Seeing a Motorboat Approaching on Your Right: Navigational Guide and Safety Tips
- by Laura Rodriguez
- November 3, 2023
When you’re out on the water, enjoying a day of boating, it’s essential to understand and follow the rules of navigation to ensure a safe and enjoyable experience for everyone. One common situation that boaters encounter is when a motorboat approaches on their right side. Knowing how to respond in such situations is crucial for maintaining safety and avoiding collisions.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the necessary actions and best practices to take when you see a motorboat approaching on your right. We’ll also address specific scenarios, such as encounters in darkness or reduced visibility and encounters with sailboats. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a solid understanding of how to navigate such situations confidently and make informed decisions on the water.
So, fasten your life jacket, grab a cup of coffee, and let’s dive into the navigational rules and safety tips that will help you navigate encounters with motorboats approaching on your right.


When a Motorboat Comes Cruising on Your Right: Keep Cool and Follow the Rule
Navigating the open waters can be a thrilling experience, but it also comes with its fair share of responsibilities. One crucial aspect is understanding how to respond when you encounter a motorboat approaching from the right. Yes, you heard that right – the one on your RIGHT!
Why the Right Matters? Don’t Sweat It!
You might be wondering, “Why does it matter if the motorboat is coming from the right?” Well, my friend, it’s not just a matter of politeness; it’s actually a well-established rule. In boating lingo, it’s known as the “right of way.” Don’t worry; you won’t need to showcase your dazzling dance moves on the deck. Just stick to this rule and you’ll be good to go!
Respect the Waterway’s Hierarchy: A Hierarchy? On the Water
Believe it or not, the waterway has its own hierarchy. It’s like a social pecking order, but without the fancy outfits and small talk. At the top of this aquatic hierarchy are non-displacement vessels (like motorboats) because they have the ability to maneuver more quickly. So, when you spot a motorboat on your right, it’s a clear-cut signal that they have the right of way.
Gentle Reminder: Red Means Give Them the Green Light!
Imagine yourself cruising on the water, admiring the scenic views, when suddenly, a motorboat sneaks up on your right side. Uh-oh, you’ve got yourself a situation! Well, don’t panic, my friend. Remember, it’s their right of way! Slow down, be patient, and give them plenty of space to pass. Just think of it like a red traffic light. When you see red on the right, it’s their turn to take the lead.
Be Predictable: Surprise Parties are Great, but Not on the Water
Surprises may be thrilling on your birthday, but they can be a recipe for disaster when it comes to boating. To ensure a smooth sailing encounter with our motorboat friends, it’s essential to maintain a steady course and speed. Abrupt maneuvers or sudden bursts of speed might send mixed signals and lead to confusion. So, keep calm, stay on your course, and let the motorboat pass without any surprises.
Communication is Key: Talking with Your Vessels? It’s Possible!
Yes, you read that correctly! Though boats don’t necessarily have vocal cords, they do have ways of communicating. When you see a motorboat approaching on your right, it’s always a good idea to establish eye contact with the operator. A friendly wave or a quick nod can act as a non-verbal agreement. It never hurts to acknowledge each other; after all, it’s all about creating a harmonious coexistence on the water!
Wrapping It Up: Smooth Sailing Awaits!
So, dear adventurer, the next time you spot a motorboat approaching on your right, remember the golden rules of the waterway hierarchy. Give them their well-deserved right of way, be predictable with your movements, and establish some non-verbal camaraderie with a friendly wave or nod. By following these simple guidelines, you’ll ensure a delightful, stress-free journey as you navigate the captivating waters. So, let’s raise our imaginary boating hats and set sail for unforgettable adventures!

FAQ: When You See a Motorboat Approaching on Your Right
Introduction:.
As boaters, we encounter various situations on the water that require quick thinking and adherence to navigation rules. One common scenario is when a motorboat approaches on your right. Knowing the proper actions to take ensures a safe and enjoyable experience for everyone involved. In this FAQ-style guide, we’ll address some frequently asked questions about encountering motorboats on your right and shed light on the best practices to follow. So buckle up and let’s dive in!
Which of the following actions is required of a powerboat when approaching the starboard side of a sailboat in darkness or reduced visibility
When approaching the starboard side of a sailboat in darkness or reduced visibility, it is crucial for a powerboat operator to exercise caution and follow the rules of navigation. In such situations, the powerboat must yield the right of way and steer clear of the sailboat. Remember, visibility can be limited, so it’s important to reduce speed while keeping a safe distance from the vessel. Safety first, always!
What must you do if you see another vessel’s red and white lights off your starboard bow
Ahoy there, sailor! If you spot another vessel’s red and white lights off your starboard bow, it’s a signal for caution. In accordance with navigation rules, you should alter your course to the right and pass the other vessel safely on its port side. By doing so, you avoid any potential collisions and maintain a harmonious flow on the water. Smooth sailing, captain!
What action should you take if you are approaching another boat at night and see a white light
Ah, the stars are shining, and the moon is out to play! When operating a powerboat at night and you spot a white light on another boat, it’s a friendly reminder to yield the right of way. Slow down, maintain a safe distance, and allow the other boat to pass ahead of you. It’s like having a dance partner – let them take the lead, and you’ll avoid any tangling of nautical feet. Happy boating under the night sky!
When operating a powerboat at night, you see red and white lights on another boat. What should you do
Lights, lights, and more lights! When you spot red and white lights on another boat while operating your powerboat at night, it’s an indication that the other vessel is navigating with restricted visibility. In this situation, you must yield the right of way and give the other boat a wide berth. Trust those lights like a sailor trusts the North Star, and you’ll sail smoothly through the night.
When operating a powerboat at night, your green side light must be visible to boats approaching from which direction
Ahoy, fellow boaters! When you’re enjoying the tranquil waters at night and operating a powerboat, it’s essential to ensure your green side light is visible to boats approaching from your starboard side. That green light serves as a beacon of guidance, signaling your presence and enabling other boaters to navigate around you safely. So keep that green light shining bright, and let the good times roll!
Which side do you pass a boat on
Ready to play a game of nautical leapfrog? When passing another boat, always remember this golden rule – keep them on your port side. A vessel should be passed on the starboard side, maintaining a safe distance and ensuring a clear path ahead. Stay vigilant, communicate your intentions, and let the waterway become a playground for harmonious boat ballet!
What should you do if you are operating a motorboat that is being overtaken by a sailboat
Hold on tight, sailor! If you find yourself in a situation where a sailboat is overtaking your motorboat, it’s crucial to maintain your course and speed. As the operator of the motorboat being overtaken, you are considered the “stand-on” vessel. The sailboat, known as the “give-way” vessel, should maneuver safely around you while ensuring a safe distance is maintained. So sit back, relax, and let the wind carry that sailboat past you.
When a sailboat is approaching a powerboat, which is the giveaway vessel
Ahoy, matey! When a sailboat approaches a powerboat, the powerboat takes on the role of the “stand-on” vessel, while the sailboat becomes the “give-way” vessel. As the powerboat operator, maintain your course and speed, and keep rockin’ those waves. The sailboat will skillfully navigate around you, ensuring smooth sailing for all. Enjoy the dance of wind and water!
Which statement correctly applies to a situation where a sailing vessel is overtaking a power-driven vessel
Let the wind and water guide you in this sailing masterclass! When a sailing vessel overtakes a power-driven vessel, it’s important to remember that the sailing vessel is the “give-way” vessel, and the power-driven vessel is the “stand-on” vessel. The power-driven vessel should maintain its course and speed while providing ample room for the sailing vessel to pass safely. Together, they create a beautiful symphony on the open seas!
What should the operator of a powerboat do when approaching a large vessel
Oh, the majestic presence of a large vessel on the horizon! When a powerboat encounters a large vessel, it’s crucial for the operator to exercise caution and maintain a safe distance. Reduce your speed, steer clear of the vessel’s path, and be aware of any potential wake that may affect your boat. Remember, respect is in style, and keeping a safe distance from these giants ensures a delightful boating experience for all!
Ahoy, sailor! If you find yourself in the exhilarating position of being overtaken by a sailboat while operating your motorboat, hold steady and maintain your course and speed. As the motorboat operator, you have the right of way and are considered the “stand-on” vessel. The sailboat, known as the “give-way” vessel, will skillfully maneuver around you, ensuring a seamless and enjoyable journey for all. Sit back, relax, and let the wind guide their course!
When a powerboat meets a sailboat, who has the right of way
Ahoy, fellow adventurers! When a powerboat and a sailboat cross paths, it’s crucial to remember that powerboats give way to sailboats. The sailboat, with its reliance on wind power, holds the right of way over a powerboat. So, channel your inner sailor, gracefully adjust your course if necessary, and enjoy the beauty of harmonious navigation on the open waters. May the wind be ever in your sails!
Are approaching another boat? Assume that, according to the navigation rules, you are the stand-on boat. Which exception to the rules means you must give way
Ah, the rules of the sea! While it’s easy to believe you’re always the “stand-on” boat, there are exceptions to every rule. In specific circumstances, you, as the “stand-on” vessel, must give way to the “give-way” vessel. One crucial exception is when you can’t take appropriate action to avoid a collision. In such cases, toss those rules aside, do what’s necessary to maintain safety, and let those exceptions guide your way. Stay safe, sailor!
What are the four sides of a boat called
Let’s decode the anatomy of a boat, shall we? The four sides of a boat are known as the bow, stern, port, and starboard. The bow? It’s the front, leading the way through the water. The stern? That’s the back, where the boat will bid you farewell. Ah, now the port and starboard! Port refers to the left side of the boat, while starboard is the fancy nautical term for the right side. So, with your newfound knowledge, go forth and impress your fellow boaters with your boat lingo!
Who has the right of way at sea
The ultimate question: who rules the seas? When it comes to right of way at sea, a hierarchy exists. Power-driven vessels generally give way to sailing vessels and vessels engaged in fishing or restricted in their ability to maneuver. Commercial vessels, such as large ships, have their own set of rules. So, remember, as a responsible boater, familiarity with the hierarchy ensures a harmonious experience, and we can all navigate the open waters with ease!
What is the first action required of a boat operator who is involved in a boating accident
Oops, what a bummer! If you find yourself involved in a boating accident, the first action you should take as a responsible boat operator is to ensure the safety of all individuals involved. Attend to any injuries, call for emergency assistance if needed, and render necessary aid to those in distress. Once everyone is safe and sound, it’s crucial to report the accident to the relevant authorities. Safety first, always – even when the water gets a little bumpy!
Which side is port
Calling all seafarers! Port is the nautical term for the left side of a boat when facing forward. A handy way to remember this is that “port” and “left” both have four letters. And if you haven’t guessed it already, “starboard” refers to the right side. So when you’re out on the water, keep those directions in mind, and never lose your way in the sea of port and starboard!
What action should be taken if a motorboat and PWC are approaching head-on
Get ready for some fast and furious watercraft action! When a motorboat and a personal watercraft (PWC) are approaching head-on, both operators must alter their course to starboard (right) to avoid a potential collision. It’s like a synchronized dance, where everyone moves to a new beat. Keep your eyes peeled, make those quick adjustments, and enjoy the thrill of safe maneuvering on the water!
What should the operator of a stand-on vessel do when encountering a give-way vessel
When the music of the waterway plays, and you find yourself as the operator of the “stand-on” vessel, it’s essential to maintain your course and speed. While you have the right of way, vigilance is key. Keep a watchful eye on the “give-way” vessel and be prepared to act swiftly if they fail to maneuver correctly. Confidence, caution, and a little bit of boating swagger will ensure a smooth encounter on the water!
When another boat is approaching from your right
Oh, the thrill of meeting someone new on the water! When another boat approaches from your right, it’s your responsibility to yield the right of way, just like a generous driver at a stop sign. Adjust your course, let them pass safely on your starboard side, and exchange friendly waves as you continue your maritime adventures. It’s all about meaningful encounters and sharing the waterway responsibly!
When one boat is overtaking another, which boat must give way
Ready for a little friendly competition on the water? In a scenario where one boat is overtaking another, the boat being overtaken is known as the “stand-on” vessel, while the overtaking boat is the “give-way” vessel. It’s like a spirited race where the overtaking boat gracefully maneuvers around the other, ensuring a safe and thrilling experience for all involved. Let the games begin!
Why do boats travel on the right
Ah, the art of boating etiquette! Boats travel on the right side, known as the starboard side, to maintain a consistent and organized flow of traffic on the water. It’s like driving on the road, but with a nautical twist. By following this practice, boaters can easily anticipate the movements of other vessels, prevent collisions, and ensure a smooth sailing experience for everyone. It’s all about staying in line and being part of the boating harmony!
What should you always do when a person falls overboard
Man overboard! In the unfortunate event of a person falling overboard, swift action and clear thinking are vital. As the operator of the vessel, you should immediately throw a lifebuoy or any other floatation device to the person in distress. Next, ring the alarm by sounding your horn or using any available means to attract attention. Finally, carefully approach the person in the water while keeping a lookout for other traffic. Time is of the essence, so act quickly, stay calm, and assist your fellow boater in need!
Remember, understanding the rules of the waterways ensures the safety and enjoyment of all boaters. By following these FAQ-style guidelines and using a dash of humor, you’ll navigate through encounters with motorboats on your right like a true boating pro. So go out there, embrace the waves, and let the waters be your playground. Happy boating, fellow enthusiasts!
- green light
- non-displacement vessels
- proper actions
- steady course
Laura Rodriguez
Who possessed foxy: unraveling the mysteries of the fnaf universe, how old is yoriichi - exploring the age and legacy of a demon slayer legend, you may also like, what does narwhal taste like.
- by Mr. Gilbert Preston
- October 27, 2023
Does MiraLax Help Gastroparesis?
- by Thomas Harrison
- October 11, 2023
Does King Sombra Have a Cutie Mark?
- October 28, 2023
Can Dogs Eat Freeze Dried Strawberries?
- by Brian Thomas
- October 8, 2023
Is There Really a Purple Planet?
- October 31, 2023
How to Become an Epic Owner in Prodigy 2023
- October 7, 2023
- 2024 BOAT BUYERS GUIDE
- Email Newsletters
- Boat of the Year
- 2024 Freshwater Boat and Gear Buyers Guide
- 2024 Boat Buyers Guide
- 2024 Water Sports Boat Buyers Guide
- 2024 Pontoon Boat Buyers Guide
- Cruising Boats
- Pontoon Boats
- Fishing Boats
- Personal Watercraft
- Water Sports
- Boat Walkthroughs
- What To Look For
- Watersports Favorites Spring 2022
- Boating Lab
- Boating Safety

When is a Powerboat the Stand-On Vessel Over a Sailboat?
- By Jim Hendricks
- February 20, 2023

I’m strictly a powerboater and proud of it. But I also respect the skill of sailboaters and was schooled from my earliest days afloat that sailboats are generally assigned the privilege of being the stand-on vessels under the rules of the road because they are restricted in their ability to maneuver.
That means powerboats are the give-way vessels.
An important note: A sailboat must be under sail to qualify as such under the rules of the road. If a sailboat uses its auxiliary motor instead of sails for propulsion, then it must abide by the same rules of the road that apply to powerboats.
Despite my mentoring to recognize the privileges of sailboats, there is one exception in which a powerboat enjoys the status of being the stand-on vessel over a sailboat. Before we go there, let’s review the rules of the road when it comes to scenarios involving power–versus-sail encounters.
Meeting Head-On
In powerboat-versus-powerboat head-on encounters, the best option is for each vessel to maneuver to starboard to allow the boats to pass safely port to port. The same applies when a powerboat encounters a sailboat traveling downwind on a straight course. But things get complicated when sailboats tack upwind on a zigzag course. In open water, sailboats have plenty of room to tack. But within the confines of a channel, a sailing vessel might be forced to come about frequently in short tacks to stay inside the channel.
In this case, the skipper of a powerboat (the give-way vessel) must provide the sailboat (the stand-on vessel) a wide berth to maneuver safely. Within a narrow channel, this might require that a powerboat slows to a dead idle or comes to a halt to give the sailboat the road on your side of the channel and allow it to cross safely well in front of you before it comes about and tacks toward the far side of the channel. Once this occurs, you might well have enough space and time to continue safely at the posted speed limit.
Paths That Cross
When it comes to crossing situations that might pose a collision threat, the rule is pretty simple: The powerboat is the give-way vessel and obliged to pass astern of the sailboat, no matter what direction either boat is traveling.
This is where the exception to the rule comes into play. In overtaking situations , the boat that is overtaking another boat is the give-way vessel, regardless of whether it is a sailboat or a powerboat.
The vessel that is being overtaken is always the stand-on vessel and should maintain its course and speed, while the vessel that’s passing (the give-way vessel) signals its intention with one short blast of the horn if passing to starboard of the stand-on vessel, and two blasts if passing to port of the stand-on vessel. Passing should be undertaken in a safe manner and provide the stand-on vessel with the widest berth possible.
So, there you have it—the exception to the rule when it comes to powerboats versus sailboats. But that leads me to another observation: The same passing procedures apply in overtaking situations between powerboats and human-powered vessels, such as canoes, kayaks, stand-up paddleboards and the like. But how often does a paddler have the opportunity to pass a powerboat or sailboat?
It can happen. It happened to me while idling out of California’s Alamitos Bay. My boat was struck from behind by a single sculler while he sprinted along during his morning workout. Scullers face aft while rowing, so they are blind to the waters ahead. I had my eyes forward and failed to glance astern, so neither of us saw each other. What’s more, sculls travel almost silently at speeds up to 13 mph, and today’s outboards are extremely quiet at no-wake speeds of 5 mph, so neither of us could hear each other. While the encounter proved startling, we suffered no injuries or property damage. After exchanging a few words, we continued on our way.
While the rules of the road favored me as the stand-on vessel, it is also important to point out the most critical rule of all: Avoid a collision, no matter what the scenario. In this case, by glancing astern regularly, I could have spotted the potential for a rear-end collision and given the sculler a wide berth. It is a lesson I learned well and have applied ever since that day.
- More: Boating Safety , How-To , March 2023 , Seamanship
More How To

On Board With: Brian Grubb

Installing Clear Acrylic Livewell Lids

Captain of Dive Boat That Caught Fire Sentenced to Four Years

How to Make DSC Fully Functional on a VHF Radio

Boat Test: 2024 Solara S-250 DC

Boat Test: 2024 Checkmate Pulsare 2400 BRX

Cox 350 Diesel Outboard

- Digital Edition
- Customer Service
- Privacy Policy
- Cruising World
- Sailing World
- Salt Water Sportsman
- Sport Fishing
- Wakeboarding
Many products featured on this site were editorially chosen. Boating may receive financial compensation for products purchased through this site.
Copyright © 2024 Boating Firecrown . All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part without permission is prohibited.

- Flashlights
- Path Lights
- Bike Lights

- Safety Lights

- Accessories
- Bike Cleats
May 20, 2022 7 min read
When a Sailboat Overtakes a Powerboat: Understanding the Stand-On Vessel

When a sailboat overtakes a powerboat, it can be confusing to determine which vessel is the stand-on vessel. Understanding the terminology and rules of the road at sea is crucial to avoid accidents and ensure safety on the water. In this article, you will learn about practical scenarios and safety considerations when encountering an overtaking situation, as well as answers to frequently asked questions about sailing and boating regulations.
In an overtaking situation, the overtaking vessel is the give-way vessel, while the vessel being overtaken is the stand-on vessel. However, if the powerboat is overtaking the sailboat from the starboard side, the powerboat becomes the stand-on vessel and the sailboat becomes the give-way vessel. When meeting head-on or crossing paths, the power-driven vessel is the give-way vessel, while the sailing vessel is the stand-on vessel. It is important to know these rules of the road to avoid collisions and ensure safety on the water.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the terminology and rules of the road at sea is crucial to avoid accidents and ensure safety on the water.
- In an overtaking situation, the overtaking vessel is the give-way vessel, while the vessel being overtaken is the stand-on vessel.
- When meeting head-on or crossing paths, the power-driven vessel is the give-way vessel, while the sailing vessel is the stand-on vessel.
Understanding the Terminology
Defining stand-on and give-way vessels.
When two vessels meet, one vessel must give way to the other. The vessel that must give way is called the give-way vessel, and the vessel that has the right of way is called the stand-on vessel. In general, a sailing vessel is a give-way vessel, and a power-driven vessel is a stand-on vessel.
Boat Types and Their Characteristics
There are different types of boats , each with its own characteristics. A sailboat is a vessel that is propelled by sails and wind, while a powerboat is a vessel that is propelled by an engine. A personal watercraft is a type of powerboat that is designed for recreational use. Knowing the type of vessel you are operating is important when determining which vessel has the right of way.
Navigational Terms and Signals
Navigational terms and signals are used to communicate with other vessels. The terms port and starboard are used to describe the left and right sides of a vessel, respectively. Sound signals, such as a short blast of a horn, are used to signal your intentions to other vessels. It is important to know and understand these terms and signals to avoid collisions.
Understanding Overtaking
When a sailboat overtakes a powerboat, the sailboat is generally the give-way vessel. However, there are certain situations where the sailboat may be the stand-on vessel, such as when the powerboat is in a narrow channel or restricted waterway. It is important to be aware of your surroundings and the vessels around you to determine which vessel has the right of way in an overtaking situation.
Overall, understanding the terminology and characteristics of different vessels, as well as navigational terms and signals, is crucial in determining which vessel is the stand-on vessel when overtaking another vessel. By staying aware of your surroundings and following proper navigation rules, you can ensure a safe and enjoyable boating experience.
The Rules of the Road at Sea
General navigation rules.
When navigating at sea, it is important to follow the rules of the road to ensure the safety of all vessels. These rules are designed to prevent collisions and help vessels avoid dangerous situations. The rules of the road apply to all vessels, including sailboats and powerboats.
Meeting Head-On and Crossing Paths
When two vessels are approaching each other head-on or crossing paths, the vessel on the starboard side has the right of way. This means that the vessel on the port side must give way and take action to avoid a collision. If both vessels are on the same course and speed, the vessel on the right should maintain its course, while the vessel on the left should alter its course to avoid a collision.
Overtaking Rules and Regulations
When one vessel is overtaking another vessel, the vessel being overtaken is the stand-on vessel, and the overtaking vessel is the give-way vessel. The overtaking vessel must keep clear of the vessel being overtaken and avoid crossing its path. The vessel being overtaken should maintain its course and speed until the overtaking vessel has passed.
In an overtaking situation, the overtaking vessel should sound a signal to indicate its intention to overtake. The vessel being overtaken should also sound a signal to indicate that it is aware of the overtaking vessel. It is important to remember that the overtaking vessel has the responsibility to avoid a collision.
In summary, understanding the rules of the road at sea is essential for safe navigation. Whether you are meeting another vessel head-on, crossing paths, or overtaking another vessel, it is important to follow these rules to prevent collisions and ensure the safety of all vessels.
Practical Scenarios
Sailboat overtaking powerboat.
When a sailboat overtakes a powerboat, the sailboat is the overtaking vessel and must keep clear of the powerboat. However, if the powerboat is also overtaking another vessel, the sailboat may be the stand-on vessel and the powerboat must keep clear of both the sailboat and the other vessel.
In this scenario, it is important for the sailboat to communicate their intentions to the powerboat. The sailboat can signal their intention to overtake by hoisting a flag or using sound signals. The powerboat should respond accordingly and take the necessary actions to keep clear of the sailboat.
Powerboat Overtaking Sailboat
When a powerboat overtakes a sailboat, the powerboat is the overtaking vessel and must keep clear of the sailboat. However, if the sailboat is also overtaking another vessel, the powerboat may be the stand-on vessel and the sailboat must keep clear of both the powerboat and the other vessel.
In this scenario, it is important for the powerboat to communicate their intentions to the sailboat. The powerboat can signal their intention to overtake by using sound signals or by making a passing maneuver that is clear and safe. The sailboat should respond accordingly and take the necessary actions to keep clear of the powerboat.
Remember, in any overtaking situation, it is important to maintain a safe distance between vessels and to communicate clearly with other vessels. Always be aware of your surroundings and take the necessary actions to avoid collisions.
Safety Considerations
Avoiding accidents.
When a sailboat overtakes a powerboat, safety should be the top priority. To avoid accidents, both vessels should maintain a safe distance from each other and keep a lookout for any potential hazards. It's important to communicate effectively with the other vessel and take necessary actions to prevent any collisions.
Understanding Substantial Action
Substantial action is a term used to describe a maneuver taken by a vessel to avoid a collision. When a sailboat overtakes a powerboat, the sailboat is generally considered the give-way vessel, and the powerboat is the stand-on vessel. However, if the sailboat is overtaking the powerboat too closely, the powerboat may need to take substantial action to avoid a collision.
Effects of Speed and Wake
Speed and wake can have a significant impact on the safety of both vessels. A powerboat that is traveling too fast can create a large wake that can be dangerous for other vessels, especially smaller sailboats. Sailboats should be aware of the powerboat's speed and the size of the wake it creates, and adjust their course and speed accordingly. Additionally, sailboats should avoid sailing too close to the stern of a powerboat to avoid the effects of the wake.
Overall, when a sailboat overtakes a powerboat, safety should be the top priority. Both vessels should communicate effectively, maintain a safe distance, and take necessary actions to avoid any potential hazards. By understanding substantial action and the effects of speed and wake, both vessels can ensure a safe and enjoyable experience on the water.
Frequently Asked Questions
When is a sailboat the stand-on vessel in relation to a recreational powerboat.
A sailboat is the stand-on vessel when it is sailing and a powerboat is overtaking it from behind. The powerboat must keep a safe distance and avoid interfering with the sailboat's course.
What should you do if you are operating a motorboat that is being overtaken by a sailboat?
If you are operating a motorboat that is being overtaken by a sailboat, you should maintain your course and speed. You should not turn towards the sailboat and should give it enough room to pass safely.
What is the stand on vessel in an overtaking situation?
The stand-on vessel in an overtaking situation is the vessel being overtaken. The overtaking vessel must keep a safe distance and avoid interfering with the stand-on vessel's course.
Which boat must give-way when one boat is overtaking another?
The boat that is overtaking must give-way to the boat being overtaken. The overtaking boat must keep a safe distance and avoid interfering with the course of the boat being overtaken.
What should you do to avoid colliding with another vessel?
To avoid colliding with another vessel, you should keep a proper lookout at all times. You should maintain a safe speed and course, and be aware of other vessels in your vicinity. You should also use navigation lights and signals to communicate with other vessels.
Why should a vessel operator keep a proper lookout?
A vessel operator should keep a proper lookout to avoid collisions with other vessels and to navigate safely. By keeping a lookout, the operator can be aware of other vessels in the area, potential hazards, and changing weather conditions. This can prevent accidents and ensure the safety of all on board.
What should the operators of two powered vessels do that approach each other in a head on situation? Boat Test Guide
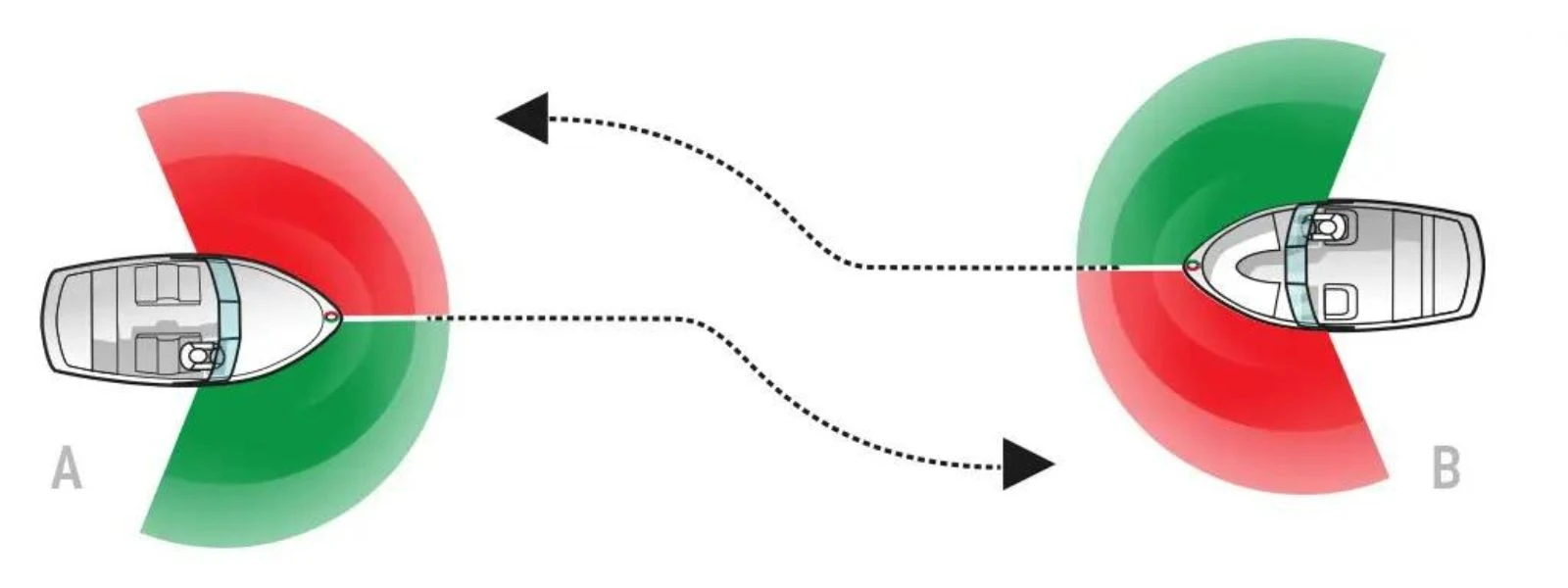
Image courtesy of BOATsmart
What should the operators of two powered vessels do that approach each other in a head on situation? Check out our boating test prep guide!
If you’re preparing for your boat licensing test, one important thing that you will have to know regarding boat safety is understanding what the operators of two powered vessels do that approach each other in a head on situation .
One question commonly seen on boating tests goes over “What should the operators of two powered vessels do that approach each other in a head on situation”. There are rules that every operator must follow and the action a vessel operator should take when encountering another vessel depends on the answers to two questions.
What should the operators of two powered vessels do that approach each other in a head on situation?
Two boats are operating in the same general area. who is responsible for avoiding a collision.
- A motorboat and a PWC are meeting head-on – Which one is the stand-on vessel?
One boat is overtaking another. Which boat must give way?
Who is responsible for avoiding a collision between two boats, two boats are operating near each other. which is the boat that must maintain its course and speed, a motorboat is crossing paths with a pwc, what action should be taken, a pwc is overtaking another vessel which vessel must give way, tips for preparing for your boating test:, check out our other study guides for boating test questions, getting certified: passing your boat exam.
When two powered vessels approach each other in a head-on situation, both operators should:
- Alter their course to starboard (right)
- Pass each other port (left) side to port (left) side.
This maneuver reduces the risk of collision by creating a predictable and safe passing arrangement. Additionally, both operators should maintain a safe speed and keep a vigilant lookout for other vessels to ensure a smooth and uneventful passage.

There are rules that every operator must follow when encountering other vessels. Two terms help explain these rules.
- Give-way vessel: The vessel that is required to take early and substantial action to keep away from other vessels by stopping, slowing down, or changing course. Giving-way should avoid crossing in front of other vessels or changing course and speed in a way that’s large enough to be apparent to the other vessel. It’s important to avoid a series of small changes in course or speed.
- Stand-on vessel: The vessel that must maintain its course and speed unless it becomes apparent that the give-way vessel is not taking appropriate action. If action is necessary, the stand-on vessel should avoid turning toward the give-way vessel or crossing in front of it.
When two boats are operating in the same general area, both operators are responsible for avoiding a collision. The right-of way is determined by answering two questions:
- How are the two vessels propelled?
- Two power-driven vessels
- Two sailing vessels
- A power-driven vessel and a sailing vessel
- How are the two vessels approaching one another?
- Meeting head-on: A vessel operator sees another vessel ahead or nearly ahead
- Paths that cross: Two vessels are on crossing paths so as to involve risk of collision
- Overtaking: A vessel is coming upon another vessel from behind or nearly behind the other vessel
Ultimately, it’s a shared responsibility to maintain a proper lookout, follow navigational rules, and take evasive action if necessary to prevent a collision. Each operator should stay alert, communicate clearly if needed, and maneuver their vessel safely to avoid any potential hazards or collisions.
A motorboat and a PWC are meeting head-on – Which one is the stand-on vessel?
In a head-on situation between a motorboat and a personal watercraft (PWC), the stand-on vessel would typically be the motorboat, assuming both vessels are under power. The motorboat should maintain its course and speed unless it becomes apparent that the PWC is not taking appropriate action.
When one boat is overtaking another, the boat being overtaken is generally considered the stand-on vessel, while the overtaking boat is the give-way vessel. The overtaking boat must maneuver in a way that ensures a safe and clear passage, keeping well clear of the boat being overtaken. It’s crucial for the overtaking boat to maintain a safe distance and avoid any actions that could potentially cause a collision or endanger the vessel being overtaken.
Both boat operators are responsible for avoiding a collision between two boats. It’s essential for both operators to maintain a proper lookout, follow navigational rules, and take necessary actions to prevent a collision. This includes maintaining safe speeds, being aware of the surrounding environment, communicating intentions clearly, and giving way when required by maritime rules and regulations. Ultimately, collision avoidance is a shared responsibility that requires vigilance and cooperation from all parties involved.

In maritime situations where two boats are operating near each other, the vessel that must maintain its course and speed is typically referred to as the “stand-on” vessel. This means that unless it becomes apparent that the other vessel is not taking appropriate action to avoid a collision, the stand-on vessel should continue on its current course and speed. However, it’s crucial for the stand-on vessel to remain vigilant and be prepared to take evasive action if necessary to prevent a collision.
When a motorboat is crossing paths with a personal watercraft (PWC), the motorboat is usually the “give-way” vessel, and the PWC is the “stand-on” vessel. As the give-way vessel, the motorboat should take early and substantial action to keep well away from the PWC by either slowing down, stopping, or altering its course. The PWC, as the stand-on vessel, should maintain its course and speed, unless it becomes clear that the motorboat is not taking appropriate action to avoid a collision. It’s essential for both operators to remain vigilant, communicate clearly, and take necessary maneuvers to ensure safety and prevent accidents.
When a personal watercraft (PWC) is overtaking another vessel, it is generally considered the give-way vessel. As such, it must maneuver to pass the other vessel safely, taking into account factors such as speed, distance, and the potential for collision. The vessel being overtaken is typically the stand-on vessel and should maintain its course and speed, allowing the PWC to pass safely. However, both operators should exercise caution, maintain awareness of their surroundings, and communicate effectively to avoid any potential collisions or accidents.
Preparing for your boating test? Studying for a boat test in Florida? Here are some helpful tips to get you ready:
- Study the Boating Regulations: Familiarize yourself with the rules and regulations specific to boating in your area. Understand navigation rules, safety requirements, and any local laws governing watercraft operation.
- Take a Boating Safety Course: Consider enrolling in a boating safety course to enhance your knowledge and skills. These courses cover essential topics such as navigation, emergency procedures, and legal requirements.
- Practice Safe Boating Techniques: Learn and practice essential boating maneuvers, including docking, anchoring, and navigating in different weather conditions. Familiarize yourself with basic safety equipment and how to use it effectively.
- Know Your Boat: If you own or plan to operate a specific type of boat, take the time to become familiar with its features, controls, and handling characteristics. Understanding your boat’s capabilities and limitations is essential for safe operation.
- Stay Updated: Keep abreast of any updates or changes to boating regulations and safety guidelines. Stay informed about local weather forecasts and waterway conditions before heading out on the water.
Remember, proper preparation is key to safe and enjoyable boating experiences. Whether you’re in Florida or anywhere else in the country, our excellent guides can help you get ready for your boating test and navigate the waters with confidence.
- How to dock a boat
- How to choose a marine gps app
- What Piece Of Equipment On A Boat Is Most Important In Preventing Propeller Strike Injuries ?
Start your safe boating journey at boat-ed.com . Their accredited courses, recognized by NASBLA, the National Association of State Boating Law Administrators, make learning boater safety, etiquette, and water rules easy and accessible. With interactive courses available on all devices, prioritize safety as you prepare for your exam.
You can get a preview of what this, and other questions may look like on a boating test by visiting our friends at Boat-Ed. Check out their study guide .
Related Posts

Boat Navigation App On Apple Store And Google Play | Top Boat GPS App & Marine Navigation App
Boat Speedometer App and Boat Speed App | Best Boating Apps

Boat Ramp App & Ramp Locator | Find Boat Ramps Near Me | App Store & Google Play

In Florida, what does the state divers-down flag/device look like? Florida Diver Down Boating Test Prep


Boating Basics Online is reader-supported. When you buy via our links, we may earn a commission at no cost to you. Learn more
When Is a Sailboat the Stand-on Vessel in Relations to a Recreational Power Boat
Written by J. Harvey / Fact checked by S. Numbers

Traffic rules and regulations are important for keeping vehicles orderly while on the road. The same applies to boats on the water, and Right of Way rules help keep waterways and boating channels safe. That’s why it’s essential to familiarize ourselves with key points that involve stand-on vessels and give-way vessels.
In this article, we’ll close in on a specific topic related to boating right of way, focusing on sailboats. So, when is a sailboat the stand-on vessel in relations to a recreational power boat?
A quick answer is, a sailboat is a stand-on vessel in most situations except for a few such as when the boat is overtaking or if the powerboat is restricted.
Keep reading to find the detailed answer.
Table of Contents
Boating Right of Way
Determining give-way and stand-on vessels, the sailing vessel as a stand-on vessel, the sailing vessel as a give-way vessel.

There are boating rules that govern boats’ actions while on the water, and these help keep waterways free from accidents. We need to be aware of these rules, especially if we are helming a boat ourselves. Regardless of type or size, watercraft are all subject to these rules for everyone’s safety.
While there is no officially recognized “right of way” for vessels on the water, the closest we have is the give-way and stand-on designation. They let us determine which party is given priority to stay their course. These terms serve to identify boats in different situations when meeting on the water. They allow us to take appropriate action to avoid any boating mishaps.
- Give-Way Vessel
The boat deemed responsible to give way to the other boat is called the give-way vessel. Being the give-way vessel means it is your responsibility to avoid the other boat to ensure no collision occurs and signal the other party of your intentions.
- Stand-on Vessel
While the give-way vessel is responsible for avoiding the other boat, this other boat’s responsibility is to maintain its course and speed; this is the stand-on vessel. It is also the stand-on vessel’s responsibility to look out for the give-way vessel’s actions and signals and respond to them as the situation dictates.

Determining between these two will allow us to act correctly in any situation. Therefore, it is important always to keep an eye and ear out for other vessels when we’re out on the water. Detecting other vessels early will allow us ample time to recognize each situation and react appropriately.
Looking at a boat’s propulsion makes it easier for us to determine which boat is which.
There are two common types of boats based on their propulsion; sailing vessels and power-driven vessels. Boats having similar propulsion makes this more complicated and is a discussion we’ll save for another time.
- A power-driven vessel makes use of any type of machinery for propulsion.
- A sailing vessel makes use of wind and sail.
Certain sailboats use both a sail and an engine. Still, any sailboat using its engine is considered a power-driven vessel at that given moment. Determining propulsion is important because, for most situations, the sailing vessel is given priority when the other vessel is a power-driven one.
When a sailboat meets a power-driven boat such as a recreational powerboat, the sailboat is the stand-on vessel in most situations. This is because the boat using an engine is more capable of making the necessary adjustment to ensure that no collision occurs.
Even when a sailboat is approaching a powerboat, the sailboat will still serve as a stand-on vessel because of its limited maneuverability.
Let’s consider another situation where a powerboat is about to cross paths with a sailboat under sail. What should the powerboat do? In such a situation, the powerboat is the give-way vessel and must adjust its course and speed to allow the sailboat passage.
Sailboats are usually stand-on vessel when meeting a recreational powerboat or any power-driven vessel, but there are exceptions.
When a sailboat overtakes a powerboat which vessel is the stand on the vessel? In such a situation, the overtaking vessel is always the give-way vessel regardless of its propulsion type.
Another situation where a sailing vessel is a give-way vessel when meeting a power-driven vessel is when the motorized boat is limited in its ability to maneuver or is not under command. This is the situation where the sailboat needs to react and adjust accordingly to avoid any untoward incident.
Other situations where a sailing vessel is a give-way vessel include but are not limited to when the other boat is restricted in its visibility, and when a vessel is engaged in fishing. Remember that it takes longer for sailboats to adjust their speed and course than boats using an engine.
The boating rules relating to stand-on and give-way vessels are important for every boater to know. We need to learn many things, but now that you know ‘when is a sailboat the stand-on vessel in relation to a recreational power boat?’, that’s one thing to strike off the list. Just make sure to keep learning more to keep ourselves and others safe.
If you have any comments or suggestions about boating right of way or any related topics, please leave them below. We’re eager to hear from you.
Remember to boat safely.

“My intention from the first day establishing Boating Basics Online is to provide as much help as possible for boaters who want to experience a first safe and convenient trip. So feel free to join us and share your beautiful journeys to the sea!”
Chapter 5: Navigation Rules
Navigation rules: overtaking.
Whenever a power-driven vessel is overtaking another power-driven vessel the vessel which is being overtaken is the stand-on vessel. Remember, the stand-on vessel has the right of way and must maintain speed and course.
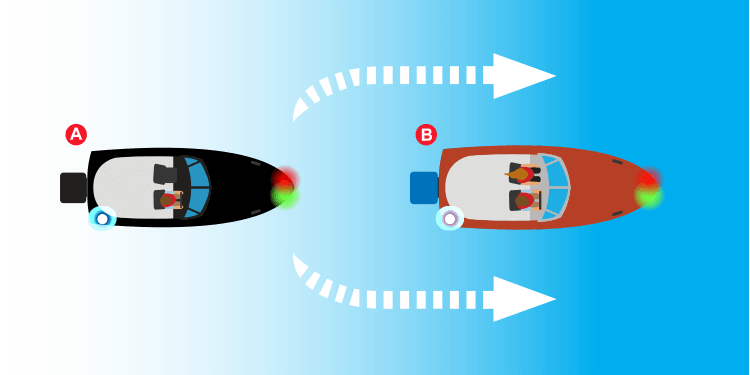
In this example, Vessel A would be the give-way vessel. That means Vessel A must take action to avoid a collision as it passes around Vessel B. This rule also applies to non-powered vessels. The vessel overtaking is the give-way vessel and the vessel being overtaken is the stand-on vessel.
For additional safety, if two power-driven vessels are interacting, one must also use sound signals to indicate intentions. So, if one wants to pass on their port side, give two short blasts for starboard. This lets the other boater know that one will be passing on their starboard side. The other operator should then return the same signal to indicate they understand and agree.
If one is approaching another vessel close enough from stern to see the other’s stern lights, but not their navigational sidelights, it is assumed one means to overtake them and should act accordingly as the give-way vessel.
Remember, if a boater ever gives five short blasts, it means that they there is no understanding of intentions and it is dangerous to approach without further communications.
Course Signup: Location
Privacy Policy
This privacy policy is intended to provide information to users of Boater's Academy's websites, and users of the services provided by Boater's Academy, about how Boater's Academy uses, stores, and protects information associated with such users. By using any of the websites or services of Boater's Academy, you represent and warrant that you have read and understood this privacy policy, and agree to its terms.
Effective Date Of Policy
The effective date of this privacy policy is 01/01/2018. Boater's Academy reserves the right, at any time and without notice, to add to, update, change, or modify this privacy policy by posting a new version on this page.
Information Collected By Boater's Academy
When you access Boater's Academy websites, Boater's Academy automatically gathers information that most web browsers automatically make available. This information may include IP addresses, Internet domain names, and types of devices and web browsers accessing Boater's Academy websites. Such information is anonymous and is not meant to personally identify you.
Boater's Academy websites also use cookies, which are files that are placed on your computer when you visit Boater's Academy websites. The purpose of cookies includes identifying you as a unique user of Boater's Academy websites and services, tailoring your experience on Boater's Academy websites, and enabling third-parties (such as Google) to optimize and serve advertisements to you.
If you do not wish to have cookies placed on your computer, you have several options, including: (a) not accessing Boater's Academy websites or using Boater's Academy services; (b) setting your web browser to refuse cookies; and (c) opting out of or customizing the use of third-party cookies through various websites operated by such third parties or by others (i.e., Google, Facebook, and Network Advertising Initiative). Please note that blocking or customizing the use of cookies may affect your experience on Boater's Academy websites or with Boater's Academy services.
If you decide to use certain features of Boater's Academy websites or services (such as ordering a product or service), you will be asked to provide certain personally identifiable information, which can include your name, phone number, email address, mailing address, credit/debit card number and expiration date, and social security number. You are under no obligation to provide such information, but refusing to do so may prevent your ability to use certain features of Boater's Academy websites or services.
How Boater's Academy Uses The Information It Collects
With respect to non-personally identifiable information automatically collected from you when you access Boater's Academy websites and information gathered through the use of cookies, Boater's Academy uses such information to: (1) help diagnose problems with our server and administer our websites; (2) track the usage of our websites so we can better understand who is using our websites and services and how they are using them; and (3) share with advertisers to help them better understand our services and the preferences of our customers.
Boater's Academy may combine certain demographic information obtained from you when you use certain features of Boater's Academy websites or services (such as registering or ordering a product or service) with site usage data to provide profiles, in aggregate form, about our users and their preferences. The aggregate, composite information may be shared with our advertisers.
The personally identifiable information you voluntarily provide to Boater's Academy when you decide to use certain features of Boater's Academy websites or services (such as registering or ordering a product or service) may be used for the following purposes: (1) contacting you regarding Boater's Academy's products or services, including those which you have ordered or requested; (2) billing you for the products or services your ordered or requested; (3) providing the information to third parties such as shipping companies, merchant account and payment gateway service providers, governmental entities, and our product and service distributors to the extent necessary to provide the products and services that you order or request; (4) providing the information to those who assist Boater's Academy with providing its products and services; (5) providing the information when required to do so by law or if necessary to protect the property or rights of Boater's Academy, third parties, or the public; (6) providing the information to a successor of Boater's Academy in the event of a merger, acquisition, bankruptcy, or sale of Boater's Academy's assets; and (7) providing the information to consumer credit reporting services, collection agencies, attorneys, and others in the event you fail to pay any amounts owed to Boater's Academy.
In disclosing your personally identifiable information, Boater's Academy will disclose only so much of the information as is necessary to provide the products and services that you request or order.
Security Of Information Provided To Boater's Academy
Boater's Academy takes security seriously and uses commercially reasonable safeguards to protect against the unauthorized access, use, modification, destruction or disclosure of any information you provide to us. However, Boater's Academy cannot guarantee that any information provided to us or obtained by us will not be accessed, hacked, disclosed, altered, or destroyed by unauthorized parties.
Children's Privacy
Boater's Academy does not solicit or knowingly collect personal information from children under the age of 13. If Boater's Academy obtains actual knowledge that it has collected personal information from a child under the age of 13, we will delete such information from our database. Because Boater's Academy does not collect personal information from children under the age of 13, we have no such information to use or disclose to third parties.
Parents of minors of any age may contact our Privacy Coordinator at the mailing address or e-mail address indicated below in order to: (1) access personally identifiable information Boater's Academy has collected from their child; (2) correct or modify such information; (3) request to have such information deleted; and (4) request that we no longer collect or maintain such information.
How To Request Changes To The Personally Identifiable Information We Collect
You can review and request changes to the personally identifiable information that Boater's Academy has collected from you by contacting our Privacy Coordinator at the mailing address or e-mail address indicated below.
Do-Not-Track Disclosure
Boater's Academy does not respond to "Do Not Track" signals sent by browsers.
Consent To Receive Communications
By providing your name, email, mailing address, and/or phone number to Boater's Academy, you consent to receive electronic and other communications from Boater's Academy. You may opt out of receiving electronic communications at any time by: (a) following the unsubscribe instructions contained in each communication; or (b) by contacting our Privacy Coordinator at the mailing address or e-mail address indicated below.
Third-Party Websites
Boater's Academy is not responsible for the content of websites operated by third parties to which it may provide links on Boater's Academy's websites or for the websites of advertisers. Such third parties and advertisers may also have privacy policies that are different from this privacy policy. Therefore, you should inform yourself of the privacy policies and practices of any websites of third parties or advertisers.
Contacting Us
If you have any questions about this privacy policy, Boater's Academy websites, or Boater's Academy products and services, please contact our Privacy Coordinator at the mailing address or e-mail address indicated below:
Boater's Academy Attn: Privacy Coordinator P.O. Box 5143 Virginia Beach, VA 23471 [email protected]
Terms of Use
Introduction
Welcome to Boater's Academy. This website is owned and operated by enLearned LLC. By visiting our website and accessing the information, resources, services, products, and tools we provide, you understand and agree to accept and adhere to the following terms and conditions as stated in this policy (the "User Agreement").
This User Agreement is in effect as of 01/01/2018.
We reserve the right to change this User Agreement from time to time without notice. You acknowledge and agree that it is your responsibility to review this User Agreement periodically to familiarize yourself with any modifications. Your continued use of this site after such modifications will constitute acknowledgment and agreement of the modified terms and conditions.
Responsible Use and Conduct
By visiting our website and accessing the information, resources, services, products, and tools we provide for you, either directly or indirectly (the "Resources"), you agree to use the Resources only for the purposes intended as permitted by (a) the terms of this User Agreement; and (b) applicable laws, regulations and generally accepted online practices and guidelines.
You agree that:
a. In order to access our Resources, you may be required to provide certain information about yourself (such as identification, contact details, payment information, and other information) as part of the registration process, or as part of your ability to use the Resources. You agree that any information you provide will be accurate, correct, and up to date.
b. You are responsible for maintaining the confidentiality of any login information associated with any account you use to access our Resources. Accordingly, you are responsible for all activities that occur under your account(s).
c. Accessing (or attempting to access) any of our Resources by any means other than through the means we provide, is strictly prohibited. You specifically agree not to access (or attempt to access) any of our Resources through any illegal, automated, unethical or unconventional means.
d. Engaging in any activity that disrupts or interferes with our Resources, including the servers and/or networks to which our Resources are located or connected, is strictly prohibited.
e. Attempting to copy, duplicate, reproduce, sell, trade, or resell our Resources is strictly prohibited.
f. You are solely responsible any consequences, losses, or damages that we may directly or indirectly incur or suffer due to any unauthorized activities conducted by you and you may incur criminal or civil liability for such unauthorized activities.
g. We may provide various open communication tools on our website, including but not limited to blog comments, blog posts, public chat, forums, message boards, newsgroups, product ratings and reviews, and various social media services. We do not always pre-screen or monitor the content posted by users of these various communication tools, which means that if you choose to use these tools to submit any type of content to our website, then it is your personal responsibility to use these tools in a legal, responsible and ethical manner. By posting information or otherwise using any open communication tools as mentioned, you agree that you will not upload, post, share, or otherwise distribute any content that:
i. Is illegal, threatening, defamatory, abusive, harassing, degrading, intimidating, fraudulent, deceptive, invasive, racist, or contains any type of suggestive, inappropriate, or explicit language;
ii. Infringes on any trademark, patent, trade secret, copyright, or other proprietary right of any person or entity;
iii. Contains any type of unauthorized or unsolicited advertising;
iv. Impersonates any person or entity, including any Boater's Academy employees or representatives.
We have the right at our sole discretion to remove any content that, we feel in our judgment does not comply with this User Agreement, along with any content that we feel is otherwise offensive, harmful, objectionable, inaccurate, or violates any copyrights or trademarks. We are not responsible for any delay or failure in removing such content. If you post content that we choose to remove, you hereby consent to such removal, and waive any claim against us for such removal.
h. We do not assume any liability for any content posted by you or any other third party users of our website. However, any content posted by you using any open communication tools on our website, provided that it doesn't violate or infringe on any third party copyrights or trademarks, becomes the property of enLearned LLC, and as such, gives us a perpetual, irrevocable, worldwide, royalty-free, exclusive license to reproduce, modify, adapt, translate, publish, publicly display and/or distribute as we see fit. The foregoing only applies to content posted via open communication tools, and does not apply to information that is provided as part of the registration process as part of your use of the Resources.
i. You agree to indemnify and hold harmless enLearned LLC, Boater's Academy, their parent company/companies and affiliates, and their directors, officers, managers, employees, agents, successors, assigns, and licensors (collectively, the "enLearned LLC Parties"), from and against all losses, expenses, damages and costs, including reasonable attorneys' fees, resulting from any violation of this User Agreement or the failure to fulfill any obligations relating to your account incurred by you or any other person using your account. We reserve the right to take over the exclusive defense of any claim for which we are entitled to indemnification under this User Agreement. In such event, you shall provide us with such cooperation as is reasonably requested by us.
Limitation of Warranties
The enLearned LLC Parties expressly disclaim any and all warranties, express or implied, regarding the Resources, arising by operation of law or otherwise, including without limitation any and all implied warranties of merchantability, quality, accuracy, fitness for a particular purpose, non-infringement, no encumbrance, or title, in addition to any warranties arising from a course of dealing, usage, or trade practice.
The Resources are provided with all faults, and the entire risk as to satisfactory quality, performance, accuracy, and effort is with the user.
The enLearned LLC Parties do not warrant that the Resources will fulfill any of your particular purposes or needs, or that the operation or use of the Resources will be uninterrupted or error-free. The enLearned LLC Parties disclaim all implied liability for damages arising out of the furnishing of the Resources pursuant to this User Agreement, including without limitation, mistakes, omissions, interruptions, delays, tortious conduct, errors, representations, or other defects arising out of the failure to the furnish the Resources, whether caused by acts of commission or omission, or any other damage occurring.
Limitation of Liability
In conjunction with the Limitation of Warranties as explained above, you expressly understand and agree that your potential recovery for any claim against the enLearned LLC Parties arising from or relating to the Resources or this User Agreement shall be limited to the amount you paid, if any, for use of products and/or services. The enLearned LLC Parties will not be liable for any direct, indirect, incidental, consequential or exemplary loss or damages which may be incurred by you as a result of using the Resources, or as a result of any changes, data loss or corruption, cancellation, loss of access, or downtime.
Copyrights, Trademarks, and License
Subject to your compliance with this User Agreement, the enLearned LLC Parties grant you a non-exclusive, non-sublicensable, revocable as stated in this User Agreement, non-transferable license to access the Boater's Academy websites, and to use the Resources. The Resources, including any portion of Boater's Academy websites, may not be reproduced, duplicated, copied, modified, sold, resold, distributed, transmitted, or otherwise exploited for any commercial purpose without the prior, express written consent of the enLearned LLC Parties. All rights not expressly granted in this User Agreement are reserved by the enLearned LLC Parties. Without limitation, this User Agreement grants you no rights to the intellectual property of the enLearned LLC Parties or any other party, except as expressly stated in this User Agreement. The license granted in this section is conditioned on your compliance with this User Agreement. Your rights under this section will immediately terminate if you breach, actually or potentially, in the sole judgment of the enLearned LLC Parties, any provision of this User Agreement.
Termination of Use
You agree that we may, at our sole discretion, suspend or terminate your access to all or part of our website and Resources with or without notice and for any reason, including, without limitation, breach of this User Agreement. Any suspected illegal, fraudulent or abusive activity may be grounds for terminating your relationship with Boater's Academy and may be referred to appropriate law enforcement authorities. Upon suspension or termination, your right to use the Resources we provide will immediately cease, and we reserve the right to remove or delete any information that you may have on file with us, including any account or login information.
By using or accessing Boater's Academy websites and the Resources, you represent and warrant that you have read and understood the Privacy Policy, which is incorporated by reference into this User Agreement, and agree to be bound by its terms. The Privacy Policy is available at http://boatersacademy.com/index#privacy .
Dispute Resolution, Governing Law, Attorneys' Fees
This User Agreement shall be governed and construed in accordance with the laws of the Commonwealth of Virginia without regard to its conflict of law principles.
Any and all claims, actions, demands, causes of action, and other proceedings ("Claim" or "Claims") involving you and any of the enLearned LLC Parties arising from or relating to the Resources or this User Agreement shall be heard in a court or courts of competent jurisdiction in Virginia Beach, Virginia. You hereby agree to personal jurisdiction by such courts, and waive any jurisdictional, venue, or inconvenient forum objections to such courts.
You agree that any Claim you bring against any of the enLearned LLC Parties will only be in your individual capacity and not as a plaintiff or class member in any purported class or representative proceeding.
If any of the enLearned LLC Parties initiates a Claim against you arising from or relating to the Resources or this User Agreement, the enLearned LLC Parties will be entitled to recover from you their reasonable costs and attorneys' fees incurred as a result of such Claim. If you initiate a Claim against any of the enLearned LLC Parties arising from or relating to the Resources or this User Agreement, and any of the enLearned LLC Parties prevail on such Claim, the enLearned LLC Parties will be entitled to recover from you their reasonable costs and attorneys' fees incurred as a result of such Claim.
REFUND POLICY
Refunds will only be issued in the event that you are unable to access the Resources through no fault of your own (i.e., due to an outage or other non-functionality of Boater's Academy websites) for a period forty-eight (48) hours commencing with the time that you register and pay for access to the Resources. No refunds will be issued once you receive a Certificate of Completion.
CONTACT INFORMATION
If you have any questions or comments about this User Agreement, you can contact us at:
Boater's Academy P.O. Box 5143 Virginia Beach, VA 23471 [email protected]
Your browser is out-of-date! You must upgrade to a different browser to experience this site.
Course Outline
- The Rules of the Road
- Important Definitions
- Required Sound Signaling Equipment
- Sounding Off - When and How to Use Sound Signals
- The Rule of Responsibility
- Proper Lookout
- Rules for Avoiding Collisions
- Overtaking a Power-Driven Vessel
- Approaching a Power-Driven Vessel Head On
- Approaching a Power-Driven Vessel From the Side
Approaching a Sailing Vessel
- Approaching Another Sailing Vessel
- Operating in Heavy Traffic
- Operating in Narrow Channels
- Operating in Darkness - Part 1
- Operating in Darkness - Part 2
- Operating in Restricted Visibility
- Visual Distress Signals
- Marine Distress Signals - Anytime Use
- Marine Distress Signals - Daytime Use
- Pyrotechnic Visual Distress Signals
- Non-Pyrotechnic Visual Distress Signals
- Pyrotechnic Equipment Storage and Handling
- Number of Required Visual Distress Signals
- Aids to Navigation
- Uniform State Waterways Marking System - Part 1
- Uniform State Waterways Marking System - Part 2
- Intercoastal Waterway Markers
- Western River Markers
- Docking Mooring
- Anchoring - Part 1
- Anchoring - Part 2
This site requires JavaScript. Your browser either doesn’t support JavaScript or you have it turned off.
For this page to function correctly, please enable JavaScript and then refresh the page.
When a power-driven vessel B encounters a sailing vessel A, the sailing vessel is ALWAYS the stand-on vessel (unless a sailing vessel is overtaking). In the case above, power-driven vessel B must take EARLY and SUBSTANTIAL action to keep clear of sailing vessel A.
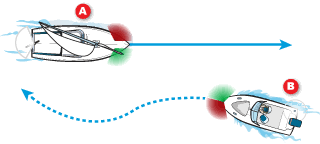
Sailing vessels stand on when being overtaken and give way when overtaking.
Understanding Boating Right of Way Rules

Since there are no yellow or white lines or stop signs on bodies of water, it can be difficult to understand who has the right of way in boating. Right of way rules (often referenced as the "rules of the road" or navigation rules ) are specifically defined maneuvering regulations designed primarily to avoid a collision between vessels. There are many rules and they differ by type of vessel, the operations that vessel is involved in at the time, and where the vessel is located (on inland or offshore waters).

Learning and memorizing all of them is a tall order for boaters of all experience levels, but it’s imperative to know the basics and then have the proper reference tools aboard to consult for all the more nuanced regulations.
5 Boating Right of Way Basics
- Vessels under sail (without auxiliary power engaged) have right of way over powerboats in most cases. There are exceptions as described above and in an overtaking situation.
- When crossing, the boat on the right (approaching from starboard) has the right of way. At night, you’ll see a red light moving across your horizon to the left. If there is a constant speed and bearing, you’re on a collision course and need to take evasive action.
- When meeting head-on, each vessel must alter course to starboard if possible to give a wide berth to the oncoming vessel. At night you’ll initially see both red and green lights.
- Any vessel overtaking another must keep clear of the stand-on vessel. You must keep clear if you’re coming up from behind and passing any vessel even if you are under sail and are coming up on a powered vessel. At night you’ll see a white light.
- When approaching another vessel whose intentions aren’t clear, take evasive actions early and make them clear in order to communicate effectively with the other vessel. In other words, slow down and make any course changes large enough to be understood and consistent (don’t drive haphazardly).
Boating Etiquette: Reading Between "The Rules"
Sailing Right of Way
When two boats that are both under sail meet, the following rules apply:
- The boat on a starboard tack has the right of way—the wind coming over the starboard rail.
- When two vessels are on the same tack (the wind is coming from the same side), the leeward boat (downwind) has the right of way over the windward boat (that presumably has clean air for better sailing conditions).
- When on the same tack in a passing situation, the vessel being overtaken has the right of way—always.
It’s your responsibility as the captain to know the basics and to act in a responsible manner to avoid a collision even if you’re the stand-on vessel. Slow down, evaluate the situation, make your intentions clear and in the end, presume the other guy has no clue and avoid an accident.
For a complete listing of navigation rules, refer to “Navigation Rules of the Road” published by the U.S. Coast Guard (COMDTINST 16672.2 Series), available through the U.S. Government printing office and also available here online .

Vessel Types, Categories & Definitions
Navigation rules focus on how and where vessels move. These are also supplemented by light and sound signaling rules that are covered under different sections of what is called COLREGS, the International Regulations for Prevention of Collision at Sea, and they govern the responsibilities of vessel operators in inland and international waters. A copy of the Rules of the Road can be purchased at chandleries and a must be carried aboard vessels of 40 feet or longer.
The type of vessel will often dictate a captain’s course of action. Powerboats are propelled by machinery. Sailboats under sail are in one category but a sailboat with its auxiliary motor turned on and in gear is considered to be a powerboat even if its sails are up. The following vessels also have priority in certain cases:
- Vessels constrained by draft (boats with a deep draft moving through shallow channels).
- Vessels restricted in their ability to maneuver (boats that may be too large to be agile in a small body of water or those actively operating as tugs, buoy tenders, or those engaged in commercial fishing with gear deployed, etc.).
- Vessels not under command (no one is in charge for whatever reason).
Vessel circumstances are defined differently. A stand-on vessel has the right of way and must maintain course and speed. It must also acknowledge understanding the intentions of the give-way vessel if signaled. The give-way or “burdened” vessel has the responsibility to maneuver safely around the stand-on vessel.
Marine Navigation: How to Navigate a Boat
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. If I’m towing a wakeboarder and another boat that’s not towing is in my way, who has the right of way?
If you’re towing on a lake or river, inland rules of the road still apply. However, your priority should be the safety of both vessels and the person you’re towing so if you must take evasive action, signal your boarder and stop, slow down or turn to avoid an accident.
Q. My boat is only 20 feet long. Do I still need to have a copy of the U.S. Coast Guard Navigation Rules onboard?
You don’t need a copy onboard, but you do need to know the basics. If you’re hazy on any part, a copy may be a good investment.
Read Next: 5 Best Marine Navigation Apps for Boaters
You Might Also Like:
- Marine GPS for Boats: Understanding the Basics
- 5 Tips for Understanding Nautical Flags & their Meanings
- Night Boating Tips
- How to Tie Up a Boat: Mooring Guide
- Find the Right Boat for Your Lifestyle
Join Our Newsletter!
Get community news, buying bargains, and how-to guides at your fingertips.

Rules of the Road
Right of way rules.
Whenever you meet another boat, it’s like approaching an unmarked intersection in your car. Knowing a few, simple right of way rules will help you avoid a collision. Just as motorists must know what to do when approaching a four way stop, every crossing situation at sea is like approaching an unmarked intersection.
Because there are so many different types of boats and styles of boating, it is important to know what to expect when you come upon another vessel.
"Vessels" are anything that floats on the water that is used, or is capable of being used as a means of transportation on water. A log, a bathtub and many other things could be considered a vessel under the Navigation Rules. The Navigation Rules distinguish one vessel from another by both its design, and by its actions. This section covers maneuvering rules only.
There are other navigation rules that you are required to know. Sound Rules are covered under the Sound Signaling Equipment section. Light Rules are covered under the Navigation Light Equipment section.
The Rules of the Road are published by the U. S. Government Printing Office, and are available in any boating supply stores. Every boat owner should have a copy, but they are mandatory to be kept on vessels over 12 meters (39.4 feet) in length.
The Rules generally used in this course are Inland Rules, unless otherwise noted. There are small but important differences in the Rules depending on where you are operating your boat. It is your responsibility to know the Navigation Rules for your boating area.
- International Rules - Apply to all vessels upon the high seas and in all waters connected to them that are navigable by seagoing vessels.
- Inland Rules - Apply to all vessels upon the inland waters of the United States, and to vessels of the United States on the Canadian waters of the Great Lakes to the extent that there is no conflict with Canadian law. Certain inland waterways may have specific provisions that apply to certain vessels.
- Great Lakes - Includes the Great Lakes and their connecting and tributary waters including the Calumet River as far as the Thomas J. O'Brien Lock and Controlling Works (between mile 326 and 327), the Chicago River as far as the east side of the Ashland Avenue Bridge (between mile 321 and 322), and the Saint Lawrence River as far east as the lower exit of Saint Lambert Lock.
- Western Rivers - Includes the Mississippi River, its tributaries, South Pass, and Southwest Pass, to the navigational demarcation lines dividing the high seas from harbors, rivers, and other inland waters of the United States, and the Port Allen-Morgan City Alternate Route, and that part of the Atchafalaya River above its junction with the Port Allen-Morgan City Alternate Route including the Old River and the Red River.
Vessel Types
- Power Driven Vessel - Any vessel propelled by machinery. This includes any boat that has an engine. Sailboats are considered powerboats when they are being propelled by a motor - even if the sails are up.
- Sailing Vessel - Any vessel under sail alone. Remember, if being propelled by a motor, a sailboat is considered to be a powerboat.
- Vessels Engaged in Fishing - Means any vessel fishing with nets, lines, trawls or other fishing apparatus which restrict maneuverability, but does not include a vessel fishing with trolling lines or other fishing gear which doesn't restrict maneuverability. This means a shrimper out of Galveston is "engaged in fishing" Someone out trolling for stripers in their Grady-White is NOT considered to be engaged in fishing under the Rules.
- Seaplanes - Are any aircraft designed to operate on the water.
- Vessels Constrained by Draft - Means that a vessel can't deviate from a course/channel because they might run aground. A freighter in a narrow channel is an example of this. Note: This is for International waters only, not Inland.
- Vessels Restricted in Their Ability to Maneuver - Means a vessel that can't maneuver as required by the rules because of the size or operation of the vessel. A fishing vessel pulling in nets and a buoy tender placing a buoy are both examples of a vessel restricted in their ability to maneuver.
- Vessels not under Command - Any vessel that for some exceptional circumstance is unable to maneuver as required by the Rules, and is therefore unable to keep out of the way of another vessel. If Joe boater slips and knocks himself out, and can no longer steer--that's a vessel not under command. If the steering cable goes out, and you can't turn the boat, that's a vessel not under command. If the captain is not paying attention and hits another boat, that's negligence.
- Underway - Means that you are not anchored, moored, at the dock, or aground. If you are even drifting along, you are underway.
- Restricted Visibility - Means any condition such as fog, mist, falling snow, rain, or other similar causes that make it difficult to see other vessels. Losing your glasses is NOT restricted visibility.
Rule, Rule, Rule your Boat
It may seem as if you can do anything you want while you are on the water (You might also think that it looks as if everyone else is going crazy on the water). Boating on a crowded waterway can be scary! The good news is that there are rules to govern the action of each vessel. The bad news is that many vessel operators do not know the rules!
Not complying with the Rules - even if you don't know them, can get you in trouble on the water. Even if you think you are following the Rules, if there is something that you can do to avoid a collision - you must do it, even if you deviate from a different Navigation Rule.
It is your responsibility as the ship's captain to be aware of your surroundings at all times, and to operate your vessel in a safe manner. Caution may not be fun, but having an accident sure stinks.
The Rules state that every vessel shall use all available means appropriate to the prevailing conditions to determine if a risk of collision exists. If there is any doubt, such risk shall be deemed to exist.
Rules Explained
The Rules are designed to tell you what to do when you operate your vessel near other vessels. The purpose of the Rules of the Road is to help you avoid an accident--not to establish responsibility or liability if you get into an accident. - Remember, if you get into an accident, you can be held liable, even if you followed the Rules to the letter!
Your primary obligation is to operate in a safe manner. Under the Rules, there is no "right-of-way" like there is on a street. For most situations, Boats are called one of the following.
- Give-Way Vessel - If you are the Give-Way vessel, you must act as if the "stand-on" vessel has the right to keep going the way it is going. It is your responsibility to signal your intentions to the stand-on vessel, and it is your responsibility to maneuver your boat around the other in a safe manner. Also known as a "Burdened" vessel, as it has the burden of.
- Stand-On Vessel - If you are the Stand-On vessel, it is your responsibility to acknowledge the intended actions of the give-way vessel. You must also maintain your current course and speed until the give-way vessel passes, or you enter a dangerous situation.
Operator Responsibilities
In addition to the Rules, you have other responsibilities as the captain as well. You are responsible for the safety of everyone aboard your vessel at all times--and you have a responsibility to those with whom you are sharing the water.
- You must always operate at a safe controlled speed for the situation in which you are boating, and any legally mandated speed requirements that there may be, such as a slow/no wake zone.
- Take care to avoid careless, reckless or negligent boat operations--such as operating too closely to other vessels, boating under the influence, or operating at an unsafe speed for the given conditions.
- Steer clear of naval vessels, and other restricted facilities such as bridges, power plants and dams. New Homeland security measures require it, as does your safety! For more information, see the Homeland Security pages.
Finally, as a boater, you have a responsibility to all other boaters--and all others who enjoy the water--to be courteous and respectful of others. This means that you should always watch your boat noise (a legal requirement) avoid congested waters as much as possible, avoid disturbing wildlife and sea grasses, and look out for the safety and well being of other boaters by giving a hand to those in need.
The Pecking Order
There is a "pecking order" that can be used as a simplified memory aid to determine right of way for vessels of different types. Get very familiar with this list, as it is important to understand it thoroughly. The lower most vessel on the list is the give way vessel, and must stay out of the way of vessels that are higher on the list.
- Overtaken vessel (top priority)
- Vessels not under command
- Vessels restricted in their ability to maneuver
- Vessels constrained by draft
- Fishing vessels engaged in fishing, with gear deployed
- Sailing vessels
- Power driven vessels
Collision Avoidance
- Rules apply to vessels in all conditions of visibility. Rules are the same at night or in fog, for instance, as they are during a bright sunny day.
- Every vessel must maintain a proper look-out by sight and hearing at all times. Operator inattention and not having an adequate look out are a leading cause of accidents each year.
- Every vessel must proceed at a safe speed at all times. Several factors should be considered when determining safe speed, including but not limited to the state of visibility, traffic density, your vessel's maneuverability, with special reference to stopping distance and turning ability. At night, consider the presence of background lights such as those from shore, or from the back-scatter of your vessel's own lights. Consider also the state of wind, sea, and current, and the proximity of navigational hazards.
- The Rules specifically require that any action taken to avoid collision, if the circumstances allow, will be positive, made in ample time, and in keeping with good seamanship. Any changes in course or speed should be large enough to be readily apparent to the other vessel. This means that you should avoid last second changes in course, and you should avoid a small series of changes. Change direction early, and make a large turn.
Maneuvering

The main situations of collision risk are overtaking, meeting head-on, and crossing. When one of two vessels is to keep out of the way (give-way vessel), the other, the stand-on vessel, must maintain course and speed. The stand-on vessel must take avoiding action when it becomes apparent that the vessel required to give way is not taking appropriate action.
The Crossing Rule
Both International and Inland Rules state that when two power-driven vessels are crossing so as to involve risk of collision, the vessel which has the other on her starboard side (the give-way vessel) must keep out of the way.
As the give-way vessel it is your duty to avoid a collision. Typically, this means you must alter speed or direction to cross behind the other vessel (the stand-on vessel).
At night, if you see a red light crossing right-to-left in front of you, you need to change your course. If you see a green light crossing from left-to-right, you are the stand-on vessel, and should maintain course and speed.
The Meeting Situation

At times there may be some doubt whether the situation is a crossing or a head-on meeting. In case of doubt, you should assume that it is a meeting situation, in which neither vessel has a clear-cut "right-of-way," and each must act to avoid the other. Each vessel in a meeting situation must alter course to starboard so that each will pass on the port side of the other. At night, you will recognize a head-on meeting situation if you see both red and green side lights at the same time.
The Overtaking Situation

Any vessel overtaking any other vessel must keep out the way of the vessel being overtaken. The former is the give-way vessel and the latter is the stand-on vessel.
This rule applies even if the overtaking vessel is propelled by wind, oars, or rubber band paddlewheel.
A vessel is deemed to be overtaking when coming up with another vessel from a direction more than 22.5 degrees abaft (behind) her beam. This is the angle prescribed by the stern light.
At night, the overtaking vessel will see only the white stern light of the vessel being overtaken. If you see either side light, it is a crossing situation.
Operating in a Narrow Channel
First and foremost, you have to avoid larger vessels that can only travel in a channel. Even if your vessel is operating under the rules otherwise, you must give way to a boat that could potentially run aground or get into a collision if they left the channel.
Try and operate on the edge of the channel. Be extra cautious if you come to a bend in the waterway, and can't see traffic coming towards you.
You may sound a prolonged blast as a warning to traffic headed your way.
On the Great Lakes and Western River system, vessels going downstream are stand-on, vessels going up stream must give-way.
Potential Collision Situation
When the distance between two vessels decreases and the relative angle of the other vessel off the bow remains the same, then you will soon be trying to occupy the same spot in the water - a collision situation. Change course or reduce speed, even if you are the stand-on vessel.

Conduct of Vessels During Periods of Restricted Visibilty
Operating a boat in areas or at times of restricted visibility requires extra concentration by the skipper and the lookout. You must operate your vessel at a speed at which you can identify and react to a situation and still have enough time to avoid a collision. This is especially important when vessels are no in sight of one another.
- Operate at a safe speed for the prevailing circumstances
- Have engines ready for immediate maneuvering - including reverse
- Don't rely on radar or other electronic imaging alone - use your buiilt in senses at all times
- Take avoiding actions early and provide ample time for the other vessels to maneuver
- Avoid sharp turns if being overtaken
- Always - you are in doubt, reduce your speed
- Every vessel shall at all times proceed at a safe speed
Other Rules
Whether under inland or international rules, power vessels must keep clear of sailing vessels in open waters. A sailboat with motor running is defined as a motor boat. The "pecking order" between sailing vessels is more complex. When two sailing are approaching one another so as to involve risk of collision, one of then shall keep out of the way of each other as follows.
- When each has the wind on a different side, the vessel which has the wind on the port side shall keep out of the way of the other.
- When both have the wind on the same side, the vessel which is to windward shall keep out of the way of the vessel which is to leeward.
- If a vessel with the wind on the port side sees a vessel to windward and cannot determine with certainty whether the other vessel has the wind on the port or the starboard side, she shall keep out of the way of the other.
- For the purposes of these rules the windward side shall be deemed to be the side opposite to that on which the mainsail is carried. On square-rigged vessels, it shall be deemed to be the side opposite to that on which the largest fore-and-aft sail is carried.
Now that you are familiar with "The Rules," go out and use them in passing, meeting, and crossing situations you find on the water. You will get many puzzled looks from inexperienced boaters with no training or testing.
Remember, if a collision does occur, your proper use of the correct signals and appropriate actions will win you points! But you know enough now to avoid a collision.
The navigation rules of the road contained in this course summarize basic navigation rules for which a boat operator is responsible. Additional and more in-depth rules apply regarding various types of waterways and operation in relation to commercial vessels and other watercraft. It is the responsibility of a boat operator to know and follow all the navigation rules.
For a complete listing of the navigation rules, refer to the document “Navigation Rules of the Road” published by the U.S. Coast Guard (COMDTINST 16672.2 Series) and available through the U.S. Government printing office or on the web here .
For state specific navigation requirements, refer to the state laws where you intend to boat.

Right of Way Rules
Whenever two boats try to occupy the same water at the same time, a right of way situation exists. When this happens, one boat is obligated to give way to the other. The boat that is supposed to give way is Called the give way vessel and the other one is called the stand on vessel The stand on vessel should keep to its course so the skipper of the give way vessel can get out of the way without collision. There are specific rules to use in determining which vessel is which.
Motor vs. Sail : A motor boat is any vessel using an engine regardless of whether it is a sailboat or a motorboat. A sailboat is considered to be a motorboat even if the SailS are up as long as the engine is running. A sailboat that is sailing generally has the right of way over motorboats. But there are some exceptions.
- Large motor vessels are given the right of way in channels where it is difficult for them to maneuver. In the case of ships, the whole San Francisco Bay is considered to be channeled so that ships always have right of way in the Bay.
- In narrow channels such as Redwood Creek, motor vessels as small as 65 feet may be limited in maneuverability enough to make them the "stand on" vessel.
- Motor vessels that are restricted in maneuverability due to the special job they are doing are "stand on" This could be anything from towing nets to dredging, pile driving, or tending buoys.
- Motor vessels don't have to give way to sail boats that are motoring when the rules for motorboats give the motor vessel right of way. (When motoring, a sailboat is treated like any other motorboat.
- If a motor vessel is experiencing some kind of difficulty restricting its maneuverability, it is given right of way.
- If a sailboat is overtaking a power boat, the power boat has the right of way.
Passing - When any boat is passing another boat, the passing boat is tile give way boat and tile boat being passed is the stand on boat. Head On - When two motor boats approach each other head on, both boats turn to the right and pass each other port to port. Crossing - When motor boats paths cross, the boat on the other's right is stand on and the one on the other's left is the give way boat This is like two cars coming to a 4-way stop except that a give way boat would alter course to go behind the other boat Sailboats When encountering sailboats that are sailing, motorboats generally should give way. If you are motoring in a sailboat, you should give way to sailboats that are sailing.
- Log in to post comments
© 2022 Spinnaker-Sailing San Francisco. All Rights Reserved.


This article is an excerpt from NauticEd’s online FREE Navigation Rules Course , an interactive online sailing course for ALL sailors to learn Navigation Rules and become a safer sailor. Or if you want to learn more, upgrade to the Skipper Course Bundle to become a competent sailor!
You can learn to sail and improve your sailing with NauticEd, the international leader in sailing education.
Overtaking Vessels
Here we quote the rules exactly because they are incredibly clear. Note that a sailing vessel is a part of “any vessel”. i.e. if you are a sailing vessel overtaking any other vessel according to (a) you must keep clear.
(a) Notwithstanding anything contained in the Rules, any vessel overtaking any other shall keep out of the way of the vessel being overtaken.
(b) A vessel shall be deemed to be overtaking when coming up with another vessel from a direction more than 22.5 degrees abaft her beam
(c) When a vessel is in any doubt as to whether she is overtaking another, she shall assume that this is the case and act accordingly.
(d) Any subsequent alteration of the bearing between the two vessels shall not make the overtaking vessel a crossing vessel within the meaning of these Rules or relieve her of the duty of keeping clear of the overtaken vessel until she is finally past and clear.
Wow, look at (d). This means that even while you are overtaking and keeping clear if the other vessel changes course you must still keep clear. But there is nothing in (d) that says if you are being overtaken you have the right to change course. If you are being overtaken you are obligated to continue to Stand-On to not make course changes.
Do you get the overall feeling here? There is a common theme. The rules are written so that everyone has the responsibility to avoid collision. Even if you feel you are in the right – you can not instigate a collision to prove your point.
Some Examples
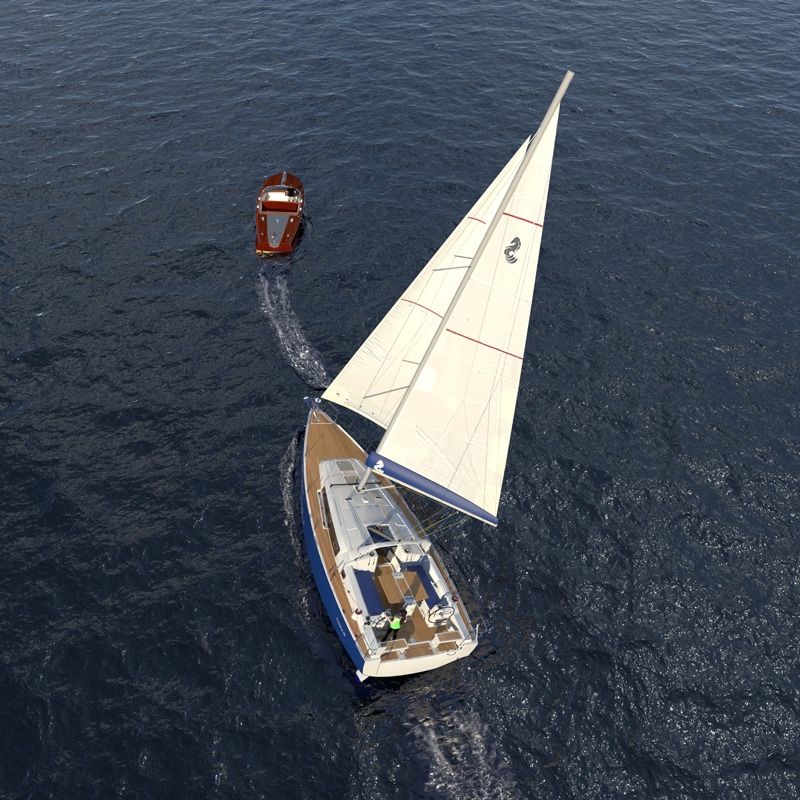

Above: The sailboat is overtaking a powerboat. Any vessel overtaking another must Give Way, therefore the sailboat must Give Way. This is also the case if the powerboat is lying adrift in this position.
However, if the powerboat was adrift in the position in the image below, the powerboat must Give-Way. The reason for this is that adrift is actually considered as “underway” even with engines off. Oftentimes in lakes or sheltered bays, we will encounter powerboats that are adrift as sunbathing, etc. The rules are clear – adrift is underway and appropriate Giving Way must be done. However, the rules are also clear in that you must avoid collision. Therefore, if you determine that the skipper of a powerboat that is adrift is not getting up and shifting out of your way then you must avoid the adrift powerboat AND you must do so in order not to create a close-quarters situation. In any case, this is one of those situations where a little courtesy should also be applied. The choice now becomes, which way should you go, windward or leeward of the vessel? Going windward in a close-hauled sail set could be dangerous because your vessel always has a certain amount of sideslip and you just might not make it – or the wind could change, causing you not to be able to make as tight of a heading as you estimated. Going in front of the boat also has its concerns, because if the captain suddenly turned on engines in a panic to get out of your way he might steer right into you. In this situation, if the boat were not taking evasive maneuvers, we’d recommend loudly announcing your intentions preferably with a whistle or horn, bearing away from the wind and passing well clear to the lee (downwind) of the vessel.

Above: the adrift powerboat must Give Way to the sailboat – even if the engines are off. However, as you know, the sailboat has every responsibility not to cause a collision – even if it is the stand-on vessel. The sailboat would be prudent (and is required) to take action early to ensure it misses the powerboat.
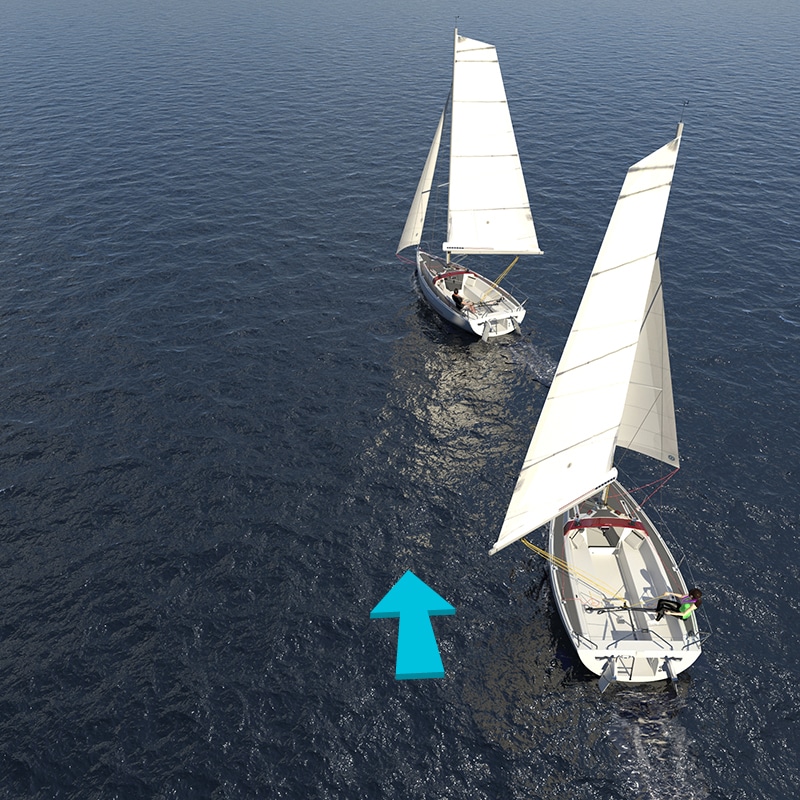

Above: This is an interesting one. The trailing sailboat on is on starboard and the leading sailboat is on port. Which do you think must Give Way? Well, for a collision to exist, the rear vessel must be overtaking the leader. The overtaking vessel must Give Way even though she is on starboard. In this case starboard Gives-Way to port. Don’t get confused, just remember that an overtaking boat Gives-Way to the other. This is a pretty obvious logical rule and as you’ll see later – being Overtaken is at the top of the pecking order of Stand-On.
Learn Navigation Rules for Free...
A FREE 3-hour course that teaches how to stay safe, avoid collisions and accidents, and learn the “Rules of the Road”. The free Navigation Rules Course is for ALL sailors, whether you’re just learning or need a FREE refresher. Or, consider upgrading to the Skipper Course Bundle to become a fully competent skipper!

- Hybrids & EVs
- Motorsports
- Marine & RVs

What You Should Do if Your Boat Is Overtaken
In the past two years, boating and RV life have gotten unexpected boosts in popularity. Drivers love hitting the open road (or waters, in boating’s case) with a reasonable distance between themselves and others. Boats are also relatively inexpensive, with many new models costing less than $30,000 .
However, many inexperienced boaters don’t realize the standard rules for operating a boat. While bodies of water are far less crowded than roads, you’re bound to encounter another boat sooner or later. What kinds of boats have the right-of-way during passing situations?
Here’s what it means when your boat is overtaken

A vessel is overtaken when another boat comes from a direction over 22.5 degrees behind it. According to the Boat U.S. Foundation , the overtaken boat is known as the stand-on vessel. This boat must maintain its speed and course until the ship behind it has safely passed.
The boat behind the stand-on vessel is called the give-way vessel. It’s this vessel’s responsibility to stay entirely out of the path of the overtaken boat. If you are the overtaking boat, you must relay signals to the overtaken boat about your passing intentions.
Overtaken vessels have top priority on the “pecking order,” meaning that every other boat must stay out of their way. So, while motorboats are the lowest on the pecking order, they’re still the stand-on vessels if overtaken by a sailboat.
However, remember that sailboats are prioritized in the standard pecking order because they have less maneuverability than motorboats. Because of that, it’s vital for motorboat drivers to stay alert and practice evasive maneuvers when needed to help the sailboat.
What if your motorboat is being overtaken by another motorboat?
Another service we work with on the Thames on a daily basis is @MPSonthewater . Here is one of the boats passing us pic.twitter.com/op6cVyMVSx — Tower RNLI (@TowerRNLI) April 16, 2013
In any passing situation, Inland Rules state that the overtaking boat has to signal its intent. One short horn blast means the give-way vessel intends to pass on the starboard (or right) side. Two short horn blasts mean that the give-way ship is passing on the port (or left) side.
In reply, the overtaken boat should always signal its consent with an identical signal. If the stand-on vehicle doesn’t supply a corresponding signal, its motor might be too loud to hear your approach. Proceed with caution, and if you feel unsafe at any time or expect a collision, make five or more short horn blasts.
How to avoid collisions with other boats
In meeting situations (where the two boats face each other), it can be challenging to determine who has the right of way. To be cautious, both drivers should maneuver their vessels to the starboard side. In a crossing situation, the ship on the starboard side acts as the give-way vessel.
It’s also important to pay attention to a vessel’s lights in situations where visibility is limited. In overtaking situations, you’ll only see the stern white light of the ship in front of you. Seeing red and green lights simultaneously means that you’re facing another boat head-on. You should alter your course immediately if you see a red light crossing right-to-left.
Since the crossing and overtaking rules apply night or day, you should always pay attention to a vehicle’s lights. At all times, every boat should also have a lookout for seeing and hearing. Additionally, never make abrupt maneuvers or increase your speed in limited visibility. Allow the other boat plenty of time to do their maneuvers and rely on your senses alongside your boat’s radar .
Every boat is expected to maintain a safe speed at all times. Regardless of which boat has the right of way, both vessels should have safety-conscious captains to avoid collisions.
Improve Your Boating Skills Before Launching This Season

How Many Axles Does an RV Have?

Play Captain Nemo Aboard Your Own Submarine Yacht

John Oliver Offers Clarence Thomas a $2.4 Million RV to Resign
Produced by Digital Editors
Our experienced team of Digital Editors works to produce all of our content from contributing authors, including everything from assigning headlines and crafting the angles that readers will be interested in, to editing and publishing the articles once they’re drafted. Our DEs are editors and writers in their own right, who each have several years of experience in digital media and publishing.
Each one caters their work to their specific interests.
- Build A Boat
- Find A Dealer

- Right of Way Rules for Boating

If you’re a new boat owner or you need a refresher on the right of way rules for boating — this article is for you.
While we all love to have fun on the water, safety is always the priority . You may be intimidated thinking about driving your new boat down a crowded waterway with all different types of vessels crossing your path. How does everyone know where to go and how to stay out of each other’s way? Fortunately, there are regulations to minimize collisions and to maintain order and safety. However, it is also important to note that despite the rules, it is always your responsibility to avoid a collision, no matter the scenario.
Every good captain must know the right way to approach interactions with other boats — just like how it’s essential to know traffic rules when driving a car. When you understand the fundamental boating right of way rules for rivers, oceans and harbors, you’ll be able to cruise through the most crowded waterways with ease. Let’s dive in.
The Importance of Knowing Boating Right of Way Rules
The United States Coast Guard reported almost 4,300 recreational boat accidents in 2017 . Surprisingly, most recreational boaters aren’t familiar with the boat right of way rules, which causes confusion and makes their boating experience less safe and more stressful. If you master even the basic principles of boat-passing rules, you’ll know how to behave in any situation and keep your cool.
As the captain of your vessel, it’s your responsibility to maintain the safety of your boat and everyone onboard. The more knowledgeable you are about how to do that — such as by knowing and understanding boating right-of-way-rules and collision regulations — the less you have to worry about something going wrong.

First things first — a few general tips and boating rules for maintaining navigational safety:
Don’t Go Too Fast
If you can increase the overall safety of your vessel or a vessel nearby by slowing down, you should. Sometimes the conditions are right to go fast, and sometimes they aren’t. It’s the job of a good skipper to know the difference. Take into account how many other boats are around you and if you have the proper space to slow down quickly.
Be Cautious of Other Boaters
Just like when you’re driving a car, just because the rules of the road exist, it doesn’t mean everyone follows them. Recreational boaters are notorious for not following the rules. If their actions seem unsafe, keep enough distance between you and them so that any unexpected maneuver won’t catch you off guard.
Always Be Respectful and Conscientious
While sometimes you may be operating under legal conditions, it’s still nice to give other boaters the respect and the space they deserve. Just because you have the right of way doesn’t mean you have to take it every time.
Avoid All Government Vessels and Restricted Areas
These vessels and areas almost always have the right of way, and it’s best to give them plenty of space.
Give Way If It Makes Sense
Even if you have the right of way in a situation that could be dangerous, it’s your responsibility to alter your course if it means avoiding an accident. If you did not change your course and an accident occurred, it’s possible you could still be at least partially at fault even if you did have the right of way. Safety always takes precedence.

Rules for Different Boating Scenarios

How two boats approach each other determines which has the right of way. Position, direction and the different levels of priority for different vessels make up the majority of the rules on the water. We’ll get into the different types of vessel priority a little later.
When a vessel has the right of way, they’re called the “stand-on” or “burdened” vessel . If you’re the stand-on vessel, you have to confirm the actions of the give-way vessel by maintaining your course and speed until you pass them or need to alter your course.
The “stand-off” or “give-way” vessel is the one that doesn’t have the right of way.
What does it mean to give another vessel right of way? You must ensure they can hold their current course and speed, which may mean substantially altering your course in a way that’s clear to the stand-on vessel.
For this article, we’re assuming you operate a power-driven vessel — the rules are a little more complicated if you’re sailing.
Here are some common scenarios you’re likely to encounter on the water:
1. Approaching a Non-Power Vessel
When you’re approaching a vessel without motor power, such as a sailboat, they have the right of way.
An important note — a sailboat must be “under sail” to qualify for the right of way over power-driven vessels. If they’re using their small outboard motor instead, they have the same right of way as a normal powerboat .
In recent years we have seen a proliferation of human-powered craft in the form of kayaks and paddle boards. The Navigation Rules refer to human-powered craft as “vessels under oars” and they are singled out only in the lighting rules. Otherwise they are simply “vessels.” We may encounter these vessels in three different navigational situations. We may encounter them in overtaking situations. The vessel being overtaken is the most privileged vessel on the high seas. Give that human-powered craft a wide birth when overtaking, being mindful of your wake as you do. The two other navigational situations in which we may encounter paddlers are head-on and crossing situations.
Interestingly, the rules don’t make specific provisions for power-driven vessels encountering vessels under oars in head-on and crossing scenarios. Rule 2 is the “responsibility” rule, and it, in essence, tells us to use good judgment based on the whole of the navigational picture. In head-on situations, the standard port to port passing should serve us well. In crossing situations, there’s no reason why we can’t apply the rules of power-driven vessels as well. The vessel that has the other to her starboard shall give way. In short, Rule 8 tells us we must take all reasonable action to avoid a collision. Vessels under oars move relatively slowly and are easy to avoid. When encountering them take early and positive action to pass at a safe distance. In any case of uncertainty, the rules tell us we should slacken our speed.
2. Approaching Power-Driven Vessels
When two boats have the same priority of right of way based on their classification, the determining factors become position and direction of travel.
To determine the position of another vessel relative to your own, you must know the different “sectors” of your vessel, i.e., starboard, port and stern. Once you identify where another boat is relative to your own, you’ll know who has the right of way.
Using the following simple rules, you’ll have a good grasp on how to behave around other powerboats :
1. If another vessel is approaching you from the port — or left — side of your boat, you have the right of way and should maintain your speed and direction.

2. If a vessel is aiming to cross your path and they’re on your starboard — or right — side, they have the right of way. Alter your course so that you will pass them at a safe distance and in a way that is apparent to the other skipper.

3. Any vessel that is approaching your boat for the stern doesn’t have the right of way. Maintain your speed and course. Whenever a boat is overtaking another, the vessel in front always has the right of way and should be allowed to continue their original course unhindered. This is the case even if the vessel behind has a higher level of right-of-way priority, such as a sailboat.

When the sun goes down, and boaters turn on their navigational lights, there’s an easy way to remember to who has the right of way:
- – When you see a red navigational light on another boat, it’s indicating their port side, and they have the right of way — red means stop.
- – When you see a green navigational light, you’re approaching a vessel from their starboard side, and you have the right of way — green means go.
- – How do you know if you’re overtaking another vessel at night? Look for their white stern light and steer clear. The stern light shines at 22.5 degrees on either side of the boat behind the widest point — the beam.
Knowing the basics listed above will have you in great shape in most boating situations. Below are some of the best practices that will help take your navigational skills to the next level:
If You’re Passing through a Crowded Harbor
One of the best tips for this scenario is to always aim for the stern of a boat you want to go behind — this lets the operator of the other boat know that you intend to go behind them and they can continue their course. Captains will sometimes use a VHF radio to communicate their intention to “take the stern” of another boat as a courtesy and to keep traffic flowing more smoothly.
If You Meet Another Boat Head-on
Under the boating rules of the road, vessels approaching each other head-on are always supposed to pass each other port to port — or left to left, just like on the road. However, crowded harbors and times when many boats come together at once make this difficult to follow all the time — stick to the rules as much as possible, but use your best judgment to keep everyone safe.
If You Want To Use a Horn To Communicate or You Hear Another Vessel’s Horn
Experienced skippers will sometimes use their horns to communicate. If you want to move past another boat in a narrow channel or if you’re overtaking another vessel and would like to pass, you may sound your horn for two short blasts. If you receive two short blasts back, the other skipper is signaling that the maneuver is okay. If they sound five short blasts in response, that means passing is unsafe, and you shouldn’t pass the vessel — in any situation, if you ever hear five short horn blasts, be on alert. This is the signal for imminent danger. Please keep in mind that international rules can differ.
If You’re on a “Collision Course” With Another Vessel
Remember, you must alter your course with ample time to safely avoid a collision, even if you are the stand-on vessel. The definition of a “collision course” is when the bearing from your boat to another isn’t changing, while the distance between your two boats is shrinking.
Once you’re familiar with the basic rules of the road, use them with your best judgment, and navigating through boat traffic will be a breeze.
Right of Way Between Different Types of Vessels

Now that you know the basic rules of the road, we’ll cover a few special situations you may encounter. Besides the basics of power versus non-power boat rules, there’s a pecking order when it comes to the right of way — different vessels and different conditions determine who is the stand-on vessel.
Here’s the U.S. Coast Guard list , from the highest level of right of way to the lowest:
1. A Vessel Not Under Command or a Vessel Restricted in Its Ability to Maneuver
The Coast Guard gives these two types of vessels the same level of priority. A boat “not under command” means that an unexpected circumstance is keeping the boat from maneuvering, like an engine or steering failure.
A vessel that restricted in its ability to maneuver is unable to move out of the way of other boats due to the nature of its work, like a buoy tender fixing a navigational aid or vessel transferring passengers while underway.
2. A Vessel Being Overtaken
Any boat approaching a vessel from astern must give them the right of way.
3. A Boat Engaged in Fishing
When a boat has commercial fishing equipment deployed, that restricts their ability to maneuver. Therefore, they have the right of way.
4. A Vessel Under Sail or Not Under Power
A vessel under sail as well as other watercraft that are not powered, — such as canoes, kayaks, paddleboards, etc. — have the right of way over powered-vessels.

5. A Power-driven Vessel
As a power-driven vessel, you must give way to all the other categories above. If you are converging on another powered boat, either head-on or astern, the right-of-way rules mentioned earlier apply.
A few more unique situations that the Coast Guard doesn’t include on their simplified list are:
- – Whenever you hear a siren or see blue flashing lights on an emergency or law-enforcement vessel, give them the right of way just like you would an ambulance or a police vehicle.
- – Keep an eye out for tugboats and other vessels towing — if in the open ocean, they can have a submerged tow-line with a lot of distance between them and their tow.
- – Always take the stern of large commercial tankers and container ships in the ocean, and never try to cross in front of them. While it may look like they’re not moving, they can be running at over 20 knots .
- – Steer clear of docked or moving ferries — some have submerged cable lines. Watch other boats and how they navigate around the ferry before crossing yourself.
- – Any boat under 65 feet is obligated to steer clear of larger, less maneuverable vessels.
It’s important to maintain a proper lookout at all times when operating your vessel. If your boat is small enough, you may be able to keep track of everything by yourself. If you have a larger boat, you’ll probably want some help from a friend onboard — especially when leaving the dock or landing. Having an extra set of eyes is helpful to any captain, no matter how seasoned.
If you apply these tips and remain alert and responsible when operating your boat, there’s no reason you should get into a collision. If someone who isn’t following the rules happens to bump into you, following the rules only helps your case.
You can find a copy of the USCG Navigation Rules in most boating supply stores, and you can also download it online . It’s a good idea for any boater to carry a copy onboard, and it’s mandatory for any vessel over 39 feet in length. Be sure to look up your state’s navigational rules before you set out, as they may vary depending on location.
Formula Boats for Safety and Performance

Here at Formula Boats, we take safety seriously. As a family company since 1976, we know the importance of protecting your most valuable assets. Owned and operated by lifelong boaters, the Porter family treats every product as a representation of themselves — that’s why we do everything we can to equip our customers with not only the most reliable boats available, but also the knowledge to be safe such as these boat rules on the water.
Our customers keep coming back because when you own a Formula boat — you’re part of the family. If you’ve thought you can’t have it all in a boat, think again. We don’t make boats for the masses — we make boats for you. With more than 60 years of continued innovation, we make precision watercraft that surpass expectations of quality and performance.
Contact us today for any other boating questions you may have or to request a quote.
Contact Dealer
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply

The motorboat crossing the paths with a pwc: What actions to take?
Motorboat crossing the paths with a pwc.
Meeting another boat at sea is like approaching an unmarked intersection on the road.
Just like you have to follow a set of rules when you reach a cross-section, you must follow specific rules when approaching another boat at sea. You must follow simple rules to avoid a collision.
It is essential to know what to expect when you cross paths with another vessel. When in water, there are rules to govern the action of each vessel.
Unfortunately, many vessel operators do not know the rules. Not complying with regulations can get you in trouble.
While taking a Boat Ed or boating exam, you may come across the question –
If the motorboat is crossing the paths with a PWC, what action should be taken?
The correct answer to this question is – The vessel on the left (port) hand side should be the one to give way.
Now let us read some more information on the topic.

What is a PWC?
A personal watercraft (PWC) is a recreational watercraft that uses an inboard jet drive as its primary propulsion source.
Also known as a water scooter, a PWC is designed to be operated by a person sitting, standing, or kneeling on it.
What action to take if a motorboat crossing the paths with a pwc?
If a motorboat is crossing the paths with a PWC, the vessel on the port(left) side should give way.
A PWC should be treated like a motorboat. The rules are the same for a PWC or a motorboat.
If one vessel is crossing from the port side and the other one is crossing from the starboard side, then the one crossing from the port side is the make-way vessel and must alter its speed to avoid a collision.
The vessel on the starboard side must be given time to cross first.
Related Posts:
How fast do pontoon boats go?
Best pontoon boat anchors
Safety equipment list for a pontoon boat
Best pontoon boat accessories
Who has the right of way on the water?
Every captain should know the basics about what one has to do when two boats approach each other on the water. Here are some guidelines that you must understand and follow –
- Stand-on vessel – The boats that enjoy the right-of-way are known as ‘stand-on vessels.’ The stand-on vessel can maintain speed and direction while approaching other vessels.
If you are the stand-on vessel, it is your responsibility to acknowledge the give-way vessel’s intended actions. You must maintain your speed and current course until the give-way vessel passes or you enter a dangerous situation.
- Give-way vessel – The boats that are not given the right-of-way are known as give-way vessels. A give-way vessel should take early, substantial measures to steer clear of the stand-on vessel. You must stop, alter the speed and direction of your boat to avoid a collision. If you are the give-way vessel, it is your responsibility to signal your intentions to the stand-on craft. It is also your responsibility to maneuver your boat around the other in a safe manner.
Which is the stand on vessel motorboat or PWC?
PWCs are considered to be powerboats, and the same rules apply to them. In the scenario when a PWC encounters a motorboat, these are the rules of the road that come into play –
Meeting head-on
When a PWC and a motorboat are about to meet head-on, each vessel should move to the starboard side and pass in a normal traffic pattern (Pass with the other vessel to port.)
Vessels crossing paths
When a PWC wishes to cross the path of a motorboat, the direction of the approach is the factor that determines which one has the right of way. If a motorboat approaches you from the starboard side, it has the right of way.
You must take early and substantial action to avoid the other craft. If the other vessel approaches you from your port side, you have the right of way and must maintain your speed and course.
Overtaking another boat
Overtaking another boat is legal. You can do so either on the port side or on the starboard side.
According to the Collision Regulations, the vessel intending to overtake another one on the starboard side should sound one blast of the horn.
After ensuring the starboard side is clear, the boat that has to be overtaken should respond by sounding a single blast of the horn, indicating that the overtaking boat can proceed.
If the intention is to pass on the port side, the overtaking vessel has to sound two blasts on the horn to indicate their intent.
After ensuring that the port side is clear, the vessel that has to be overtaken should respond by sounding two blasts of the horn, indicating that the overtaking boat can proceed.
What should a powerboat do when crossing paths with a sailboat?
If you are operating a powerboat, you must always give way to a sailing vessel unless the sailing vessel is overtaking your vessel.
There is a pecking order that determines the right of way for vessels of different types. Understand this list and get familiar with it.
The vessels lower on the list are the give-way vessels and must stay out of the way of the boats that are higher on the list.
1. Overtaken vessel (top priority)
2. Vessels not under command
3. Vessels that are restricted in their ability to maneuver
4. Vessels that are constrained by draft
5. Fishing vessels that are engaged in fishing, with gear deployed
6. Sailing vessels
7. Power-driven vessels
What should a sailboat operator do when approaching a PWC head-on?
The sailboat operator should maintain its current speed and the current course as it is the stand-on craft.
The motorized PWC is the give-way craft, so it should maneuver to avoid the sailboat as the sailboat lacks maneuverability. On a head-to-head collision, both vessels should pass port to port.
What do you do if you are operating a motorboat that is being overtaken by a sailboat?
If you are operating a motorboat being overtaken by a sailboat, you should keep going as you are. The vessel that is being overtaken is always the stand-on vessel.
The vessel you are overtaking is the give-way vessel, regardless of whether it is a power-driven vessel or a sailboat.
Now, let’s look at some frequently asked questions related to PWC and what actions to when motorboat crossing the paths with a pwc.
Can you consider a PWC a boat?
The US Coast Guard classifies the PWC as a Class A Inboard Boat (a boat less than 16 feet in length).
They are designed to carry up to three persons and can be operated by a person sitting, standing, or kneeling on the watercraft.
A PWC does not look like a boat but is subjected to the same laws as a yacht, and all boating licenses also work the same way.
What are the legal requirements to operate a PWC?
The legal requirements to operate a PWC include –
- A person should be a minimum of 16 years of age to operate a PWC.
- You need to wear a personal floatation device to operate a PWC.
- If you want to ride in the dark, you will need to have navigational lights.
- All operators of personal watercraft must have a Boating Safety Education Certificate in their possession.
- All operators of PWC should adhere to boating law as violating these laws can have legal consequences.
Is it safe to ride PWC at night?
It is illegal to ride a PWC at night in most states in the US. In some states, it is allowed, but you have to have to correct navigational lights installed and turned on.
However, it is not safe to drive PWCs at night as the rider can get seriously hurt. The navigational lights of the PWC can confuse the other boats, especially from a distance.
A PWC can move fast and suddenly change direction, which can confuse the other boaters at night.
Are you required to wear a PFD on a PWC?
Each person on board a PWC must wear a US Coast Guard-approved wearable Type I, II, or III PFD.
How much distance should one PWC maintain from another PWC or boat?
A PWC should maintain a distance of 50 feet from any other boat, PWC, or jet ski. A PWC should maintain a similar distance from other people in the water, stationary platforms in the water, and shorelines.
What actions to take if a sailboat under sail is about to cross paths with a PWC?
If a sailboat under sail is about to cross paths with a PWC, the PWC should change its speed and course. The power-driven vessel is the give-way vessel, and the sailing vessel is the stand-on vessel.
If two boats are traveling on paths that will cross, what determines which boat is the give-way vessel?
The answer depends on these two factors –
1. How are the vessels propelled?
- Two power-driven vessels
- Two sailing vessels
- A power-driven vessel and a sailing vessel
2. How are the two vessels approaching one another?
- Meeting head-on – the vessel operator can see another vessel ahead.
- Paths that cross- this involves a risk of collision
- Overtaking – A vessel is trying to overtake another vessel from behind.
Final thoughts on the motorboat crossing the paths with a pwc
I hope you are now familiar with all the rules and laws regarding passing, crossing, and overtaking different vessels in the water.
In this post, we have tried to answer all your questions regarding PWCs, including what to do when the motorboat crossing the paths with a pwc. We hope you find this information helpful for your boating exams.
Related posts:
How to Run a Boat HIN / HULL ID Check Instantly
Where is the Best Place to Store a Fire Extinguisher on a Boat?
A boat is towing two skiers at the same time. How long should the tow lines be?
Can you ski behind a pontoon boat?
Overtaking another vessel - Boating Right of way Rules Collision regulations
- Free Boating License Study Guide
- Navigation Rules
- Overtaking another vessel - Boating Right of way Rules
What must you do if you wish to overtake another vessel?
When two vessels are moving in the same direction, the vessel passing is the give-way vessel and should keep out of the way of the vessel being passed. The vessel being passed is the stand-on vessel and must maintain its course and speed. If the stand-on vessel realizes that the course intended by the give-way vessel is not safe, it should sound the danger or doubt signal.
During nighttime, only the sternlight (white light) of the vessel being overtaken would be visible, with neither sidelight in sight.
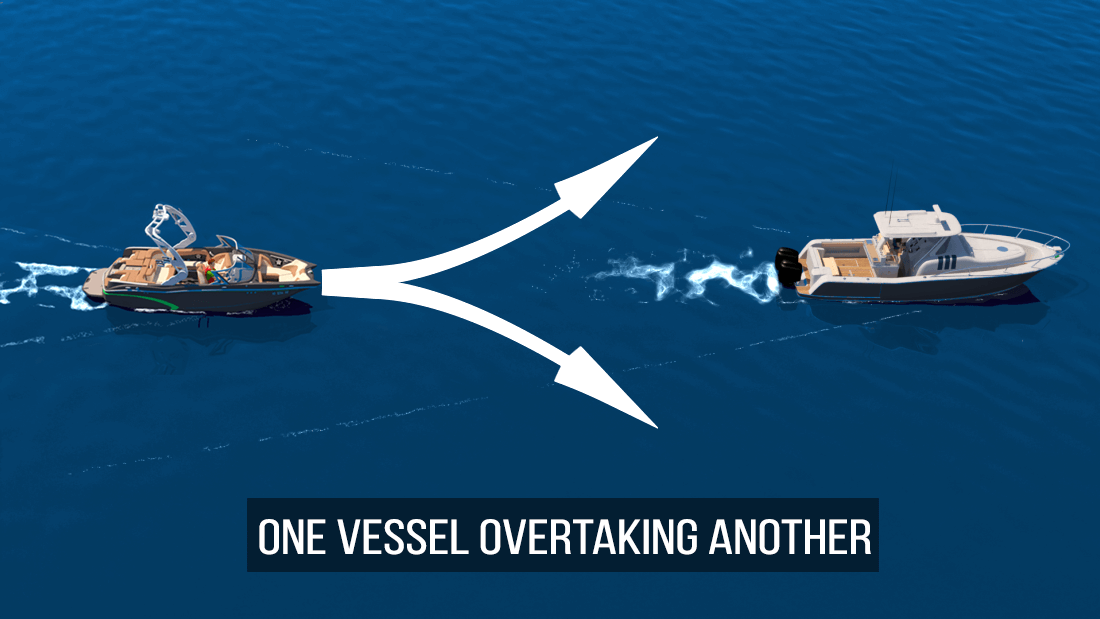
How many blasts must you sound when overtaking another vessel?
When overtaking a vessel, always remember that you are the give-way vessel until you are well past and safely clear of the stand-on vessel. Avoid cutting in front of, obstructing, or putting another vessel in danger.
The boat behind (give-way vessel): "I intend to pass you on your starboard side" - 1 short blast (1 sec.)
The boat in front (stand-on vessel): "Agreement" - 1 short blast (1 sec.)
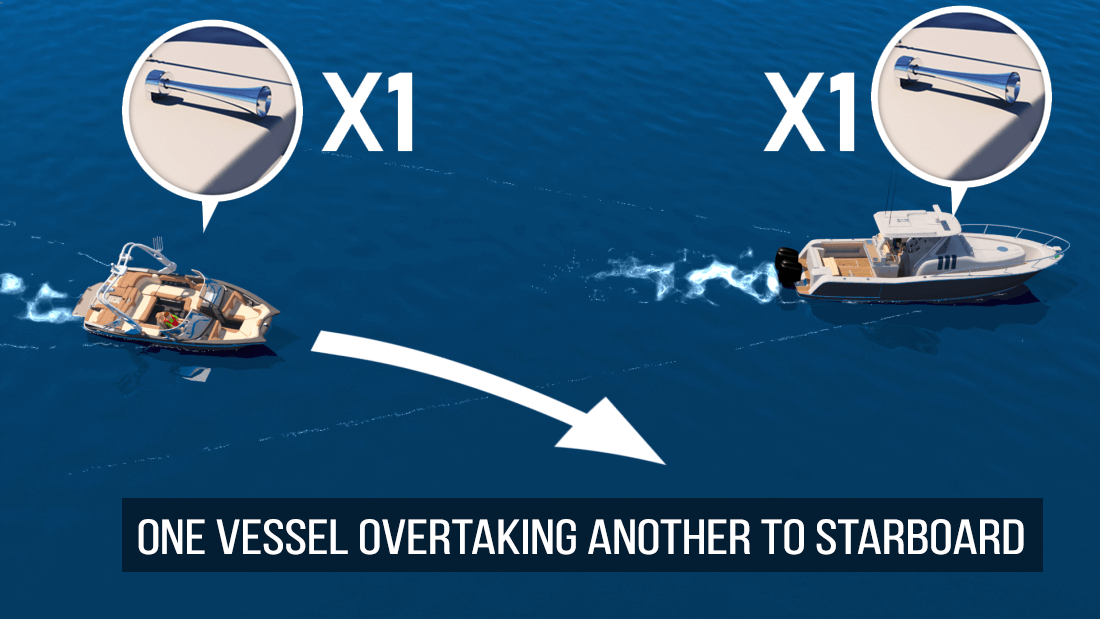
The boat behind (give-way vessel): "I intend to pass you on your port side" - 2 short blasts
The boat in front (stand-on vessel): "Agreement" - 2 short blasts
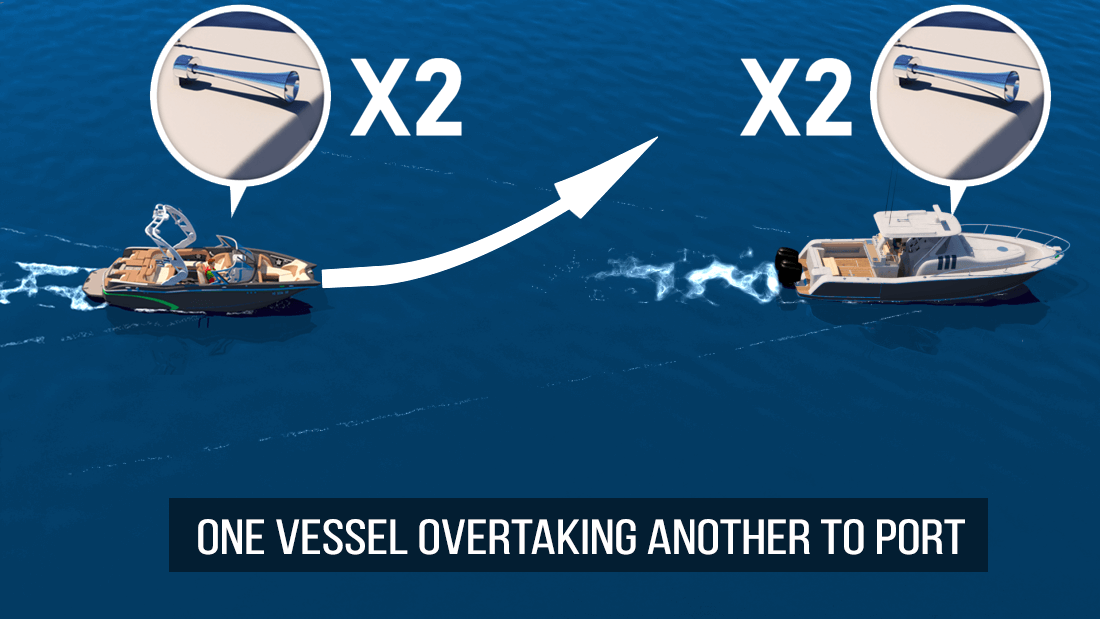
What actions should be taken by the operator of a power-driven vessel that is being overtaken by a sailboat?
Whether it's a sailing vessel or a power-driven vessel, the stand-on vessel is always the one being overtaken, regardless of the type of boat.
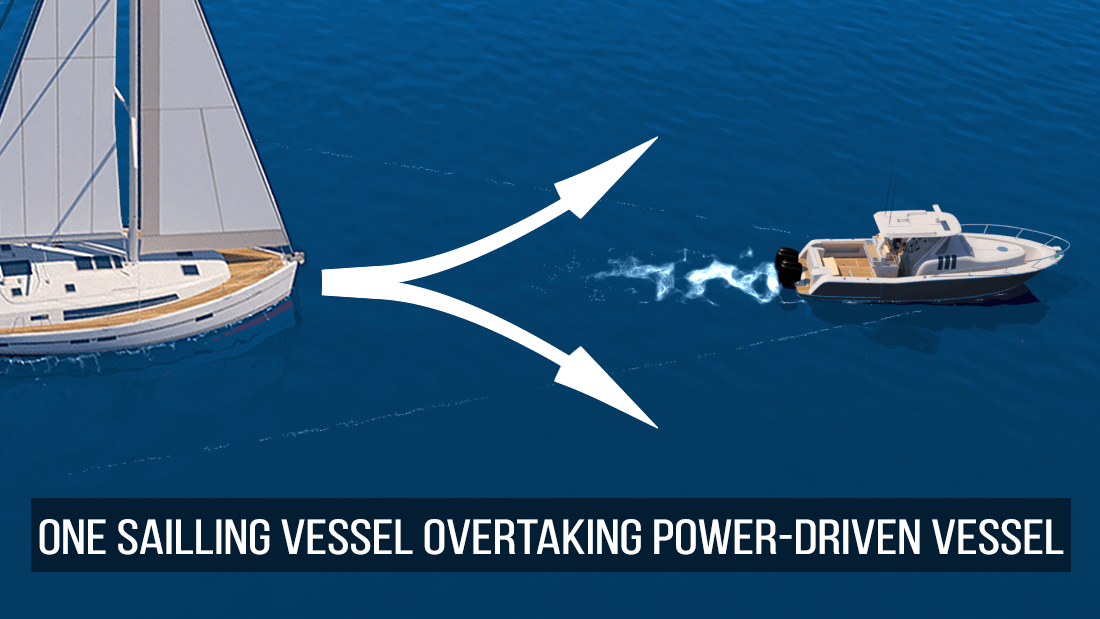
- Follow Ace Boater on YouTube
- Join Ace Boater on Facebook
- Contacts Us
Boating safety course and boating exam accredited in USA
Motorboat And A PWC Are Approaching Head-On: What Action Should Be Taken?
When you meet another vessel on the sea, it is necessary that you know what to do in order to prevent an accident. Just as it is with road safety rules and regulations, navigating the ocean also requires certain guidelines.
Being well informed of these guidelines is necessary so as to be prepared upon encountering another vessel at sea. Many craft operators are ignorant of these guidelines. That is why it is important you know them, so as to avoid unnecessary mishaps.
When A Motorboat Encounters A PWC, What Is The Next Step To Take?
This is a common exam question for those who take the Boat Safety Education course. The answer to this is that each vessel should veer off to its right side, speed up, keep its course until they are very close by, and then the vessel coming from the left (port) side should reduce its speed and give way for the other vessel coming from the right (starboard) side to pass on.
Motorboat And A PWC Are Approaching Head-On, What Action Should Be Taken?

Some Guidelines For Encountering Other Vessels On The Water. There are a few essential rules the captain of every vessel should know, in order to expertly navigate the waters.
The vessels with right-of-passage
These are also called stand-on vessels; These are vessels that keep their speed and do not alter their direction when they come in contact with another vessel at sea.
They must act in accordance with the rules assigned to stand-on vessels until the intersection is passed, except a precarious situation presents itself.
The give-way vessels
These are vessels that have to stand by; reduce their speed and alter their directions when they come across another vessel at sea. They come from the port or left side of the intersection.
When an interaction occurs, these vessels are to adhere to the rules that are assigned to vessels that give way, and send a signal to the other vessel to proceed, while looking for a way to safely navigate around the oncoming craft.
Should A PWC Give Way For A Motorboat?
When a PWC & a motorboat meet, there are certain rules to follow; This is because a PWC is often regarded as a motorboat hence, the rules that apply to motorboats are also applicable to them. These rules are:
- In the occurrence of a PWC & a motorboat meeting, since they are both motorboats, they are both to move to their individual right sides, and pass by each other according to regular traffic rules.
- If an event occurs, such that a PWC seeks to cut across the path of an oncoming motorboat, two things take place. First, if the PWC is coming from the right side, then it is by rule allowed the right of passage, and therefore should stay its course and speed.Whereas, if it’s coming from the port side, which is the left side, then it has to reduce its speed, send a signal to the oncoming craft to pass on, and safely find a way to navigate around the other boat.
Precautions To Take Upon Encountering A Sailboat At Sea.
If your craft is a PWC or a motorboat, then, when you come across a sailboat on the sea, it is according to rules that you make way for them, especially when they plan to overtake your boat.
There are some guidelines that point out which vessel has the right of passage and which doesn’t. Keep these guidelines always on your mind when at sea.
On this list, vessels listed near the top have the right of way, while those nearer the end of the list have to give way for other vessels to pass by.
- A vessel that wants to overtake.
- A vessel that is unmanned.
- A craft that cannot be easily maneuvered.
- Draft-constrained crafts
- Fishing boats containing fishing equipment
Precautions For Sailboats When Encountering A PWC
The sailboat should continue on its course. It has the right of passage, and therefore, the oncoming PVC should slow down its speed, change direction and find a way to successfully navigate around the sailboat. This is because; the sailboat cannot be easily maneuvered like the PWC.
If navigation around the sailboat is impossible, the crafts should go by each other, port-side to port-side
Action Steps For Powerboat Operators When A Sailboat Signifies Interest To Overtake.
Whenever a vessel is about to be overtaken by another craft, the vessel doing the overtaking has the right-of-way, while the other vessel has to stand back and ease off on its speed.
So, as an operator of a powerboat that is about to be overtaken by a sailboat, you should ease off on your speed, and make way for the overtaking vessel to pass on.
Can The PWC Be Regarded As A Vessel?
According to the U.S Coast Guard, the PWC is a “Class A” Inboard Boat. These crafts are smaller than sixteen feet length-wise and are meant to accommodate just three passengers.
It does not have the physical features of a regular boat, but it is operated by the guidelines of a yacht and has the same boating licenses as other vessels.
Criteria For Operating A PWC
Before operating a PWC, there are some requirements to take note of.
- The intending operator should be no less than sixteen years old.
- A life jacket is compulsory for all occupants of the PWC.
- Navigation lights are an absolute must for night rides.
- Before you can drive a PWC, you must be certified by Boating Ed, that is, Boating Safety Education.
- All intending PWC operators should know the Boating rules and regulations and strictly follow them. Failure to do so attracts legal repercussions.
More About PWC
PWC is the abbreviated version of the name, Personal WaterCraft. This craft is often used as a means of recreation and is propelled by an inboard-jet drive. It is also called a water scooter and one can operate it either by kneeling, sitting, or standing on it.
Is It Advisable To Take A PWC For Night Rides?
The answer to this is, No. This is applicable for most states within the United States. But in the remaining states, you can actually take a PWC out on night rides, but you must have your navigator light turned on.
That is a top requirement. Driving a PWC at night, however, is a dangerous venture, as there are higher chances of someone getting hurt, most especially the PWC’s operator.
This is because, due to the PWC’s speed and easy maneuverability, it can easily and swiftly change direction and its headlights can be a source of confusion for other oncoming vessel operators.
See Also: What should you do to Reduce the Risk of Capsizing or Swamping your Boat in Rough Water?
Do You Need A PFD While Abroad A PWC?
Yes, you do. Before boarding a PWC, you need to have an approved U.S. Coast Guard wearable. Be it a Type One, Two, or Three PFD.
What Is The Safest Distance Allowed Between A PWC And Other Crafts?
Fifty feet is the safest. For whatever boat type it encounters on the water. The same thing goes for people as well as stationary objects in the water.
When A Sailing Sailboat Encounters A PWC And There’s An Intersection Of Paths, What Is The Necessary Course Of Action?
A sailboat that encounters a PWC, while on a sail, is to carry on and not change direction or speed.
This is because it has the right of way as the stand-alone vessel. The PWC has to reduce its speed, change direction and find a way to maneuver around the sailboat.
When Two Vessels Are About To Cross Paths, What Are The Right Procedures To Follow?
For two boats about to cross paths on the waters, there are various factors that determine which boat has to give way, and which boat gets to stand-alone, that is, proceed without any change in course or direction. These factors are:
What kinds of vessels are they? Are they both power-driven? or both are sailboats? Or one is a sailboat while the other is a motorboat?
From which direction are they approaching each other? There are three ways vessels encounter each other on the water.
One, it could be a head-on encounter, whereby there is another craft coming directly in front. Two, it could be that one boat is cutting across the path of the other.
Three, it could be that one vessel is about to overtake the other. Whichever way the vessels encounter each other on the waters, the rules remain the same:
Vessels approaching from the starboard side have the right of passage while the other stands down. Easily maneuvered crafts give way to unmanned, bigger, or restricted vessels.
Read Also: In Areas Of Heavy Boat Traffic, How Can The Operator Reduce The Chances Of A Collision?

Ever wondered how you can have a cruising boat without getting into financial problems? The answer is here. That is the reason why we set up this blog to share with you, safety tips, answers to questions that have to do with fishing and hunting. You are going to love it!
Hey! I am Armstrong!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

WaterCraft 101
Your guide to fun on the water!

Sailboat vs. Powerboat: Which Is the Give-Way Vessel? Understanding Navigation Rules on the Water
Navigating the waters is an exciting adventure, whether you’re at the helm of a sleek sailboat or commanding a powerful motorboat. However, along with this thrilling journey comes the responsibility of understanding and adhering to the marine navigation rules, specifically those concerning the right of way or the “give-way” vessel. This aspect is vital to maritime safety, ensuring orderly movement and preventing potential collisions on the high seas.
Under the International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea (COLREGs), a powerboat is typically the give-way vessel when encountering a sailboat under sail. The powerboat should alter its course to avoid a collision. Always confirm specific situations with local and international rules.
This article will delve into the intriguing debate between sailboats and powerboats. We’ll dissect the intricate navigation rules on the water, shedding light on the factors determining which boat must yield.
This piece promises to be an enlightening read for seasoned mariners and beginners alike, providing essential information for anyone who wishes to tackle the waves responsibly. Remember, knowing these rules isn’t just a matter of etiquette—it’s a crucial component of maritime safety.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Nautical Navigation Rules

Navigating the vast expanse of our world’s waters requires skill and a profound understanding of maritime movement rules. These rules, known as the International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea (COLREGs), have been established by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) and are adhered to by seafarers worldwide. They provide a comprehensive framework for nautical navigation, ensuring that all vessels move in a safe and orderly manner.
Key points in understanding nautical navigation rules include:
- Understanding COLREGs: COLREGs are the universal road rules for boats and ships worldwide to prevent collisions between two or more vessels.
- Right of Way or Give-Way Rules: These rules determine which vessel is responsible for keeping out of the way in encounters with other vessels to avoid collisions.
- Sound and Light Signals: COLREGs establish a system of sound and light signals so vessels can communicate their intentions in various scenarios, especially in poor visibility.
- Navigation Lights and Shapes: Vessels must display specific lights and shapes in different situations to indicate their status to other vessels.
- Steering and Sailing Rules: These rules determine vessels’ actions in the sight of one another to prevent collisions.
- Special Circumstances: There are also rules for special circumstances, such as vessels not under command, constrained by draft, engaged in fishing , or sailing in narrow channels.
Understanding the Concept of the Give-Way Vessel
Understanding the concept of the give-way vessel is fundamental to maritime navigation. In nautical terms, a ‘give-way’ vessel refers to the boat required to alter its course or speed to avoid colliding with another boat, the ‘stand-on’ vessel. Essentially, the give-way vessel must yield to the stand-on vessel.
These designations help create an orderly flow of traffic on the water and significantly reduce the risk of collisions. It’s important to note that these roles can change based on various factors, including the type of vessels involved, their relative positions, and the environmental conditions.
The responsibility of the give-way vessel does not absolve the stand-on vessel of all duties. If it becomes apparent that the give-way vessel is not taking appropriate action to avoid a collision, the stand-on vessel must take evasive action.
Regardless of their designation, both vessels share a mutual obligation to avoid incidents at sea. Understanding these dynamics and responsibilities is crucial for all mariners, as it contributes to safer navigation and fosters a culture of mutual respect and cooperation on the waterways.
Sailboats vs. Powerboats: A Basic Overview
Sailboats and powerboats represent two distinct modes of marine transportation, each with unique characteristics, advantages, and challenges. Sailboats, propelled primarily by wind action on their sails, offer an eco-friendly, serene, and often sportive seafaring way. On the other hand, powerboats, driven by mechanical engines, provide speed, power, and often more control, particularly in challenging weather conditions. Each type requires different skill sets and knowledge to operate safely and efficiently.
Key characteristics of sailboats and powerboats include:
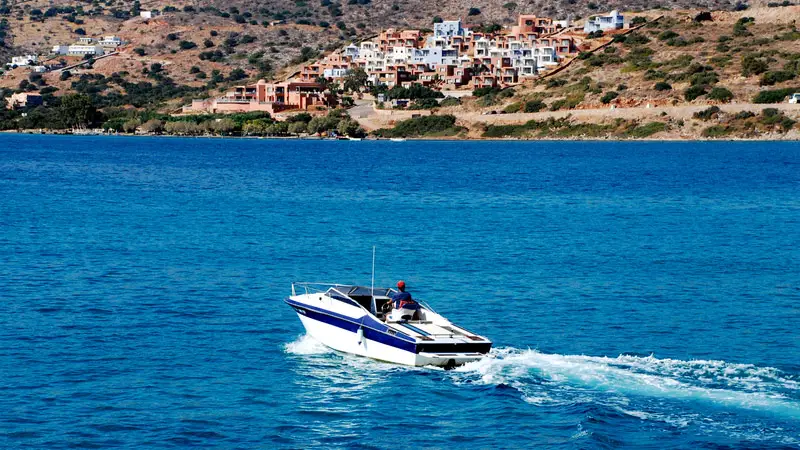

- Propulsion: Sailboats rely on the wind acting on sails, rigging, and hull for propulsion. In contrast, powerboats use engines (inboard, outboard, or stern-drive) for movement.
- Speed: Powerboats generally offer higher speeds than sailboats, making them suitable for water skiing, racing, or quick transportation. Sailboats, being wind-dependent, can’t match the speed of a motorboat but offer a more leisurely pace.
- Maneuverability: Powerboats usually have superior maneuverability due to their engines. Sailboats, reliant on wind and currents, require more skill and understanding of these elements for effective control.
- Fuel efficiency and environmental impact: Sailboats are more environmentally friendly and fuel-efficient as they use wind power. Powerboats rely on fuel, which leads to emissions and potential environmental impact.
- Skills and knowledge required: Operating a sailboat requires knowledge of sailing techniques and wind patterns. Powerboat operation is typically more straightforward but requires an understanding of engine operation and maintenance.
The Role of a Powerboat in Marine Traffic
Powerboats play a significant role in the vast and diverse arena of marine traffic due to their speed, maneuverability, and versatility. These vessels can range from small personal watercraft and motorboats to larger yachts and ships, all powered by engines.
Their mechanical propulsion allows them to move independently of wind and current conditions, giving them an advantage in certain navigational situations. They can quickly respond to changes in direction, making them particularly valuable in congested waters or emergencies.
However, this power and speed come with responsibilities. Powerboats are generally considered the give-way vessel when encountering sailboats under sail, mainly because they have more control over their course and speed. They are expected to be vigilant and proactive in avoiding collisions, altering course or speed as needed.
Also, due to their potential to create a significant wake, powerboat operators must also be mindful of their vessel’s impact on other boats, wildlife, and shoreline erosion. Thus, the role of a powerboat in marine traffic extends beyond its capabilities—it includes the duty to navigate responsibly for the safety of all water users.
The Role of a Sailboat in Marine Traffic

Sailboats hold a unique and enduring presence in marine traffic. They are characterized by their dependence on the wind for propulsion, using sails to catch and harness its power. These vessels, varying from small dinghies to large sailing yachts, offer a sense of tradition, adventure, and connection with nature that is often unmatched.
Sailboats can navigate in areas with depth restrictions where larger powerboats cannot go, and their silence and absence of emissions make them an eco-friendly choice for seafaring.
Despite their slower speeds and lesser maneuverability than powerboats, sailboats generally have the right of way under the COLREGs when they are under sail and in a crossing situation with power-driven vessels. This rule recognizes the limitations of a sailboat’s maneuverability due to its dependence on wind direction and strength.
However, this privilege does not free them from the responsibility of maintaining a proper lookout and taking corrective action when it’s clear that the give-way vessel isn’t taking appropriate action or when both vessels are in such proximity that immediate action is necessary. Therefore, the role of a sailboat in marine traffic is not just about leveraging wind power but also about understanding and adhering to the navigation rules for everyone’s safety.
The Powerboat-Sailboat Encounter: Identifying the Give-Way Vessel
Navigating encounters between powerboats and sailboats is a fundamental aspect of marine safety. In general, according to the International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea (COLREGs), the powerboat is usually the give-way vessel when encountering a sailboat that is under sail. This is because a powerboat with an engine is typically more maneuverable than a sailboat that relies on the wind for propulsion.
The give-way vessel, in this case, the powerboat, has the responsibility to take early and substantial action to avoid colliding with the stand-on vessel, which in this case would be the sailboat. This may involve altering the course, reducing speed, or combining both. These rules aim to create a predictable path for both vessels to prevent a collision.
However, it’s essential to understand that these rules can have exceptions based on specific scenarios. For instance, when a sailboat overtakes a powerboat, it becomes the give-way vessel, regardless of its propulsion method. Furthermore, if the sailboat is operating its engine and not clearly showing sails, it is considered a powerboat under the COLREGs.
Both powerboat and sailboat operators must know these rules to ensure safe navigation. Importantly, the ultimate rule is to avoid collision – even if this means the stand-on vessel has to give way. Knowledge, caution, and mutual respect are key to maintaining safety on the water.
Factors Influencing the Give-Way Decision For Boats

Several factors influence the decision of which vessel is the give-way vessel. These include the type of vessels involved, their relative positions, and the specific scenario they are in. While the general rule is that powerboats give way to sailboats under sail, there are exceptions and other factors that can change this rule. Understanding these factors is critical for safe navigation and collision avoidance.
Key factors influencing the give-way decision include:
- Type of Vessels Involved: The type of vessels involved in an encounter greatly influences the give-way decision. For example, vessels not under command, vessels limited in their ability to maneuver, boats constrained by their draft, fishing vessels, and sailboats generally have right of way over power-driven vessels.
- Relative Positions: The relative positions of the vessels also influence the giveaway decision. For example, a vessel overtaking another is generally the give-way vessel, regardless of the type of vessel involved.
- Operating Conditions of Vessels: Whether a vessel is under power or sail can influence the give-way decision. A sailboat under power is considered a power-driven vessel subject to the same rules as other vessels.
- Navigational Hazards: Navigational hazards may also impact the giveaway decision. A vessel in a position where it can safely navigate may be required to give way to a vessel closer to navigational hazards.
- Traffic Density: In areas of high traffic density, vessels may be required to maintain a higher level of vigilance and may need to take action to avoid collisions earlier than in areas of low traffic density.
Remember, while the give-way rules provide a framework for determining who has the right of way in a given situation, the ultimate responsibility of all mariners is to take whatever action is necessary to avoid a collision.
Special Situations: Exceptions to the Rule
While the general rules of navigation provide a solid foundation for maritime safety, there are special situations where exceptions to the rule apply. These exceptions account for the complexity and unpredictability of marine conditions and ensure that the primary goal of collision avoidance is always met.
- Overtaking Situations: Regardless of the type of vessel, the overtaking vessel is usually the give-way vessel. The stand-on vessel should maintain its course and speed, while the overtaking vessel should keep out of the way until it is past and clear.
- Narrow Channels: In narrow channels, all vessels should keep as near the channel’s outer limit on their starboard side. A boat shorter than 20 meters in length or a sailing vessel can not hinder the passage of a vessel that can navigate only in a narrow channel or fairway.
- Traffic Separation Schemes: In traffic separation schemes, a vessel should join or leave a traffic lane at the smallest angle to the general direction of traffic flow. A vessel should try to avoid crossing traffic lanes and should cross on a heading as close as possible to right angles to the prevailing traffic flow direction if obliged.
- Vessels Not Under Command or Restricted in their Ability to Maneuver: These vessels, due to exceptional circumstances, cannot maneuver as required by the COLREGs and are, therefore, usually given the right of way.
- Vessels Engaged in Fishing: Vessels engaged in fishing, when underway, shall have the right of way over other vessels, except those not under command or restricted in their ability to maneuver.
Bryan is a Las Vegas resident who loves spending his free time out on the water. Boating on Lake Mohave or Lake Havasu is his favorite way to unwind and escape the hustle and bustle of the city. More about Bryan.
Similar Posts

How Tight Should Sailboat Lifelines Be? (Need to Know!)
A lifeline is a safety device frequently found on sailboats and on construction sites. It’s composed of wire and stanchions, which are secured around the ship’s perimeter to prevent passengers from being thrown overboard or accidentally falling. But how tight should they be? Sailboat lifelines should be tight enough so they only stretch about two…

Does a Boat Motor Charge the Battery? (Explained)
If you own a car, you probably know that a car engine charges the car battery when it runs. But does your boat motor work the same way? A boat motor charges the battery when it runs by using an alternator to replenish the battery. However, the battery loses energy every time the boat starts,…

How Far Can a Sailboat Heel? (The Simple Answer)
Heeling is when a sailboat leans to one side, which can occur naturally or deliberately. When done deliberately, proper heeling enables a sailboat to travel faster. This, in turn, begs the question of how far a sailboat can heel? The optimal heeling range for sailboats varies by model and preference but usually sits between 10…
Boat Engine Submerged in Freshwater: Steps to Salvage and Prevent Damage
There’s something profoundly serene about the gentle bobbing of a boat on a tranquil freshwater lake. But the harmony is swiftly broken when the unexpected happens, such as your boat engine taking an unanticipated plunge beneath the surface. This article isn’t about the peaceful afternoons spent on the deck or the exhilarating moments of catching…

How to Know When Boat Thermostat Is Open: A Quick Guide to Check
A boat thermostat is a vital component of the engine cooling system that regulates the temperature of the engine coolant*. The thermostat ensures that the engine maintains a consistent temperature and prevents it from overheating. The ways to know if a boat thermostat is opening properly include checking the boat’s temperature gauge, looking for excessive…

Boat Fuel: Everything You Need To Know (Explained)
Powerboats require fuel to run. But what fuel do they run on, and which is the best fuel for my boat? There are a lot of things to know about boat fuel. In this article, you will find out everything you need to know about boat fuel including: Different Types Of Boat Fuel Boat fuel…

Two dead and five missing following a boat collision on Danube River in Hungary
Two people are dead and five are missing following a boat collision on the Danube River in Hungary.
Hungarian police received a report late on Saturday night, local time, that a man had been found bleeding from his head on the shore of the Danube near the town of Verőce, around 50 kilometres north of the capital, Budapest.
The bodies of a man and a woman were later discovered nearby.
Hours after police began their search, they discovered a damaged boat in the water, which they towed to shore.
They are still searching for five adults — three men and two women — who they believe were on the boat.
Police said they had determined that a river cruise boat had been in the area at the time of the accident.
They stopped a cruise boat with a damaged hull near the town of Komarom, more than 80 kilometres further upriver.
Hungarian public television station M1 reported that the cruise boat, Heidelberg, is a 109-metre Swiss craft that can accommodate 110 people.
No passengers on that boat sustained injuries, M1 said.
The Danube at Verőce is roughly 460 metres wide and is in the centre of an area called the Danube Bend where the river makes a sweeping, nearly 90-degree turn to the south.
The area is a popular recreational and boating destination and is on a route often used by cruise boats between Budapest and the Austrian capital, Vienna, some 230 kilometres upriver.
The deadly accident comes five years after at least 27 people were killed in Budapest when a river cruise boat collided with a smaller tourist vessel, sinking it in seconds.
The tourist boat Hableany, carrying 35 people who were mostly South Korean tourists, was overtaken from behind by the much larger cruise boat, Viking Sigyn, beneath Budapest's Margit Bridge, in May 2019.
The Ukrainian captain of the Viking Sigyn was found guilty in 2023 of negligence leading to a fatal mass catastrophe and sentenced to five years and six months in prison.
He has appealed the decision.
On Sunday police said they have initiated criminal proceedings against an unknown perpetrator on suspicion of endangering water transport and causing the death of several people.
Disaster response units, including 95 personnel, 25 vessels and drones were still searching for the five missing people along the entire Hungarian section of the Danube downstream from the site, police said in a statement.
- X (formerly Twitter)
- Death and Dying
- Maritime Accidents and Incidents

Sailing Skills – Rules Of Overtaking And Right Of Way On The Water
Written By:
Post Date – Updated:
When sailing a sailboat, one of the most important things you need to understand is some of the rules on the water. These rules are similar to driving a car on the road.
There are basic rules for who has the right of way in the water. A good skipper should clearly understand who the stand-on vessel is and who the give-way vessel is. A skipper must also understand when his boat is the stand-on boat, when his boat is the give-way vessel, and who has the right of way on the waterways. The main object of all the rules of the water is to avoid a collision.
Table of Contents
Starboard tack has the right of way over port tack, leeward vessel has right over windward vessel, the overtaken vessel has right over overtaking vessel, a sailboat has the right of way over a powerboat, a sailboat should stay clear of large vessels, general sense rules of water safety, frequently asked questions, are there dead bodies inside the great wall of china, what is tacking in sailing steps to a proper tack, what is the best way to remember the points of sail when sailing, sailing skills – basic rules for overtaking and right of way on the water.
There are primary navigation and water rules that every sailor should know. The purpose of these rules is to avoid collisions on the water.
There is a stand-on and give-way vessel when two boats are near the same area. Here is what each of these sailing terms means:
- Stand-on vessel – The stand-on vessel is the sailboat with the right-of-way.
- Give-way vessel – The give-way vessel must give way when it may be on a collision course.
Even though the rules of the water have both stand-on and give-way vessels, every boat on the water should do all it can to avoid a collision. t is crucial for every boat on the water to understand some of the water’s primary navigation and safety rules.
Below are the basic five basic navigation rules for who is the stand-on vessel and the give-way vessel.
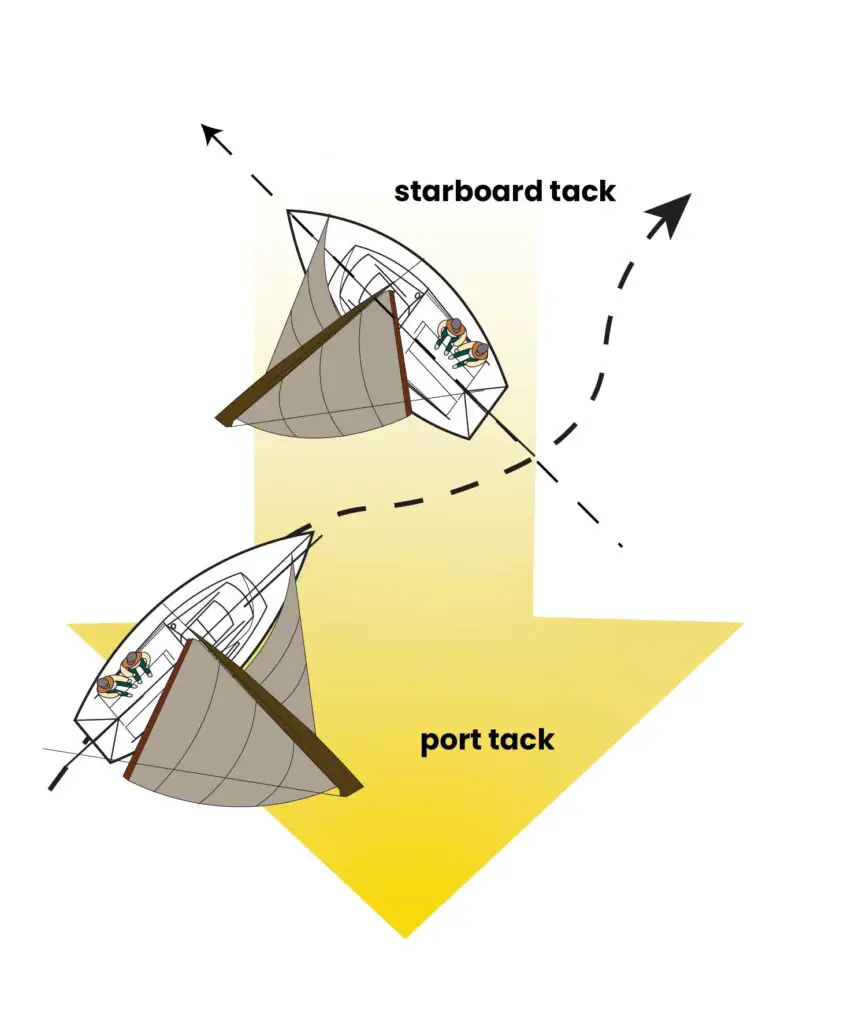
A sailboat on the starboard tack has the right of way over the sailboat on the port tack.
As boats on opposite sides approach each other, the boat on the port tack needs to give way to the boat on the starboard tack. The boat’s skipper on the port tack should change course and aim the boat well behind the stern of the starboard tack boat.
The boat on the starboard tack is the stand-on vessel; they should hold their course and continue in their sailing direction.
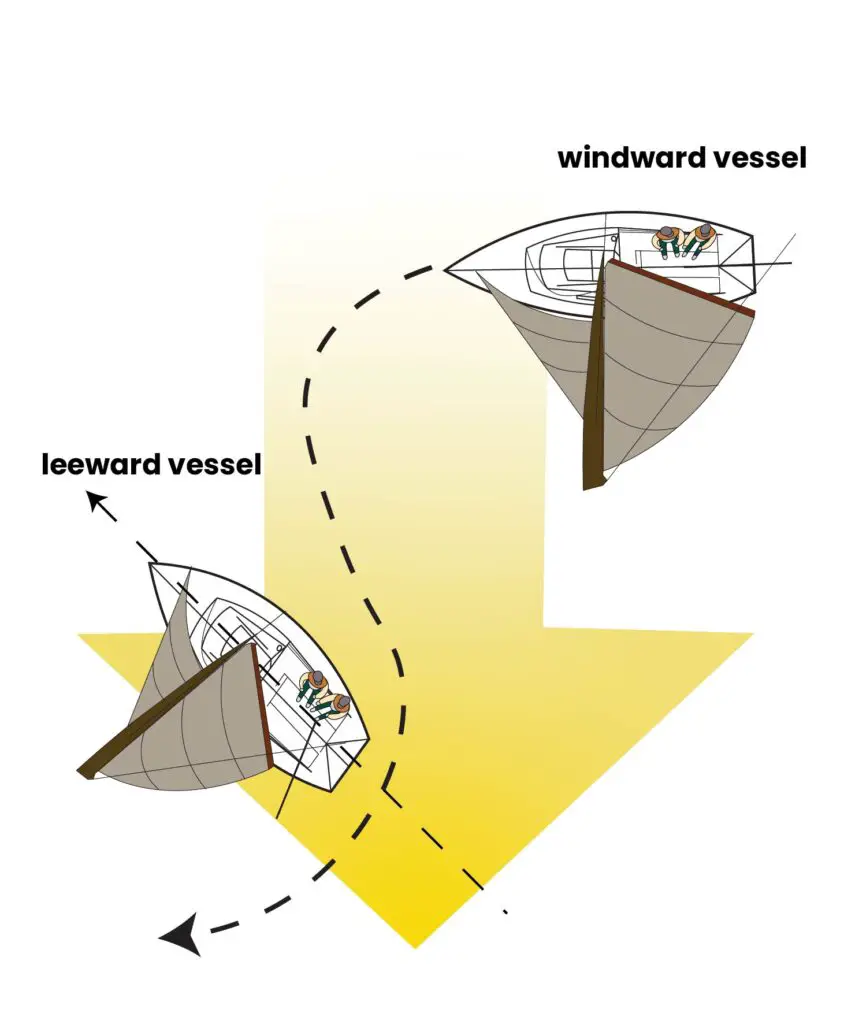
When two boats are approaching each other and on the same tack, the boat that is not upwind or the leeward boat has the right of way over the windward vessel.
The windward vessel should give way to the leeward vessel and steer the boat safely behind or out of the way of the leeward vessel. The leeward vessel is the stand-on vessel and should remain on course.
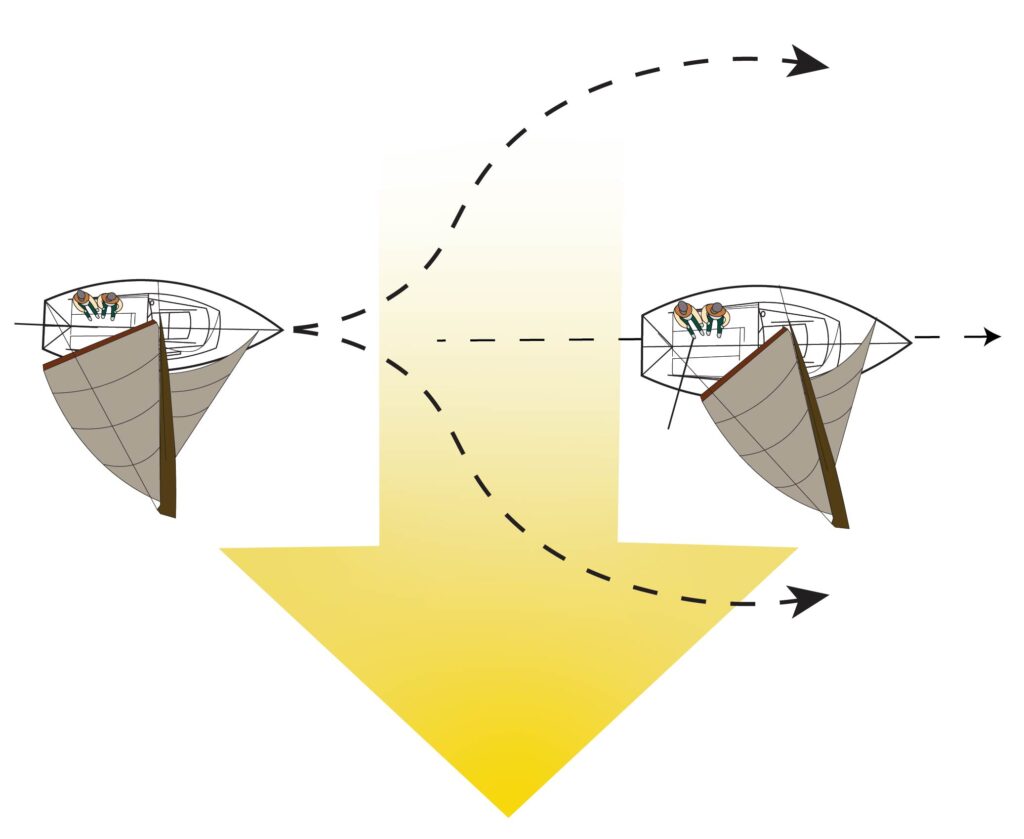
The boat that is passing another boat should not expect the slower boat to clear a path for them. The boat doing the passing is the give-way vessel, and its skipper must change the course to maneuver their boat around the slower or overtaken vessel.
The boat being overtaken is the stand-on vessel and should remain on the course and speed they were previously on so that the overtaking boat can safely pass them. If a sailing boat decides to pass a powerboat, it must also keep clear of the powerboat to pass them safely.
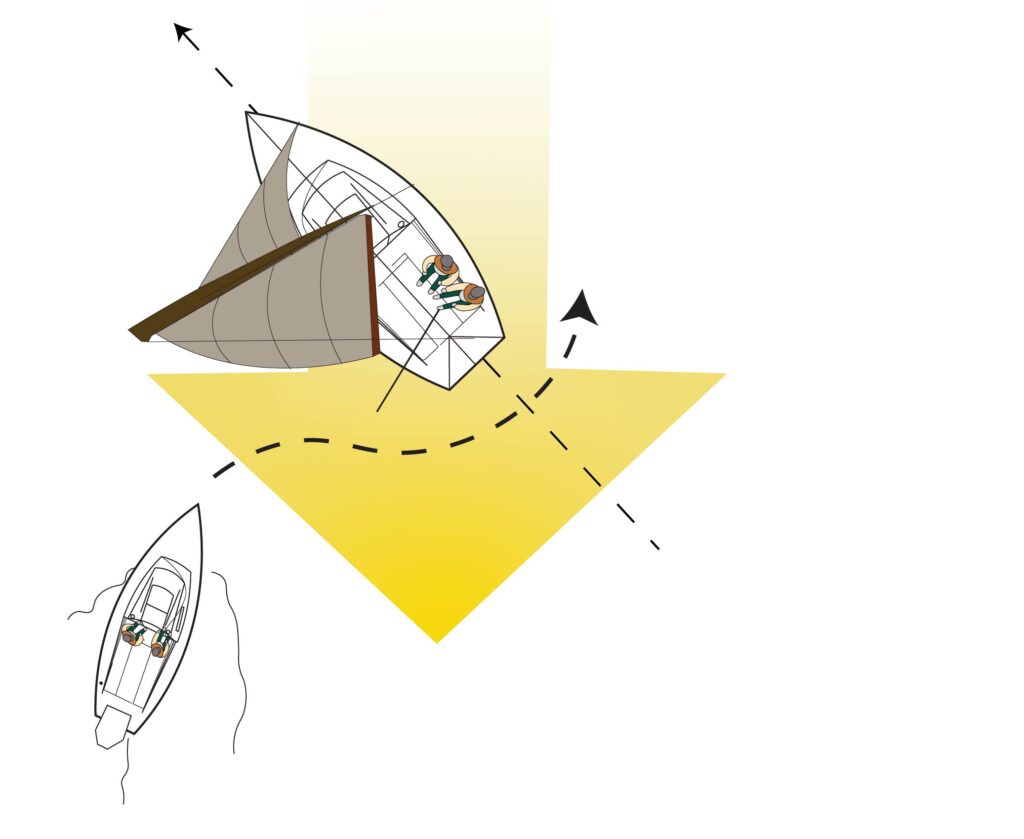
Because a powerboat or even a sailboat under power is more maneuverable, the sailboat that is not under power is the stand-on vessel, and the powerboat or sailboat under power is the give-way vessel.
It is vital with this that the stand-on boat’s sailboat holds its course unless the other boat comes so close that the skipper feels they need to change course to avoid a collision.
Sailing on Lake Michigan, where they can be many powerboats or fishing boats out on the lake, many of the skippers of these boats do not fully understand these rules, so it is always best to do what you need to do to avoid a collision.
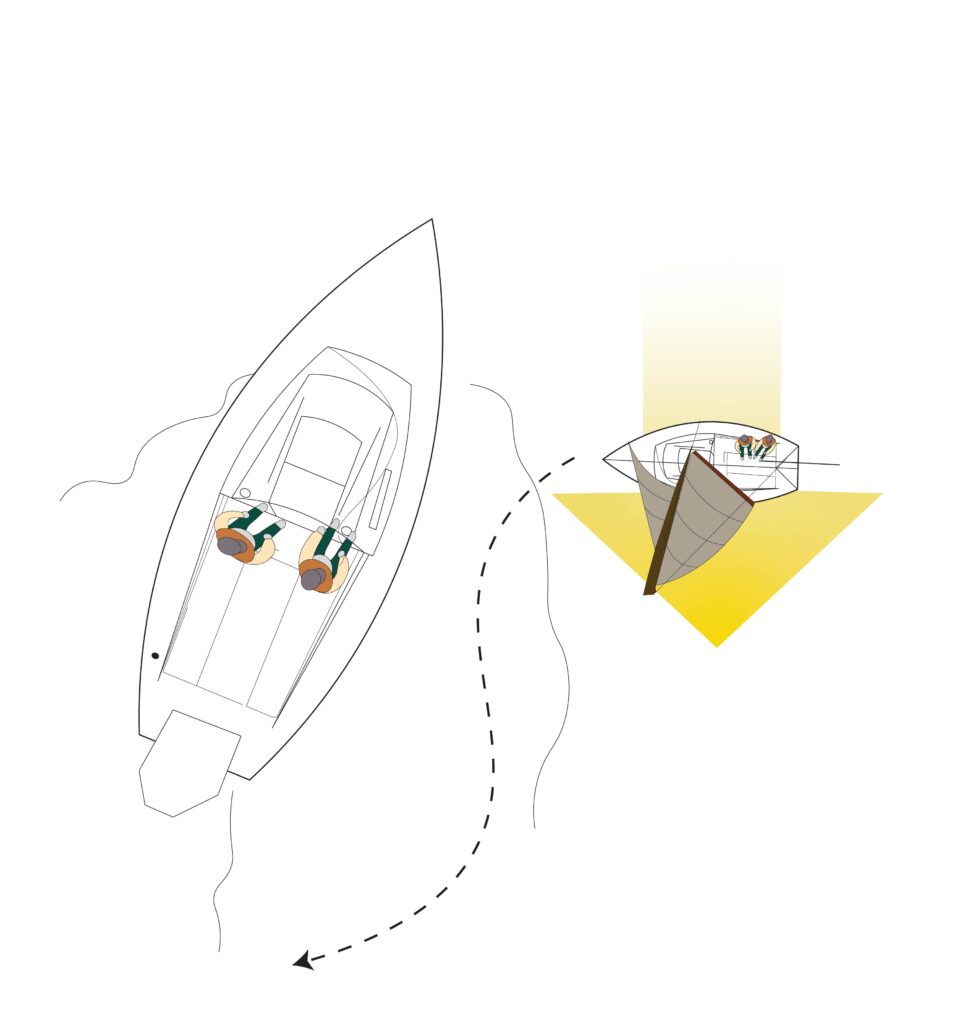
Many large vessels, such as larger ships and tug boats have difficulty maneuvering. A sailboat should always give them the right of way or be the give-way vessel when sailing near a larger vessel such as a tug boat or large ship .
A general rule is that the sailboat should give those boats a wide berth, so there is no chance of any collision, and always consider those larger boats the stand-on vessel they will give way to.
If a barge is towing something behind it, never attempt to cross the towing line and get between the tug boat and their tow. Also, if fishing vessels have traps behind them, the same safety and caution should be taken.
The main rule of water safety is to ensure that you sail your boat without collisions on the water; There are also some general rules of water safety.
- A vessel is disabled.
- A vessel is difficult to maneuver, such as a tug boat or a larger vessel.
- A craft, such as a tanker in a channel, restricts a vessel.
- A vessel that is engaged in commercial fishing, you need to watch out for their traps.
- Always stay alert when skippering a sailboat.
- If you are unsure if the other boat knows or understands the right-of-way rules, then stay clear of them and sail in another direction.
- Make sure that your course and actions are apparent to the other vessels.
- Be polite and willing to share the water so everyone can be out on the water safely.
- A swimmer in the water would always have the right of way. If you see someone swimming, avoid them and go another direction or way.
The primary purpose of right-of-way rules is that you can avoid a collodion. A good skipper will do all they can to avoid a collision with any vessel or object that is out there in the water.
At A Bus On A Dusty Road, we talk about travel, life, sailing, and ex-pat living. We are all about “Living Life As A Global Citizen.” We explore social, cultural, and economic issues and travel.
We would love to have you be part of our community. Sign up for our newsletter to keep up-to-date by clicking here . If you have any questions, you can contact me, Anita, by clicking here.
Listen to our Podcast called Dusty Roads. You can find it on all major podcast platforms. Try out listening to one of our podcasts by clicking here.
Subscribe to our A Bus On A Dusty Road YouTube Channel with great videos and information by clicking here.
What are the basic rules for right of way in the water?
The basic rules for right of way in the water include identifying the stand-on vessel (which maintains its course and speed) and the give-way vessel (which must yield and take appropriate action to avoid a collision).
How can a skipper determine who is the stand-on vessel and who is the give-way vessel?
A skipper can determine the stand-on and give-way vessel by understanding the specific rules of navigation, such as the International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea (COLREGS). These rules outline various scenarios and vessel types to determine the right of way.
What is the role of a skipper in understanding right of way?
A skipper must have a clear understanding of when their boat is the stand-on vessel (which has the right of way) and when their boat is the give-way vessel (which must yield the right of way).
Why is it important for a skipper to know when their boat is the stand-on vessel?
Knowing when their boat is the stand-on vessel allows the skipper to maintain their course and speed with confidence, ensuring other vessels give way and avoiding potential collisions.
Why is it important for a skipper to know when their boat is the give-way vessel?
Understanding when their boat is the give-way vessel enables the skipper to take appropriate action to avoid a collision by yielding the right of way to the stand-on vessel.
What are the consequences of not following the right-of-way rules?
Not following the right-of-way rules can lead to collisions, endangering the safety of people on board and potentially causing damage to vessels and property.
Are the right-of-way rules the same for all types of vessels?
While many right-of-way rules apply to all vessels, there are specific rules and considerations for different types of vessels, such as sailboats, powerboats, commercial vessels, and vessels operating in narrow channels.
How can a skipper determine who has the right of way on waterways?
Determining who has the right of way on waterways involves applying the relevant rules and regulations based on the specific situation, vessel types, and the location of the vessel.
Related Questions
Bodies would not have been buried right into the wall, but they could have been buried in the earth near and even under the wall. They would not have put them right into the wall, as it would have caused structural damage when the bodies decomposed. The bodies are probably buried right by the wall, under some stone, and other slabs.
You can learn more by reading Are There Dead Bodies Inside The Great Wall Of China? by clicking here.
Tacking is when you move the boat’s bow into the wind to turn the boat’s direction. It is a very common maneuver that all sailors must learn to master. But with any sailing maneuver , you must understand the proper steps to do a safe tack.
To learn more, you can read our blog on What Is Tacking In Sailing? Steps To A Proper Tack by clicking here.
A jibe in sailing is when the boat moves with the stern through the wind . In a jibe, the stern will move through the wind. Like any sailing maneuver, when you have a crew, the helmsman or the captain steering the boat needs to adequately communicate with the crew about what is happening so that they know; this is especially true when jibing .
By clicking here , you can discover What Is The Best Way To Remember The Points Of Sail When Sailing? .
- Latest Posts
- Reflections On Modern Travel:Learning To Travel In The Moment – April 30, 2024
- Discover The Authentic Hanoi-Style Vietnamese Pho: A Traditional Recipe – April 26, 2024
- Buraku Or Burakumin Of Japan, Who Are They? – April 24, 2024
Share Our Content
Anita L Hummel


Two killed in boat crash after injured man found bleeding on riverbank
Two people have been killed and five others are missing after two boats crashed on the Danube River.
Hungarian police say the crash between a small motor boat and a cruise ship happened late on Saturday evening, and was reported after a man with a bleeding head wound was found on the riverbank.
He was found by the river near Veroce, which is 34 miles north of the capital Budapest. A man’s body was found close by, while the body of a woman was recovered further downstream.
The damaged motor boat was found close to the woman’s body, near a bridge on the northern outskirts of Budapest.
Disaster response units are still searching for the five other passengers – three men and two women – who were aboard the small motor boat, with drones, boats, and rescue divers involved in the search.
Soma Csecsi, a spokesperson for Budapest police, said: ‘Police talked to the man and from his initial communication they drew the conclusion that he was probably the victim of some kind of boat accident.
‘At the time of the accident a cruise ship was located in the area, which was stopped at the town of Komarom where police have determined that the ship is damaged on one side.’
Police believe the other ship involved is the 109-metre-long cruise ship identified as Swiss-based Heidelberg.
It’s not known how many people were on board at the time, or their nationalities, and police stopped the Heidelberg more than 50 miles upriver.
An investigation against an ‘unknown perpetrator’ on suspicion of endangering water transport and causing the death of several people has now been launched by police, to discover if anyone is criminally liable for the crash.
The deadly incident comes five years after at least 27 people were killed in Budapest when a river cruise boat collided with a smaller tourist vessel, sinking it in seconds.
Tourist boat Hableany, carrying 35 people who were mostly South Korean tourists, was overtaken from behind by the much larger cruise boat, Viking Sigyn, beneath Budapest’s Margit Bridge, in May 2019.
The Ukrainian captain of the Viking Sigyn was last year found guilty of negligence leading to a fatal mass catastrophe and sentenced to five years and six months in prison. He has appealed the decision.
Get in touch with our news team by emailing us at [email protected] .
For more stories like this, check our news page .
Get your need-to-know latest news, feel-good stories, analysis and more by signing up to Metro's News Updates newsletter

- Today's news
- Reviews and deals
- Climate change
- 2024 election
- Fall allergies
- Health news
- Mental health
- Sexual health
- Family health
- So mini ways
- Unapologetically
- Buying guides
Entertainment
- How to Watch
- My watchlist
- Stock market
- Biden economy
- Personal finance
- Stocks: most active
- Stocks: gainers
- Stocks: losers
- Trending tickers
- World indices
- US Treasury bonds
- Top mutual funds
- Highest open interest
- Highest implied volatility
- Currency converter
- Basic materials
- Communication services
- Consumer cyclical
- Consumer defensive
- Financial services
- Industrials
- Real estate
- Mutual funds
- Credit cards
- Balance transfer cards
- Cash back cards
- Rewards cards
- Travel cards
- Online checking
- High-yield savings
- Money market
- Home equity loan
- Personal loans
- Student loans
- Options pit
- Fantasy football
- Pro Pick 'Em
- College Pick 'Em
- Fantasy baseball
- Fantasy hockey
- Fantasy basketball
- Download the app
- Daily fantasy
- Scores and schedules
- GameChannel
- World Baseball Classic
- Premier League
- CONCACAF League
- Champions League
- Motorsports
- Horse racing
- Newsletters
New on Yahoo

- CA Privacy Notice
2 dead and 5 missing after a boat collision on the Danube River in Hungary
Hungary boat collision.
BUDAPEST, Hungary (AP) — Police say two people have died and five are missing following a boat collision on the Danube River in Hungary.
Hungarian police received a report late Saturday night that a man had been found with a head injury on the shore of the Danube near the town of Veroce, around 30 miles (50 kilometers) north of the capital, Budapest. The bodies of a man and a woman were later discovered nearby.
Hours after police began their search, they discovered a damaged boat in the water, which they towed to shore. They are still searching for five adults — three men and two women — who they believe were on the boat.
Police said they determined that a river cruise boat had been in the area at the time of the accident. They stopped a cruise boat with a damaged hull near the town of Komarom, more than 50 miles (80 kilometers) further upriver.
Hungarian public television station M1 reported that the cruise boat, Heidelberg, is a 109-meter (357-foot) Swiss craft that can accommodate 110 people. No passengers on that boat sustained injuries, M1 said.
The Danube at Veroce is roughly 1,500 feet (460 meters) wide and is in the center of an area called the Danube Bend where the river makes a sweeping, nearly 90-degree turn to the south. The area is a popular recreational and boating destination and is on a route often used by cruise boats between Budapest and the Austrian capital, Vienna, some 140 miles (230 kilometers) upriver.
The deadly accident comes five years after at least 27 people were killed in Budapest when a river cruise boat collided with a smaller tourist vessel , sinking it in seconds.
The tourist boat Hableany, carrying 35 people who were mostly South Korean tourists, was overtaken from behind by the much larger cruise boat, Viking Sigyn, beneath Budapest's Margit Bridge, in May 2019.
The Ukrainian captain of the Viking Sigyn was last year found guilty of negligence leading to a fatal mass catastrophe and sentenced to five years and six months in prison. He has appealed the decision.
Police on Sunday said they have initiated criminal proceedings against an unknown perpetrator on suspicion of endangering water transport and causing the death of several people.
A spokesperson for the Directorate General for Disaster Management told Hungarian news agency MTI that a group of nearly 90 people from several regional disaster management agencies were conducting the search for the missing from the land, water and sky.
Twelve boats and three drones are involved in the search, and two rescue divers are also involved, Imre Doka said.
Recommended Stories
Longtime oakland raiders center, hall of famer jim otto dies at 86.
Jim Otto appeared in 210 straight games for the Raiders and was one of just three players who appeared in every single regular season AFL game throughout his career.
NBA playoffs: Timberwolves rally from 20-point deficit to stun Nuggets in Game 7, reach conference finals
For the first time in two decades, the Minnesota Timberwolves are headed to the Western Conference finals.
NASCAR: Joey Logano leads 199 of 200 laps to win All-Star Race
Logano started on the pole and never got passed under green.
New York Knicks 2024 NBA offseason preview: Staying the course should be the focus
This team is built to compete now and could carve out a nice five-year window if it can keep the right players. A Finals run in the near future can't be ruled out.
Edwin Diaz's future as Mets closer is 'fluid' amid recent poor outings
New York Mets reliever Edwin Diaz's immediate future as the team's closer is "fluid," according to manager Carlos Mendoza.
NBA playoffs: Timberwolves vs. Nuggets Game 7 updates, score, highlights, analysis
Do the Nuggets or Timberwolves have what it takes to survive Game 7?
Scott McLaughlin leads Penske front row sweep for Indianapolis 500; Kyle Larson to start 5th
McLaughlin posted a four-lap average of 234.220 MPH.
iFixit’s teardown of the new M4 iPad Pro reveals an easier-to-replace battery
As seen in an iFixit teardown, it's much easier to access the battery in the new 13-inch iPad Pro compared to previous models, which required removing "every major component inside."
Junkyard Gem: 1995 Mazda B4000 LE Cab Plus
A 1995 Mazda B4000 LE Cab Plus pickup truck, rebadged twin to the Ford Ranger, found in a North Carolina wrecking yard.
Iran's president was in a helicopter crash: Here's what we know — and what we don't
Iran's president was involved in a helicopter crash. Here's what we know — and what we don't so far.
Auburn RB Brian Battie critically wounded in Sarasota shooting
Battie's older brother Tommie was killed and three others were shot early Saturday morning .
NBA playoffs: Pacers blow out Knicks in Game 7 as Jalen Brunson leaves game with fractured hand
One team will go on to the Eastern Conference finals. The other will go home.
Score big on The North Face Gear during REI's Anniversary Sale
REI's Anniversary Sale is one of the best times to shop for outdoor gear. Here’s why you should take advantage of the 25% off on The North Face products.
The 40+ best Amazon early Memorial Day deals: Save up to 80% on summer essentials, vacuums, tech and more
A No. 1 bestselling Ninja air fryer for $80 is calling our name, as is a sleek stick vac marked down by over 50%. That's just for starters.
I’m rooting for Melinda French Gates to fix tech's broken ‘brilliant jerk’ culture
On Monday, Melinda French Gates resigned from the philanthropy organization she ran with ex-husband Bill Gates. French Gates will leave next month with an additional $12.5 billion, she said. The Gates Foundation famously works on projects to help impoverished people, especially in developing countries, such as fighting malaria, polio or improving sanitation.
Dow at 40,000: Why stocks still have 'plenty of room to run'
Wall Street pros say there's more room to grow with stock markets around record highs.
Indie developers are trying to make horse games that don’t suck. It’s not easy
With ambitious new projects, developers are hoping to revive a genre plagued with bad games and worse anatomy.
Trading stocks all day and all night might be an 'inevitability' for investors
Around-the-clock stock trading is likely the future, executives at several trading platforms say, thanks to increased demand from international markets and a new generation of investors who expect constant online access.
Blue Origin successfully sends tourists to the edge of space again after a long hiatus
Jeff Bezos’ spaceflight company successfully flew six paying customers to the edge of space and back this morning, breaking its nearly two-year-long hiatus from crewed missions. This was Blue Origin’s seventh trip with humans on board.
Never scrub your fridge again! These easy-wipe liners are on sale for only $1 apiece on Amazon
'Makes cleanup so very easy,' wrote one happy fan.
NEWS... BUT NOT AS YOU KNOW IT
Two killed in boat crash as injured man found bleeding on riverbank

Share this with

Two people have been killed and five others are missing after two boats crashed on the Danube River.
Hungarian police say the crash between a small motor boat and a cruise ship happened late on Saturday evening, and was reported after a man with a bleeding head wound was found on the riverbank.
He was found by the river near Veroce, which is 34 miles north of the capital Budapest. A man’s body was found close by, while the body of a woman was recovered further downstream.
The damaged motor boat was found close to the woman’s body, near a bridge on the northern outskirts of Budapest.
To view this video please enable JavaScript, and consider upgrading to a web browser that supports HTML5 video
Disaster response units are still searching for the five other passengers – three men and two women – who were aboard the small motor boat, with drones, boats, and rescue divers involved in the search.
Soma Csecsi, a spokesperson for Budapest police, said: ‘Police talked to the man and from his initial communication they drew the conclusion that he was probably the victim of some kind of boat accident.
‘At the time of the accident a cruise ship was located in the area, which was stopped at the town of Komarom where police have determined that the ship is damaged on one side.’
Police believe the other ship involved is the 109-metre-long cruise ship identified as Swiss-based Heidelberg.
It’s not known how many people were on board at the time, or their nationalities, and police stopped the Heidelberg more than 50 miles upriver.
An investigation against an ‘unknown perpetrator’ on suspicion of endangering water transport and causing the death of several people has now been launched by police, to discover if anyone is criminally liable for the crash.
The deadly incident comes five years after at least 27 people were killed in Budapest when a river cruise boat collided with a smaller tourist vessel, sinking it in seconds.
Tourist boat Hableany, carrying 35 people who were mostly South Korean tourists, was overtaken from behind by the much larger cruise boat, Viking Sigyn, beneath Budapest’s Margit Bridge, in May 2019.
The Ukrainian captain of the Viking Sigyn was last year found guilty of negligence leading to a fatal mass catastrophe and sentenced to five years and six months in prison. He has appealed the decision.
Get in touch with our news team by emailing us at [email protected] .
For more stories like this, check our news page .
Sign Up for News Updates
Get your need-to-know latest news, feel-good stories, analysis and more.
Privacy Policy

Get us in your feed
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
2 dead and 5 missing after a boat collision on the Danube River in Hungary
Police say two people have died and five are missing following a boat collision on the Danube River in Hungary. Police said they determined that a river cruise boat had been in the area at the time of the accident. They stopped a cruise boat with a damaged hull near the town of Komarom, more than 50 miles (80 kilometers) further upriver.
Damage is seen on the front of the cruise ship which was involved in a Danube River accident earlier in Budapest Hungary, Sunday, May 19, 2024. Police say two people have died and five are missing following a boat collision on the Danube River in Hungary. (AP Photo/Bela Szandelszky)
- Copy Link copied
Police investigators examine the bow of a river cruise ship after an incident, in Komarom, Hungary, Sunday, May 19, 2024. Police say two people have died and five are missing following a boat collision on the Danube River in Hungary. Hungarian police received a report late Saturday night that a man had been found with a head injury on the shore of the Danube near the town of Veroce, around 30 miles (50 kilometers) north of the capital, Budapest. (Csaba Krizsan/MTI via AP)
The bow of a river cruise ship is examined by police experts after the ship was stopped in Komarom, Hungary, Sunday, May 19, 2024. Last night the ship crashed with a motor boat with eight persons onboard on River Danube, north of Budapest. One person has been rescued with serious injuries, two bodies have been recovered and five passengers of the boat are being looked for. (Csaba Krizsan/MTI via AP)
Police look at a river cruise ship after an incident, in Komarom, Hungary, Sunday, May 19, 2024. Police say two people have died and five are missing following a boat collision on the Danube River in Hungary. Hungarian police received a report late Saturday night that a man had been found with a head injury on the shore of the Danube near the town of Veroce, around 30 miles (50 kilometers) north of the capital, Budapest. (Csaba Krizsan/MTI via AP)
Police officers stand on the deck of a river cruise ship after an incident, in Komarom, Hungary, Sunday, May 19, 2024. Police say two people have died and five are missing following a boat collision on the Danube River in Hungary. Hungarian police received a report late Saturday night that a man had been found with a head injury on the shore of the Danube near the town of Veroce, around 30 miles (50 kilometers) north of the capital, Budapest. (Csaba Krizsan/MTI via AP)
A view of the damage of the bow of a river cruise ship after an incident, in Komarom, Hungary, Sunday, May 19, 2024. Police say two people have died and five are missing following a boat collision on the Danube River in Hungary. Hungarian police received a report late Saturday night that a man had been found with a head injury on the shore of the Danube near the town of Veroce, around 30 miles (50 kilometers) north of the capital, Budapest. (Csaba Krizsan/MTI via AP)
A car of the diving service of the fire brigade is parked behind the closed gate of a military port where rescuers search for victims of a boat accident in Northern Budapest, Hungary, Sunday, May 19, 2024. Last night a motor boat with eight persons onboard crashed with a large river cruise ship on River Danube, north of Budapest. One person has been rescued with serious injuries, two bodies have been recovered and five passengers of the boat are looked for. (Peter Lakatos/MTI via AP)
his photo provided by BRFK Facebook shows a damaged boat at the northern edge of Budapest where it was towed, after being discovered in the water by police following a boat collision on the Danube River Sunday, May 19, 2024. Police say people have died and several are missing. (BRFK Facebook via AP)
This photo provided by BRFK Facebook shows a damaged boat at the northern edge of Budapest where it was towed, after being discovered in the water by police following a boat collision on the Danube River Sunday, May 19, 2024. Police say people have died and several are missing. (BRFK Facebook via AP)

BUDAPEST, Hungary (AP) — Police say two people have died and five are missing following a boat collision on the Danube River in Hungary.
Hungarian police received a report late Saturday night that a man had been found with a head injury on the shore of the Danube near the town of Veroce, around 30 miles (50 kilometers) north of the capital, Budapest. The bodies of a man and a woman were later discovered nearby.
Hours after police began their search, they discovered a damaged boat in the water, which they towed to shore. They are still searching for five adults — three men and two women — who they believe were on the boat.
Police said they determined that a river cruise boat had been in the area at the time of the accident. They stopped a cruise boat with a damaged hull near the town of Komarom, more than 50 miles (80 kilometers) further upriver.
Hungarian public television station M1 reported that the cruise boat, Heidelberg, is a 109-meter (357-foot) Swiss craft that can accommodate 110 people. No passengers on that boat sustained injuries, M1 said.
The Danube at Veroce is roughly 1,500 feet (460 meters) wide and is in the center of an area called the Danube Bend where the river makes a sweeping, nearly 90-degree turn to the south. The area is a popular recreational and boating destination and is on a route often used by cruise boats between Budapest and the Austrian capital, Vienna, some 140 miles (230 kilometers) upriver.
The deadly accident comes five years after at least 27 people were killed in Budapest when a river cruise boat collided with a smaller tourist vessel , sinking it in seconds.
The tourist boat Hableany, carrying 35 people who were mostly South Korean tourists, was overtaken from behind by the much larger cruise boat, Viking Sigyn, beneath Budapest’s Margit Bridge, in May 2019.
The Ukrainian captain of the Viking Sigyn was last year found guilty of negligence leading to a fatal mass catastrophe and sentenced to five years and six months in prison. He has appealed the decision.
Police on Sunday said they have initiated criminal proceedings against an unknown perpetrator on suspicion of endangering water transport and causing the death of several people.
A spokesperson for the Directorate General for Disaster Management told Hungarian news agency MTI that a group of nearly 90 people from several regional disaster management agencies were conducting the search for the missing from the land, water and sky.
Twelve boats and three drones are involved in the search, and two rescue divers are also involved, Imre Doka said.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
What should you do if you are operating a motorboat that is being overtaken by a sailboat. Hold on tight, sailor! If you find yourself in a situation where a sailboat is overtaking your motorboat, it's crucial to maintain your course and speed. As the operator of the motorboat being overtaken, you are considered the "stand-on" vessel.
Under the rules of the road, powerboats must give way to sailboats, with one exception. The vessel that is being overtaken is always the stand-on vessel. Tim Barker. I'm strictly a powerboater and proud of it. But I also respect the skill of sailboaters and was schooled from my earliest days afloat that sailboats are generally assigned the ...
The vessels are shown closer to each other than they should be when actually encountering another vessel on the water. Meeting Head-On: The power-driven vessel is the give-way vessel. The sailing vessel is the stand-on vessel. Paths That Cross: The power-driven vessel is the give-way vessel. The sailing vessel is the stand-on vessel. Overtaking ...
In an overtaking situation, the overtaking vessel is the give-way vessel, while the vessel being overtaken is the stand-on vessel. However, if the powerboat is overtaking the sailboat from the starboard side, the powerboat becomes the stand-on vessel and the sailboat becomes the give-way vessel. When meeting head-on or crossing paths, the power ...
The overtaking boat must maneuver in a way that ensures a safe and clear passage, keeping well clear of the boat being overtaken. It's crucial for the overtaking boat to maintain a safe distance and avoid any actions that could potentially cause a collision or endanger the vessel being overtaken. ... When a motorboat is crossing paths with a ...
When two power driven boats are approaching at right angles or nearly so, and risk of collision exists, the boat on the right is the stand-on vessel, has the right of way and must hold its course and speed. The other boat, the give-way vessel, shall maneuver to keep clear of the stand-on vessel and shall pass it by its stern. If necessary, slow, stop or reverse until the stand-on vessel is clear.
When two power driven boats are approaching at right angles or nearly so, and risk of collision exists, the boat on the right is the stand-on vessel, has the right of way and must hold its course and speed. The other boat, the give-way vessel, shall maneuver to keep clear of the stand-on vessel and shall pass it by its stern. If necessary, slow, stop or reverse until the stand-on vessel is clear.
The Sailing Vessel as a Stand-on Vessel. When a sailboat meets a power-driven boat such as a recreational powerboat, the sailboat is the stand-on vessel in most situations. This is because the boat using an engine is more capable of making the necessary adjustment to ensure that no collision occurs. Even when a sailboat is approaching a ...
Navigation Rules: Overtaking. Whenever a power-driven vessel is overtaking another power-driven vessel the vessel which is being overtaken is the stand-on vessel. Remember, the stand-on vessel has the right of way and must maintain speed and course. In this example, Vessel A would be the give-way vessel. That means Vessel A must take action to ...
Approaching a Sailing Vessel. When a power-driven vessel B encounters a sailing vessel A, the sailing vessel is ALWAYS the stand-on vessel (unless a sailing vessel is overtaking). In the case above, power-driven vessel B must take EARLY and SUBSTANTIAL action to keep clear of sailing vessel A.
Sailing Right of Way. When two boats that are both under sail meet, the following rules apply: The boat on a starboard tack has the right of way—the wind coming over the starboard rail. When two vessels are on the same tack (the wind is coming from the same side), the leeward boat (downwind) has the right of way over the windward boat (that ...
Avoid sharp turns if being overtaken; Always - you are in doubt, reduce your speed; Every vessel shall at all times proceed at a safe speed; Other Rules. Whether under inland or international rules, power vessels must keep clear of sailing vessels in open waters. A sailboat with motor running is defined as a motor boat.
Motor vs. Sail: A motor boat is any vessel using an engine regardless of whether it is a sailboat or a motorboat. A sailboat is considered to be a motorboat even if the SailS are up as long as the engine is running. A sailboat that is sailing generally has the right of way over motorboats. ... Overtaking Boats Give Way to Boats Being Overtaken.
The Rule. (a) Notwithstanding anything contained in the Rules, any vessel overtaking any other shall keep out of the way of the vessel being overtaken. (b) A vessel shall be deemed to be overtaking when coming up with another vessel from a direction more than 22.5 degrees abaft her beam. (c) When a vessel is in any doubt as to whether she is ...
A vessel is overtaken when another boat comes from a direction over 22.5 degrees behind it. According to the Boat U.S. Foundation, the overtaken boat is known as the stand-on vessel. This boat must maintain its speed and course until the ship behind it has safely passed. The boat behind the stand-on vessel is called the give-way vessel.
A vessel that restricted in its ability to maneuver is unable to move out of the way of other boats due to the nature of its work, like a buoy tender fixing a navigational aid or vessel transferring passengers while underway. 2. A Vessel Being Overtaken. Any boat approaching a vessel from astern must give them the right of way. 3.
After ensuring the starboard side is clear, the boat that has to be overtaken should respond by sounding a single blast of the horn, indicating that the overtaking boat can proceed. ... If you are operating a motorboat being overtaken by a sailboat, you should keep going as you are. The vessel that is being overtaken is always the stand-on vessel.
Avoid cutting in front of, obstructing, or putting another vessel in danger. The boat behind (give-way vessel): "I intend to pass you on your starboard side" - 1 short blast (1 sec.) The boat in front (stand-on vessel): "Agreement" - 1 short blast (1 sec.) The boat behind (give-way vessel): "I intend to pass you on your port side" - 2 short blasts.
In the occurrence of a PWC & a motorboat meeting, since they are both motorboats, they are both to move to their individual right sides, and pass by each other according to regular traffic rules. If an event occurs, such that a PWC seeks to cut across the path of an oncoming motorboat, two things take place. First, if the PWC is coming from the ...
Navigating the waters is an exciting adventure, whether you're at the helm of a sleek sailboat or commanding a powerful motorboat. However, along with this thrilling journey comes the responsibility of understanding and adhering to the marine navigation rules, specifically those concerning the right of way or the "give-way" vessel.
Maintain present course and speed. an observer on board or a wide-angle rearview ski mirror. Keep contact between the tank and the fuel spout. Clean all aquatic plants and mud from your boat and trailer before leaving the waterway. Don't know? 13 of 13. Quiz yourself with questions and answers for Boating exam, so you can be ready for test day.
The tourist boat Hableany, carrying 35 people who were mostly South Korean tourists, was overtaken from behind by the much larger cruise boat, Viking Sigyn, beneath Budapest's Margit Bridge, in ...
There is a stand-on and give-way vessel when two boats are near the same area. Here is what each of these sailing terms means:. Stand-on vessel - The stand-on vessel is the sailboat with the right-of-way.; Give-way vessel - The give-way vessel must give way when it may be on a collision course.; Even though the rules of the water have both stand-on and give-way vessels, every boat on the ...
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like What is the best way to cast off if the wind or current direction is away from the dock? Cast off all lines. Keep the boat clear of the dock. Shift into forward gear and slowly leave the area. Cast off all lines, shift into reverse and turn the bow sharply toward the dock, and then add power. Keep the stern line tied to the dock ...
Tourist boat Hableany, carrying 35 people who were mostly South Korean tourists, was overtaken from behind by the much larger cruise boat, Viking Sigyn, beneath Budapest's Margit Bridge, in May ...
The tourist boat Hableany, carrying 35 people who were mostly South Korean tourists, was overtaken from behind by the much larger cruise boat, Viking Sigyn, beneath Budapest's Margit Bridge, in ...
The crash between a small motor boat and a cruise ship happened late on Saturday, and was reported after a man was found bleeding on the riverbank. ... was overtaken from behind by the much larger ...
Last night a motor boat with eight persons onboard crashed with a large river cruise ship on River Danube, north of Budapest. One person has been rescued with serious injuries, two bodies have been recovered and five passengers of the boat are looked for. ... was overtaken from behind by the much larger cruise boat, Viking Sigyn, beneath ...