They are not expensive, look well made and perform exactly as promised.PV (Photovoltaic, aka solar panel) modules have three different voltage ratings that are handy to understand:
- The nominal voltage of a panel could also be called the “conversational voltage.” When we talk about the voltage of the panels and the other components of the system, we’ll most often use the nominal voltage. Nominal voltage actually refers to the voltage of the battery that the module is best suited to charge; the term is a “leftover” from the days when solar panels were used only to charge batteries. The actual voltage output of the panel changes as lighting and temperature conditions change, so there’s never one specific voltage at which the panel operates. Nominal voltage allows us, at a glance, to make sure the panel is compatible with a given system without having to look at the exact voltage. Our panels have a nominal voltage of 24V. We wired them in series which gives us 48V. It reality, they put out about 75V on a sunny day. But our charge controller allows us to charge a battery bank from 48V all the way down to 12V with the same solar panel set up. We’ll talk more about our charge controller later.
- The second voltage rating is the maximum power voltage (Vmp). This is the highest voltage the panel can produce while connected to a system and operating at peak efficiency. As mentioned above, the max our panels will produce is around 75V, even though we talk about them as a 48V panel system.
- The third voltage is open circuit voltage (Voc). This is the maximum voltage that the panel can produce when not connected to an electrical circuit or system. Voc can be measured with a meter directly contacting the panel’s terminals or the ends of its built-in cables.
Panels also have two different current ratings: current at maximum power (Imp) and short circuit current (Isc), both listed in Amps. The maximum power current is similar to Vmp: it’s the maximum current available when the panel is operating at peak efficiency in a circuit. Ours can produce 35Amps at max efficiency, They consistently produce 30A on a sunny day and we’ve seen as much as 32A. Similar to Voc, the short circuit current is the current measurement your meter would show when in contact with the positive and negative terminals of the panel while not connected to a system or load.All these voltage ratings and current ratings are often found on the back of a panel. Use them to estimate how much power they will be able to produce.
Two rules of thumb:
- 1kW or solar will produce 4kWh/day
- Rated Watts / 3 will get you approximate Ah/d @ 12V.
So, according to this, our 480W panels should give us 160aH on an average day, which we’ve found to be quit accurate. Although, we’ve only ever needed more that 100Ah of charge on one occasion. So usually, our batteries are charged back up before lunch, and we spend the rest of the day on “float” charge.
Types of Panels
Monocrystalline.
These are single silicon cells grown into larger crystals, then cross-section cut into small wafers to form individual cells that are later joined together to form a solar panel. This cell type has high conversion efficiency which means it takes up less space on deck. These cells are generally not shadow protected and are often more expensive per watt.
Multicrystalline (Polycrystalline)
These cells are also single silicon cells constructed by utilizing multiple amounts of smaller crystals to form a cell. This cell type has very high conversion efficiency but is also not shadow protected. Although, you should really be installing any panel so it doesn’t get blocked by shadows throughout the day. It will drastically increase the output if you install them in a proper location.
Amorphous silicon
These are the most inexpensive to manufacture. They are produced by depositing an active silicon material on various substrates like stainless steel sheet. The conversion efficiency is not as good as the single crystal type, but Uni-Solar panels are this type of panel and are shadow protected. Shadow protected means that a panel continues to charge when part of the cells are in a shadow, like a stay, which is a great advantage on a sailboat.
Our Charge Controller . . .
Is at the heart of it all..
The next, and possibly most important component in our charging circuit, is our Midnite Solar KID charge controller. This thing is amazing. Midnite also joined our Uma Angels Family when we asked them to send us a controller and they agreed. We spent a lot of time researching solar charge controllers and learning all about PWM vs MPPT. Bottom line is, if you can afford it, get the MPPT controller. We chose the Kid because it’s just the most efficient at collecting power from your panels. It is also easy to program and understand. We currently run it at 12V and just rewire our motor bank to 12V when we need to charge it. However, we will soon be adding a smaller, simple 12V charger to the “load” circuit of the Kid. This will allow the Kid to be permanently charging the 48V house bank. But, when it is full, switch over to the “load” circuit and charge our house bank through the smaller controller. It may all sound too complicated now, but once it’s installed and working, we’ll be sure to share everything with you in more detail.
“We have never gone 24hrs without fully charged batteries.”
On a boat, where space is at a premium, you need all the efficiency you can get. Right now, I’m sitting on the boat, it is overcast and raining outside, it’s noon and we’re getting around 100W of power in from our panels (about 8-9A @ 12V). Our house bank will be charged back up by dinnertime, same as the last few days, and we haven’t seen the sun all week. When it is sunny, our house bank is usually charged back up before we wake up in the morning. No we don’t wake up THAT early, usually around 10am, but seriously, if it’s sunny in the morning, we put 30+aH into our batteries before 10am. The charge controller runs silently, however it makes a tiny click when it switches from “resting” to “BulkMPPT”. Since on a boat, we’re attuned to every tiny sound, we usually here it click on and off a few times before the sun even rises. Mind you, it’s only putting in 0.5aH then, but still, the sun isn’t even over the horizon yet and we’re already charging our batteries.
Check out “Step 26” when we install our solar panels and charge controller.
The rule of thumb we used when designing our system is that 1 – 100W panel can charge a single deep cycle battery from 50% discharged in a single sunny day. So we have 6 batteries, so ideally we would have 600W of solar. Now, that just wasn’t practical for us, so we settled for 480W and it keeps up just fine. However, if we discharged our motor and house bank down 80% we would need about two sunny days to get them both topped back up fully. Or, about 4 rainy days. For us, this isn’t an issue since we typically use the motor for very short periods of time right before anchoring or when setting off for a multi day passage. So, by the time we need them again, their both fully charged and ready to go. If not, we’ll just hang out and drink a beer. So far it’s never been an issue or even come close to it. We have never gone 24hrs without fully charged batteries.
Many have suggested we have a small generator on board as a back up, just incase there is no sun for many days and our batteries are dead. So far, we have gone a full week without sun and our solar has kept up just fine. Although, we may design a system with the ability to be hooked up to a genset for extending motoring, like say the Panama Canal, so that if we ever needed to, we could just set a generator on deck for a few days and then get rid of it as soon as we’re done. But, for now the whole point was to get away from petrol dependance.
So far, solar is our only means of power production. We do have plans to get working regeneration from the prop while sailing. The possibility is definitely there, and we have tested for voltage while sailing. But as of today, we haven’t hooked up a charge controller to it. Mainly because we just don’t need it…yet. Our power requirements are so minimal and we use the motor so little, that we haven’t bothered to hook it up yet. But, it is on our short to-do list. So stay tuned for future updates.
HERE is a link to a great forum talking about solar systems, battery banks and how to balance them.

How far can you motor?
Maybe the most asked question we receive..
It’s a valid question for sure, and one that many have asked us. But, we have yet to find out. We are still early on in our testing phase of the experiment. We’ve used the motor many times but rarely for more than 10-15 min and never more than 30. It is also hard to find “ideal conditions” to test in. There either isn’t enough space, time or light. Or the tide and wind aren’t in our favor. Sounds like excuses we know, but it’s the truth.
“We are in no hurry to go anywhere, ever.”
From what we have done, we can tell you this. Our max speed has been right at 4kts. but it was against a slight current, maybe 1kt max. So, that would mean our theoretical top speed is closer to 5kts.
Here again, we haven’t actually found out. Mostly because without a tow boat right beside us, it would be dangerous to run out of power in the middle of a channel or bay where there are “calm conditions”. But, we’ve motored for 2 nautical miles at 3kts (with a 1kt tide in our favor) and it drained our batteries down to 70%. So, that would mean that in “ideal conditions” we could motor at 2kts for 6 nautical miles. Doesn’t sound like much, we know. But, with a favorable tide and even a slight favorable wind, we can extend that tremendously. We also wait for the wind and tide to be favorable and then just sail to where ever we need to go.
With limited area to mount solar panels and without a genset, we knew if we used more power that we could generate, we would always have dead batteries. So, from the beginning, we focused more on how much power we could consistently generate, and base our system off of that. To us, the meant using less, not necessarily making more. Our solar has kept up great so far, but our power needs have also been minimal. We have autopilot and a chart plotter that are always on when sailing. We also use our laptops constantly and run a small inverter for tools and small cooking appliances like blenders. We have all LED lights too. We don’t have a refrigerator yet or windlass. But they are on the short list. We also have yet to capture any power from the prop while sailing. So there is still room to capture more power if we need it.
As we continue to sail further and upgrade and modify our system, we will also continue to update you on how it all works here. So keep a look out for updates on our Facebook page and in future videos.
WHAT’S NEXT

We may have a spinning Motor . . .
But the fun has just begun..
Well, our motor works. It pushes our boat reliably. The Electro-Beke experiment is a success, at least in our eyes. Now the real fun begins. We’ve proven to ourselves that we can sail further that we thought and use the motor less than we originally planned. So, what’s next?
“We have a few more project on the list of upgrades and modifications.”
We have a few more projects on the list of upgrades and modifications. The first thing on the list is to rewire our system and remove the redundant components left over from the direct drive phase. After that, installing some better gauges and monitoring systems would be really nice. There is a “fuel gauge ” we would like to install for the motor bank and house bank. It is simple and relatively smart. It will give us an accurate state of charge in a quick glance.
Next on the list will be installing a charge controller or developing a similar system to allow us to capture power from the spinning prop while under sail. Technically our motor is capable of it, and early tests have augmented this theory. We are currently working with a few companies to figure out what the best system will be.
We also need to install a larger heat sink for our motor controller. The one that came with it is designed for air movement across its fins and is therefore undersized for our needs. However, we may be upgrading to a true SEPEX motor controller before long, so it will handle regeneration and would require a different heat sink anyway.
The big ticket item on the list is to install a large LiFePO4 battery bank. We have our eyes out for a salvaged Nissan Leaf or Chevy Volt that still has its battery bank intact. We’ve seen them for sale before and would love to get our hands on one. LiFePO4s are much more stable than other types of Lithium Ion batteries. But, we’ll talk about that if and when we actually get our hands on some.

Signed in as:
Hercules Electric Marine
Introducing Hercules Electric Marine. We are a producer of an electric drive system that is revolutionary in its approach. More horsepower, more efficiency, more control and more pleasure out of your boating experience.
Hercules Signs Supply Agreement with Coach Marine Group
Hercules Electric Marine signs agreement with Coach Marine Group to supply electric propulsion systems for their Coach & Xcursion brand pontoons. Initial deliveries to start in 2023.
Get exactly the power you need! Clean, Quiet and Easy! Just unplug and play!
Available for all boat hull types
Hercules Electric Marine Featured Channel 4 WDIV in Detroit
Electric boats making waves....
Our founders, James Breyer and Julie Tolley were interviewed by WDIV Channel 4 here in Detroit discussing marine electrification as well as our electric propulsion system. We took the reporter, Rod Meloni, and his crew out for a spin demonstrating our system. Electric boats are coming, powered by Hercules!
Why Electric?
We designed a system that is highly capable, offers superior performance to gas engines and can survive harsh environments. An electric propulsion system offers numerous benefits over a gas engine including less maintenance and lower total cost of ownership.
Hercules Product Offerings
Manufacturer, re-power / new power.
Hercules Electric Marine is bringing advanced electric propulsion technology to the boating industry. With our efficient design we offer boat builders design freedom as the Hercules e-Drive system seamlessly integrates into your existing configuration taking up significantly less space than traditional gas or diesel engines.
You can utilize our integrated e-Drive system or we can work together to create a custom solution that will fit your and your customer’s needs. We are bringing quiet, clean, and powerful marine propulsion to recreational boating. 250hp equivalent, multiple battery options, and customization options to provide a superior boating experience. The Hercules e-Drive system can give your customers a better experience than gas engines with no gas, no fumes, no maintenance, optimized performance, and all-day power.
Contact us to find out more or set up a demonstration.
If you are looking to Re-Power or get New Power for your boat our Hercules e-Drive system may be right for you. The Hercules e-Drive system is our proprietary technology platform designed to revolutionize recreational boating. We can create a custom electric solution to fit your current or new boat. Our advanced electric powertrain can be configured to fit almost any boat taking up a fraction of the space of a combustion motor. The Hercules e-Drive system is more efficient, environmentally friendly, requires less maintenance and is more fun than gas outboards or inboards. No more hauling gas cans to the dock or filling up at the marina. Just unplug and go!
The Hercules e-Drive system utilizes powerful permanent magnet motors, all digital drive-by-wire controls, and up to 94kWh of battery storage for all day power. Hercules marine packages include state of the art on-board chargers to charge your craft using 110V, 220V outlets or auto industry fast chargers. This system also acts as a 12V battery to power all your stereos, marine electronics, and accessories all day long. We even have integrated solar charging systems coming soon.
Check out our specs and contact us to see how Hercules Electric Marine can provide you with an electric powertrain without compromise and delivers exactly what you are looking for.
Hercules Electric Marine Platform "Powered by Hercules"
Up to 250 HP marine propulsion with all digital controls and multiple battery options.
Hercules Electric Marine Approach
Powered by Hercules Electric Marine drive system. Take a look. We are coming early 2022. Fun Electrification by Hercules.
Stay tuned for details of our electric boat options.
43100 West 9 Mile Road, Novi, Michigan 48375, United States
Drop us a line!
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Have Fun With Hercules Electric Mobility!
Connect with us.
Copyright © 2023 Hercules Electric Marine - All Rights Reserved.
Powered by Hercules
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
This website uses cookies.
We use cookies to analyze website traffic and optimize your website experience. By accepting our use of cookies, your data will be aggregated with all other user data.
JavaScript functionality for your browser has been deactivate. Please activate JavaScript so you can use all functions on this page.
- ‹ Return |
- › Products
- › Hybrid Drives
Deep Blue Hybrid
Deep blue is a fully integrated propulsion and energy management system, industrially engineered and customizable with modular components. the result is exceptional performance, compliance with international safety standards, and highly intuitive operability.
- Relaxation: no noise from the motor and only a little noise from the generator
- Environmental protection: use renewable forms of energy
- Independence: adequate energy on board, less need to head for a marina
- Convenience: simple joystick docking
- Simplicity: only one type of fuel – and less of it required
System Overview of the Hybrid Drive System
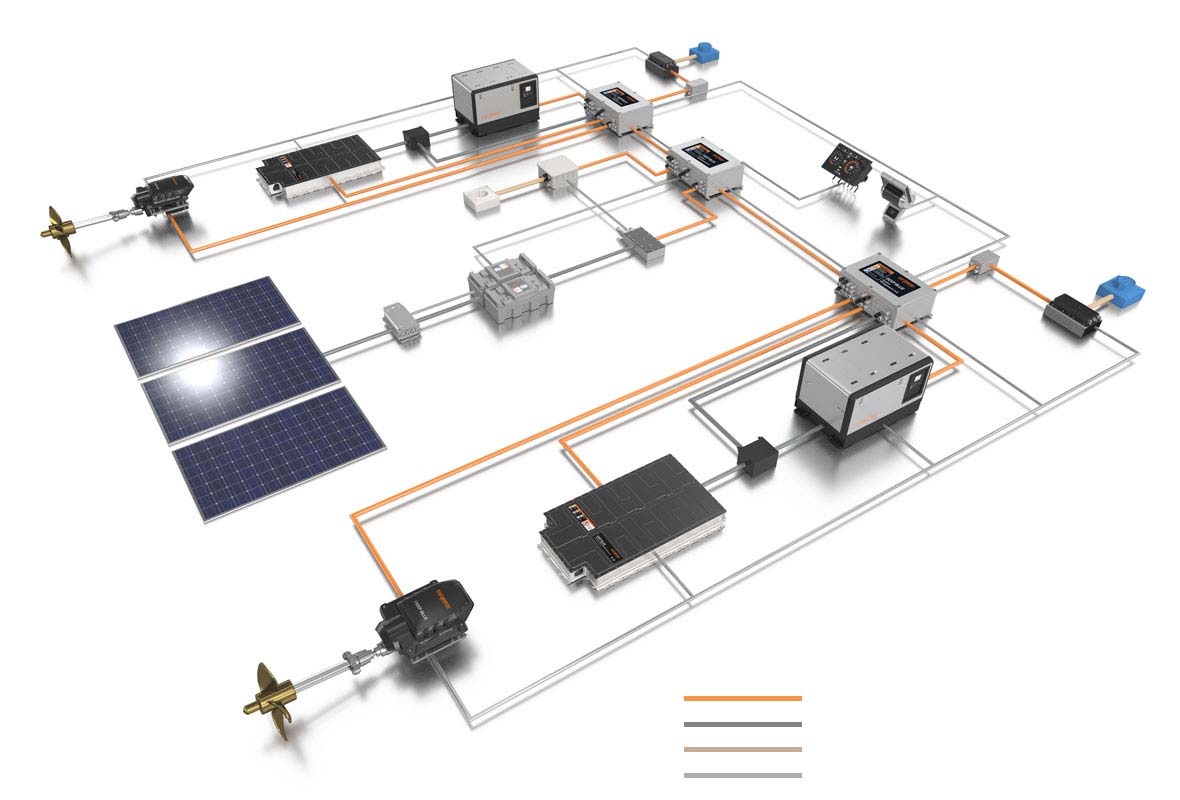
System Components
High-capacity lithium battery technology.
Lithium-based batteries are the technology of choice for electric mobility applications. They store significantly more energy than all other batteries, they maintain a high current, they do not lose their charging capacity, they supply power reliably, and have no memory effect. They also have a much longer useful life than lead-based batteries.
The benefits for customers:
• High energy density
• Lower costs
• Long service life
• Highest quality and safety standards
Dimensions and preliminary specifications
Click here to learn more about battery technology

Economical auxiliary power
Third-party generators can be integrated into the Deep Blue system via the DC generator interface developed by Torqeedo. The converter generators eliminate the fixed ratio between rotational speed, power and voltage output.
Integrated into the information, safety and energy management system of the Deep Blue Hybrid, the generators produce any combination of power and voltage as required, adopted to individual setting.

Third-party generators can be integrated into the Deep Blue system via the DC generator interface developed by Torqeedo, providing long-range motoring and efficient backup power for serial hybrid systems. The converter generators eliminate the fixed ratio between rotational speed, power and voltage output.
Integrated into the information, safety and energy management system of the Deep Blue Hybrid, the generators produce any combination of power and voltage as required, adopted to individual setttings.
Technical Data

Typical application areas
Perfect for ...
• Torqeedo Deep Blue Hybrid drives with shaft power from 25 to 100 kW (equivalent to 40 – 160 HP)
• Sailing yachts, ferries, water taxis, etc., with hull lengths from 40 to 110 feet (12 – 33 m)
Highly flexible thanks to four operating modes
The Deep Blue Advanced Energy Management System offers four ways of conveniently operating the hybrid system automatically:
Electrical drive power, on-board power and charging power of the highest standard
The Advanced Hybrid Control System for the Torqeedo Deep Blue Hybrid system controls the generator to optimum effect (single or twin installations). It provides a reliable supply of electricity for 360V DC boat drive systems as well as all other 110/230V AC and 24V DC power supply systems on board:
Hybrid and charging power for the Torqeedo Deep Blue system
• AC on-board power supply for galley, air conditioning, water maker and other electrical consumers on board (hotel loads)
• Low-voltage DC power for lighting, radio, navigation, winches, etc.
Always in control
Deep Blue Hybrid offers intuitive operation presented on the multifunctional display, providing a complete overview of the entire system and access to all control functions.
The software keeps an eye on everything and prevents errors like deep-discharging batteries. An easy-to-understand graphical user interface is available as either multihull or monohull and delivers complete, up-tothe- minute system visualisation.
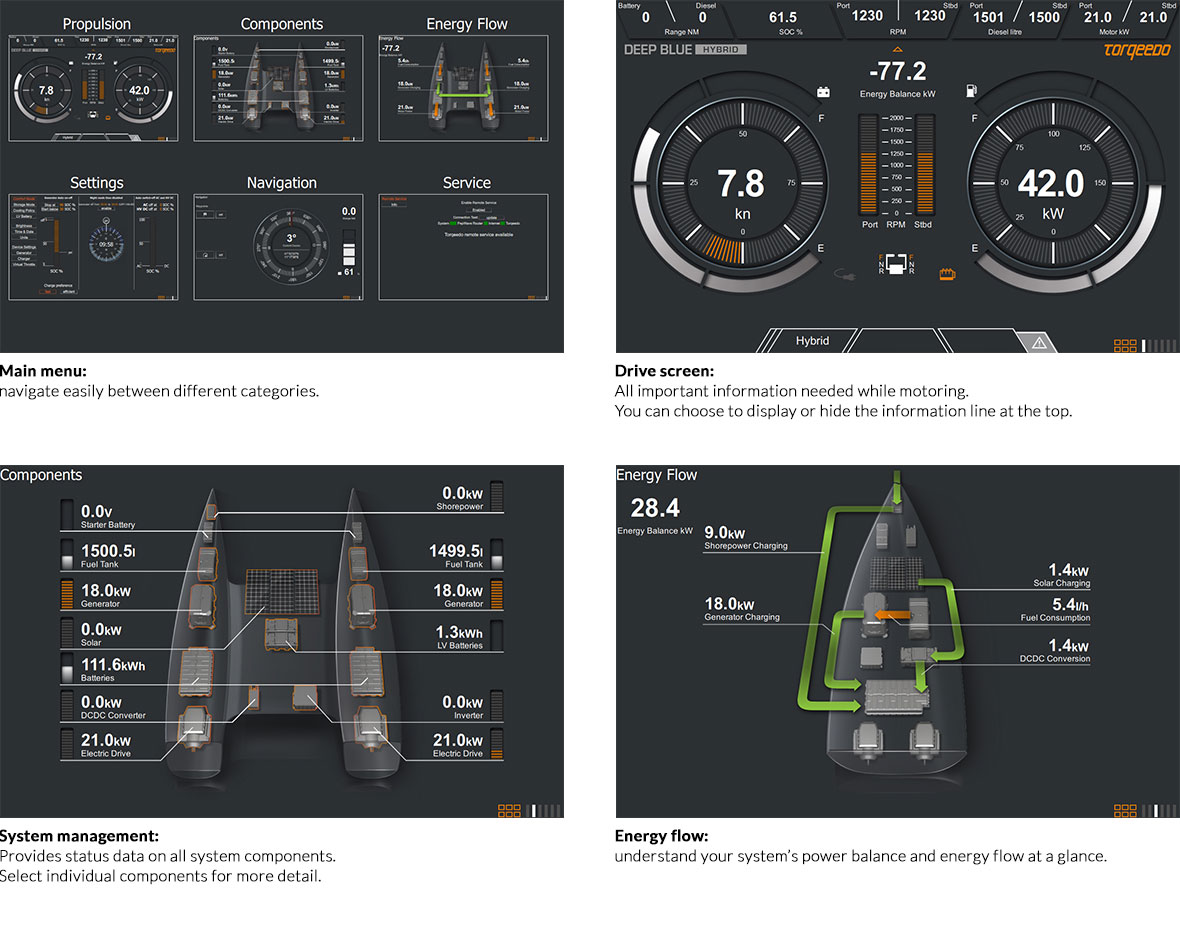
Premium throttles
We’ve come to expect an intuitive way to operate our technical devices. We expect detailed information, nicely displayed and clearly arranged. We expect that the objects we use are both beautiful and functional.
This is what spurred us to create the new Torqeedo throttle family and improved user interface for Deep Blue.
Our premium throttles offer the right solution for every application, whether for sailboats or on motorboats – ergonomic, strong and functional. All premium throttles come with Bluetooth built in for simple integration of Torqeedo’s TorqTrac smartphone app.
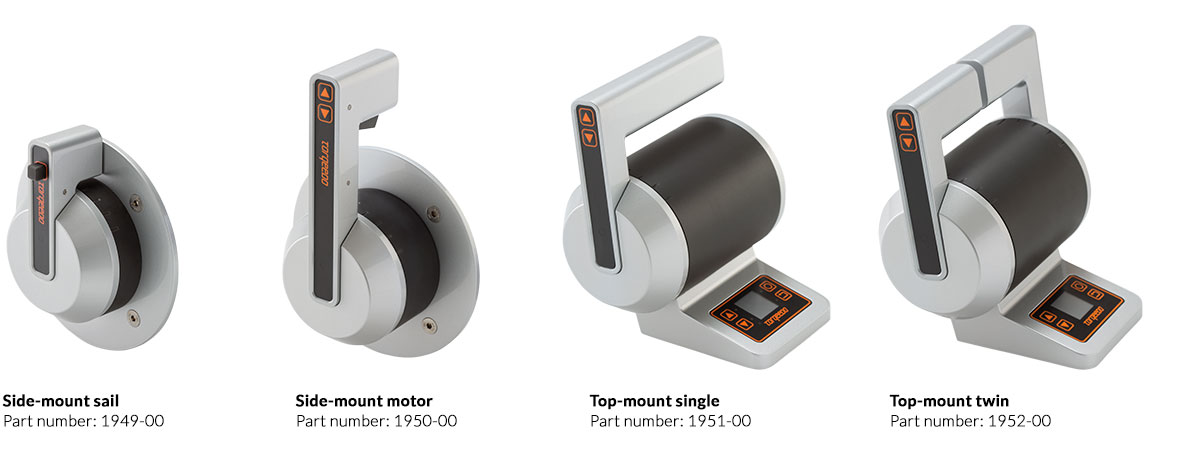

Hybrid Drive System and Integrated Energy Management
Hybrid drive system.
Powerful and silent electric drive systems allow manoeuvring and sailing at hull speed.
High-performance batteries adapted from the automotive industry enable prolonged motor-cruising for up to 50+ nautical miles without use of a generator. Solar power generated on board and hydro-generated energy – the propeller rotates while boat is under sail – provide additional propulsion. Besides, the integrated generator provides sufficient energy to cover long distances, if required.
The slowly rotating electric drives allow precise maneuvering and in combination with joystick docking makes putting out to sea and berthing as easy as pie.
Integrated energy management
The integrated management system of Deep Blue Hybrid makes it possible to use available power in any way you wish – for the powerful high-voltage drive system, for the 24 V on-board power supply or to operate equipment with 230 V AC current. Deep Blue Hybrid is designed in such a way that energy is always available where it's needed.
The combination of energy generated from renewable sources and by the generator means that there is always sufficient power available. However, the generator does not need to run for as long.
Clean and safe electricity can be used for all equipment and so it is no longer necessary to have propane or petrol on board. A tender can also be run electrically and can be charged from the Deep Blue Hybrid on-board power system.
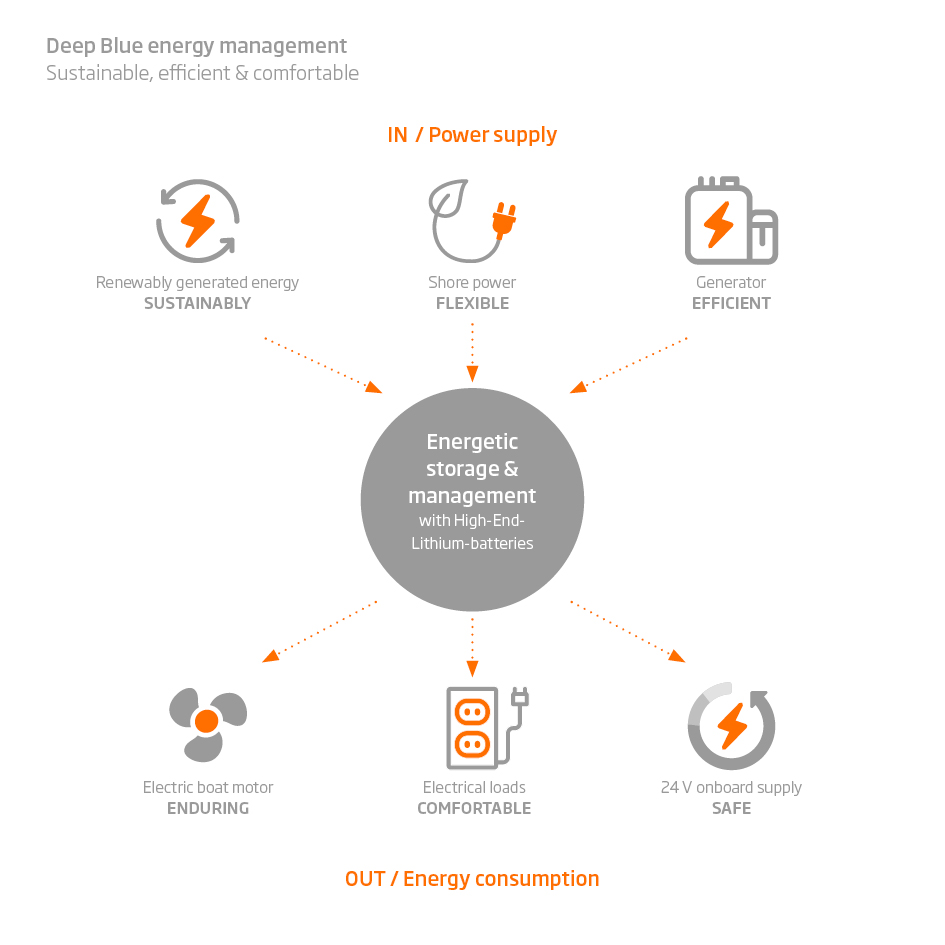
Professional Safety
Professional safety for your sailing yacht.
Particular attention should be paid to standards compliance and safety during the development of a hybrid drive system. During the years spent on developing the Deep Blue Hybrid system we followed safety concepts that, for example, are standard in the automotive industry – but which previously could not be found in powerful electric drive systems for electric sailing yachts.
In addition, electrical drive systems for electric sailing yachts pose special challenges that are not relevant for other industries. In this respect, it is not enough to just follow the standard of other industries for high-voltage boat drives. As we are used to setting new standards, we have done so with regard to safety. Below you will find a number of examples of the Deep Blue Hybrid's unique safety concept.
Isolation monitor: constantly monitors that the voltage from all 360 V components is completely isolated from the boat – not just for individual system components but for all of them. If damage is detected, e.g. to the cable insulation, the system will issue an alert. In the event of dangerous insulation failure, the system will be shut down.
All components are waterproof: Components that were not specifically developed for boats are not always waterproof. All the components of a high-power system on a boat must be waterproof to guarantee safe operation. That is why all of our components are waterproofed.
Automotive industry-level battery safety: The first lithium batteries for the marine industry with the advanced quality standards of the automotive sector are the result of Torqeedo's collaboration with established battery manufacturers. Integrating a battery into a drive system and the associated safety concept alone requires considerable effort that can only be achieved by working together with the battery manufacturer.
Battery venting: In the unlikely event that the redundant safety mechanisms of the battery fail, the battery cells can reduce their temperature and pressure via a pressure valve. While batteries are installed in electric cars in such a way that they can discharge battery gases directly onto the road, on electric boats the gases must be channelled safely off the vessel. We developed the first safe venting system for boats for the Deep Blue System.
Battery damping: All components on fast and seagoing boats are subject to constant high levels of shock that exceed shock levels on the road – in some cases over 12 g of acceleration force. The same holds true when trailering the boat. Since batteries and battery electronics are not designed for these constant impacts, they need their own damping system on boats (in addition to the damping mechanisms within the battery). Torqeedo is the only company in the world that provides this for maritime use.
Benefits for Boatbuilders
Custom-built solutions are often pursued in order to meet a user's requirements. These individual hybrid projects raise a number of difficulties:
- High-end components do not exist for the custom project. High-tech safe lithium batteries, for example, require an intensive design-in process in close cooperation with the battery manufacturer's research and development department. However, reputable high-voltage battery manufacturers do not supply their batteries for custom solutions that they are not familiar with and that have not been coordinated with them in detail.
- Creating an integrated hybrid system requires a comprehensive research and development project accompanied by many person-years in the field of development running to the tune of several million euros. These efforts are not undertaken for custom projects, leading to lower reliability and a lack of complex but important safety features (such as pilot lines).
- The system integrator has the statutory duty to ensure that the hybrid system complies with all the relevant and mandatory standards such as the Machinery Directive and the EMC Directive. Custom hybrid systems do not generally meet these standards. Since a boatbuilder is responsible for ensuring that the entire boat complies with standards, the installation of custom-built hybrid systems constitutes a serious risk for boatbuilders.
Unlike custom-built hybrid systems, DEEP BLUE HYBRID addresses the requirements of environmentally aware customers, offering a turnkey solution that guarantees compliance with the relevant norms and standards.
- DEEP BLUE HYBRID was created in an extensive research and development project involving a large number of mechanical and electrical engineers over several years. The components were carefully selected and coordinated with an overall system. Essential inspections and certifications were performed at system level.
- High-end components such as hybrid batteries from the automotive industry were integrated into the system.
- Torqeedo assumes responsibility for the functionality and compliance with relevant standards for the whole system.
- DEEP BLUE HYBRID was developed on the basis of modular components. It allows flexibility and scalability without affecting system integration and reliability.
- DEEP BLUE HYBRID for electric ferrys, electric sailing yachts, electric catamarans & electric water taxis.
If we have awakened your interest in our products we would be pleased to send you more detailed information. Simply enter your details in the contact form below and we will get in touch with shortly.
The little (electric) engine that could: The Port of San Diego unveils the nation’s first all-electric tug boat

The 82-foot eWolf expects to eliminate 3,100 metric tons of carbon dioxide
- Show more sharing options
- Copy Link URL Copied!
The nation’s first all-electric tug boat has docked at the Port of San Diego and expects to begin emissions-free operations in about a month.
Operated by Crowley Maritime Corporation , the 82-foot eWolf will escort ships entering and leaving the Tenth Avenue Marine Terminal using electric power instead of diesel fuel, helping slash greenhouse gas emissions at the port and its neighbors in Barrio Logan and National City.
For the record:
1:58 p.m. March 13, 2024 This story has been updated to show the correct amount of government funding that went to the project.
“This is a big deal,” said port chairman Frank Urtasun at a news conference Monday. “This is new technology.”
Capable of speeds of up to 12 knots, the eWolf is powered by a 6.2 megawatt-hour main propulsion battery and two electric drives. The tug has thrust — also known as bollard pull in the parlance of the shipping industry — of 76.8 short tons, which is more powerful than the diesel-powered counterparts at the port.
Constructed in Alabama, the eWolf is equipped with two small generators for emergency use that allow the boat to travel longer distances at a reduced speed.
“Like an electric car, you step on the gas and it jumps,” said Paul Manzi, vice president of Crowley Shipping, based in Jacksonville, Fla. “All of the attributes that you have with an electric motor operation in a car or in an electric truck, you see here in the (eWolf) at massive scale. And it’s extremely quiet so when it pulls away from the dock you literally won’t hear any noise.”
The tug boat’s electricity will come from a charging station that is part of a microgrid facility equipped with two energy storage containers. Battery modules in each container have storage capacity of nearly 1.5 megawatt-hours.
Interconnected with the help of San Diego Gas & Electric, the charging station at the port is designed to allow the vessel to recharge quickly and reduce peak loads on the electric grid.
Operators plan to charge the eWolf overnight so it can perform its chores during daytime hours.
“This technology has individually been around for a while, but it hasn’t necessarily been integrated and optimized to all work together — and that’s kind of our role,” said Bruce Strupp, vice president at ABB Marine & Ports , the company that designed the boat’s propulsion system. “Some of the technology is our technology, some of it’s third-party technology, but we integrate it all together.”
The electric tug boat is expected to begin commercial operations at the port in mid- to late-April, depending on the completion of the charging station.

Officials at Crowley did not release the eWolf’s price tag Monday, saying only that it cost about twice as much as a conventional diesel-powered tug boat of comparable size.
But, Manzi said, the company expects the eWolf’s maintenance and operating costs will be “dramatically lower” than what’s spent on a diesel-powered tug boat because the electric model has fewer moving parts.
The entire project — the vessel as well as the charging station — received four grants that added up to $13.67 million, with two grants of $10.9 million from the San Diego Air Pollution Control District, one grant of just over $2 million from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and $750,000 from the federal government’s Maritime Administration.
In 2020, Gov. Gavin Newsom signed an executive order that directed state agencies to transition off-road vehicles — including tug boats — and equipment to 100 percent zero emissions by 2035.
By replacing one of the port’s diesel-powered tugs, the eWolf is expected to eliminate the consumption of about 35,000 gallons of diesel fuel per year. In its first 10 years of use, the electric tug boat is expected to reduce about 3,100 metric tons of carbon dioxide from the port and its surrounding areas such as Barrio Logan and National City.
“We’re trying to be good neighbors and trying to be able to help to reduce emissions here to help the electrification movement,” Urtasun said, adding that the port has spent about $130 million on various electrification projects.
Last year, the Port of San Diego became the first in North America to install a pair of all-electric cranes to load and off-load heavy cargo. Each 262 feet high, the cranes replaced an older crane that ran on diesel fuel. Together, the cranes expect to help the port reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 47 metric tons per year.
Get U-T Business in your inbox on Mondays
Get ready for your week with the week’s top business stories from San Diego and California, in your inbox Monday mornings.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the San Diego Union-Tribune.

More from this Author

Wind project in San Diego’s backcountry runs into turbulence
March 22, 2024

San Diego Community Power signs agreement for big energy storage project that could power 45,000 homes
March 21, 2024

If the city of San Diego ran its own municipal utility instead of using SDG&E, how much would it cost?
March 15, 2024

Blowin’ south of the border: Sempra subsidiary will build a new wind farm in Mexico

San Diego EV charging company completes $1 million deal with the U.K.’s defense ministry
March 12, 2024
Here’s how many San Diego customers are behind on their utility bills
March 10, 2024
More in this section

National Business
Serbians are petitioning against a planned luxury project backed by Trump son-in-law’s firm
An opposition group in Serbia has launched a petition against a real estate development project that would be financed by the firm of Donald Trump’s son-in-law Jared Kushner

Judge dismisses lawsuit by Musk’s X against nonprofit researchers tracking hate speech on platform
A federal judge has dismissed a lawsuit by Elon Musk’s X Corp. against the non-profit Center for Countering Digital Hate, which has documented the increase in hate speech on the site since it was purchased by the Tesla owner

UK farmers in tractors head to Parliament to protest rules they say threaten livelihoods
Farmers are driving dozens of tractors in a slow-motion convoy towards Britain’s Parliament to protest post-Brexit rules and trade deals that they say are endangering livelihoods and food security

As Boeing turbulence persists: A look at past crashes and safety issues involving the plane maker
Boeing keeps hitting more and more turbulence

A London court will rule on Tuesday whether WikiLeaks’ Assange can challenge extradition to the US
A London court is due to rule whether WikiLeaks founder Julian Assange can challenge extradition to the United States on espionage charges
Binance executive detained in Nigeria amid a crypto crackdown has escaped custody
Authorities in Nigeria say an executive of global cryptocurrency exchange Binance has escaped custody in the West African nation where a criminal investigation has been launched against the platform accused of being used for money laundering

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Perfectly matched system integration rather than an assortment of components. The most powerful electric saildrives come from Torqeedo series production. The Deep Blue 25 SD propels sail yachts of up to 40 feet in length to speeds of up to almost ten knots (18 km/h), or smaller boats even faster when planing. This makes cruising with large sail ...
Guide to electric saildrive and pod boat motors has everything you need to know - over 150 motors with info on power, weight, boat size, price, and more. ... Electric Yacht QuietTorque™ LC 45 Sail Drive (boats <17 tons) Electric Yacht QuietTorque™ LC 60.0 Sail Drive (boats <22 tons) Recommended Boat Size: 14 tons - 22 tons, 45'- 60 ...
With the Spirit 1.0 Evo electric sailboat motor, you can go 5.5 mph (8.8 kph) at top speed on the 21 ft RS21 sailing boat, or troll for 20 hours continuously at 2.2 mph (3.5 kph) according to our test. This electric sailboat motor with regeneration allows you to recover energy from the prop while under sail.
OCEANVOLT sail drive motors Oceanvolt offers a range of sail drive motors to provide propulsion and hydro generation for vessels ranging from 15 to 80 feet. Sail Drive (SD) Synchronous permanent magnet electric motor. Sail Drive with 1.93:1 reduction. Lightweight: weighs as little as 42.5kg (motor & sail drive). The only complete electric inboard propulsion system with EMC certified closed ...
Cheoy Lee Clipper on Lake Superior. Jan 2, 2023. Sailing with an Electric Motor In 2021 we installed the QuietTorque™ 10.0 Electric Motor by Electric Yacht on our 1972 Cheoy Lee Clipper Sailboat, which we use for day charters from May through October on Lake Superior. We have been extremely satisfied with the...
Oceanvolt offers Hybrid or Electric systems as a power & propulsion option in partnership with many leading monohull boat builders - adding new partners continuously. We also offer repowering solutions for converting away from legacy diesel engines - removing the diesel engine, fuel tanks and exhaust system - cleaning up greasy, smelly engine ...
This summer, the world of competitive sailing is set to witness a historic moment as the Dutch sailing organization introduces their first-ever emission-free, hydrogen-powered coach boat, equipped with a Torqeedo Deep Blue electric motor. Learn why this is a pivotal moment in the effort to protect our climate and local air quality.
Pod Drive Series electric boat motors are impressively efficient to go further. Pod Drive 1.0 + E40 / 2 kWh. Half Speed Runtime / 8 Hrs. Full Speed Runtime / 2 Hrs. Pod Drive 3.0 + E80 / 4 kWh. Half Speed Runtime / 5 Hrs 20 Min. Full Speed Runtime / 1 Hrs 20 Min. Pod Drive 6.0 + E175 / 9 kWh.
Cruise Pod Drives for Motorboats and Sailboats. The Cruise FP models are installed in a fixed position (therefore the abbreviation FP - fixed pod) as generally desired for sailboats and also for some motorboats. The eletric pod motors for sailboats are available with folding propellers. Other boats would choose our standard, highly efficient ...
July 9, 2023. Free Spirit - 1968 34ft B15 Upgrade. Glenn & his wife upgraded their 1968 coastal cruiser with the Powerflow Marine B15 and incorporated solar power for a completely renewable propulsion system.
Imported into the US market by Green Marine, the Swedish-built Arcona 435Z is a rarity: an all-electric cruising sailboat. Jon Whittle. This past October, I saw one of the most interesting exhibits in more than 500 new cruising sailboats I've reviewed over two decades. It was the Arcona 435Z, built in Sweden and introduced by Graham Balch of Green Yachts in San Francisco.
We Will Sail a Lot. Bottom line, we need to understand that any boat with electric drive, which will not rely on recharging from shore power, will be relying on sail 95% of the time, or better, even if a low-drag speedster. Think days of regeneration-sailing, assisted by solar (a little), for a few hours of motoring.
Electric Drive Only. Duffy Electric Boats has for years been building electric launches and lake boats that have the simple capability of puttering around in sheltered waters for a period of time determined by battery capacity and speed maintained. A battery charger powered by shore power charges the batteries overnight.
Best electric drive system for sailboats uses the existing transom exhaust opening, offering an easy low cost installation without making additional holes in the hull. Existing transom exhaust opening is used to connect the inboard electrical motor with the carbon propeller shaft. Regenerating when under sail.
Electric motors achieve instant torque with Electromotive Force while internal combustion engines need to build RPMs gradually by increasing piston firing frequency. Hydro Generation At sailing speeds over 6 knots Oceanvolt systems are able to generate significant power for recharging the battery bank by activating at the touch of a button.
OUR BOAT DISPLACES 13,500 POUNDS. SO, 13,500 / 1500 = 9HP ELECTRIC MOTOR. NOW 1HP (OF ELECTRIC) DRAWS ABOUT 750 WATTS. SO, 9HP X 750W = 6.75KW ELECTRIC MOTOR. At 48V, our motor should give us 6.3kW, which is slightly less than what we would need to push our boat to hull speed in calm conditions.
Apr 24, 2018. Hanse's E-motion electric rudder drive represents a true breakthrough in auxiliary propulsion for saiboats. When news that Hanse Yachts had launched a new form of electric-powered yacht first broke in the winter of 2016, it was widely reported. After all, Hanse is one of the world's biggest builders of sailing boats, so this ...
The Hercules e-Drive system utilizes powerful permanent magnet motors, all digital drive-by-wire controls, and up to 94kWh of battery storage for all day power. Hercules marine packages include state of the art on-board chargers to charge your craft using 110V, 220V outlets or auto industry fast chargers. This system also acts as a 12V battery ...
Power 48-5000 48 V. Private Applications. Ultralight - the companion for fishing kayaks. Travel - for dinghies and small boats up to 2t. Cruise - for motorboats and sailboats up to 12t. Saildrives - for sailing yachts and catamarans. Commercial. Cruise ≡ 6 - 25 HP. Deep Blue ≡ 40 - 80 HP.
The innovative Swedish electric boat maker Candela has just announced its biggest funding round ever, reeling in €24.5M (US $26.6M). Fresh off the announcement of the first commercial user of ...
The nation's first all-electric tug boat has docked at the Port of San Diego and expects to begin emissions-free operations in about a month. Operated by Crowley Maritime Corporation, the 82 ...
General Dynamics Electric Boat to Christen Submarine Idaho (SSN 799) GROTON, Conn. (March 15, 2024) - General Dynamics Electric Boat will christen the Virginia-class submarine Idaho (SSN 799) March 16 at its shipyard in Groton, Conn. Electric Boat is a business unit of General Dynamics (NYSE: GD). The relationship between a ship's sponsor and crew endures throughout the lifetime of the boat.
Getting back to the bright side, Enautic seems to be directing its electric tuning toward more time on the water instead of all-out speed. It estimates a range up to 67 miles (108 km) and a ...
Today we have a look at Shenandoah Studios "Drive on Moscow"! Don't forget to like, comment and subscribe. Also hit the bell for notifications! Make sure to ...
STEREOMUZA-медиа портал о музыке,подписывайтесь на наш канал на YouTube:http://www.youtube.com/user/stereomuzachannel,а ...
Beautiful, classic vibes, which will be on repeat for awhile. Perfect for a night drive (in Moscow, or anywhere).•https://www.facebook.com/onyxmusicds••https...
If you enjoyed this video then please leave a like and maybe a comment.Drive on Moscow: War in the Snow, a new strategy game from the award-winning makers of...