
No products in the cart.
Sailing Ellidah is supported by our readers. Buying through our links may earn us an affiliate commission at no extra cost to you.

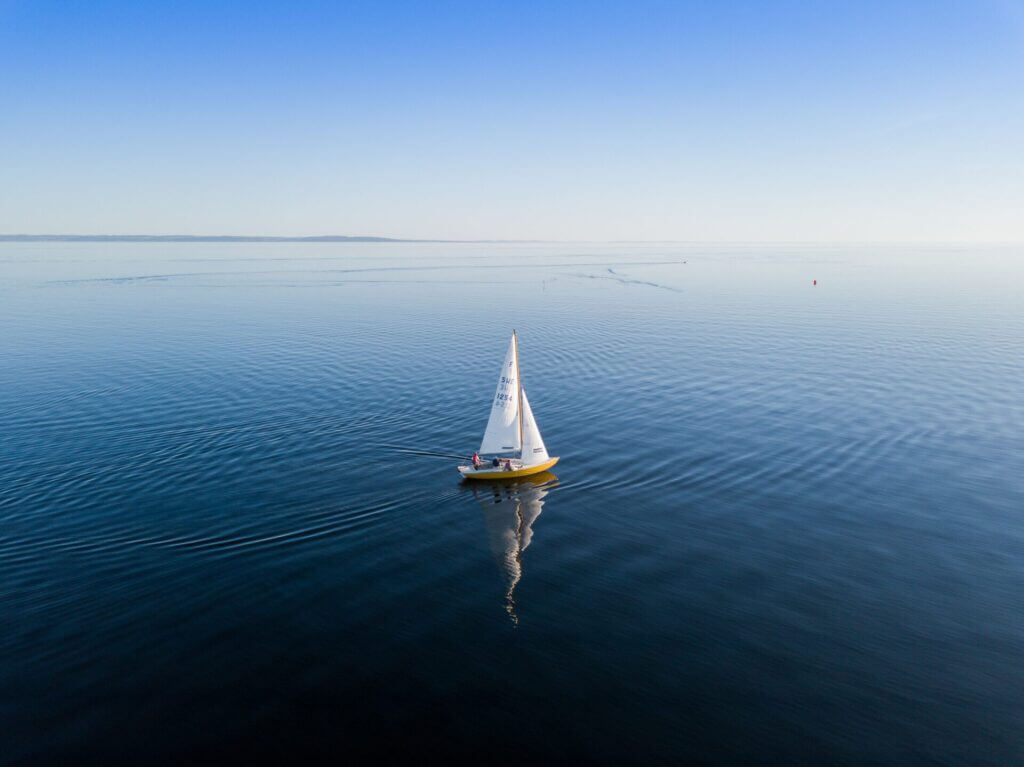
The Different Parts Of A Sailboat Explained
A sailboat consists of hundreds of parts, each with its specific term and function. From stern to bow, keel to mast, each part and its equipment plays a vital role in making the vessel seaworthy and able to sail.
In this guide, I’ll show you most of the components so you can better understand what they are and their function. We’ll begin with the main components, move to the basic features, and finish with our interior and equipment.
The main parts of a sailboat

The main parts of a sailboat are the key components that make it a vessel able to sail. You’ll notice that the structure has several distinct differences from powerboats.
We can categorize the main parts into the following:
- Hull: The main structure, or “body” part of a boat.
- Keel: The heavy fin at the bottom allows stability under sail.
- Rudder: The fin sticking down at the stern, allowing us to steer the vessel.
- Mast: The “spars” or “poles” holding the sails.
- Rigging: The standing rig is the wires that supports the mast. The running rigging is all the lines that control the sails.
- Boom: The horizontal spar supporting the bottom of the mainsail.
- Sails: The canvas used to harness the energy of the wind.
Let’s dig a bit deeper into each of the components.
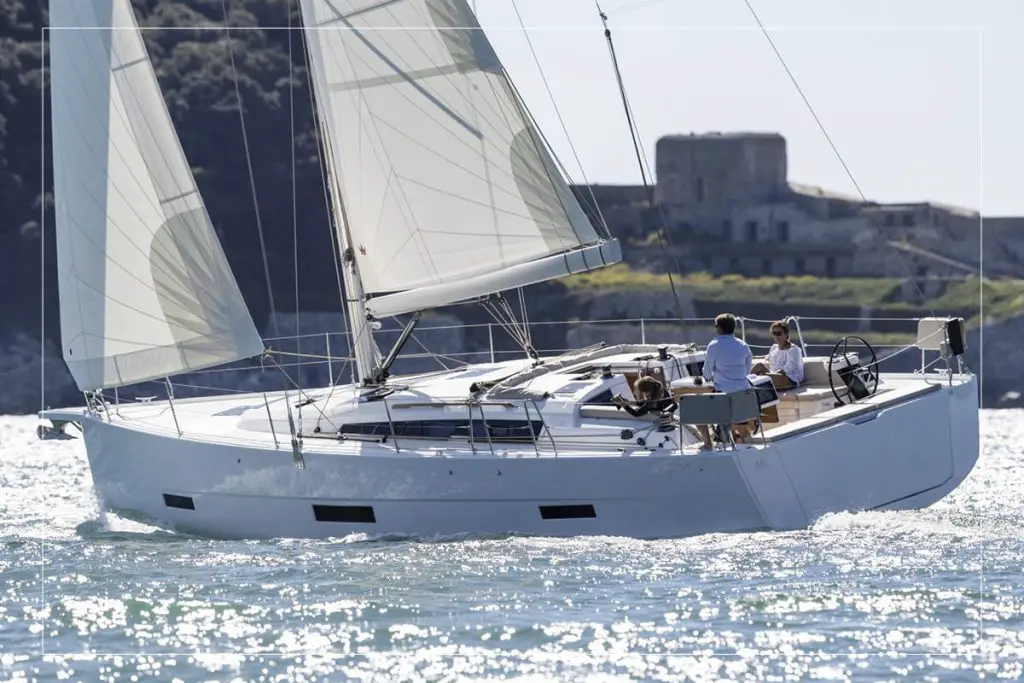
Hull – The main structure
A sailboat’s hull is the vessel’s main body or structure. The shape is vital to the boat’s performance and stability, and you have probably seen boats in many different forms. Older vessels are typically narrow, with a rounded underbody and a small stern. Modern designs have a flatter belly and broad stern supporting dual helm stations.
One of the hull’s primary functions is to displace water and provide buoyancy to keep the boat afloat. The hull is also the structure that holds the vessel’s living compartments and all its equipment. The main structure must be strong enough to withstand the forces of the water and any rough weather conditions that Mother Nature might throw at it.
Fiberglass (GRP), steel, aluminum, and wood are the most commonly used hull materials, each with pros and cons.
You can learn more about hull materials and their strengths in this article .
A monohull is a type of sailboat that has a single hull. Monohulls are classified into two categories based on weight and shape: planing and displacement hulls.
Sailboats with more than one hull are called multihulls. There are two types of multihulls: catamarans, which have two, and trimarans, which have three. These boats are typically designed with planing hulls.
Keel – The fin under the boat
The keel of a sailboat is a structural fin that extends downward from the bottom of the hull. There are several types of keels, each with unique characteristics and advantages. They all serve the same fundamental purpose of stabilizing the boat when we sail by adding lateral resistance in the water and weight at the vessel’s bottom.
Standard keel designs include:
- Lifting Keel
Some sailboats have a retractable centerboard functioning as their keel, allowing them to take the boat into shallower areas.
Rudder – To steer the boat
The rudder is a flat surface that sits perpendicular to the waterline. It is connected to the boat by a pivot point, allowing it to swivel left and right. When the steering wheel or tiller is turned, the rudder moves, creating drag in the water causing the boat to turn. The size and shape of the rudder can vary depending on the size and type of boat.
The most commonly seen rudder designs:
- Full skeg-supported
- Semi skeg-supported
Skeg-supported rudders are structurally one of the most reliable and robust constructions, but they are less efficient than a balanced rudder performance-wise. Balanced rudders pivot around their vertical center, giving less drag in the water and higher maneuverability at the cost of being a more vulnerable construction.
Twin rudders are often seen on modern performance sailboats with a wide stern. When the sailboat heel over , the leeward rudder gets better track through the water than a single rudder placed at the vessel’s center line. Contrary to some misconceptions, they can’t be controlled individually, even if the boat has two steering wheels.
Mast and Rigging – Supporting the sails

The mast is the long vertical spar that extends upward from the deck of a sailboat and holds the sails. It is the tallest part of the boat and is typically made of wood, aluminum, or carbon fiber. The mast is held in place by stays and shrouds, which form the sailboat’s standing rigging.
Depending on the rig the boat is manufactured with, there are several different types of masts. For example, a sloop-rigged sailboat will have only one main mast, while a ketch-rigged vessel will have a smaller additional mizzen mast placed further aft from the main mast.
There are two types of rigging:
- The Standing rigging consists of the stays and shrouds that keep the mast or masts in place.
- The Running rigging is the lines we use to hoist, lower, and control the sails.
Pro Tip: “S par” is a general term for a pole made of a solid material like wood, metal, or composite and is used to support a boat’s sail. The mast, boom, spreaders, and poles are defined as spars.
Boom – Supporting the mainsail
The boom is a horizontal beam extending from the mast and supporting the mainsail’s tack and clew (bottom two corners). It is attached to the mast by a hinge called a Gooseneck .
We use the boom to control the shape and angle of the mainsail to optimize its efficiency and power. Some booms also have a Vang or Rod-Kicker installed to assist in trimming the mainsail.
Sails – The canvas used to harness the energy of the wind
Most vessels have at least two sails, depending on the rig type and boat setup.
The Mainsail flies behind the mast, on top of the boom. Although it may not always be the largest sail on the vessel, we commonly refer to it as “the main.”
The Headsail(s ), located in front of the mast, are often of different sizes and shapes, and many sailboats have more than one. The Jib and Genoa are two of the most common types.
Different types of sails are used for various sail plans and situations, and you can learn more about them in this guide .
Now that we had a look at the main parts of the boat, let us dive deeper and look at the rest of the vessel.
The starboard and port side of the boat
Learning about the boat’s components is very important, but we must also know how to orient ourselves on the vessel. Using the words “left and right” on onboard often leads to confusion.
If you refer to something on the left side of the boat, the person facing you will be confused. He won’t know if you are referring to his or your left. This is where the terms “Port” and “ Starboard ” make better sense.

When facing the front of the boat or the bow , your left side of the boat is the port side, and the right-hand side is the starboard . If you turn around and face the back of the boat or the stern , your right-hand side will be the port side.
- A red light identifies the port side of a vessel.
- A green light identifies the starboard side of a vessel.
Windward and Leeward
- The windward side of the boat is the side facing the wind. If the wind comes from your right-hand side while facing forward, the starboard side is windward. This will be the boat’s high side as the wind heels the boat over.
- The leeward side of the boat is the side opposite to the wind. This will be the lower side of the ship while sailing as the wind heels the boat over.
Windward and leeward are two of the most important aspects to understand when sailing and navigating. Not only to identify equipment and gear on each side of the boat but to avoid collisions when sailing close to other vessels. There are rules on the water dictating which boat is “Stand On” and which has to “Give Way” depending on whether you are the windward or the leeward vessel in the situation.
Read this article to access a free course on navigation rules .
Basic parts of a sailboat

The boat’s bow is the front part, typically shaped like a “V” to cut through the waves. Larger vessels often have a locker for their anchor chain in this section, holding the anchor at the front.
The midship section is the center of the boat. Some refer to this part as amidships.
The stern is the rear or back part of the boat. It is also referred to as the aft . I’ve had French crew calling the stern the butt of the vessel, which is funny but also correct!
The beam is the widest part of the boat. Also referred to as the sides on the middle.
The transom is a flat surface across the stern of the boat.
The waterline is the part where the hull (body) of the boat meets the water. Many vessels have a painted stripe to mark the waterline, indicating how loaded the ship is. If you have too much stuff on board, the waterline goes underwater, and it is time to do some housekeeping!
The freeboard is the vertical part of the ship side between the water and the deck. When you see a blue boat like Ellidah, the freeboard is the blue part.
The deck is the “floor” of the boat when you are outside. You have probably heard the term “All hands on deck!” The front deck is the deck space in front of the mast. Side decks are the decks on the boat’s sides.
The mid-deck is between the cockpit and the mast. The aft deck is the deck behind the cockpit. Sailboats with aft cockpits often don’t have any aft decks, but some have a swimming platform instead.
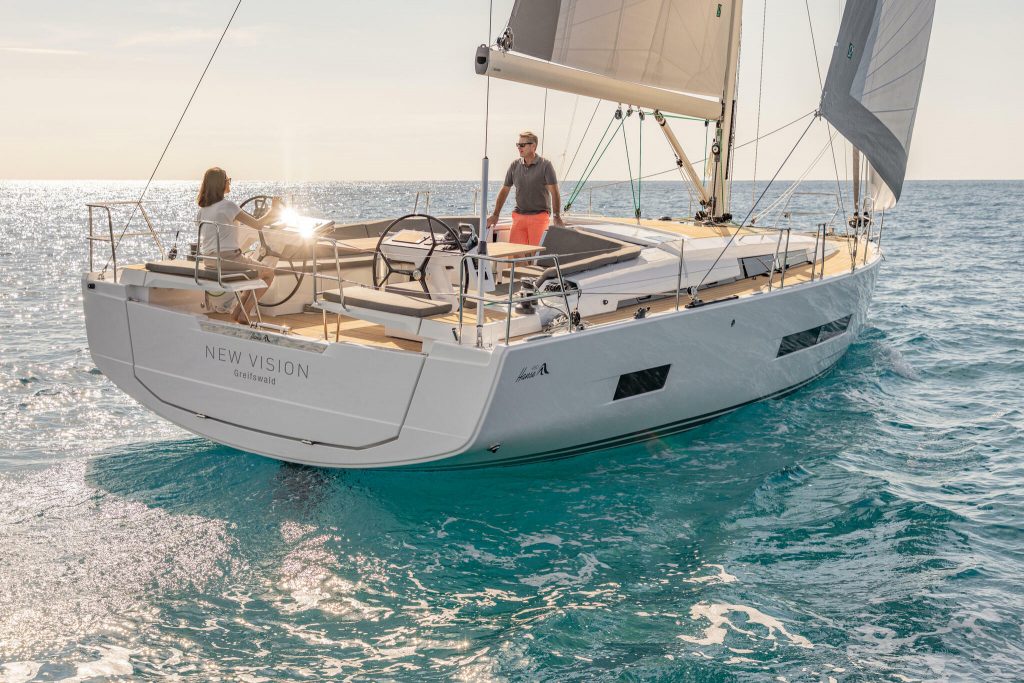
The cockpit is the boat’s steering position and where you will find the helm.
The helm is the position the helmsman uses to steer the boat. Smaller sailboats often use a tiller to navigate, while most bigger yachts have one or two steering wheels.
Main parts below deck (inside the boat)
Let us look at the interior to highlight and learn about the parts we have below the deck.

The Companionway
The companionway is the “front door” of the boat. This is where the steps lead from the cockpit or deck down below. It is usually opened and closed using a hatch, two doors, or a plate.
The Galley
The galley is the boat’s kitchen. This is where sailors prepare their delicious meals.
The Saloon
The saloon is basically the boat’s living room, usually where you find the settee and dinette. This is where delicious meals from the galley are served together with refreshing beverages in good company.
The settee is the sofa or couch in a boat. It is also used as a sea berth to sleep in when sailing.
The dinette is the area where you can sit down at a table and eat your dinner. It’s also perfect for consuming rum and a game of cards in good company.
A cabin is often used as a bedroom in a boat but is not necessarily where you sleep. Many boats have more than one cabin.
A berth is a place in the boat where you can sleep. This doesn’t necessarily have to be a bed and can often include the sleeping space in the saloon. Sea-berth usually refers to a sleeping position where you are tucked well in and can sleep when the boat is heeling over and moving around.
The head is the toilet on a boat. If your skipper tells you to go and clean the head, getting out the shampoo won’t do you any good!
Nav station
The navigation station is usually a chart table and a console with mysterious instruments like radios, switchboards, and complicated electronics. This is where adventures are planned and the skipper’s favorite seat onboard.

The bilge is a space in the bottom of the hull where water collects and sometimes a storage space for all sorts of things. It usually contains a bilge pump to pump out water that finds its way into the boat in various places.
A v-berth is a bed in the front cabin shaped like a V.
A bulkhead is a wall inside the boat, usually supporting the structure.
Hardware and Equipment
Sailboats come equipped with a variety of different hardware and equipment. While the specific items may vary from boat to boat, there are some essentials that nearly every sailboat has.

A winch is a metal drum that gives you a mechanical advantage and is used to control and tighten lines. These can be operated by turning a line around it and pulling manually or by a winch handle to get more force.
Most modern winches are so-called “self-tailing,” which means they lock the line on so you can winch the line without holding on to it. Some boats even have electrical winches operated by a button.
A cleat is a fitting used to fasten a rope. Most boats have at least 6 of these. One on each side on the bow, midship and stern. These are used to secure the boat to a mooring buoy or key. Many ships have more cleats than this for various lines and ropes, and they can be used for anything as they are strong points fitted to the hull.
The sprayhood is the boat’s windshield that protects the people in the cockpit from sea spray. Some vessels have a canvas sprayhood that can be folded down or removed. Others have solid sprayhoods, often called a hard dodger or a doghouse .
The bimini is the cockpit’s “roof.” It protects you from the elements and shelters you from spray, rain, and burning sun rays! A bimini can be made of canvas or hard material. A hard bimini can also be called a hardtop .
Dinghy

A dinghy is a little boat you use to get from the mothership to shore when you are at anchor, also called a tender or annex . It can be everything from a small inflatable rubber kayak to a RIB or even a solid boat.
An essential and valuable piece of kit as it is the daily driver for most cruisers. It is like the car of a land crab, used for all commuting on the water and hauling important stuff like beer, rum, and food onboard. Dinghies often have electric or petrol engines, which we call outboards.
Dinghies are also great to use for watersports, such as wakeboarding!
Like Captain Ron said in the movie, fenders are the rubber bumper things you hang off your boat to prevent it from scratching against something like the pontoon or another ship. It is conveniently also used to sit on or as a backrest while relaxing on deck.
A boat hook is a long stick with a hook at the end. Used to grab lines, items, and stuff that is too far to reach by hand, like cushions flying overboard. It is also convenient as a tool to push the boat away from another craft or the key. Most vessels have them on board.
The guard rail can be a flexible wire or a solid metal rail surrounding the boat to prevent us from falling overboard. Some also use a net as an addition for increased safety.
The pushpit is a metal guard rail around the stern of the boat. This is where the guard rail is secured on the stern: a common place to mount the BBQ, life raft, and the outboard for the dinghy.
The pulpit is the metal guardrail on the bow. This is where the guard rail is secured onto the bow.
The stanchions are the metal bars that keep the guard rail in place around the boat between the pushpit and the pulpit.
An arch is a typical structure made of stainless steel on the back of a boat and is often used to mount a variety of items like antennas, radars, solar panels, wind generators, etc. It is also convenient to use for lifting the dinghy and its outboard.

Ground Tackle
The ground tackle consists of several things:
- Your anchor
- Your anchor chain
- The link between the two
- The connection between the chain and your boat
It includes all equipment holding your boat to the ground. Larger boats sometimes have two anchors on the bow.
A windlass is a winch that hoists and lowers the anchor and chain. Most boats have one on the bow and some on the stern. These incredible things can be electrical or manual (some are both) and are essential to anchor your boat when not in a port or marina.
VHF stands for “Very High-Frequency Radio.” It broadcasts on the VHF network and allows you to communicate with others around you. Sadly, you won’t be able to tune in to your favorite radio show on these.
Still, they are essential for contacting other boats and port authorities. It is also the radio you will transmit an emergency mayday over in case of emergency. VHF radios sometimes require a license, depending on the country you are in.
Chartplotter
A Chartplotter is a navigation computer that shows various information on a screen, like charts, routes, radar images, etc. It is another vital piece of equipment that helps you navigate and maneuver the boat.
Final words
I hope this guide has been helpful and not too overwhelming for you. We’ve covered many of the parts of a sailboat and its terms and functions, but this article only touches on the basics. If you want to keep learning about sailing, I have written several other guides to help you get started.
Now that you have a basic understanding of sailboats, it’s time to take the next step and dive into a sailboat’s standing rigging .
Sharing is caring!
Skipper, Electrician and ROV Pilot
Robin is the founder and owner of Sailing Ellidah and has been living on his sailboat since 2019. He is currently on a journey to sail around the world and is passionate about writing his story and helpful content to inspire others who share his interest in sailing.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Types of Sailboats
- Parts of a Sailboat
- Cruising Boats
- Small Sailboats
- Design Basics
- Sailboats under 30'
- Sailboats 30'-35
- Sailboats 35'-40'
- Sailboats 40'-45'
- Sailboats 45'-50'
- Sailboats 50'-55'
- Sailboats over 55'
- Masts & Spars
- Knots, Bends & Hitches
- The 12v Energy Equation
- Electronics & Instrumentation
- Build Your Own Boat
- Buying a Used Boat
- Choosing Accessories
- Living on a Boat
- Cruising Offshore
- Sailing in the Caribbean
- Anchoring Skills
- Sailing Authors & Their Writings
- Mary's Journal
- Nautical Terms
- Cruising Sailboats for Sale
- List your Boat for Sale Here!
- Used Sailing Equipment for Sale
- Sell Your Unwanted Gear
- Sailing eBooks: Download them here!
- Your Sailboats
- Your Sailing Stories
- Your Fishing Stories
- Advertising
- What's New?
- Chartering a Sailboat
The Parts of a Sailboat (of which there are a great many!)
Some parts of a sailboat are very small and cheap, but are far from insignificant. Take the humble clevis pin for example; find one of these on the foredeck and you've cause to be concerned for the security of your rig!
If we were going to discuss all the parts of a sailboat here, it would be a very long article indeed - but relax, that's not going to happen.
Let's make a start with...
The Parts of a Sailboat Above Deck

Dacron is the usual choice of sailcloth for cruisers although laminated sails are becoming more common, and moulded sails are the first choice for racing sailors.
Read more about sails...
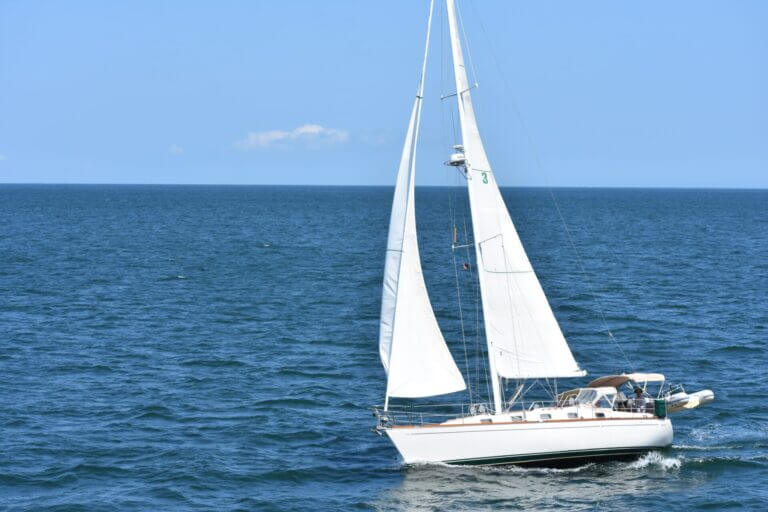
The Rigging
The standing rigging , generally made up in 1x19 stainless-steel wire, supports the mast.
The forestay and backstay secure the mast in the fore-and-aft plane, and the shrouds secure it athwartships.
The ends of the stays and shrouds are secured to the structural elements of the hull via chainplates.

The running rigging is the collective name for the lines (halyards, sheets, topping lifts, uphauls, downhauls etc) that control the sails. Their working ends are attached either directly to the sails or, in the case of the headsail, to the boom.
Read more about sailboat rigging...
These are the rigid struts, generally fabricated in alloy, wood or carbon fibre whose job it is to deploy the sails. For example:
- The spinnaker pole;
- The whisker pole;
- The bowsprit;
- The boomkin.
Read more about sailboat masts...
The Cockpit

Like many cruising boats, the Ted Brewer designed Whitby 42 ketch pictured above has a centre-cockpit, which allows for the provision of a sumptuous aft-cabin below. Nevertheless, aft-cockpit boats have a great following with seasoned cruisers too. So what the aft versus centre-cockpit pro's and con's?
Tillers and Wheels
Smaller boats tend to be tiller-steered while larger ones, as in the image above, have wheels. Tillers are attached directly to the rudder stock; wheels are located remotely and operate the tiller through chain or hydraulic linkage.
Each approach has their devotees, but what are the arguments for and against?
The Parts of a Sailboat Below the Waterline
Keels & rudders.

Keels provide three key attributes in varying amounts depending on their design : directional stability, ballast, and lift to windward.
Rudders provide steerage and a small contribution towards lift to windward. They are either:
- Outboard or inboard rudders, which can be
- Unbalanced, balanced or semi-balanced, and be
- Keel-hung, skeg-hung, transom-hung or spade rudders.
Rudder types are discussed here...

Driven by the boat's diesel engine, the propeller allows good progress to be made when the wind is not cooperating.
Under sail though the propeller is redundant and the fixed blades provide nothing but unwanted drag. This is greatly reduced if the blades can fold aft in a clamshell arrangement or feather in self-alignment with the water flow.
Sailboat propellers are either 2 or 3-bladed - and you can read more about them here...
Below Decks

There's no 'standard' layout for the below-decks accommodation on a sailboat, although the one shown above is a popular choice.
Some layouts work well for offshore sailing whereas others are much less suitable - here's why some succeed where others fail...
Recent Articles
A Hunter Passage 42 for Sale
Jul 16, 24 01:41 PM
The Wauquiez Centurion 40 Sailboat
Jul 15, 24 04:50 AM
The Elan 431 Sailboat
Jul 13, 24 03:03 AM
Here's where to:
- Find Used Sailboats for Sale...
- Find Used Sailing Gear for Sale...
- List your Sailboat for Sale...
- List your Used Sailing Gear...
Our eBooks...

A few of our Most Popular Pages...

Copyright © 2024 Dick McClary Sailboat-Cruising.com

Understanding the Parts of a Sailboat: A Comprehensive Guide to Sailboat Anatomy in 2023
- June 10, 2023

Sailboats are fascinating vessels that rely on the power of the wind to navigate the open waters. Understanding the parts of a sailboat are essential whether you’re a seasoned sailor or someone who’s just getting started. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the anatomy of a sailboat, exploring each component and its role in harnessing the wind and propelling your vessel forward. So, grab your sailing hat and let’s embark on this educational journey!
Table of Contents
Hull and keel.
The hull forms the main body of the sailboat and provides buoyancy and stability. It keeps the boat afloat and acts as a protective shell. Typically constructed from materials like fiberglass, wood, or metal, the hull’s shape and design impact the boat’s performance and seaworthiness.
Located beneath the hull, the keel is a weighted fin or centreboard that provides stability and prevents sideways drift. It counterbalances the force of the wind on the sails, helping to maintain the sailboat’s upright position and minimizing the risk of capsizing. Check out this article for further information.
The rudder is a vertically mounted flat plate or fin located at the stern (rear) of the sailboat. It is responsible for steering the boat by controlling the flow of water passing by it. Connected to the helm or tiller, the rudder allows the sailor to change the boat’s direction and navigate through the water.
Motor and Propeller
Some sailboats are equipped with an auxiliary motor for manoeuvring in tight spaces or when there is no wind. The motor propeller helps propel the boat when the sails alone are insufficient.
Deck and Cockpit
Positioned on top of the hull, the deck is a flat surface that serves as a platform for crew members to move around. It also houses various fittings and equipment.
Found in the rear portion of the deck, the cockpit is the area where the helmsman or skipper steers the sailboat. It is typically equipped with the helm, tiller, or steering wheel, as well as necessary instruments and controls.
Winches are mechanical devices used to handle and control the tension of the lines on a sailboat. They consist of a drum and a crank handle. By turning the handle, sailors can increase or decrease the tension of the lines, allowing for efficient control of the sails and the various rigging elements.
Cleats are fittings found on the deck used to secure lines and ropes. They provide a means of temporarily holding the lines in place, allowing sailors to free up their hands and focus on other tasks. Cleats come in various shapes and sizes and are essential for maintaining control and stability while sailing.
Anchor and Windlass
The anchor and windlass are essential for mooring the sailboat. The anchor secures the boat in place, while the windlass is a mechanical device used to raise and lower the anchor efficiently.
Mast, Boom, and Rigging
The mast is a tall, vertical spar located on the deck, extending upward. It provides support for the sails and enables their efficient capture of wind. Typically made of aluminium or carbon fibre, the mast plays a vital role in the boat’s stability and performance.
Connected to the mast, the boom is a horizontal spar that holds the lower edge of the mainsail. It allows for control over the sail’s position and shape, influencing the boat’s speed and maneuverability. The boom is pivotal in adjusting the angle and tension of the mainsail.
The rigging refers to the network of cables, wires, and lines that support and control the sails. This includes components such as shrouds, forestays, backstays, and halyards. Rigging plays a crucial role in maintaining the mast’s stability, tensioning the sails, and controlling their position.
Sails and Related Components
The mainsail is the largest sail on a sailboat, positioned on the mast and boom. It captures the wind’s power and generates forward propulsion. Adjusting the mainsail’s angle and tension influences the boat’s performance.
Jib and Genoa
The jib and genoa are smaller headsails located at the bow or front of the boat. They work in conjunction with the mainsail to optimize sail area and enhance manoeuvrability.
The spinnaker is a larger, lightweight sail used for downwind sailing. It is typically deployed when the wind is coming from behind the boat.
The berths are sleeping quarters on a sailboat. These are designated areas, often equipped with cushions or mattresses, where crew members can rest during extended voyages. Berths come in various sizes and configurations, ranging from single to double or bunk beds.
The head refers to the sailboat’s bathroom facilities. It typically includes a toilet, sink, and sometimes a shower. On smaller sailboats, the head may be compact and shared, while larger vessels may have multiple heads for increased convenience.
The galley is the sailboat’s kitchen area. It usually includes a stove, sink, and storage space for food and cooking utensils. Some sailboats may also feature a refrigerator or icebox for preserving perishable items during longer journeys.
The saloon is the main living area of the sailboat. It often serves as a multipurpose space, combining seating, dining, and socializing. The saloon may feature a table, seating benches or settees, and storage compartments for personal belongings.
Navigation Station
The navigation station is a dedicated area on the sailboat where navigational equipment, such as charts, compasses, and GPS systems, are kept. It serves as a central hub for planning routes, monitoring the boat’s position, and communicating with other vessels or shore stations.
Understanding the different parts of a sailboat is fundamental to becoming a proficient sailor. By familiarizing yourself with the anatomy of your vessel, you gain the knowledge and confidence to navigate the open waters with skill and precision. From the hull and deck to the mast, sails, and rigging, each component plays a crucial role in harnessing the wind’s power and propelling your sailboat on unforgettable adventures. So, keep learning, keep exploring, and may fair winds always fill your sails!
Related Posts

Exploring the Different Types of Sailboats and Their Versatile Uses
- May 20, 2023

Keelboat Sailing 101: A Beginner’s Guide to Navigating the Seas with Stability

Yacht Sailing 101: A Beginner’s Guide to Embarking on Luxurious Adventures
Parts of a Sailboat: Essential Components Explained
Sailboats are fascinating vessels that have been used for centuries to explore and navigate the world's oceans. These boats harness the power of the wind to propel themselves across the water.

To fully appreciate and understand sailboats, it's important to familiarize yourself with their various parts and components.
There are several vital parts to a sailboat that help it function smoothly on the water. These components can be broadly divided into the hull, the sailing hardware, and the living quarters.
Understanding each component's role in maintaining the boat's speed, stability, and maneuverability will enhance your sailing experience and allow you to tackle various challenges out on the water.

Key Takeaways
- Understanding sailboat anatomy is essential for appreciating the art of sailing
- Knowledge of rigging, sails, stability, and navigation is crucial for a smooth sailing experience
- Sailboats vary in types and size, each with its own unique characteristics and requirements
Sailboat Anatomy
The hull is the main body of a sailboat, providing buoyancy and stability in the water. It's crucial for keeping us afloat and is typically made of materials like fiberglass, wood, or metal 1 .
The shape and design of the hull can vary, depending on the type of sailboat.
There are various parts of the hull that are essential to know, such as the bow (forward part), stern (aft part), waterline, bilge, and rudder 1 .
The deck is the horizontal surface that covers the hull of a sailboat. It's where I walk, sit, and operate the boat.
The deck is an essential part of the sailboat because it provides structural strength and supports features such as the mast, rigging, and winches 2 .
Some key deck components include the bow, stern, lifelines, cleats, and hatches for accessing the cabin below.
The cockpit is the area where I control and steer the boat, usually located towards the stern 3 .
It can be either an open or enclosed space, depending on the boat's design and intended use.
Key components I find in the cockpit are the helm, tiller, or wheel for steering, as well as the navigation and communication instruments. The cockpit also usually contains the primary winches, lines, and clutches for sail control 3 .
The cabin is located below the deck and is the living space on a sailboat 4 .
It offers shelter from the elements and is typically where I find berths for sleeping, a galley for cooking, a head for bathroom facilities, and storage for personal belongings.
The cabin layout and size can vary greatly depending on the boat's size and design 4 .
Rigging Components
The mast is the tall vertical spar that supports and extends the sails on a sailboat . It stands on the boat's hull, usually at its center, and serves as the backbone of the sailboat's rigging system.
In my experience, there are various types of mast s, such as single masts, double masts, and even triple masts, depending on the design and size of the sailboat.
The boom is the horizontal, supporting spar that attaches to the foot (bottom edge) of the mainsail and runs perpendicular to the mast.
It helps control the shape and angle of the sail relative to the wind, enhancing the boat's performance.
I always make sure that the boom is securely attached to the mast and that all necessary hardware is in good working condition.
Standing Rigging
Standing rigging refers to the set of fixed components that support the boat's mast and keep it properly aligned and positioned.
The primary components in this category are the stays and shrouds.
Stays are the wires or rods that run forward, aft, or diagonally from the mast, while shrouds run from the mast to the sides of the sailboat.
These components are crucial to the structural integrity of the rigging, so I always check them for wear and tear, and proper tension.
- Stays : These can be further divided into forestays, backstays, and side stays.
- Shrouds : These include upper, intermediate, and lower shrouds, depending on their position.
Running Rigging
Running rigging encompasses the adjustable components of a sailboat's rigging system that help me control the sails' position and tension.
Key elements of running rigging are halyards, sheets, and blocks.
- Halyards : These are the lines (ropes) used to hoist (raise) and lower the sails. On my sailboat, I use a mainsail halyard, jib halyard, and a spinnaker halyard when needed.
- Sheets : They are the lines I use to control the angle of the sails relative to the wind, adjusting their trim for optimal efficiency. The mainsheet, jib sheet, and spinnaker sheet are the most common ones I encounter.
- Blocks : Blocks or pulleys are essential for making my work easier when handling the rigging. They help redirect the force in the lines and provide mechanical advantage when I need to tension the sails or handle the sheets.
Sails and Sail Handling
The mainsail is the primary sail on a sailboat and is attached to the mast and boom. It plays a crucial role in propelling the boat forward by capturing the wind.
The mainsail consists of three edges: the luff , which is the forward edge, the leech , the aft edge, and the foot , the bottom edge.
To control the shape of the mainsail, I can use the following techniques:
- Adjust the tension on the outhaul , which controls the foot tension.
- Adjust the tension on the halyard to control the luff tension.
- Modify the boom vang tension to control the leech tension.
Headsails are the sails located in front of the mast. They include the jib and the genoa .
A jib is a smaller sail, which is easier to handle and suitable for moderate to strong wind conditions. The genoa is a larger headsail that provides more power in lighter winds. Both these sails feature a luff, leech, and foot similar to the mainsail.
When using a jib or genoa, I can trim the sail by adjusting the sheet (the line that controls the angle of the sail relative to the wind) and the lead position (which is where the sheet attaches to the sail).
By properly trimming the headsail, I can optimize its performance and maintain a balanced sail plan. The guide to sail anatomy is helpful for understanding specific parts of a sail.
A spinnaker is a specialized sail designed for sailing downwind, away from the wind's source. It is a large, lightweight, and billowing sail, constructed from a thin fabric that captures the wind from behind and propels the boat forward.
When setting up a spinnaker, I handle the sail by using:
- Tack line : A line that controls the sail's lower corner, where it meets the bow of the boat.
- Halyard : A line that hoists and lowers the sail.
- Sheet : The line that controls the angle of the sail relative to the wind.
Spinnakers can be challenging to handle due to their size and sensitivity to wind gusts. However, with practice and proper sail handling techniques, I can use the spinnaker effectively to enhance my downwind sailing performance and enjoyment.
Keel and Stability
There are several types of keels that serve different purposes and provide varying levels of stability to a sailboat. The most common types of keels are fin keels , bulb keels , wing keels , bilge keels , and lifting keels .
- Fin keels are quite popular and extend straight down from the hull. They provide a great balance between stability, performance, and ease of movement in the water. You can read more about fin keels in this Illustrated Guide .
- Bulb keels consist of a fin keel with a heavy bulb at the bottom to lower the center of gravity and improve the boat's stability.
- Wing keels feature horizontal "wings" to enhance the sailboat's ability to sail close to the wind and minimize drift.
- Bilge keels are twin keels that run parallel along the port and starboard sides of the hull, typically found on smaller sailboats.
- Lifting keels are adjustable keels that can be retracted upwards to decrease the boat's draft, making it easier to navigate shallow waters.
Some sailboats also have canting keels , which can pivot from side to side to provide maximum stability when sailing at extreme angles.
A critical component of keel design is the ballast, which is typically made of heavy materials like lead or iron. The main purpose of the ballast is to provide stability by lowering the sailboat's center of gravity and counteracting the heeling forces generated by the wind on the sails.
Different types of keels have varying ballast configurations. For example, fin keels have ballast concentrated in a narrow fin, while bulb keels have the ballast located in a bulb at the bottom of the keel. In each case, the ballast ensures that the sailboat remains stable and upright, even in challenging sailing conditions.
In some smaller sailboats, such as dinghies, it's common to find a centerboard design instead of traditional keels. A centerboard is a retractable plate that provides lateral resistance, allowing the boat to sail upwind. In this case, the sailboat relies on the weight of the crew as ballast to maintain stability.
Steering System
The rudder is one of the essential components of a sailboat's steering system. It's mounted vertically on the stern (rear) of the boat and functions as the primary means of steering by deflecting water flow, which in turn changes the boat's direction.
There are different types of rudders such as the spade rudder, which is a common type used in modern sailboats. A spade rudder is fully submerged in water and not connected to the hull, giving it better maneuverability and control.
The tiller is a simple and traditional method for controlling the rudder. It is essentially a long lever attached directly to the top of the rudder.
I find that using a tiller offers me direct and immediate feedback from the rudder, making it easier to feel the boat's response to my steering inputs. Tiller steering is often preferred by many sailors on smaller sailboats due to its simplicity and connection with the sailing experience.
Larger sailboats tend to have wheel steering systems in place of a tiller. As a helmsman , I use the wheel to control the direction of the boat by turning it clockwise or counterclockwise.
The wheel is connected to a system of cables and pulleys, which in turn steer the rudder, allowing me greater leverage and control over the boat's steering.
Various parts of a sailboat's steering system:
| Component | Function | Preferred on |
|---|---|---|
| Rudder | Primary means of steering by deflecting water flow | All types of sailboats |
| Tiller | Direct lever attachment to the rudder, providing immediate feedback | Smaller sailboats |
| Wheel | Steering system that provides greater leverage and control | Larger sailboats |
Navigation and Safety Equipment
As a sailor, I rely on my compass to navigate and maintain a steady course.
There are two main types of compasses on sailboats, the fixed-mount compass and the handheld compass .
The fixed-mount compass is typically installed near the helm , providing me with continuous bearing information. Meanwhile, having a handheld compass on board serves as a backup in case the main compass fails or is damaged.
Safety is paramount when I am sailing, and having secure lifelines around the deck is essential.
Lifelines are made of stainless steel wire and are attached to the stanchions around the boat. I use them to minimize the risk of falling overboard while moving on the deck, particularly in rough seas or strong winds. They are crucial for my safety and the safety of my crewmates, ensuring we all stay onboard and secure.
When anchor ing my sailboat, I rely on an anchor and a windlass to secure the boat in place.
There are different types of anchors, such as the CQR , Danforth , and Bruce anchors, each with their unique design that suits different seabed conditions.
I typically use a windlass to deploy and retrieve the anchor. A windlass is a mechanical device that makes handling heavy anchors more manageable.
It is essential to regularly inspect and maintain the windlass and anchor to ensure they function as expected when anchoring in various weather conditions and locations.
In addition to the anchor, I also make use of a chain and rode , which connect the anchor to the sailboat:
- Chain: The chain attaches to the anchor and adds weight, helping the anchor dig into the seabed.
- Rode: The rode connects the chain to the boat and can be made of rope or a combination of rope and chain.
Sailing Hardware
Winches are an essential part of a sailboat. They help control the lines and sheets by providing mechanical advantage.
I find that winches are most commonly used for tightening or loosening the jib sheets and the mainsheet. They consist of a drum, a handle, and gears that allow for smooth operation.
The sailboat hardware available on the market today includes different types and sizes of winches to suit various boats and sailing needs.
When using a winch, it's important to wrap the line around the drum in a clockwise direction, making sure there are no overlaps or twists.
To control the tension, I always ensure that the winch handle is in the "ratchet" position. This allows me to easily apply force in one direction and hold the line in place when not turning.
Cleats are another vital piece of sailing hardware that come in various shapes and sizes. Their primary function is to secure lines, particularly when adjusting tension on sails.
I often use cleats on my boat to ensure that sheets and halyards stay in place while sailing.
Horn cleats are the most common type, with two projecting horns that allow the line to be passed around them in a figure-eight pattern.
Cam cleats, on the other hand, have two spring-loaded jaws that grip the line. This allows for easy adjustment and quick release if necessary.
In my experience, blocks are critical components of a sailboat's rigging system. They serve as pulleys that help redirect lines and reduce friction, making it easier to control sails.
Blocks are available in various materials such as stainless steel or aluminum . They also come with different configurations like single, double, or triple sheaves depending on the specific application.
For instance, I use a mainsheet block system in conjunction with a vang to control the tension and angle of the mainsail. Similarly, topping lift lines may pass through blocks to help raise and lower the boom easily.
Auxiliary Systems
One important auxiliary system in a sailboat is the motor . Sailboats often have an inboard or outboard engine , which provides extra maneuverability when needed.
This is particularly useful when the wind conditions aren't favorable. The motor's main components include the engine, transmission, and propeller . These work together to move the boat through the water when there's limited or no wind available.
A boat's electrical system is responsible for powering various devices onboard. The critical aspects of this system include the battery, alternator, and wiring, which connect different electronic components.
Some common devices that rely on the electrical system are navigation systems, LED lights, electronic sensors, and communication equipment.
In addition to navigation and communication, the electrical system also powers the bilge pump .
The bilge pump is a vital piece of equipment that helps remove water accumulated in the boat's bilges, preventing the vessel from flooding.
Here's a simple list of typical electrical system components:
- Switches and fuses
- Electronic devices (navigation, communication, etc.)
A sailboat's plumbing system usually consists of a freshwater system and a wastewater system.
The freshwater system supplies water to the boat's faucets, showers, and sometimes engine cooling. It includes a water tank, water pump, and piping to distribute the water.
The wastewater system, on the other hand, deals with disposing of used water and waste.
This generally includes a black water tank for toilet waste and a grey water tank for water from sinks and showers. These tanks need to be regularly emptied and maintained to prevent foul odors and maintain the boat's sanitation.
To recap, the plumbing system's main components are:
- Black water tank (toilet waste)
- Grey water tank (sink and shower waste)
Living Quarters
The galley is the sailboat's kitchen, where food is prepared and cooked. It's typically a small, compact area in order to maximize space and efficiency.
In most sailboats, the galley features a stove, sink, refrigerator, and storage.
Storage space, such as cabinets and drawers, is crucial because every inch of space is valuable on a sailboat.
To ensure user-friendly access to the utensils, cookware, and food items, sailboats may have organized storage solutions .
As for the saloon , it serves as the primary living area on a sailboat. This is where the crew gathers to relax, dine, and socialize.
The saloon usually features comfortable seating, a dining table, and additional storage space s.
I often find that this space is customizable, allowing for the conversion of tables into extra sleeping areas when necessary.
Natural light is also an essential aspect of the saloon, so it often has hatches and windows to allow sunlight in while providing a view of the surroundings.
Berths are the sleeping quarters on a sailboat. These designated areas, often equipped with cushions or mattresses, provide the crew with a place to rest during extended voyages.
Berths come in various sizes and configurations , ranging from single to double or bunk beds, depending on the size of the sailboat and the number of crew members.
As with other spaces on the sailboat, thoughtful design and attention to maximizing storage space is key.
In many berths, additional storage areas can be found under the beds or in nearby compartments.
Types of Sailboats
A monohull sailboat , as the name suggests, consists of a single hull. This design is common and comes in various forms, including cruising sailboats and racing sailboats .
One advantage of monohulls is that they generally have better upwind performance compared to multihulls.
A cruising sailboat is versatile and well-suited for long-distance sails, equipped with amenities to make life on board comfortable.
In contrast, racing sailboats prioritize speed and performance and often feature lightweight materials and specialized designs.
Multihull sailboats include both catamarans and trimarans, featuring two or three hulls connected by a central platform.
Catamarans have a pair of parallel hulls, which provides a wide and stable platform that reduces heeling. According to this guide , catamarans are known for their speed, comfort, and spaciousness, making them popular choices for vacationing and cruising.
Trimarans, on the other hand, have three hulls - a central hull flanked by two smaller outriggers.
The trimaran design offers a balance between stability, speed, and maneuverability, resulting in a quick, agile, and comfortable sailing experience.
A dinghy is a smaller sailboat , usually less than 15 feet in length.
Dinghies are simple, easy to maneuver, and relatively affordable. They can be used for various purposes, such as recreational sailing, sailing lessons, or as a tender for a larger sailboat.
Dinghies can have one or two sails and either a centerboard or a daggerboard to provide lateral resistance to the water.
Many beginners start their sailing journey with a dinghy because it's an excellent way to learn essential sailing skills before venturing onto larger sailboats.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different components of a sailboat's rigging?
The rigging on a sailboat consists of a system of ropes, wires, and chains that support the mast and sails. It can be divided into two main categories: standing rigging and running rigging.
Standing rigging includes the shrouds and stays, which are responsible for providing support to the mast.
Running rigging comprises all the lines used to control the sails, such as halyards, sheets, and outhauls.
Rigging components help sailors effectively control the sailboat and its movements.
How do the various parts of a sailboat function together?
The different parts of a sailboat work together to provide an efficient sailing experience.
The hull is the main body of the boat, while the keel provides stability and prevents sideways motion. The rudder is responsible for steering.
The mast and sails capture wind energy and enable propulsion. Rigging is crucial for controlling the position of the sails and ensures the boat's maneuverability.
This helpful guide offers an illustrated explanation of sailboat parts and their functions.
Can you name the sails typically found on a sailboat?
A common type of sailboat is the sloop, which has two sails: the mainsail and the jib.
Other sails that can be found on sailboats include the spinnaker, a large, lightweight sail used for downwind sailing, and the genoa, a larger version of the jib for increased sail area in light wind conditions.
You can read more about sail types in this comprehensive guide .
What is the purpose of the keel on a sailboat?
The keel is a critical component of a sailboat as it provides stability and prevents the boat from moving sideways in the water.
It acts as a counterbalance to the forces exerted by the wind on the sails and ensures directional control. The keel also contributes to the boat's hydrodynamic properties, reducing drag and promoting smooth movement through the water.
How is the mast of a sailboat structured and what are its key parts?
The mast is a vertical pole on a sailboat responsible for supporting the sails and rigging.
It is typically made of aluminum or carbon fiber for strength and lightness. Key parts of the mast include the spreaders, which help distribute the load along the shrouds, and the tangs, which are attachment points for stays and shrouds. Masts also have fittings for halyards and other rigging components essential to sail control.
What are the common features found in a sailboat's cockpit?
The cockpit is the central area of a sailboat where the crew controls the boat's operation. It typically includes the steering wheel or tiller (connected to the rudder), engine controls, and instruments for navigation and communication.
Additionally, the cockpit may feature winches and cleats for handling the sheets and other lines. You might also find seating or benches for the crew as well as storage compartments. More details on sailboat features can be found in this informative article .
Related Articles

Eliminator Boat: A Comprehensive Guide to Performance and Style

Boat Financing: Key Factors to Secure Your Dream Vessel

Used Pontoon Boats for Sale: Expert Guide on Making a Smart Purchase
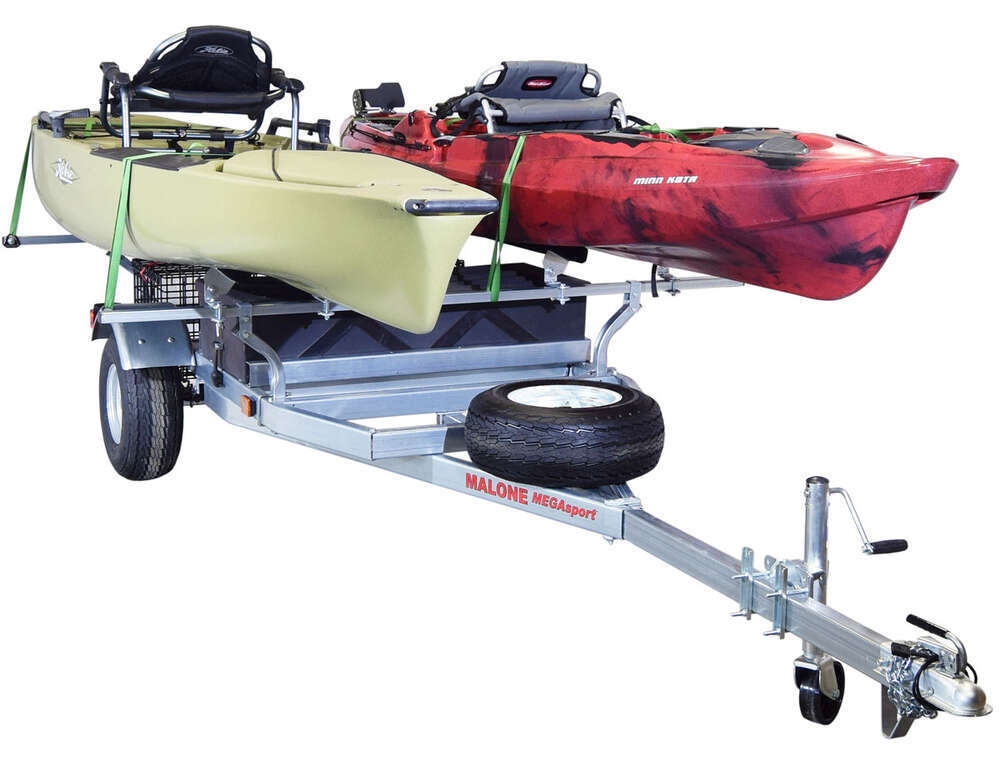

Kayak Trailers: The Ultimate Guide to Hassle-Free Transport
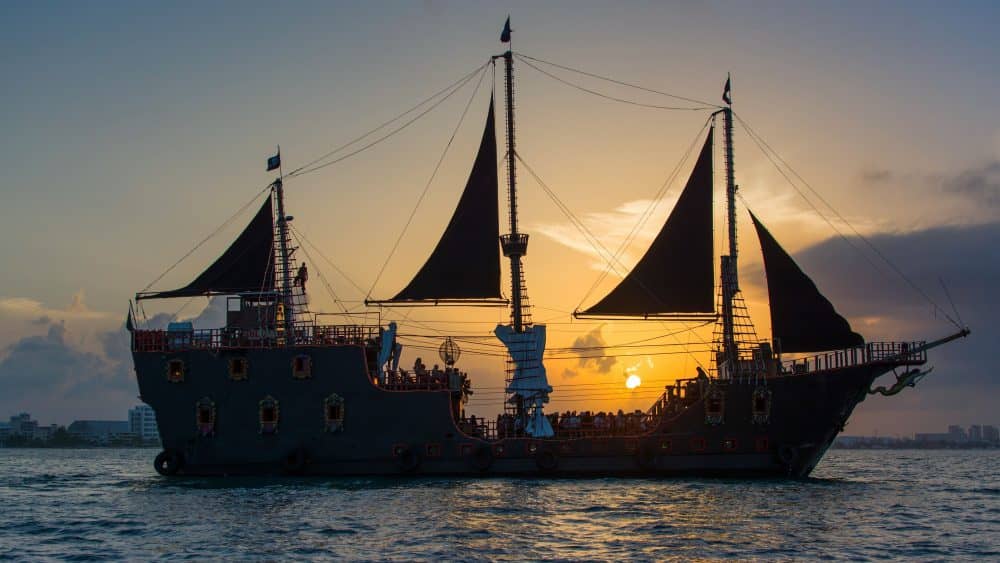

Parts of a Pirate Ship: A Comprehensive Breakdown

Ikon Bass Boats: Ultimate Guide for Fishing Enthusiasts

What Is Most Likely to Cause Someone to Fall Overboard? Key Risk Factors Explained

Stern Ship Design: Innovations and Modern Applications

Basic Sailing Terminology: Sailboat Parts Explained
Sailing is a timeless activity that has captivated the hearts of adventurous souls for centuries. But, let’s face it, for beginners, sailing can be as intimidating as trying to navigate through a dark, labyrinthine maze with a blindfold on. The vast array of sailing terminology, sailboat parts and jargon can seem like a foreign language that only the most experienced seafarers can comprehend.
Fear not, intrepid sailor, for this comprehensive guide on basic sailing terminology for beginners will help you navigate the choppy waters of sailing jargon with ease. From learning the difference between the bow and stern to mastering the intricacies of sail trim, this article will equip you with all the knowledge you need to confidently take to the seas. So hoist the mainsail, batten down the hatches, and let’s set sail on this exciting journey of discovery!
Parts of a Sailboat
Before you can begin your sailing adventure, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the different parts of a sailboat. From the sleek bow to the sturdy keel, each component plays a vital role in keeping your vessel afloat and propelling you forward through the waves.

- Hull The main body of the boat that sits in the water and provides buoyancy and stability.
- Bow The front of the boat that meets the water and helps to determine its direction.
- Stern The rear of the boat where the rudder and motor are located.
- Deck The flat surface of the boat that you stand on, which can include various features such as seating, storage compartments, and hatches.
- Cockpit The recessed area of the deck where the skipper and crew sit or stand while sailing, which allows for easy access to the sail controls and provides protection from the wind and waves.
- Keel The long, fin-shaped structure beneath the waterline that helps to keep the boat stable and upright.
- Rudder The flat, vertical surface located at the stern of the boat that is used to steer and control the direction of the boat.
- Tiller or wheel The mechanism used to steer the boat, either in the form of a tiller (a handle attached to the rudder) or a wheel (similar to the steering wheel of a car).
- Mast The tall, vertical pole that supports the sails and allows you to catch the wind and move through the water.
- Boom The horizontal pole extending off the bottom of the mast that holds the bottom edge of the mainsail.
- Mainsail The large, triangular-shaped sail attached to the mast and boom that captures the wind’s power to propel the boat forward.
- Jib The smaller, triangular-shaped sail attached to the bow that helps to steer the boat and balance the force of the mainsail.
- Rigging The network of ropes and cables that hold the mast and sails in place and help control their movement.
Sail Terminology
Understanding the terminology associated with sails is critical to becoming a successful sailor. Here are 12 of the most important sail terms you should know, along with brief explanations for each:

- Luff The forward edge of a sail that is attached to the mast, allowing you to adjust the sail’s shape and angle to catch more wind.
- Leech The aft edge of a sail that is attached to the boom, which helps to control the sail’s shape and release the wind as needed.
- Foot The lower edge of a sail that is attached to the boom, which helps to control the sail’s shape and power.
- Head The top of a sail that is attached to the mast and controls the sail’s overall shape and angle.
- Battens The long, thin strips inserted into the pockets of a sail to help maintain its shape and stiffness.
- Clew The bottom corner of a sail that is attached to the boom or sheet, which helps to control the sail’s shape and power.
- Tack The bottom forward corner of a sail that is attached to the boat or a line, which helps to control the sail’s shape and power.
- Sail Area The total area of a sail, which is measured in square feet or meters.
- Sail Draft The curve or depth of a sail, which affects its performance and power.
- Sail Shape The overall form and contour of a sail, which is critical for catching the wind effectively.
- Reefing The process of reducing the sail area by partially lowering or folding the sail, which can be necessary in strong winds or heavy seas.
- Furling The process of rolling or folding a sail to reduce its size or stow it away, which is often used when entering or leaving port or in rough conditions.
Wind Direction and Sail Positioning
Understanding wind direction and sail positioning is crucial for successful sailing. Here are the key terms you need to know:
Types of Wind

- Apparent Wind The wind that is felt on the boat, which is a combination of the true wind and the wind generated by the boat’s movement.
- True Wind The actual direction and strength of the wind.
Points of Sail
You can find a detailed explanation of the points of sail here

- Close-Hauled Sailing as close to the wind as possible, with the sail set at a sharp angle to the boat.
- Beam Reach Sailing perpendicular to the wind, with the sail set at a right angle to the boat.
- Broad Reach Sailing with the wind at a diagonal angle behind the boat, with the sail angled away from the boat.
- Running Sailing directly downwind, with the sail on one side of the boat.
Other Terms
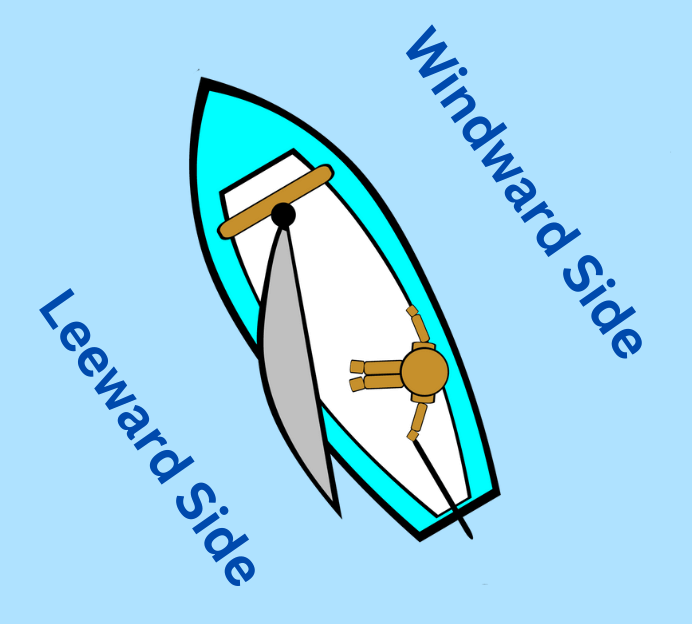
- Windward The side of the boat that is facing the wind.
- Leeward The side of the boat that is sheltered from the wind.
- Sail Trim Adjusting the sail and rigging to maximize the power and efficiency of the sailboat.
Navigation Terminology
Navigating a sailboat requires an understanding of a variety of nautical terms. Here are some of the most important terms you should know:
- Starboard Side The right side of a boat
- Port Side The left side of a boat
- Compass A device used for determining the boat’s heading or direction.
- Bearing The direction from the boat to a specific point on land or water.
- Chart A map or nautical publication that displays water depths, navigational aids, and other important information for safe navigation.
- Latitude The angular distance between the equator and a point on the earth’s surface, measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds.
- Longitude The angular distance between the prime meridian and a point on the earth’s surface, measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds.
- Course The direction in which the boat is traveling.
- Plotting The process of marking a course on a chart or map.
- Waypoint A specific point on a navigational chart or map that serves as a reference point for plotting a course.

- Tacking This maneuver involves turning the bow of the boat through the wind in order to change direction. To tack , the sailor will turn the helm towards the wind until the sails begin to luff, then quickly steer the boat in the opposite direction while adjusting the sails to catch the wind on the new tack.
- Jibing This maneuver is similar to tacking, but involves turning the stern of the boat through the wind. To jibe, the sailor will steer the boat downwind until the sails begin to luff, then quickly turn the stern of the boat in the opposite direction while adjusting the sails to catch the wind on the new tack.
- Heading up This maneuver involves turning the boat closer to the wind in order to sail upwind. To head up, the sailor will turn the helm towards the wind while simultaneously trimming the sails in to maintain speed and prevent the boat from stalling.
- Falling off This maneuver involves turning the boat away from the wind in order to sail downwind. To fall off, the sailor will steer the helm away from the wind while simultaneously easing the sails out to catch more wind and accelerate the boat.
- Docking This maneuver involves bringing the boat alongside a dock or other fixed object in order to moor or disembark. To dock, the sailor will typically approach the dock at a slow speed while using lines and fenders to control the boat’s position and prevent damage.
Knots and Lines
Learning the right knots and lines to use is essential for any sailor. Here are some of the most important knots and lines to know:
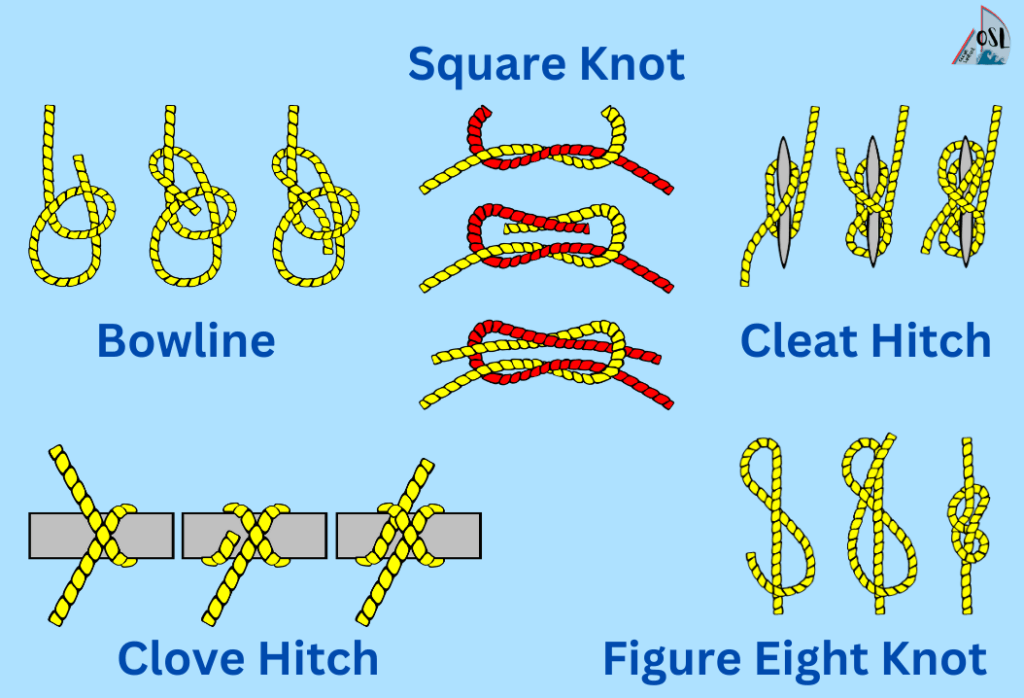
- Bowline This is a versatile knot used for many purposes, including attaching a line to a fixed object, such as a mooring or cleat.
- Square Knot A simple knot used to join two lines of the same diameter.
- Clove Hitch A quick and easy knot for attaching a line to a post or piling.
- Figure-Eight Knot A knot used to stop the end of a line from unraveling.
- Cleat Hitch A knot used to secure a line to a cleat.
- Sheet Bend A knot used to join two lines of different diameters.

- Main Halyard A line used to raise the mainsail.
- Jib Sheet A line used to control the angle of the jib.
- Mainsheet A line used to control the angle of the mainsail.
- Jib Furling Line A line used to furl the jib.
Sailing Safety
- Personal Flotation Devices (PFDs) These are the life jackets or vests that you must wear when on board to ensure your safety. Choose a PFD that fits you properly and is appropriate for your body weight.
- Tethers and Harnesses These are designed to keep you attached to the boat and prevent you from falling overboard. Make sure to clip yourself onto the boat when you’re on deck or going up to the mast.
- Man Overboard ( MOB ) Drill This is a critical safety procedure to practice with your crew. Learn how to quickly identify and recover someone who has fallen overboard.
- Emergency Position Indicating Radio Beacon (EPIRB) An EPIRB sends a distress signal and your location to rescue services in an emergency. Make sure it’s properly registered and in good working condition.
- Navigational Lights Ensure your boat has the required navigational lights and know how to use them properly. These lights help other boats see you in low-light conditions.
Remember that safety is always the top priority when sailing, and it’s essential to take it seriously.

Sailing Terminology Conclusion
As we come to the end of our sailing terminology crash course, it’s important to remember that the world of sailing is vast and varied. Learning even the basics can be a daunting task, but with practice and perseverance, you’ll be able to hoist your sails and set a course for adventure.
Whether you’re a seasoned sailor or just starting out, understanding the terminology is crucial to ensure a safe and enjoyable voyage. From the parts of the boat to the knots and lines, each aspect plays a significant role in the overall sailing experience.
So, as you prepare to embark on your next sailing adventure, keep in mind the importance of safety, navigation, and proper etiquette on the water. And remember, when all else fails, just hoist the Jolly Roger and hope for the best! (Just kidding, don’t actually do that.) Happy sailing!
What is the difference between apparent wind and true wind?
Apparent wind is the wind felt by the sailor on the boat, while true wind is the wind direction and speed relative to the ground.
What are the points of sail?
The points of sail are the directions that a sailboat can travel in relation to the wind. They include upwind, close-hauled, beam reach, broad reach, and downwind.
What does it mean to be “on a reach”?
Being “on a reach” means sailing with the wind coming from the side of the boat, at a perpendicular angle to the boat’s direction.
What is tacking?
Tacking is the maneuver used to turn the boat’s bow through the wind, allowing the boat to change direction while still sailing upwind.
What is jibing?
Jibing is the maneuver used to turn the boat’s stern through the wind, allowing the boat to change direction while sailing downwind.
What is the difference between windward and leeward?
Windward is the side of the boat that is facing into the wind, while leeward is the side of the boat that is sheltered from the wind.
What is a boom vang?
A boom vang is a line used to control the position of the boom, which helps control the shape and position of the sail.
What is a cleat?
A cleat is a device used to secure a line to the boat, allowing the sailor to adjust the tension of the line without having to hold onto it constantly.
What is a winch?
A winch is a mechanical device used to control lines and adjust sails. It typically consists of a drum and handle that can be turned to wind or unwind a line.
Similar Posts

How to conduct a safety briefing on a sailing yacht
Sailing is a thrilling and adventurous activity that requires a certain level of knowledge and skill to ensure the safety of the crew and vessel. One of the most critical aspects of sailing is conducting a safety briefing before setting sail. A safety briefing is essential to ensure that all crew members are aware of…

9 Essential GPS Navigation Tips for Sailing
Sailing is an exhilarating experience that offers an escape from the hustle and bustle of everyday life. However, navigating the open water can be challenging, especially when it comes to staying on course and avoiding potential hazards. That’s where GPS navigation comes in. GPS technology has revolutionized sailing, making it easier and safer than ever…

What is a Sloop? Definition, Types and History
A sloop is a type of sailboat that has a single mast and a fore-and-aft rig. Sloops are a type of sailboat that has been around for centuries. They are known for their versatility and ease of handling, making them popular among sailors of all skill levels. Sloops have a single mast and a fore-and-aft…

Mainsail Furling Systems – Which one is right for you?
With the variety of options of mainsail furling systems available, including slab, in-boom, and in-mast systems, it can be challenging to determine which one best suits your needs. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the pros and cons of each system, enabling you to make an informed decision that aligns with your sailing requirements….

Advantages of Catamaran Sailboat Charter
A catamaran sailboat charter is an exciting way to explore the beauty of the sea. Whether you are an experienced sailor or a first-timer, booking a catamaran sailboat charter has a lot of advantages that you can enjoy. In this article, we will discuss the advantages of booking a catamaran sailboat charter, so that you…

Anchoring Tips for Beginners
Are you ready to set sail on a journey to become anchoring aficionados? Anchoring a sailing yacht may seem like a simple task, but let me tell you, it’s no small feat. It requires a blend of nautical knowledge, careful planning, and a dash of luck (and a pinch of salt, if you ask any…
Parts of Sailboat: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Essential Components
by Emma Sullivan | Jul 14, 2023 | Sailboat Racing

Short answer parts of sailboat:
A sailboat consists of various essential components, including the hull, keel, rudder, mast, boom, sails, rigging, and cockpit. These parts work together to enable sailing and control the boat’s movement and direction.
Understanding the Key Parts of a Sailboat: A Comprehensive Guide
Ah, the allure of sailing! There’s something undeniably magical about gliding across the water, powered solely by the wind. But before you embark on your maritime adventures, it’s essential to understand the key parts that make up a sailboat. This comprehensive guide will not only help you navigate the vast sea of knowledge but also provide professional, witty, and clever explanations along the way. So hoist your sails and let’s dive in!
1. Hull: Let’s start with the foundation of any boat – the hull. Resembling an elegant swan gracefully floating on water or a majestic beast slicing through waves, the hull is essentially the body of your sailboat. It can come in various shapes and sizes, each designed for differing purposes. From slender racing boats built to skim effortlessly across the surface to sturdy cruising vessels made for long-distance voyages, choosing the right hull for your needs is crucial.
Pro tip: Remember that lighter hulls are more agile and faster in calm conditions, while heavier ones excel at handling rough seas. Choose wisely!
2. Keel: Beneath every sailboat hides its secret weapon – the keel! Acting as a counterbalance to prevent capsizing under strong winds, this appendage extends from beneath the hull into the water like a underwater fin. Think of it like a ballerina en pointe stabilizing herself during a daring spin; without a keel, your sailboat would be left adrift amidst tempestuous waters.
Clever analogy: Just as an owl spreads its wings silently flying through darkness with ease, your keel allows you to glide swiftly cutting through turbulent waves.
3. Mast: Now we come to one of sailing’s most iconic features -the mast. Rising tall and proud from your deck like an ancient sycamore reaching towards endless skies; it carries the very essence of sailing – the sail! Made from strong and lightweight materials like aluminum or carbon fiber, the mast provides essential support for your sails and acts as a vertical pivot point, allowing you to harness the power of the wind.
Witty remark: A sailboat without a mast is like a book without pages – directionless and lacking a tale to tell!
4. Sails: Ah, the sails – these magnificent fabric wings that transform your boat into a vessel powered by nature herself. Your sails come in various shapes and sizes, each suited for different wind conditions. From the large mainsail stretching from mast to stern, capturing the relentless breath of Aeolus, to jibs and spinnakers that dance playfully with every gust, mastering these ethereal cloths is an art form in itself.
Professional advice: Clever sailors know how to trim their sails just right – aligning them perfectly with wind direction for optimal speed and efficiency. Remember, it’s all about catching that perfect gust!
5. Rudder: Navigating through treacherous waters requires finesse and precision – enter the rudder! Suspended below your hull at the rear end of your boat, this hinged fin-like appendage allows you to steer your sailboat’s course effortlessly. As you turn its small wheel or tiller handle, orchestrating an elegant pirouette across shifting tides becomes second nature.
Clever metaphor: The rudder is like your boat’s best friend- always there to guide you through choppy waves with unwavering loyalty.
Armed with this comprehensive guide to understanding sailboat parts, you’re now ready to set sail on magnificent adventures upon azure seas! Remember, sailing combines both science and artistry; only those who respect these elements can truly become masters of their vessels. So embrace the thrill of harnessing nature’s power on a sailboat – where professionalism meets wit meets cleverness, resulting in a lifetime of unforgettable experiences.
How Do the Different Parts of a Sailboat Work Together? Explained Step by Step
When it comes to sailboats, the art of sailing involves the perfect coordination and harmony among various parts. Every component has a specific purpose and contributes to the overall functioning of the vessel. In this article, we will delve into each part of a sailboat and explore how they work in sync to propel the boat through water effortlessly.
1. Hull: The hull is like the foundation of a sailboat. It provides buoyancy and determines stability in water. Its shape plays a crucial role in reducing drag and increasing speed by minimizing resistance against the water.
2. Keel: Attached to the bottom of the hull, the keel is responsible for maintaining stability by counteracting forces that could tip or capsize the boat. Its design helps provide lateral resistance, preventing sideways slip when sailing against wind.
3. Rudder: Located at the back of the boat, below water level, the rudder acts as a steering mechanism. By changing its angle or position, sailors can control the direction in which they want their sailboat to move.
4. Mast: The mast serves as support for sails and rigging components like halyards and shrouds; it stands upright on top of a keel-stepped or deck-stepped base called a step or partners respectively.
5. Sails: Perhaps one of the most essential parts of any sailboat – sails are what capture wind energy to propel forward motion. There are different types of sails, such as mainsails and headsails (jibs/genoas), each serving distinct purposes according to wind conditions.
6. Boom: The boom functions as an attachment point for foot/footrope portion(s) near/on/at aft edge(s) – clew(s) – foot-end – shorter edge(s) – leech(es) / spanker/jibboom —of sail(s). It attaches via vang or topping lift system(s), controlling vertical movement/restriction. Its purpose is to help maintain sail shape and control the angle at which wind enters the sail.
7. Rigging: The rigging consists of wires, lines, and hardware used to support and control the sails. It includes various elements such as standing rigging (stays/shrouds), running rigging (sheets/halyards), and blocks/pulleys that allow for proper tensioning and adjustment of sails during maneuvering.
8. Winches: These mechanical devices are mounted on deck or cabin sides; they help sailors generate immense force required to trim/adjust/control sails effectively. By turning winch handles, sailors can raise or lower sails while maintaining desired tension.
9. Cleats: Cleats are fittings attached to the boat’s deck that secure lines in place after adjusting them through winches or other mechanisms. They provide a reliable way to hold ropes under significant strain without slipping, allowing sailors to easily control the position and shape of their sails.
10. Sheets: Sheets refer to lines that connect sails to elements like boom or jib/genoa tracks – function being controlled by winching system(s). Their adjustment determines the angle, shape, and trim of a sail, influencing performance in different wind conditions.
11. Tiller/Wheel: The tiller or wheel serves as the primary means of controlling the rudder’s direction either directly (with tiller) or indirectly (via mechanical linkages/controllers with a wheel).
In conclusion, a sailboat is an intricate blend of components that work together harmoniously to harness wind energy efficiently. From the hull maintaining stability and reducing resistance against water to the mast supporting rigs and enabling steering via rudder – every part plays an integral role in achieving optimum sailing performance. Understanding these dynamics helps sailors navigate uncharted waters with finesse while embracing both physics and nature’s elements. So embark on your next sailing adventure with confidence, knowing how each part contributes towards an exhilarating maritime experience.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Various Components of a Sailboat
Title: Frequently Asked Questions about the Various Components of a Sailboat – Your Sailing Companion Demystified!
Introduction: Sailing is a captivating sport that captivates enthusiasts around the world. As you venture into this thrilling realm, familiarizing yourself with the various components of a sailboat becomes paramount. In this comprehensive guide, we have gathered frequently asked questions to help unravel the mysteries behind these essential elements. So brace yourself as we set sail on our journey of exploration and understanding!
1. What is a Mast? Ahoy fellow sailors! The mast serves as the vertical spine of your sailboat, anchoring its rigging and providing support for your sails. Not only does it give height to your boat, but it also plays a crucial role in harnessing the wind’s mighty power. Think of it as your ship’s conductor, orchestrating perfect harmony between captain and nature.
2. Tell me more about Sails. Hoist the sails and let’s answer your queries! Sails are like wings for your vessel – they propel you forward using nothing but nature’s invisible breath – wind! They come in various shapes and sizes, tailored to specific sailing conditions. From majestic mainsails that fly high above you to jib sails that complement their every move, each type has its purpose within the orchestra of sailing.
3. How does a Rudder work? Ahoy there helmsman! The rudder lies submerged beneath the waterline at the stern (rear) of your sailboat and acts as its steering mechanism. Just like a lever moves objects by changing direction or redirecting force, manipulating the rudder kicks off an intricate dance with hydrodynamics—giving you complete control over where your vessel glides across vast seas.
4. Can you explain Keel functionality? Keels keep our voyage steady; they’re like ballasts beneath our floating feet! These weighty fin-like appendages attached directly to the hull counteract tipping and provide stability. The keel’s primary job is to resist lateral movement, ensuring your vessel doesn’t slant excessively when the wind catches your sails. Clever engineering, isn’t it?
5. What role does a Winch play? Ahoy there, sailors in need of strength! A winch is a mechanical marvel designed to make life easier on board. Resembling a drum with levers or handles affixed to it, winches are used for hoisting sails and maneuvering heavy lines. They utilize gears and pulleys, multiplying force to overcome the mighty pull of nature. With a winch onboard, you’ll feel like Hercules himself!
Conclusion: Navigating the world of sailing becomes simpler once you familiarize yourself with its essential components. From the mast to the sails, rudder to keel, and winches on deck – every part plays an integral role in harnessing nature’s elements and guiding you towards new horizons. So as you embark on this thrilling journey of mastering the seas, remember that knowledge is your most reliable crew member! Bon voyage!
Exploring the Anatomy of a Sailboat: Insights into the Essential Parts
Title: Exploring the Anatomy of a Sailboat: Insights into the Essential Parts
Introduction: Have you ever wondered what sets a sailboat apart from other seafaring vessels? Whether you’re an experienced sailor or a curious landlubber, understanding the anatomy of a sailboat is key to unleashing its full potential on the open waters. In this blog, we will delve into the intricacies of these maritime marvels, unraveling the essential parts that come together to make sailing a truly captivating experience.
1. The Hull – Giving Shape and Purpose: At the core of every sailboat lies its hull, an elegant symphony of form and function. Crafted from strong and lightweight materials typically including fiberglass, wood, or aluminum, the hull’s sleek design cuts through water effortlessly while providing buoyancy to keep the vessel afloat. Its carefully shaped exterior minimizes drag for enhanced speed, ensuring your sailboat glides gracefully against winds both mild and fierce.
2. The Keel – Stabilizing Force: While hidden beneath the surface, the keel plays a crucial role in maintaining stability at sea. Extending downward from the hull into depths unexplored by human eyes, this weighted appendage counterbalances wind forces acting upon your sails. By resisting lateral motion caused by gusts or turbulence, it ensures your journey remains on course even amidst challenging conditions.
3. Sails – Capturing Wind’s Embrace: A sailboat without sails would be akin to soaring through clouds without wings – utterly futile! Sails provide power and momentum to push your vessel forward using Mother Nature’s most dynamic force: wind. Meticulously constructed using modern synthetic fabrics designed for strength and durability, they can be skillfully adjusted in response to changing wind angles and intensities. The artistry involved in harnessing these billowing canvases embodies sailing’s timeless beauty.
4. Mast – Towering Guardian of Sails: Standing tall and proud, the mast acts as the backbone of your sailboat’s rigging. Typically made from aluminum or carbon fiber, this towering structure supports and elevates the sails to catch the wind effectively. Its height allows sails to reach soaring heights, harnessing stronger winds that would otherwise elude a shorter vessel. Plus, it adds a dash of grandeur to the whole spectacle.
5. Rigging – The Artful Web: An intricate network of ropes, wires, and lines intricately woven across your sailboat’s mast and deck constitutes its rigging system. These vital elements provide support and control over various aspects of sail manipulation – from adjusting tension on sails through cleats to fine-tuning angles using winches. Mastering this delicate web is essential for skilled sailors seeking precise control over their vessel’s performance in different weather conditions.
Conclusion: As we’ve embarked on a captivating journey exploring the essential parts that make up a sailboat, one cannot help but marvel at the symphony of design, engineering, and human ingenuity that coalesces into these nautical wonders. Each component serves its purpose meticulously while collectively enabling sailors to harness nature’s elements for thrilling adventures on the open seas. So next time you set foot onto a sailboat or simply gaze upon one in awe, remember its anatomy – a fascinating testament to mankind’s age-old quest for exploration and adventure on sparkling waters.
Breaking Down the Various Sections and Elements that Comprise a Sailboat
Sailing is an incredible adventure that allows individuals to harness the power of the wind and explore the vastness of the sea. But have you ever wondered what exactly makes up a sailboat? In this blog post, we will delve into the various sections and elements that comprise a sailboat, breaking them down in a detailed, professional, witty, and clever manner.
1. Hull: Let’s start with the foundation of any sailboat – the hull. The hull is essentially the body of the boat, commonly made from fiberglass or wood. It determines not only the boat’s shape but also its stability in water. Think of it as a vessel’s superhero suit – sleek, strong, and ready to conquer any aquatic challenge.
2. Keel: Next up is the keel, located at the bottom center of the boat’s hull. This fin-like structure keeps your floating wonder from tipping over like a teeter-totter on choppy waves. Like Batman’s trusty utility belt, it provides stability by counteracting those pesky side forces from wind and waves.
3. Rudder: In our Batman metaphorical journey through boat parts, let us introduce you to our sailboat’s control center – yes folks, we’re talking about none other than the rudder! Located at the stern (or rear) of the sailboat beneath it sits gracefully to guide our vessel in its intended direction just like Batman guides Gotham City toward justice!
4.Mast: Moving further up in our exploration quest, behold -the mast! Rising tall toward infinity (well almost!), it holds aloft our majestic sails capturing every gust of wind like Superman soaring into battle! This vertical pole extends high into space (okay maybe not quite that high) allowing us to experience unforgettable sailing moments while showcasing its strength just as impressively as Thor wields his hammer!
5.Sails: Ah yes -the sails themselves- these magnificent cloths that capture the wind’s energy and propel our vessel forward, elegantly maneuvering through the vastness of the ocean! Just like Spiderman’s silk threads, they cling to life and allow us to harness nature’s power while adding a dash of colorful grace to our sailboat.
6. Rigging: Now for some behind-the-scenes elements – enter the rigging. These ropes, wires, and chains meticulously interconnect various parts of our sailboat system enabling us to tweak it as required! They’re like the meticulous web woven by Hawkeye signaling his fellow Marvel heroes into action!
7.Cabin: Ahoy there! Aboard the ship lies a hidden treasure -the cabin- providing a cozy home away from home amidst your aquatic escapades. It offers refuge from stormy seas or scorching sun, making you feel like Tony Stark chilling in his lavish Iron Man suite.
8.Deck: Finally, we arrive at the deck – the ultimate space where sailors command their ship’s destiny! Your private universe encompassing friends, family, and salty air all perfectly combined. Think Captain Jack Sparrow casually striding across this stage, commanding both respect and admiration!
In conclusion, sailing is not just about jumping on board any floating object; it is an intricate dance between several sections and elements that come together harmoniously to create the soulful experience we call sailing. Each component serves its purpose with unwavering determination just like superheroes fighting evil forces while exuding sheer elegance and charm.
So next time you set sail on your adventure-packed voyage, take a moment to appreciate all these different sections and elements working together – because just like in any superhero movie blockbuster – their collaboration is what truly makes your sailing journey enchanting and unforgettable!
A Closer Look at the Functions and Importance of Every Part in a Sailboat
Title: Sailboat Anatomy: Unveiling the Intricate Functions and Crucial Importance of Every Component
Introduction:
Ahoy, fellow seafarers! Step aboard as we embark on a journey that delves into the heart and soul of sailboats. Join us in exploring the intriguing world of sailing by uncovering the multifaceted functions and paramount significance behind every part incorporated into these magnificent vessels. So hoist your sails, tighten your rigging, and let’s set sail into this comprehensive guide!
1. Hull – The Nautical Backbone: At the core of any sailboat lies its hull—the elemental structure responsible for buoyancy and stability. Crafted from durable materials like fiberglass or wood, it helps to keep us afloat while gracefully slicing through water. A meticulously designed hull shape creates minimal drag—an essential feature enabling efficient navigation.
2. Keel – Defying Gravity’s Temptations: Beneath our vessel lies an unsung hero—the keel—a fixed appendage counterbalancing the force exerted by wind on sails while keeping us upright against gravity’s pull. This integral component provides exceptional stability, minimizing excessive rolling motion caused by waves and ensuring safer sailing conditions.
3. Rudder – The Navigator’s Ally: Allowing sailors to direct their course deftly is the rudder—captain of steering mechanisms. Attached to the stern, this ingenious device interacts with water currents in response to helm movements, enabling controlled turns while maintaining balance. With its guidance, we navigate uncharted waters with confidence.
4. Mast – Harnessing Nature’s Power: Commanding awe in all its towering glory stands the mast—a vertical pillar connecting earth with sky—that hoists our sails high into the heavens where they can kiss favorable winds sweetly. Built resiliently from aluminum or carbon fiber, this majestic entity converts wind energy into propulsion efficiency – propelling us forward towards distant horizons.
5. Boom – Taming the Wind’s Whispers: Partnering with the mast, the boom plays a vital role in regulating sail shape and controlling wind power. Affixed at an angle to the mast, it stretches out when sails are hoisted, keeping them taut and maximizing their performance potential. This artful balance ensures our sails capture the wind’s essence while resisting its unruly gusts.
6. Sails – Empowering Dreams: What lends enchantment to a sailboat is none other than its sails—the iridescent wings that harness nature’s allure. Crafted from durable fabrics like Dacron or nylon, these artful masterpieces manipulate wind currents to provide propulsion and steer our vessel towards infinite possibilities. A perfect harmony between aesthetics and functionality, they carry us across oceans of dreams.
7. Standing Rigging – The Guardian Angels: Silently standing tall against gusting winds and turbulent weather conditions are the unseen heroes known as standing riggings—the interconnected network of cables that provide unyielding structural integrity to the mast and bow sprit. Ensuring our safety by absorbing tremendous forces exerted on mast during navigation, they exemplify strength beyond measure.
8. Running Rigging – Dance Steps in Harmony: Creating a symphony of coordinated movements are the running riggings—colorful arrays of ropes meticulously adjusted to control various sail functions. From halyards raising or lowering sails to sheets trimming their position according to wind directions, this elegant ensemble allows us to dance harmoniously amidst shifting sea melodies.
Conclusion:
As we conclude our journey through various components comprising a sailboat, we begin to fathom just how ingeniously each part has been designed over centuries of seafaring wisdom. Beyond their functional significance lies an indescribable beauty in seeing these pieces come together—propelling dreams and embracing adventure like no other vessel can. So next time you embark on a sailing escapade, take some time to appreciate the intricate functions and vital importance behind every part in your sailboat, for they truly make the difference between an ordinary voyage and a remarkable odyssey.
Recent Posts

- Sailboat Gear and Equipment
- Sailboat Lifestyle
- Sailboat Maintenance
- Sailboat Racing
- Sailboat Tips and Tricks
- Sailboat Types
- Sailing Adventures
- Sailing Destinations
- Sailing Safety
- Sailing Techniques

My Cruiser Life Magazine
Illustrated Guide to Sailboat Parts [Updated 2023]
The lingo of sailing is baffling to many newcomers. While the actual sailing is pretty easy, it’s hard to wrap your mind around the bookwork when it seems like every little thing on a boat goes by its own nautical term.
Here are a few names for parts of a sailboat that you might not have thought about before. For even more nautical word play, check out our complete guide to sailing terms .

Parts of Sailboat Hulls
The boat’s hull is its main body. Most are made of fiberglass, but there are a few aluminum sailboat models out there too. Wood is more traditional but more difficult to maintain than these modern alternatives. Sailboat hulls are displacement hulls, which means they sit low in the water and move relatively slowly. The hull’s job is to displace water, so you stay afloat!
Bow The forward “pointy end” of the boat.
Stern The rear end of the boat.
Transom If the stern of a boat has a flat section, it is called the transom. (I wrote about it in detail here: What Is the Transom on a Boat )
Canoe Stern or Double-Ender Some boats lack a transom; instead, their stern comes to a point like a bow. This is a “double ender” or a canoe stern.
Port and Starboard Sides Port is the left side, and starboard is the right side.
Freeboard This is the height of the sides of the boat above the water.
Deck The upper portion of the boat that you walk on.
Sheer Sheer is the curve of the deck when viewed from the side. Some boats have none, and some boats have a lot.
Cabin Coach Roof Most sailboats have a raised coach roof on top of the cabin area.
Bottom of a Sailboat – Keels and Things
There are tons of parts on a sailboat that you only ever see if it’s out of the water. Boats are hauled out at boatyards by giant cranes, or a special machine called a travel lift .
Keel The boat’s keel is the underwater feature that counters the effects of wind pressure on the sails. It keeps the boat from tipping over, but it also keeps the boat going in a straight line as it moves through the water. If a boat has no keel, the wind will push it downwind.
A keel is heavy–it is weighted with thousands of pounds of ballast (usually lead). So when someone refers to a “keelboat,” they mean that it is a big boat with a weighted keel built for cruising. The built-in weight of a keel keeps the boat from capsizing. Also, the water flow over the curved surface of the keel helps the boat sail into the wind.
Smaller boats with centerboards or daggerboards are on the opposite end of the spectrum from keelboats. These aren’t weighted and could tip over (capsize) in the wrong conditions.
Types of Keels
Full Keel A classic and time-tested design, full keel boats are favorites among passage-making and ocean-crossing cruisers. They’re stable and comfortable at sea and very safe. However, they have a reputation for being slow compared to more modern designs.
Modified Full Keel The modification is a cut-away forefoot. That means it looks like a full keel, but there isn’t as much keel up near the bow. This reduces the underwater “wetted surface area” and makes the design a little bit faster while preserving the other good things about full keel designs.
Fin Keel The fin keel looks like a shark’s fin pointed downward. Some are narrow and very deep, while others are longer and shallow. Fin keels are bolted to the bottom of an otherwise flat-looking hull design. The fin has a foil shape that creates a lifting force as water flows over it. In addition to its ballasted weight, this opposes the sails and leeway. Most modern sailboats have some version of a fin keel.
Bulb Keel The ballast should be placed as low as possible to lower the boat’s center of gravity. The bulb keel is a fin keel with a lead bulb added to the bottom. The bulb has an efficient shape, making it more efficient than just the fin alone.
Wing Keel Like a bulb, a wing keel works by adding more weight and hydrodynamic force to the bottom of the keel. As a result, the wings look like a little airplane mounted on the bottom of a fin keel.
Swing Keel A swing keel is a fin that pivots up and into the boat, meaning that you can have a very shallow draft when you are docking or anchoring but also a very deep draft when you are sailing in open waters. This heavy keel requires a powerful and complicated electric or hydraulic-electric system.
Lifting Keel A lifting keel is similar to a swing keel, only the keel lifts up into the hull vertically.
Bilge Keels A bilge keel boat has two fin keels mounted at 45-degree angles below the hull. The advantage is that the boat can “dry out.” This makes them very popular in harbors around England, where the massive tidal range means that the harbor is only mud for half the day.
Centerboard Centerboards look like swing keels, but the “keel” part is just a board. It isn’t weighted with lead or iron, so it doesn’t change the ballast of the boat any. They are often found on smaller sailboats like sailing dinghies, but there are also large cruising boats that have full keels or long-fin keels with centerboards, too.
Daggerboard A daggerboard is like a centerboard, only it doesn’t swing. Instead, it goes straight up and down like a dagger into its sheath. They’re not only common on very small sailing dinghies but also large cruising catamarans.
Canting Keel Canting keels are some of the latest technology items in racing, so they aren’t found on cruising boats yet. They move from side to side, allowing the crew to precisely control the forces made by the keel.
Types of Rudders – What Steers a Sailboat
As with keels, you’ll see various types of rudders on sailboats. The rudder is one of the most critical parts of a sailboat’s equipment, so the differences in rudders are mostly about how protected it is from damage.
Rudder The rudder is the thing that steers the sailboat. It’s mounted on the back of the boat, sometimes looking a bit like a second keel. When the operator turns the steering wheel or tiller, it moves the rudder one way or the other. That, in turn, turns the yacht’s bow left or right.
Transom-Hung Rudder The most basic type of rudder is hung on the transom. It’s usually controlled with a tiller instead of a wheel. You can see a transom-hung rudder above the water.
Keel-Mounted Rudder On a full keel boat, the rudder will be mounted on the back edge of the keel. This protects it completely from damage since anything the boat might hit will hit the keel first.
Skeg-Mounted Rudder The rudder might be mounted to a skeg if a boat has a fin keel. A skeg is a small fixed surface that holds the rudder and supports it. In the case of a full skeg, it also protects the rudder as a full keel would.
Spade Rudder Spade rudders have no skeg, so the entire underwater surface moves when you turn the wheel. Most modern yachts have spade rudders because they are incredibly effective. They are easily damaged, however, which is why some offshore sailors still prefer skeg-hung rudders.
Bottom of Sail Boat – Running Gear
Running gear is the generic name given to all equipment under the boat that connects to the engine and moves the boat under power. It consists of the propeller, prop shaft, and supports.
Propeller Also called the prop or screw, the prop is what converts the engine power into thrust. The water flow over its blades creates a pushing force that moves the boat. Since the sailboat doesn’t use the propeller when it is sailing, sailboats often have folding or feathering props that stop moving.
Prop Shaft The metal shaft that connects the engine to the propeller is called the prop shaft.
Cutlass Bearing Where the prop shaft exits the hull, a rubber cutlass bearing keeps it centered and rotating freely.
Saildrive A saildrive is a common arrangement on modern sailboats that uses a vertical drive leg with the propeller. The saildrive installs on the back of the engine and includes the transmission. It’s like the lower unit of an outboard motor, but you cannot raise it out of the water.

Up Top – Types of Sailboat Designs
Aft Cockpit The “classic” design of the modern sailboat, if there is such a thing, is called the aft cockpit. This layout has the cockpit in the rear-most section of the hull, behind the cabin.
Center Cockpit The center cockpit sailboat has the cockpit closer to the mast. That leaves a lot of space in the rear of the hull for a huge stateroom. This design means that the cockpit will be closer to the boat’s center, making handling easier. But it is also higher, making more windage and motion at sea.
Pilot House A pilot house sailboat has a second helm inside a protected area. These are popular in colder climates, where the pilot house provides a warm place to steer the boat from. The rear cockpit is usually smaller than a typical aft cockpit, but it’s still where the sail handling occurs. A pilot house has a raised level, so the salon typically surrounds the interior helm to utilize that space and visibility when not underway.
Deck Salon Like a pilot house, a deck salon has big windows and better visibility than a typical sailboat cabin. But it lacks a true interior helm. Many, however, have nav stations with forward visibility and autopilot controls, making it a comfortable place to sit and keep watch during a passage.
Flush Deck Most sailboats have a raised coach roof where the interior cabin is. But some designers make their decks flush with the sides of the boat, making a wide open deck that is easy to move around on.
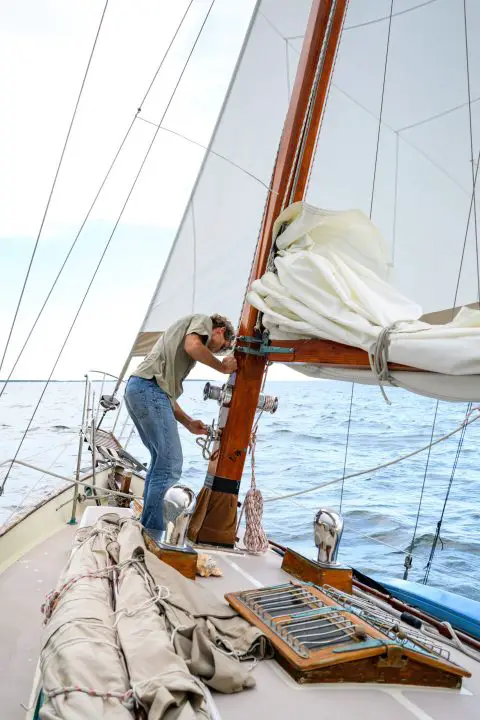

On Deck Sailboat Components – Sailboat Front
The deck of a sailboat is all about safety at sea. Most modern cruising boats are rigged such that there are few things you might need to go “out on deck” or “go forward” for. Instead, these things are rigged back to the cockpit, so you can stay safe and dry while doing your thing.
Since the wet pitching deck of a sailboat at sea is tricky, many of the things you’ll find there are safety-related.
Handholds Places to grab should be located all over the boat, so there’s never a risk of not having something to hold onto to stabilize yourself.
Lifelines Lifelines run the perimeter of the boat and provide a last-ditch safety device. You can grab them, and they should be high enough that they’ll keep you from going overboard.
Stantions The stands that lifelines attach to.
Bow Pulpit The solid rail around the front of the boat provides a safe handhold and a starting point for the lifelines.
Stern Pushpit The same, but on the stern of the boat.
Bulwarks The raised edges of the deck on the sides so that you can’t slip overboard on accident.
No-Skid Decks In areas where people will be walking, the deck is treated with a special product to make the deck “no-skid.” That way, it isn’t slippery, even when wet.
Harness Sailing harnesses are designed to clip onto the boat and keep a sailor onboard even if the boat takes a huge wave or the sailor slips. The harness is the staple of offshore safety.
Jack Lines Jack lines are temporary lines secured on the deck where sailors can attach their harnesses.
Safety Rails Many boats also have extra rails and handholds located in spots where sailors might work on deck, like around the base of the mast.
At the bow of the sailboat, you’ll find her ground tackle.
Bowsprit The bowsprit is the spar that extends from the deck forward of the bow. They’re used on sailboats to gain more sail area since getting the sail farther forward means you can fit a bigger sail. Some have just a spar, while others have a bow platform that is part of the deck.
Ground Tackle The generic word for the anchor, chain, and all the equipment needed to use it.
Anchor The anchor is “the hook” that digs into the seabed and keeps the boat in the same place. Anchors are safety devices since they allow you to stop in shallow water. But they also provide access to areas with no marinas since you can anchor offshore and go in on your dinghy.
Windlass A winch that pulls up the anchor and chain. They can be manual, with a handle, or electric, with a button.
Anchor Rode The generic name for the anchor line. It can be a chain or rope.
Snubber A short length of rope that attaches to the chain to secure it to the boat.
Cleat A horn-shaped piece of deck hardware used to secure a line or rope.
Dorade A large vent opening on the deck of a boat which is designed to let air in but not water.
Hatch Hatches are upward-facing windows that you can open to increase ventilation in the cabin.
Locker A generic term for a cabinet or compartment on a boat.
Going Aloft – Basic Boat Parts of a Sailing Rig
The rig of a boat is the mast and all of its associated parts. If you’re wondering about the many different kinds of rigs that are out there, check out our rundown on sailing terms . There you’ll find definitions for boats with just one mast or multiple masts, like sloop rig and what a boat with two sails in front might be called. It’s a cutter, if you’re wondering.
Spar A generic name for a mast, boom, or any other long pole used to hold a sail. It can be wood or metal or vertical or horizontal.
Mast A vertical spar upon which a sail is hoisted.
Boom A horizontal pole that holds a sail and gives it shape.
Standing Rigging The wires or rope that holds the mast upright.
Stay Standing rigging that goes fore to aft. The head stay runs from the masthead to the bow, and the backstay runs from the masthead to the stern.
Shroud Standing rigging that goes to the sides of the boat. From the masthead to each side runs a cap shroud. Some masts also have intermediate and lower shrouds.
Running Rigging All lines that are used for sail handling are called running rigging.
Halyard A halyard hoists a sail to the top. Each halyard is named for the sail it hoists, i.e., main halyard, jib halyard, spinnaker halyard.
Sheet The sheet controls the sail. If you ease the sheet, the sail is loosened. If you winch the sheet in, it is tightened. Like all running rigging, each sheet is named for the sail it controls, i.e., main sheet, jib sheet, etc.
Traveler If a sail has a boom, the traveler can be used to adjust it from side to side. The sheet is attached to the traveler. Most main sail travelers are located near or in the cockpit.
Gooseneck Fitting The articulating attachment that holds a boom on a mast.
Topping Lift A line that holds the rear end of a boom up. It runs from the masthead to the boom.
Vang A control line pulls the boom down and puts pressure on the sail to keep it flatter. Large boats may have hydraulic or solid vangs.
Blocks The rest of the world would call this a pulley, but sailors call it a block.
Fairleads Deck organizers that keep the lines tidy and running in the direction they should go on deck.
Furler Wraps the sail around the stay so that it doesn’t not have to be raised and lowered each time. Instead, you pull on the sheet and the sail unrolls or “unfurls.”
On Deck – Back of Sailboat
On most boats, the cockpit is located at the back.
Cockpit The main operations center and party central on a sailboat. This is where the skipper sits at the helm, and the linesmen control the sheets.
Coaming The cockpit is protected from waves and splashes by the coaming, the tall walls that enclose it. It also makes the cockpit safe since you are unlikely to get swept overboard from here.
Lazarette The main storage locker in the cockpit.
Helm The station where the skipper steers the boat from.
Tiller If a boat doesn’t have a wheel, it will have a tiller. A tiller is just a handle connected to the rudder, and the skipper pushes or pulls it to steer. Even if a boat has a wheel, it probably has an emergency tiller in case the steering system breaks.
Winch Winches provide a mechanical advantage to make it easier to haul in lines. In the cockpit, all the sheets have winches.
Rope Clutch A clutch locks a rope in place so it can be taken off a winch, even when loaded.
Jammer A jammer does the same as a clutch, but it’s a simpler device found on smaller boats.
Weathervane Steering A weathervane is used to steer the boat like an autopilot but uses wind direction and mechanical linkages. As a result, they use no power and never complain about their workload. They mount on the stern of the boat and are controlled by simple lines to the cockpit. Windvanes are often referred to by their brand name, i.e., Monitor or Hydrovane
Davits Arms on the back of the boat that lift the dinghy or tender.
Swim Platform A flat area on the transom that allows you easy access in and out of the water. A standard feature on newer boats but not on older ones that just had long swim ladders.
Catamaran Sailboat Parts Explained
For the most part, the components of a catamaran share the same terms and labels that they would on a monohull. Cats often have a few extra features with other names, however.
Hulls A catamaran is made with two hulls connected together. Each hull has an interior, just like a monohull sailboat does. The cabins and heads are usually located in the hulls, and sometimes the galley is also down below.
Owner’s Version A catamaran layout that is made for private owners. Usually, one hull will be dedicated to the owner’s stateroom with a private door, a huge head with a walk-in shower, and a large berth.
Charter Version It has more staterooms and heads than an owner’s version does. Usually, a charter cat has at least two staterooms and heads in each hull.
Bridge Deck The deck connects the two hulls, which usually has the salon and cockpit. If the design is “galley up,” the galley will be on the bridgedeck with the salon.
Cockpit Just like on a monohull, the cockpit is the operations center. But catamarans have huge cockpits, and there is usually a large outdoor dining table and entertainment area as well.
Forward Cockpit Some designs have lounge seating forward of the salon on the bridgedeck.
Flybridge Some designs have the main helm mounted on top of the salon on an upper level. It’s almost the catamaran equivalent of a center cockpit.
Trampolines Forward of the salon, the bridge deck stops, and a trampoline connects the hulls over the water. This is a great place to hang out, but it’s an integral safety feature for a catamaran. The trampolines allow any water to immediately drain away, not weighing the boat down on the bow. This prevents a pitchpole when a boat capsizes by tipping forward into the water.
Cross Beam and Dolphin Striker Since there is no center bow to mount the head stay and foresail, catamarans use a cross beam that connects the hull. A piece of rigging keeps this in place, and it’s called the dolphin striker. No dolphins were hurt in the rigging of these boats, however.
Anchor Bridle Instead of a single snubber line on the anchor, catamarans use a wide bridle that connects each hull bow to the anchor line.
Parts of a Sail Boat FAQs
What are parts of a sailboat called.
Sailing is a challenging hobby, and one reason it’s so difficult for beginners is because every part of a sailboat has its own name. From each wire and rope to every piece of deck hardware, a beginner must learn the basics before they can even start.
What is the front part of a sailboat called?
The front part of a sailboat is called the bow. Many boats also have a spar extending forward of the hull, called the bowsprit.
What are the 5 basic parts of every sailboat?
Every sailboat has at least these five parts, but most boats have many more. Hull Keel Rudder Rigging Sails
Matt has been boating around Florida for over 25 years in everything from small powerboats to large cruising catamarans. He currently lives aboard a 38-foot Cabo Rico sailboat with his wife Lucy and adventure dog Chelsea. Together, they cruise between winters in The Bahamas and summers in the Chesapeake Bay.
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.


Parts of a Sailboat

Last Updated by
Daniel Wade
September 28, 2022
Sailboats share many parts with other boats, such as keels, decks, and sometimes engines. But parts like halyards, sheets, and blocks are unique to sailboats.
Sailboats require four main parts to operate: a hull, mast, sail, and rudder. The hull is the body of the boat, and all other parts are directly or indirectly connected to it. The mast is a long pole that serves as a guide and mounting point for the sail. The sail catches the wind and propels the boat, and the rudder directs the boat and acts as its steering.
Here are all the main parts of a typical cruising sailboat , including hardware, lines, controls, cabin items, and a rundown of common sailing terminology.
Table of contents
Port, Starboard, Bow, Stem, and Stern
Before we get into the parts of a sailboat, let’s get a handle on sailboat direction. The bow of the boat is the front (forward), and the stern is the rear (aft). The stem is the forward-most part of the bow and determines its shape. These words describe the general area of front and back.
When determining port and starboard, picture looking down on the boat with the bow oriented forward. The port side is the left side of the boat, and the starboard is the right side. Now picture yourself at the controls of your boat.
If your lookout sees an obstacle off the port bow, which direction should you look? That’s right—the obstacle is forward and to the left of you. Now, we’ll go over the basic parts of a sailboat.
Basic Parts of a Sailboat
What are the basic parts of a sailboat? These are items that are essential to the operation of the boat and universal across most sailing craft. Every sailor should know where these parts are and what they do. Here are nine fundamental sailboat parts, their function, and why they’re important.
The hull is the ‘boat’ itself. It comprises the frame of the boat, the skin that keeps the water out and serves as the mounting point for everything else on the boat (both directly and indirectly). Simply put, if you punch a hole in the hull, water will come into the boat. Sailboat hulls are constructed most commonly out of fiberglass or hardwood (such as white oak), but some boat hulls are made out of aluminum, steel, and even a material called ferrocement.
The deck is the platform that covers the hull. It’s the place where you walk when you’re not inside the boat. Most people would consider the deck as any place ‘on top’ of the hull. The deck serves as a mounting point for essential boat hardware such as the mast and winches. We’ll get into those later; just think of the deck as the visible top area of the vessel. Decks are often made of fiberglass as well, but traditional boats use teak wood planking in this area. You’ll often find abrasive anti-slip material on the deck, as sailors often walk across it in wet conditions.
The keel is the structural backbone of the boat. It’s located in the bottom of the hull and serves as a sort of ‘spine’ to which all frame members are mounted during construction. The keel is an essential part of the boat and cannot be broken or damaged. You’ll often hear the term ‘keelboat’ in the sailing community. This word describes a sailboat with a long and deep keel, which is like a thin fin that runs the length of the hull. Keelboats are seaworthy vessels, as the elongated hull adds stability and keeps the boat on a straight track.
Centerboard
Many sailboats don’t have a long, deep keel, but they still need some sort of fin to keep the boat tracking straight. To substitute a long keel, many boats utilize a dagger-like board called a centerboard . This plate protrudes underneath the center of the boat, usually between one and three feet below the bottom of the hull. Centerboards are often retractable, which is great for towing and beaching. Centerboards are most common on small sailboats designed for inland or coastal cruising.
The cockpit is usually located in the rear of the boat. It features seating for the crew and controls for the steering, sails, and engine. The cockpit is the command center of the sailboat and often features storage lockers under the seats. Many cockpits are self-draining, which means they’re located above the water line and clear themselves of water accumulation. Some sailboats have enclosed cockpits for off-shore sailing. In a typical cruising sailboat , the cockpit usually takes up ⅓ of the total length of the boat or less.
The mast is the big pole extending from the deck of the sailboat. It connects the sail to the boat and serves as a frame for all sails carried by the vessel. The mast is a key part of the sail plan and helps determine what kind of boat you’re looking at. Most sailboats have just one mast, but others have numerous masts. A schooner, for example, has two masts and a specific sail plan. A yawl also has two, but each mast serves a separate function.
The rudder steers the boat and is located on or under the stern of the vessel. Rudders are an essential part of the boat, and they’re particularly sensitive to impact or misalignment. On some boats, the rudder is completely invisible when in the water. Other boats have retractable rudders for beaching or towing. Fundamentally, a rudder is just a plate that’s hinged to move side to side. It’s connected to the tiller or the helm, which we’ll cover in a bit.
The sail is what propels the boat, and most boats have more than one. The aft (rear) sail on a single-masted boat is called the mainsail , and it’s the largest of the two primary sails. The triangular forward (front) sail is called the jib, and it’s generally smaller than the mainsail. Other sails include the spinnaker, which is like a loosely-mounted parachute that flies in front of the boat during conditions of low wind.
The boom is a hinged rod that extends perpendicular to the mast. It’s mounted on the lower part of the mast, and it controls the side-to-side position of the mainsail. The best way to remember the boom is to consider what happens when it swings side to side. If you’re not paying attention, a swinging boom could give you a nice crack on the head. Think of the boom as the throttle of the boat. If you’re properly pointed relative to the wind, pulling in the boom will increase the speed of the boat. This is where the bottom of the sail connects to the mast. The boom is also connected to the deck and adjustable using a winch and a crank.
Here is some of the hardware you’ll find on a typical sailboat. These items are usually mounted to the hull, on the deck, or to the mast. Boat hardware consists of control systems and other items that are essential to the operation or integrity of the boat.
Cleats are the universal mounting points for ropes on the deck. Cleats are used for tying up to the dock, securing lines, and tethering important items that can’t fall overboard. There’s a special kind of knot called a ‘cleat knot,’ which is essential to learn before sailing. A properly tied cleat will stay secure in almost all conditions, and it’ll be easy to untie if the need arises. An important distinction must be made for clam cleats, which are spring-loaded sets of jaws that secure rigging lines that need to be adjusted frequently.
Block is a nautical word for a pulley. Blocks (pulleys) are everywhere on a sailboat, and they’re an essential part of the rigging system. Blocks distribute and regulate force. For example, a deck-mounted block can change the direction of a line from vertical to horizontal, allowing you to apply a horizontal force to lift something vertically. Blocks also reduce the force required to lift heavy loads and help make adjustments more precise.
Winches are cylindrical mechanical devices that transmit force. Winches are often located on either side of the boat. They’re multi-directional like a socket wrench and feature one-way locking mechanisms for raising, lowering, tightening, and loosening lines. Winches have a hole in the top for a crank, which makes it easy to wind rope in and out. Winches are present on almost every medium to large sailboat. They’re either manual or electrically-powered.
A hatch is a watertight or water-resistant door used to enter the cabin or storage compartment of a boat. Hatches can be flush with the deck and hinged, threaded like a large screw, or they can slide back and forth. The purpose of a hatch is to keep water out when closed and allow easy access to the interior parts of the boat.
Tiller and Helm
The tiller and helm are used to control the direction of the rudder and steer the boat. Usually, a boat has either a tiller or a helm. The tiller is the most basic steering control and consists of a simple rod connected to the rudder or rudder shaft. Tillers move side to side and point in the opposite direction that the boat steers. The helm is essentially a steering wheel, and it operates the same way that a car steering wheel does. The helm is connected to the rudder by complex mechanical or hydraulic linkage.
Mast and Sail Components
Mast and sail components are referred to as ‘rigging’ in most cases. These items are part of the wind-powered propulsion system of the boat. You’ll operate these systems to control the speed of the boat. Here are three common sail components that you’ll need to understand before hitting the water.
Stays are the lines that secure the mast to the boat. Usually, the mast is bolted or tied to the deck of the boat; but much of the load and pressure created by the wind is transferred to the stays. Stays are usually made of strong stainless steel cable. Losing a stay at sea is a serious problem, as these small cables keep the mast from collapsing.
Halyards are the ropes used to hoist and lower the sail on the mast. They also hoist flags, spars, and other components that need to be raised and lowered. Halyards are usually found on the mast and are fixed to cleats or winches around the boat.
Sheets and halyards are often confused, but they serve a very different function. Sheets are the control lines of the sail. These ropes control how far in or out the sail is, and they’re usually found connected to the jib (jib sheet) and the mainsail (mainsheet). Sheets are controlled by winches and blocks and secured onto cleats or clam cleats on the deck. Sheets can be controlled from the cockpit of the boat.
Navigation components are the parts of the sailboat used to find direction and alert other boats of your position. These four items aren’t the only navigation items found on sailboats, but they’re the most common.
This item should be self-explanatory, but it’s essential nonetheless. A compass is arguably the most basic and important marine navigation item. It shows you what direction you’re heading. Sailboat compasses are precise instruments designed to display an accurate heading no matter how much the boat rolls up and down or side to side. Compasses are usually mounted in the cockpit, in clear view of the captain.
Charts are old-fashioned navigational tools and indicate important information such as water depth and the location of ship channels. Learning to read and purchasing charts is essential, even in the age of modern GPS navigation. When all else fails, a chart can help guide you and your vessel to safety and away from hazardous areas. No electricity is required.
Navigation Lights
Navigation lights are mandatory beacons located around the boat. These lights help other boats figure out where you are and where you’re going. Sailboats are required to have red and green bow lights. Red indicates port, and green indicates starboard. This is how boats determine if they’re looking at your bow or stern. Other lights, such as a white stern light, a mast light, are also necessary during specific circumstances. Check your state requirements for lighting.
VHF radios are the standard marine over-the-air communication system. You can use a VHF radio to communicate with the coast guard, other boats, harbors, towing services, and drawbridges. It’s important to learn and write down the specific channels and call signs for each situation, as you need to be able to properly communicate on the radio.
The cabin is the ‘below decks’ area of the sailboat and usually contains living quarters for the captain and crew. Not all boats have cabins, and cabin size varies widely. Some sailboats have rudimentary cabins with basic sleeping accommodations and sitting headroom. Other boats have full standing headroom, shower and wash facilities, full-size kitchens, and separate staterooms for sleeping and sitting. The cabin is usually located forward of the cockpit. Here are some common sailboat parts located within the cabin.
The berth is the sleeping area of a boat. Berths are often convertible, which means they fold or rearrange into a table and seating area. There are numerous kinds of berths. The ‘V’ or ‘vee’ berth is a triangle-shaped sleeping area located in the bow of the boat. Side berths typically convert into couches or settees, and pole berths are essentially cots that roll up and stow away easily.
The bilge is the bottommost interior part of the boat. It’s usually located under the floor in the cabin. When water finds its way into the boat, it drains down to the bilge and gets pumped out by bilge pumps. Bilge pumps are an essential piece of hardware, as they keep the boat dry and prevent sinking. Some boats have a wet bilge, which means it’s always full of water (and supposed to be). Most boats have a dry bilge.
Portlights are watertight windows located in the upper part of the cabin. They can usually be opened or secured using threaded latches. Portlights are generally smaller than traditional portholes and offer a watertight barrier between the inside and outside of the cabin. They’re also useful for ventilation.
Gimballed Utilities
A gimbal is a special type of hinge that keeps an item vertical when the boat rolls. Oil lamps are commonly fitted to gimbals, so they stay upright when the boat bobs around. Stoves are also gimballed, which is extremely useful for cooking or boiling water when the weather gets rough.
Head is the nautical term for a toilet. Most medium-sized sailboats have compact wash facilities that sailors refer to as the ‘head,’ or a porta-potty at the bare minimum. A sailboat’s bathroom usually consists of a marine toilet, a sink, and often a shower with a drain in the floor.
Related Articles
I've personally had thousands of questions about sailing and sailboats over the years. As I learn and experience sailing, and the community, I share the answers that work and make sense to me, here on Life of Sailing.
by this author
Sailboat Parts
Learn About Sailboats
Most Recent

What Does "Sailing By The Lee" Mean?
October 3, 2023

The Best Sailing Schools And Programs: Reviews & Ratings
September 26, 2023
Important Legal Info
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies.
Similar Posts

Affordable Sailboats You Can Build at Home
September 13, 2023

Best Small Sailboat Ornaments
September 12, 2023

Discover the Magic of Hydrofoil Sailboats
December 11, 2023
Popular Posts

Best Liveaboard Catamaran Sailboats
December 28, 2023

Can a Novice Sail Around the World?
Elizabeth O'Malley
June 15, 2022

4 Best Electric Outboard Motors

How Long Did It Take The Vikings To Sail To England?

10 Best Sailboat Brands (And Why)
December 20, 2023

7 Best Places To Liveaboard A Sailboat
Get the best sailing content.
Top Rated Posts
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies. (866) 342-SAIL
© 2024 Life of Sailing Email: [email protected] Address: 11816 Inwood Rd #3024 Dallas, TX 75244 Disclaimer Privacy Policy
The simplest entrance to the world of sailing
Parts of a Sailboat – A Practical Overview
Main parts of a sailboat are explained for a Bermuda rigged sloop. This is the most widespread modern type of sailing boat and it is the boat type considered in this blog, as well as in Your First Sailing Handbook . For overview of other sailboat types and their classification see our post: Types of Sailboats .
The sloop normally sails with two sails: one mainsail and one foresail that is called a jib. Larger boats use an inboard engine, while smaller boats (usually shorter than 25 feet) may have an outboard engine. The engine drives the propeller providing thrust when sails are not used.

A typical sloop is shown in the figures below. The front part of a boat is called the bow, while the rear part is called the stern. A cockpit is a working area, towards the stern of a boat, from which the boat is steered and controlled. A boat is steered by turning the tiller which results in turning the rudder, since these two are connected with a shaft. When the rudder is turned off the centerline it makes the boat turn left or right. On bigger boats a steering wheel is used instead of a tiller. Forestay, backstay and shrouds are steel wires or rods that support the mast (collectively called standing rigging).
Some important lines are drawn in various colors in the figures below (see the legend where colors tell you which line is which). Halyards and topping lift are led to the top of the mast, then down through the mast; they exit the mast near the deck and are then directed to the cockpit as shown in the figures. Similarly, outhaul is led from the rear end of the boom, through the boom towards the mast and then to the cockpit. The main halyard and outhaul are used to stretch the mainsail, while the jib halyard is used for hoisting the jib. The topping lift supports the boom when the mainsail is not hoisted and it is run in the same way as the main halyard.
Mainsheet and vang are used to control the boom and the mainsail during sailing. Traveler and jib car are adjustable blocks running along tracks, through which sheets (mainsheet and jib sheets) are attached to the deck. Jib sheets are used to control the jib during sailing. All the above mentioned lines are collectively called running rigging.
Remark: The term rig comprises mast, boom, sails and rigging (both standing and running). A Bermuda rigged sloop may have different rig configurations.

All the lines running from the mast to the cockpit are led through the system of blocks and then through rope clutches, so that they can be put on the winches. Each line has its own clutch and each clutch has two positions: opened and closed. When the clutch is opened, the line can move freely in both directions. When the clutch is closed, the line can be pulled in only one direction (towards the cockpit), while the other direction is blocked. For example, pulling a halyard from the cockpit results in a sail being hoisted (a clutch is normally closed). To lower a sail, halyard must be eased (a clutch must be opened).
Winches facilitate tightening of the lines when they are under tension. Lines must always be put on the winch in the clockwise direction with a suitable number of turns. The stronger the force on the line, the more turns should be put on the winch. When the tension in the line becomes too strong to be pulled by hand, a handle is used.
Winches can be standard or self-tailing. They are both operated in the same way, except when using a handle. In this case, standard winches are best operated by two persons, i.e. one is tailing (pulling the free end of the line) while the other is turning the handle. On the other hand, self-tailing winches allow simple one-person operation, since they have self-tailing jaws. After the line has been put in these jaws, it is tailed automatically as the handle is being turned.

Vedran Bobanac
Vedran Bobanac has been sailing since the age of 10, while he has been working as a skipper and as a sailing instructor for almost 20 years now. He also holds PhD degree in electrical engineering and he enjoys using his technical knowledge, as well as pedagogical skills to teach sailing and publish sailing handbooks .
A Guide to the Different Parts of a Sailboat

Table of Contents
Last Updated on November 29, 2023 by Boatsetter Team
When you use Boatsetter, you have the opportunity to choose from a myriad of different sailboat rentals from all over the United States and beyond . A sailboat is a perfect way to relax on the water, either on a solo adventure or on an excursion with friends and family.
When you rent a sailboat with Boatsetter, you will have the option to book a captained sailboat to enjoy your day out on the water or book bareboat to hone your sailing skills. Either way, you may be interested in the intricacies of a sailboat and its different parts. If this sounds like you, you have come to the right place. In this article, we go in-depth about the different parts of a sailboat so that you can be more knowledgeable about whatever boat you may choose and come away from reading this feeling more confident about the whole sailing experience.
A basic sailboat is composed of at least 12 parts: the hull , the keel , the rudder , the mast, the mainsail, the boom, the kicking strap (boom vang), the topping lift, the jib, the spinnaker, the genoa, the backstay, and the forestay. Read all the way through for the definition of each sailboat part and to know how they work.
Explore sailboats for rent near you or wherever you want to go

In short, the hull is the watertight body of the ship or boat. There are different types of hulls that a sailboat may have, and these different hulls will often affect the speed and stability of the boat.
Displacement Hulls
Most sailboats have displacement hulls , like round bottom hulls, which move through the water by pushing water aside and are designed to cut through the water with very little propulsion. The reason these are called displacement hulls is that if you lower the boat into the water, some of the water moves out of the way to adjust for the boat, and if you could weigh the displayed water, you would find that it equals the weight of the boat, and that weight is the boat’s displacement. One thing to know about displacement hulls is that boats with these hulls are usually limited to slower speeds.
Planing Hull
Another type of hull is a planing hull. These hulls are designed to rise and glide on top of the water when enough power is supplied. When there is not enough power behind the boat, these boats often act as displacement hulls, such as when a boat is at rest. However, they climb to the surface of the water as they begin to move faster. Unlike the round bottom displacement hulls, these planing hulls will often have flat or v-shaped bottoms. These are very common with motor-driven water vessels, such as pontoon boats, but they can also be found on smaller sailboats which allow them to glide quickly over the water.
Finally, sailboats can differ depending on the number of hulls that they have. There are three options: monohulls (one hull), catamarans (two hulls), and trimarans (three hulls).
Monohulls , which have only a single hull, will usually be the typical round bottom displacement hull or occasionally the flat bottomed or v-shaped planning hull. Catamarans have two hulls with a deck or a trampoline in between, with the extra hulls providing increased stability. Finally, trimarans have three hulls — a main hull in the middle and two side hulls used for stability. These trimarans have gained popularity because of their excellent stability and ability to go at high speeds.
When evaluating a sailboat , it is important to pay attention to the type of hull that the boat has because the type of hull a sailboat has can drastically change the sailing experience, especially when it comes to stability and speed.
All sailboats have a keel, a flat blade sticking down into the water from the sailboat’s hull bottom. It has several functions: it provides counterbalance, life, controls sideways movement, holds the boat’s ballast , and helps prevent the boat from capsizing. When a boat leans from one side to the other, the keel and its ballast counteract the movement and prevent the boat from completely tipping over.
As with hulls, there are a number of different types of keels, though the two most common types of keels on recreational sailboats are the full keel or the fin keel. A full keel is larger than a fin keel and is much more stable. The full keel is generally half or more of the length of the sailboat. However, it is much slower than the fin keel. A fin keel, which is smaller than the full keel, offers less water resistance and therefore affords higher speeds.
A more recent feature on sailboats is the “winged keel,” which is short and shallow but carries a lot of weight in two “wings” that run sideways from the keel’s main part. Another more recent invention in sailing is the concept of the canting keels, which are designed to move the weight at the bottom of the sailboat to the upwind side. This invention allows the boat to carry more sails.
The Rudder
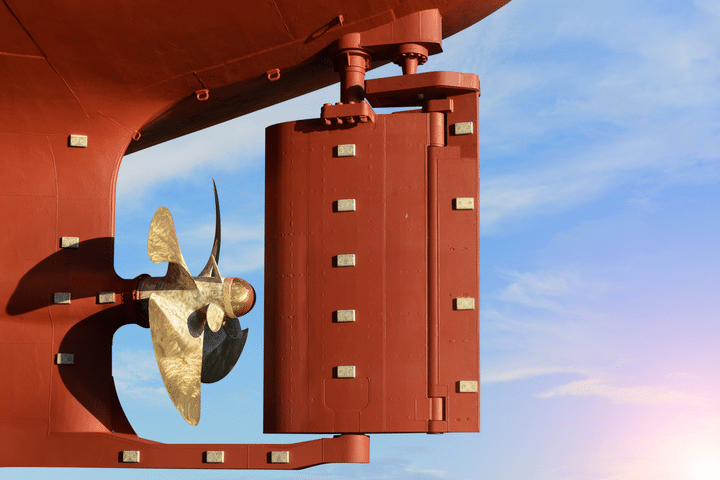
A rudder is the primary control surface used to steer a sailboat. A rudder is a vertical blade that is either attached to the flat surface of the boat’s stern (the back of the boat) or under the boat. The rudder works by deflecting water flow. When the person steering the boat turns the rudder, the water strikes it with increased force on one side and decreased force on the other, turning the boat in the direction of lower pressure.
On most smaller sailboats, the helmsman — the person steering the boat — uses a “ tiller ” to turn the rudder. The “tiller” is a stick made of wood or some type of metal attached to the top of the rudder. However, larger boats will generally use a wheel to steer the rudder since it provides greater leverage for turning the rudder, necessary for larger boats’ weight and water resistance.

The mast of a sailboat is a tall vertical pole that supports the sails. Larger ships often have multiple masts. The different types of masts are as follows:
(1) The Foremast — This is the first mast near the bow (front) of the boat, and it is the mast that is before the mainmast.
(2) The Mainmast — This is the tallest mast, usually located near the ship’s center.
(3) The Mizzen mast — This is the third mast closest to the stern (back), immediately in the back of the mainmast. It is always shorter than the mainmast and is typically shorter than the foremast.
The Main Sail
The mainsail is the principal sail on a sailboat, and it is set on the backside of the mainmast. It is the main source that propels the boat windward.

A boom is a spar (a pole made of wood or some other type of lightweight metal) along the bottom of a fore-and-aft rigged sail, which greatly improves the control of the angle and the shape of the sail, making it an indispensable tool for the navigation of the boat by controlling the sailes. The boom’s primary action is to keep the foot (bottom) of the sail flatter when the sail angle is away from the centerline of the sailboat.
The Kicking Strap (Boom Vang)
The boom vang is the line or piston system on a sailboat used to exert a downward force on the boom, enabling one to control the sail’s shape. The vang typically runs from the base of the mast to a point about a third of the way out the boom. It holds the boom down, enabling it to flatten the mainsail.
The Topping Lift
The topping lift is a line that is a part of the rigging on a sailboat, which applies an upward force on a spar (a pole) or a boom. Topping lifts are also used to hold a boom up when it’s sail is lowered. This line runs from the free end of the boom forward to the top of the mast. The line may run over a block at the top of the mast and down the deck to allow it to be adjusted.
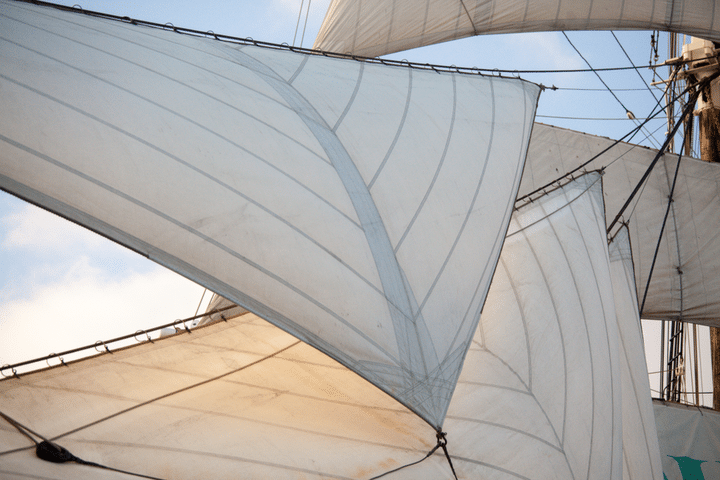

A jib is a triangular staysail set ahead of the foremost mast of a sailboat. Its tack is fixed to the bowsprit, the bow, or the deck between the bowsprit and the foremost mast. Jibs and spinnakers are the two main types of headsails on modern boats.
The Spinnaker
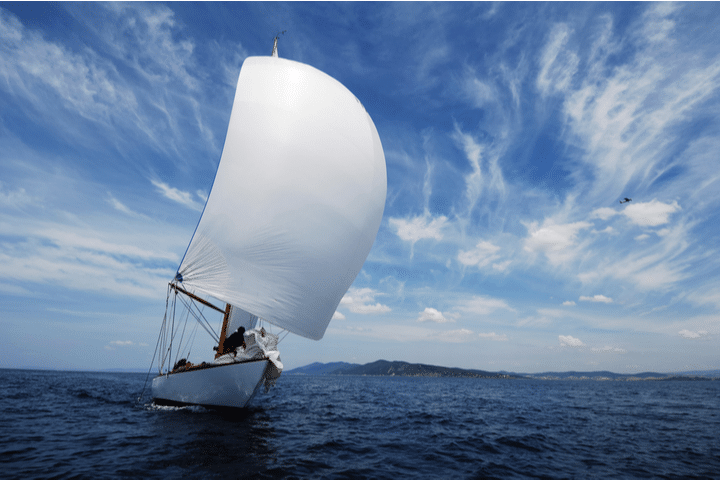

A spinnaker is a type of sail designed specifically for sailing off the wind from a reaching downwind course. The spinnaker fills up with wind and balloons out in front of the sailboat when it is deployed. This maneuver is called “flying.” The spinnaker is constructed of very lightweight material, such a nylon fabric and on many sailing vessels, it is very brightly colored.
Another name for the spinnaker is the “chute” because it often resembles a parachute, both in the material it is constructed from and its appearance when it is full of wind.
People often use the term genoa and jib as if they were the same thing, but there is a marked difference between these two types of sails. A job is no larger than a foretriangle, the triangular area formed by the mast, the deck or bowsprit, and the forestay. On the other hand, a genoa is larger than the jib, with part of the sail going past the mast and overlapping the mainsail. These two sails, however, serve very similar purposes.
The Backstay
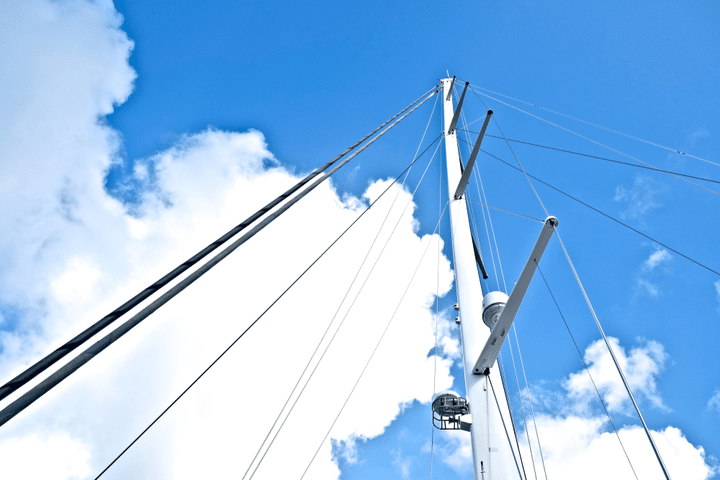

The backstay is a standing rigging that runs from the mast to the transom (the vertical section at the back of the boat), counteracting the forestay and the jib. The backstay is an important sail trip, control and directly affects the mainsail’s shape and the headsail.
There are two general categories of backstays:
1) A permanent backstay is attached to the top of the mast and may or may not be readily adjustable.
2) A running backstay is attached about two-thirds up the mast and sometimes at multiple locations along the mast. Most modern sailboats will have a permanent backstay, and some will have permanent backstays combined with a running backstay.
The Forestay

A forestay is a piece of standing rigging that keeps the mast from falling backward. It is attached at the very top of the mast, or at certain points near the top of the mast, with the other end of the forestay being attached to the bow (the front of the boat). Often a sail, such as a jib or a genoa, is attached to the forestay.
A forestay might be made from stainless steel wire, stainless steel rod or carbon rod, or galvanized wire or natural fibers.
Parts of a sail
Sails are vital for sailboats, made up of complex parts that improve performance and maneuverability. In this section, we’ll take a closer look at the different parts of that make up the sails.
Luff – The luff is a vertical sail part that maintains its shape and generates lift by interacting with the wind. It attaches securely with a bolt rope or luff tape for easy hoisting.
Leech – The leech controls air flow and reduces turbulence. Battens or leech lines are used to maintain shape and prevent fluttering.
Foot – The foot of a sail connects the luff and leech at the bottom edge. It helps define the sail’s shape and area. The outhaul is used to adjust its tension and shape.
Head – The sail’s head is where the luff and leech meet. It has a reinforced section for attaching the halyard to raise the sail.
Battens -The b attens are placed horizontally in sail pockets to maintain shape and optimize performance in varying wind conditions. They provide structural support from luff to leech.
Telltales – Sailors use telltales to adjust sail trim and ensure optimal performance.
Clew – The clew is important for shaping the sail and connecting the sheet, which regulates the angle and tension, producing energy. It’s located at the lower back corner of the sail.
Sailing is a favorite pastime for millions of Americans across the country. For some, there is nothing better than gliding across the water propelled by nothing more than the natural force of the wind alone. For both experienced and non-experienced sailors alike, Boatsetter is the perfect place to get your ideal sailboat rental from the mouthwatering Florida keys to the crystal blue waters of the Caribbean .
Smaller sailing boats are perfect for a single day out on the water, either by yourself or with friends and family. In comparison, larger sailing boats and sailing yachts can allow you days of luxury on longer excursions full of adventure and luxury.
Whatever your sailing dreams are, it is always good to know, for both the experienced sailor and the novice, all about the sailboat’s different parts. In this article, we learned all about the boat’s hull, the keel, the rudder, the mast, the mainsail, the boom, the kicking strap (boom vang), the topping lift, the jib, the spinnaker, the genoa, the backstay, and the forestay, which make up the basic parts of any sailboat you might find yourself on.
About us
Boatsetter is the go-to app for boat rentals and on-water experiences. Whatever the adventure, we’ve got a boat for that—Set sail , start the party , go yachting , make your trophy catch , and hone your watersports skills! Download the Boatsetter app ( App Store | Google Play ). Make sure to follow @boatsetter on Instagram, and tag us in all your boat day pictures for the chance to be featured.
Rent. List. Share—Only at Boatsetter

Boatsetter empowers people to explore with confidence by showing them a world of possibility on the water. Rent a boat, list your boat, or become a Boatsetter captain today.
Browse by experience

Explore articles

What does your boat's name say about you?

Trolling with Live or Dead Bait: 5 Tricks from Fishermen

App Update: Owner App 2.0

Float Away this Valentine's Day

The Main Parts of a Sailboat
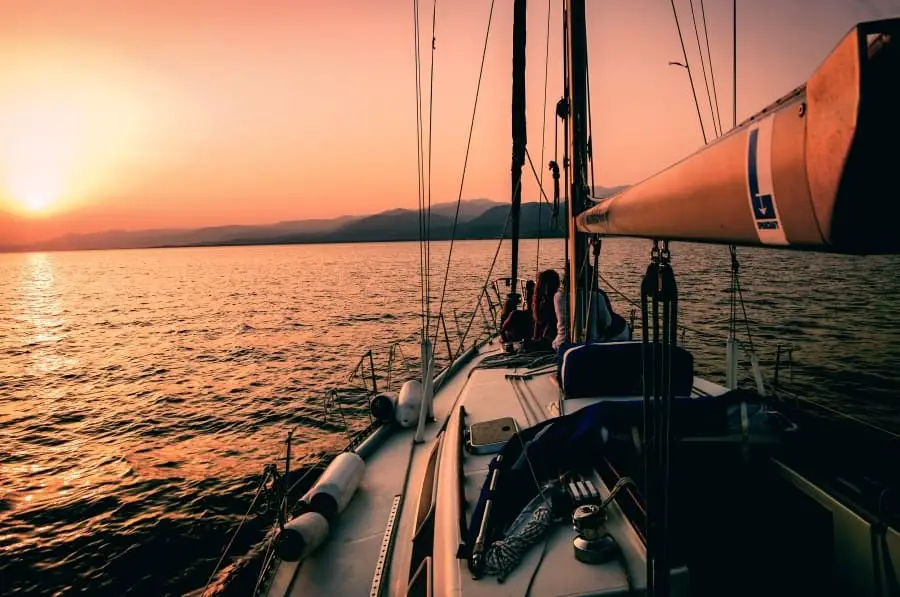

When I first learned how to sail, I couldn’t for the life of me remember all of the different terminology involved with sailing.
There are definitely a lot of different terms to memorize and they’re all important. In my opinion, one of the best ways to start improving your sailing vocabulary and general knowledge is to learn about the main parts of a sailboat.
So what are the main parts of a sailboat? The main parts of a sailboat include the hull, wheel/tiller, rudder, keel, mainsail, jib/headsail, mast, and boom. While there are many other important parts of a sailboat, these are the main parts that serve specific purposes that are vital for successfully operating a sailboat.
Learning about the main parts of a sailboat is going to allow you to better communicate with your skipper and fellow crew members when things need to get done.
Along with improving the communication among your team, it helps create a stronger bond between you and everyone else since you’ll all be on the same level of understanding.
On top of that, you get to learn more about one of the most exciting outdoor activities in the world!
Main Parts of a Sailboat
There are many different parts of a sailboat that serve specific purposes when out on the water, but there are several main parts that every captain and crew should be knowledgable in.
If you learn these eight main parts of a sailboat, you’ll have a strong foundation for the many other important parts of a sailboat.

One of the most important parts of a sailboat is the hull, which is the outer shell of the sailboat that’s directly in contact with the water.
The hull is important because it serves as a protective shell for all the internal components of a sailboat by keeping water out. This means a hull needs to not only be water resistant but strong enough to withstand beatings from other environmental elements.
The hull of a sailboat is always symmetrical and also helps properly channel the water it’s in contact with. This ensures that the sailboat is well balanced and reduces the drag well-enough to keep the sailboat moving along safely.
Sailboats have what are called displacement hulls, which require less power resulting in a longer cruising range and increased load carrying ability.
Wheel/Tiller
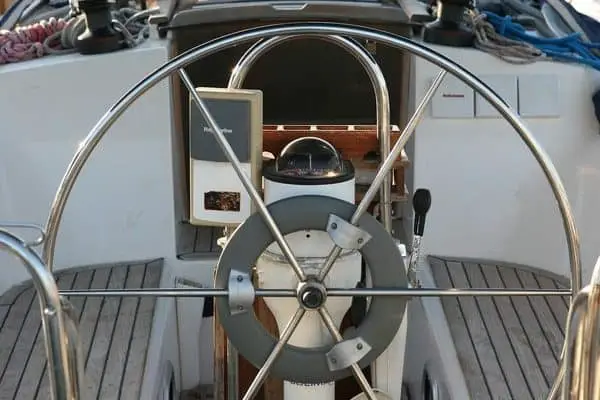

You might have already suspected that being able to steer a sailboat’s rather important, thus the inclusion of the wheel or tiller of a sailboat.
A wheel is most commonly found on sailboats while a tiller is often found on a dingy or rigid-inflatable boat (RIB). You’ll find either of these parts inside the hull at the stern, or back of the sailboat.
Both the wheel and tiller are directly attached to the rudder of the sailboat, which, as you might have suspected, controls the direction in which the sailboat goes.
It’s definitely the case when sailing that there’s a slight delay between moving the wheel or tiller and the boat actually making the directional change.
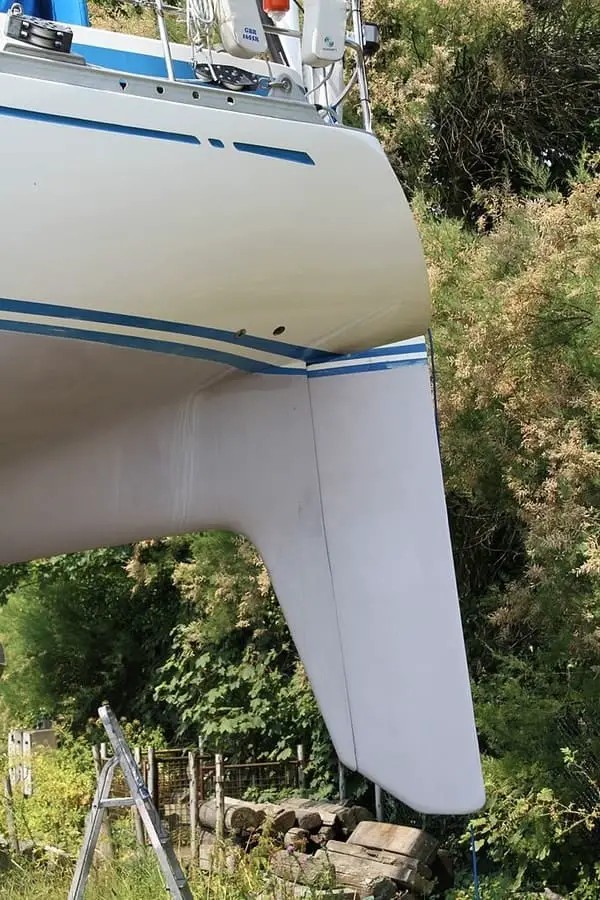

That piece of the sailboat that’s directly connected to the wheel or tiller is the rudder, which is the main part of a sailboat that controls the direction the sailboat will move.
The rudder sits underneath the stern directly in the water and acts as the “tire” of your sailboat. An automobile analogy to the wheel/tiller can be your car’s steering wheel and the rudder your car’s tire.
There are several types of rudders when looking at sailboats including the spade rudder, skeg rudder, and transom hung rudder. These different types of rudders serve different purposes and usually affect the type of keel as well as the shape of the hull.
The skeg rudder is the most common type of rudder nowadays due to it’s improved speed performance and thus more efficient.
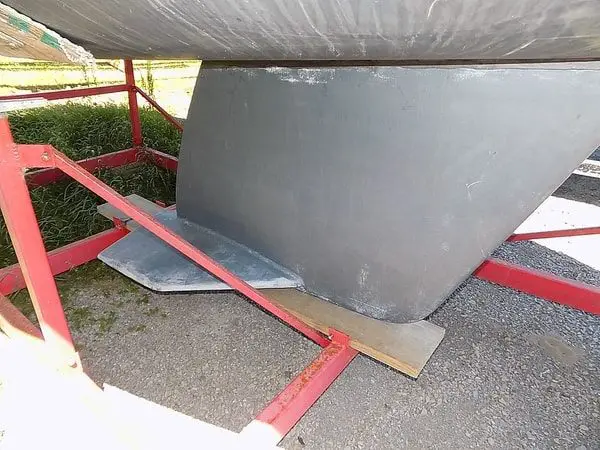

One of the most important main parts of a sailboat is the keel, which is a long plank that sticks out of the bottom of the sailboat’s hull. Think of it like a shark fin but underneath the shark.
The main job of a keel is to make sure that the correct balancing force underwater is kept so that the boat doesn’t tip over.
Apart from it providing a proper balance of the sailboat, the keel is also responsible for converting the sideways or angled wind captured by the sails into forward motion.
This also produces a lift effect which is why as the wind picks up the hull of the sailboat starts coming out of the water resulting in the sailboat increasing in speed.
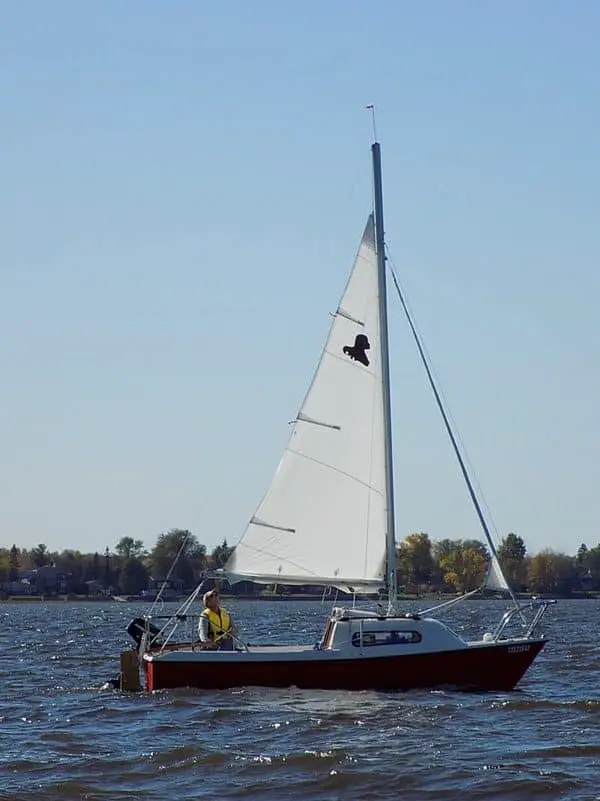

What’s a sailboat without some good wind in our sails? This probably should be on top of the list, but better late than never to mention the mainsail as being a main part of a sailboat .
The mainsail has the job of capturing the coming winds and translate that into forward propulsion. Similar to the wheel/tiller and rudder automobile analogies, you can think of the mainsail as your sailboat’s “engine”.
The mainsail is a tall, vertical heavy-duty fabric that’s held up by the mast and “pulled out” by the boom.
Being able to properly trim a sail allows you to capture the wind more efficiently and sail along more smoothly. Honestly, it’s very easy to dive into the specific parts of a mainsail itself since it’s such an important main part of a sailboat.
Headsail/Jib

The headsail, or jib, is another main part of a sailboat that provides further forward propulsion support along with the mainsail, but is generally smaller and placed at the front of the sailboat.
If you’re sailing along and the force of the wind starts to get rather intense, it’s quite common to trim the mainsail completely and solely rely on the headsail.
The headsail, being smaller than the mainsail, provides less power to the forward movement of a sailboat mainly due to it’s smaller surface area.
However, there are different types of headsails , like the Genoa jib, that are huge and are able to capture a massive amount of wind. There are also spinnakers which are commonly used on racing yachts for downwind sailing.

Have you ever wondered what that massive vertical pole was that sits in the middle of a sailboat?
Well, that’s the mast and is an important main part of a sailboat since it holds both the mainsail and headsail in place.
As you can imagine, the mast has to be particularly strong since it has to resist an immense amount of force produced by the wind hitting both sails.
Most sailboats have a single mast that holds both the mainsail and the headsail, but there are larger sailboats that have more than one mast to support a number of sails.
The mast is securely attached to the sailboat and can be seen going through the sailboat by a quick visit of the companionway, or cabin.

When you go out sailing, you know one of the most important facts to keep in mind is where that darn boom is located and if it’s going to give a good swing when tacking or jibing.
The boom is the horizontal spar directly connected to the mast and the mainsail, and controls the angle at which the mainsail is oriented.
The boom is rotated horizontally so that the mainsail is able to capture the optimal amount of wind depending on the chosen point of sail. Since wind can change at the drop of a hat, it’s common to adjust the boom to ensure the mainsail is shaped well-enough to properly capture the wind.
Other Important Parts of a Sailboat
It’s important that we covered the main parts of a sailboat in the previous sections since it helps to form an important foundation for any crew member.
However, there are a lot of other parts of a sailboat that are also important and serve important functions when out on the water.
The cockpit serves two purposes: it’s where the captain or crew member stands while steering the sailboat and it’s also where water that’s got inside the boat gets drained.
This is a good location to get a good view of the whole sailboat as well as the direction its moving.
The sheets of a sailboat are simply ropes used throughout the sailboat. Sheets are used in a number of scenarios, including trimming the sails, positioning the boom, and more.
The bow is simply the front part of a sailboat, which is where the headsail and anchor are also situated. It’s also often a nice location to lay or sit down when cruising along.
The stern is simply the back part of a sailboat, which is where the cockpit is located. If you’re sailing with a group of people, this is often the location where most people hang out, chat, and relax.
A pulpit is a metal frame protruding from the bow and stern of a sailboat that provides support to crew members when at either the bow or stern of the sailboat. The stern pulpits are often the “best seats in the house” when cruising along on a sailboat.
Stanchions are the vertical metal uprights surrounding the sailboat that hold up a protective rail to prevent anyone from falling overboard. They essentially provide the necessary support when grabbing onto the protective rails.
Companionway
The companionway is the stairway that leads from the deck down to the saloon. Washboards are commonly used to keep water from entering the saloon through the companionway.
The saloon, or cabin, is where the companionway leads to from the deck, which is considered the “living room” of the sailboat. It’s a great place to sit, play cards, eat meals, watch TV, and have a few late night drinks.
Get the very best sailing stuff straight to your inbox
Nomadic sailing.
At Nomadic Sailing, we're all about helping the community learn all there is to know about sailing. From learning how to sail to popular and lesser-known destinations to essential sailing gear and more.
Quick Links
Business address.
1200 Fourth Street #1141 Key West, FL 33040 United States
Copyright © 2024 Nomadic Sailing. All rights reserved. Nomadic Sailing is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means to earn fees by linking to Amazon.com and affiliated sites.


Parts of a Sailboat: The Definitive Guide
Sailing is a sport that has a lot of terms that may sound like a foreign language. Port, Starboard, beam, stern, bow, etc. Some of these terms, you might have heard of before, but many of them will be new to you.
Below Are Some Of The Most Basic Parts Of A Sailboat:
Below I have discussed some most basic parts of a sailboat that are found common in almost all kinds of sailboats.
Port side – This is the left side of the boat when viewed from the back of the boat looking forward.
Starboard side – This is the right side of the boat when viewed from the back of the boat looking forward.
Stern – This is the rear of the boat.
Bow – This is the front of the boat.
Beam – This is the widest point of the boat.
LOA – Length Overall – Length of the boat at its longest point. Most of the time, the boat is longer above the water than it is at the waterline and below.
Cockpit – This is the part of the boat where the crew sits when riding in the boat. This is usually in the rear of the boat but could be in the center, depending on the style of the boat.
Rudder – Located below the waterline and connected to the stern of the boat, this is used to make the boat turn. It is connected to either a steering wheel or a tiller. When the rudder is turned from side to side, it changes the angle that the water flows under the boat. This change in the direction of the water flow is what makes the boat turn.
Tiller – This is usually a wooden lever or arm that is connected to the rudder and allows you to turn the boat.
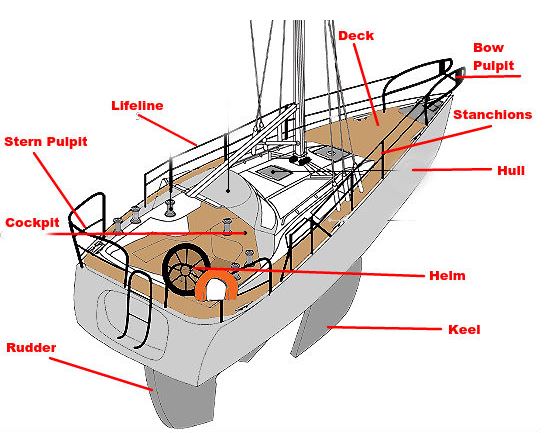
Helm – This is the area of the boat where the person who is piloting the boat is either sitting or standing.
Helmsman – The person that is piloting the boat and at the helm.
Steering wheel – This is connected to the rudder via cables or pulleys and is used in place of a tiller to steer the boat.
Hull – This is the entire body of the boat.
Deck – This is the flat surface on the top of the boat.
Keel – This is a fin connected to the bottom of the sailboat. The keel is weighted and provides a counterbalance to the sail and the wind blowing against the sail. Without this keel, the boat would tip over when the wind blew against it. The keel comes in many shapes and sizes and does several other important things to allow you to sail better, these will be covered in other posts.
Bow Pulpit – This is the metal tubing that surrounds the bow (front) of the boat.
Stern Pulpit – The metal tubing that surrounds the stern (rear) of the boat.
Lifeline – A wire cable running from the bow pulpit to the stern pulpit and connected to the deck in several different locations. This is a safety feature designed to keep people from falling off the deck of a sailboat.
Stanchions – Two-foot tall metal tubing that is used to connect the lifeline to the deck.
Some Specific Parts of a Sailboat
For this next part, I am going to talk about what is above the deck, the rigging. The rig includes the sails, the supporting cables, and everything that controls all of this. These are the parts of a sailboat that make it a sailboat and not just a mere boat.
Everything we went over, prior to this, had fairly normal, easy-to-remember names. Now we are going to learn about some more complicated sounding parts of a sailboat. Even though the names are complicated, it is stuff that you will use every time you sail, so it will be easy to remember. Ready? Great, let’s learn more!
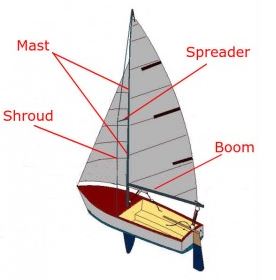
Mast – This is the main part of the sailboat that makes it look like a sailboat and also pretty much everything else is attached to it.
Boom – The horizontal beam that extends out from the mast towards the stern (rear) of the boat.
Standing Rigging – In order for the mast and the boom to remain upright, something has to hold it up. This is what the standing rigging does. Many of the cables that you see on a sailboat are only there to help hold the mast up.
Shrouds – These are the cables that run down the port (left) and starboard (right) side of the mast. These keep the mast from falling to the left or right. They are attached to the deck on the sides of the boat. Sometimes there are upper and lower shrouds, depending on the height of the mast.
Spreaders – These are attached to the mast about halfway down and push the shrouds out further than they would be if they were attached straight down to the deck. This provides a more effective angle of support for the shroud.
Chainplates – These are plates on the deck that provide a great anchor for the shrouds, and stays, to attach too. Without these, it would be hard to attach a cable to the deck and it not get ripped out.
Backstay – This is a wire cable that runs from the top of the mast to the stern (rear) of the boat. This keeps the mast from falling forward.
Forestay (aka Headstay) – This is a wire cable that runs from the top of the mast to the bow (front) of the boat. This keeps the mast from falling backward.

Mainsail – This is the large sail that is attached to the mast and the boom. This sail is usually the first sail raised and does the majority of the work when sailing.
Batten – These are either plastic, wood, or possibly fiberglass. They are inserted into pockets on the mainsail and are used to help shape the sail. We will discuss why the shape of the sail is important in another post.
Jib – This is a sail that is attached to the forestay (head stay). There are many different sizes of sails that can go on this forestay, depending on the type of sailing being done or the weather. This sail is a very important sail and is used almost as much as the mainsail.
Roller Furling Drum – This is a tube that fits over the forestay and one end of the jib is inserted inside it. This gives the sailor the ability to roll up the jib and wrap it around the forestay for storage. This is the easiest way to store the job when not in use. Some newer masts are actually using a similar system for the mainsail, but that is only for the newer boats.
Gooseneck – This is a turnbuckle that attaches the boom to the mast. The boom is not attached in a fixed manner, it uses this buckle to allow it to move around and be somewhat flexible. The problem with this is that it also allows the boom to be pulled up when the sail is full.
Boom Vang – This is a series of pulleys and ropes that are used to hold the boom down when the sail is full. This helps the gooseneck be flexible without allowing the boom to just fold up.
Boom Topping Lift – This is a wire cable that runs from the top of the mast all the way down the mainsail to the boom. It attaches to the end of the boom and keeps the boom from falling down. So the Boom Vang keeps the boom from going up and the Topping Lift keeps the boom from falling down.
Now you know a lot more about the rigging used on a sailboat. You can see that these terms are strange for a novice sailor to learn, but trust me, you get used to them, it just takes practice. There are more parts, but I want to go over those parts in more detail in other posts.
I know I was overloaded when I first went to training and wished I had spent more time learning these terms. Sailing class is much more fun when you can learn to sail and not have to worry about what they are talking about!
Do you have more to add about the parts of a sailboat or do you have a question about this post? Please leave a comment and make this post even better and more educational.
Related Posts

Nevertheless it was not until 2008 that the group received approval to refurbish and develop the resort. Greta Horst Boynton
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Parts of a Boat
http://images.google.com/imgres?imgurl=https://www.boat-ed.com/images/graphics/parts_vessel_sideview.gif&imgrefurl=https://www.boat-ed.com/fl/course/p1-3_boatparts.htm&usg=__EREt89uEWCgyZMqdsbi5ccWrNOo=&h=232&w=466&sz=25&hl=en&start=6&um=1&tbnid=TAXCxy7VRWnkfM:&tbnh=64&tbnw=128&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dparts%2Bof%2Ba%2Bboat%26hl%3Den%26rls%3Dcom.microsoft:en-us:IE-SearchBox%26rlz%3D1I7ADBS_en%26sa%3DX%26um%3D1

Join Our Newsletter!
Get community news, buying bargains, and how-to guides at your fingertips.
Parts of a Sailboat
The allure of sailing lies in the harmonious dance between wind and water, propelling sailboats on mesmerizing voyages across the open seas. However, before one can hoist the sails and embark on a maritime journey, it is essential to understand the intricacies of a sailboat’s anatomy.
In this article, we will delve into the captivating world of sailboats, unravelling the essential parts that compose these graceful vessels, allowing them to gracefully navigate the vast expanse of the ocean.
From the towering mast that reaches for the heavens to the delicate rigging that weaves the sails into the wind’s embrace, each component plays a vital role in the enchanting symphony of sailing. Whether you are an aspiring sailor or a seasoned mariner, join us on this enlightening voyage as we uncover the secrets behind the anatomy of a sailboat.
Hull and Deck

The hull of a sailboat is its foundational structure, serving as the backbone of the vessel. It is the part of the boat that interacts directly with the water, providing buoyancy and stability as it glides through the waves. Understanding the hull is essential for any sailing enthusiast, as it forms the basis of a sailboat’s design and performance.
The hull is typically made of a sturdy and watertight material, such as fiberglass, wood, aluminum, or even carbon fiber in high-performance racing boats. Its shape and design are carefully crafted to optimize the boat’s performance in different water conditions, ensuring a smooth and efficient sailing experience.
One of the primary functions of the hull is to provide buoyancy, allowing the boat to float on the water’s surface. It displaces water equal to its own weight, creating an upward force that keeps the boat afloat. This buoyancy is essential for the stability and safety of the sailboat.
Stability is another crucial aspect of the hull. Sailboats are designed to resist tipping over or capsizing, and the hull’s shape plays a significant role in achieving this stability. Sailboats can have either a monohull or a multihull design. Monohull sailboats have a single hull, while multihull sailboats, such as catamarans or trimarans, have two or more hulls. Each design has its advantages and characteristics, influencing the boat’s stability, speed, and comfort.
In addition to providing buoyancy and stability, the hull also houses various compartments and storage areas, including the cabin, where sailors can find shelter and accommodation during longer journeys. The deck, which is the upper surface of the hull, provides a platform for crew members to move around and perform various tasks while aboard the sailboat.
The hull and deck work together harmoniously to create a seaworthy vessel, capable of withstanding the forces of wind and waves. Whether you’re a seasoned sailor or a curious novice, understanding the importance of the hull is the first step toward unlocking the secrets of sailing and embracing the wonders of the open water.
What are the different hull types, such as monohull and catamaran, and their characteristics?
When it comes to sailboats, there are different hull types to choose from, each with its own unique characteristics and advantages. The two main types of sailboat hulls are monohull and catamaran. Let’s explore these hull types and their distinguishing features:
Monohull sailboats have a single hull, which is a single, continuous structure that runs from bow to stern. Monohulls are the most common type of sailboats and have been used for centuries. They offer several advantages:
- Versatility: Monohulls are versatile and well-suited for various sailing conditions, from calm coastal waters to rough offshore passages.
- Excellent upwind performance: Monohulls generally perform well when sailing upwind due to their ability to cut through the water and tack efficiently.
- Comfortable heeling: Monohulls have a natural tendency to heel, or lean to one side, which some sailors find enjoyable and exhilarating.
- Ample storage space: Monohulls often provide more interior space, including cabins, galleys, and storage compartments, making them suitable for longer journeys or living aboard.
Catamaran:
Catamarans have two hulls connected by a bridge or deck, creating a wide and stable platform. Catamarans have gained popularity in recent years, particularly for cruising and charter purposes. Here are some key characteristics:
- Stability: Catamarans offer exceptional stability, both at anchor and underway. The wider platform reduces heeling and provides a more comfortable experience, particularly for those prone to seasickness.
- Spaciousness: Catamarans generally have a larger interior living space, including multiple cabins, saloons, and outdoor areas. This extra space makes them popular for long-term cruising and leisure activities.
- Shallow draft: Catamarans have a shallower draft compared to monohulls, allowing them to navigate in shallower waters and access anchorages that may be inaccessible to deeper-draft boats.
- Speed potential: Due to their design and reduced drag, catamarans can achieve higher speeds, particularly reaching or running with the wind. This makes them popular among performance-oriented sailors.
Both monohulls and catamarans have their merits and are suitable for different sailing preferences and conditions. Ultimately, the choice between them depends on factors such as personal preferences, intended use (racing, cruising, chartering), and the specific requirements of your sailing adventures.
Whichever hull type you choose, the hull is the backbone of your sailboat, providing stability, buoyancy, and the foundation for an enjoyable and safe sailing experience.
What is the purpose and features of the deck?
The deck of a sailboat is the horizontal surface that covers the top of the hull. It serves several important purposes and is designed with various features to enhance functionality and safety. Let’s explore the purpose and key features of the deck:
- Cockpit: The cockpit is a designated area on the deck where the helmsperson controls the sailboat. It typically includes a steering wheel or tiller, compass, and various controls for sails, such as sheets and halyards. The cockpit provides a comfortable and secure space for the helmsperson to maneuver the boat and adjust while maintaining a clear view of the surroundings.
- Hatches: Hatches are openings on the deck that provide access to the interior compartments of the sailboat. They allow for ventilation, natural light, and access to storage areas, cabins, and engine compartments. Hatches are typically fitted with watertight seals to prevent water from entering the boat in rough seas or during heavy rain.
- Winches: Winches are mechanical devices mounted on the deck used to handle lines (ropes) on a sailboat. They provide mechanical advantage and make it easier to control and adjust the tension of the sails. Winches are commonly used for raising and trimming sails, adjusting the tension of halyards, and controlling the position of lines such as sheets and reefing lines.
- Cleats and Clutches: Cleats and clutches are deck fittings used to secure lines in place. Cleats are usually metal or plastic fixtures with two or more horns where lines can be wrapped or tied off to keep them secure. Clutches are cam-shaped devices that grip lines when engaged, allowing for easy adjustment and locking of lines without the need for tying knots.
- Toe Rails and Lifelines: Toe rails are raised ridges or rails running along the edge of the deck, primarily designed to provide foot support and prevent crew members from slipping overboard. Lifelines are horizontal safety lines that run along the perimeter of the deck, usually supported by stanchions. They serve as a barrier and help prevent crew members from falling off the boat.
Other deck features may include cleats, padeyes (attachment points for lines and hardware), handrails for stability, and various equipment for anchoring, such as anchor rollers and windlasses.
The deck is an essential component of a sailboat, providing a safe and functional platform for the crew. Its design and features are carefully considered to ensure comfort, control, and accessibility during sailing adventures.
Mast and Rigging

The mast is a fundamental component of a sailboat, serving as the vertical structure that supports the sails and plays a crucial role in the propulsion of the boat. Let’s delve into the characteristics and functions of the mast:
- Structure and Material: The mast is typically a tall, vertical spar made of materials such as aluminum, carbon fiber, or wood. It is designed to withstand the forces exerted by the wind on the sails and transfer them to the hull.
- Height and Length: The height and length of the mast can vary depending on the size and type of sailboat. Larger sailboats generally have taller masts to accommodate larger sail areas and provide more power and speed. Smaller sailboats, like dinghies or day sailors, have shorter masts.
- Step: The mast is stepped or secured at the bottom to the deck or keel of the sailboat. The step provides stability and ensures that the mast remains in an upright position.
- Spreaders: Spreaders are horizontal crossbars attached to the mast to prevent it from bending excessively under the pressure of the sails. They also help maintain the correct angle and shape of the shrouds (rigging wires that support the mast from the sides) and aid in distributing the forces evenly.
- Masthead and Headboard: The masthead is the topmost part of the mast, where various components, such as the sheaves for halyards (lines used to raise and lower sails) and the attachment point for the forestay (rigging wire that supports the front of the mast), are located. The headboard is a plate or fitting attached to the top of the mainsail, which slides into a track on the mast and helps secure the sail in position.
- Mast Tracks: Mast tracks are vertical grooves or slots running along the front of the mast. They allow the sails to be raised, lowered, and adjusted to different heights by means of halyards and sail slides.
The mast, along with its accompanying rigging, is an integral part of a sailboat’s propulsion system. It provides support for the sails, allowing them to capture the energy of the wind and transfer it into forward motion. The mast’s height, step, spreaders, and other components work together to ensure stability, proper sail shape, and efficient power transfer, contributing to the sailboat’s performance and maneuverability.
Let’s explore the various types of masts commonly found on sailboats:
Single-masted:.
- Single-masted rigs are the most common and versatile type of sailboat rigging. They feature a single mast that rises vertically from the deck.
- Single-masted rigs can support a variety of sail configurations, including a mainsail and one or more headsails (jibs or genoas).
- This rig is suitable for different types of sailboats, ranging from small day sailors to larger cruising and racing vessels.
Double-Masted:
- Double-masted rigs, also known as ketch or yawl rigs, consist of two masts: a main mast and a smaller mizzen mast located aft of the main mast.
- The mizzen mast is shorter than the main mast and is often positioned near the stern.
- Double-masted rigs provide additional sail area and flexibility in sail combinations, allowing for better balance and maneuverability.
- These rigs are commonly found on cruising sailboats and can handle a wide range of wind conditions.
Fractional Rigs:
- Fractional rigs are characterized by a mast that is shorter than the boat’s overall length.
- The mast is positioned further aft, and the forestay (rigging wire that supports the front of the mast) is attached at a point lower than the masthead.
- Fractional rigs offer increased control and versatility, making them popular on performance-oriented sailboats and racing yachts.
- They allow for easy adjustment of sail shape and balance, optimizing performance in different wind conditions.
Each type of rig offers its own advantages and characteristics. Single-masted rigs are versatile and suitable for various sailing applications. Double-masted rigs provide additional sail area and enhance maneuverability. Fractional rigs offer enhanced control and performance for competitive sailing. The choice of rig type depends on factors such as the boat’s size, intended use, and personal preferences of the sailor.
It’s important to note that there are additional rig variations beyond the ones mentioned here, including schooners, sloops, cutters, and more. Each rig type has its own unique features, and sailors often select the rig that best suits their sailing style, preferences, and the specific demands of their sailing adventures.
What are the key rigging components such as shrouds, stays, halyards, and sheets, and their functions?
Rigging refers to the network of wires, lines, and fittings that hold and control the sails on a sailboat. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the mast and ensuring efficient sail handling. Let’s take a closer look at the components of rigging:
- Shrouds: Shrouds are thick stainless-steel wires or cables that extend from the mast to the sides of the boat. They provide lateral support and prevent excessive side-to-side movement of the mast. Shrouds help maintain the integrity and stability of the mast.
- Stays: Stays are like shrouds but are positioned fore and aft to control the forward and backward movement of the mast. The forestay is a forward-facing stay that connects the mast to the bow of the boat. Backstays, or backstay in the case of a single-masted rig, connect the top of the mast to the stern of the boat. Stays help counterbalance the forces exerted by the sails and provide additional support and stability to the mast.
- Halyards: Halyards are lines (ropes) used to raise and lower the sails. They are typically attached to the head (top) of the sails and run through pulleys or blocks. The main halyard is used to raise the mainsail, while jib halyards are used for headsails. Spinnaker halyards are used for spinnaker sails. By adjusting the tension of the halyards, sailors can control the position and shape of the sails.
- Sheets: Sheets are lines used to control the trim and shape of the sails. They are attached to the clew (lower aft corner) of the sails and run through blocks or winches. The mainsheet controls the mainsail, while jib sheets control the headsails. Spinnaker sheets are used for controlling spinnaker sails. By adjusting the tension and angle of the sheets, sailors can optimize the sail shape and adjust the power and efficiency of the sails.
- Blocks and Pulleys: Blocks and pulleys are essential components of the rigging system. They consist of one or more grooved wheels with a central axle. Lines are threaded through these wheels to change the direction and increase mechanical advantage when tensioning or releasing the rigging. Blocks and pulleys allow for smooth and efficient movement of the lines and reduce the effort required to control the sails.
These rigging components work together to hold and control the sails, allowing sailors to adjust their position, shape, and tension. By manipulating the shrouds, stays, halyards, and sheets, sailors can optimize the performance of their sailboat and adapt to changing wind conditions. Understanding and effectively using the rigging is crucial for safe and efficient sail handling.
Sails and Sail Controls
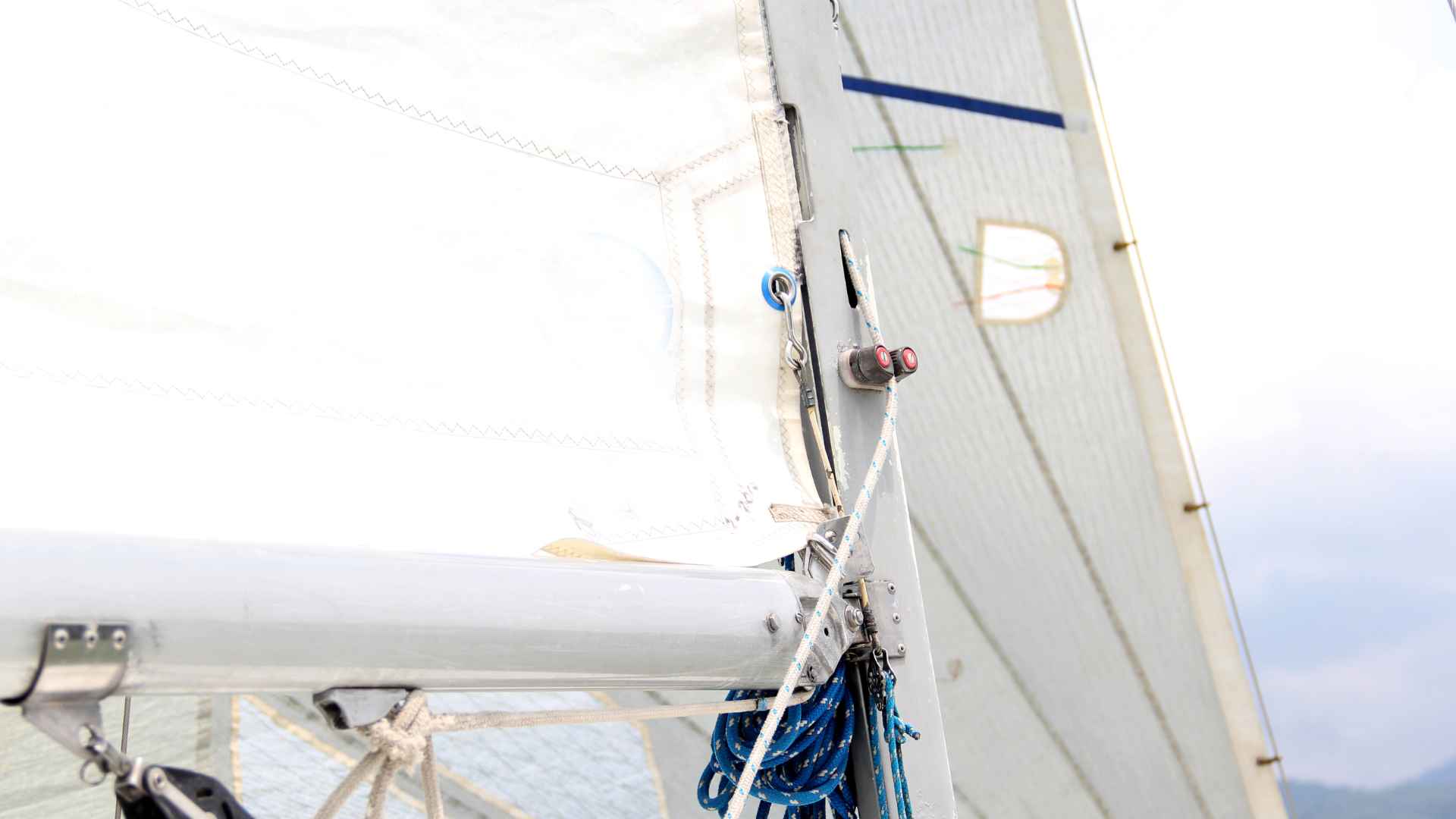

Sails, with their billowing canvas catching the wind, are the beating heart of a sailboat. They serve as the primary means of propulsion, transforming the invisible force of the wind into forward motion. The elegance and power of sails have allowed sailors to explore the world’s oceans for centuries, harnessing nature’s energy to embark on incredible journeys.
Sails come in various shapes and sizes, each designed to suit different sailing conditions and purposes. The mainsail is the largest and most significant sail, typically positioned behind the mast. It captures the wind from behind the boat and drives the vessel forward. Attached to the mast and boom, the mainsail can be adjusted to optimize its shape and angle to the wind, maximizing the boat’s speed and efficiency.
In addition to the mainsail, sailboats often have headsails, such as jibs or genoas, located near the bow of the boat. Headsails are smaller and more maneuverable than the mainsail, enhancing the sailboat’s performance and allowing it to sail closer to the wind. These sails are typically used in conjunction with the mainsail to provide additional power and control.
Specialty sails, such as spinnakers, are designed for specific sailing conditions and maneuvers. Spinnakers are large, colorful sails shaped like a balloon, which are used when sailing downwind or on a broad reach. They capture the wind from the front of the boat, significantly increasing the sail area and generating extra speed.
Sail controls play a vital role in managing the position, shape, and trim of the sails. Sail controls include various systems and mechanisms that allow sailors to adjust the sails to achieve optimal performance. These controls can include:
- Boom: The boom is a horizontal spar that extends aft from the mast and supports the foot (lower edge) of the mainsail. It helps control the shape and position of the sail.
- Traveler: The traveler is a movable track mounted on the deck or cockpit. It allows for lateral movement of the mainsheet and helps control the angle of the mainsail relative to the boat’s centerline.
- Cunningham: The cunningham is a control line attached to the luff (leading edge) of the mainsail. It allows sailors to tension the sail’s luff, flattening the sail and reducing its draft in stronger winds.
- Outhaul: The outhaul is a control line that adjusts the tension along the foot of the mainsail. By adjusting the outhaul, sailors can control the depth and shape of the sail.
- Reefing System: Reefing systems are used to reduce the area of the sails in strong winds. They allow sailors to partially lower or roll up the sails, reducing their overall size and power.
By skillfully adjusting these sail controls, sailors can optimize the shape, angle, and power of their sails, enabling them to sail efficiently, maintain control in varying wind conditions, and extract maximum speed from their sailboat.
Sails are not only functional but also beautiful, filling the horizon with their graceful forms. They capture the spirit of adventure, freedom, and the timeless allure of the sea. Understanding the intricacies of sails and their controls is essential for harnessing the wind’s power and unlocking the full potential of a sailboat’s performance.
Steering and Navigation
Steering a sailboat and navigating the waters require a combination of skill, knowledge, and the right equipment. Let’s explore the steering system, the role of the rudder, and the essential navigation instruments used on sailboats.
The steering system of a sailboat allows the helmsperson to control the direction of the boat. Depending on the boat’s design, you will find either a tiller or a wheel as the primary steering mechanism. The tiller is a long handle connected directly to the rudder, while the wheel is a circular device linked to a steering mechanism that transfers the movement to the rudder. By manipulating the tiller or turning the wheel, the helmsperson can steer the sailboat left or right, adjusting its course according to the wind and navigational needs.
The rudder, located beneath the waterline at the stern of the sailboat, plays a crucial role in maneuvering the boat. It is a vertical or horizontal fin-like structure that can be rotated from side to side. When the helmsperson steers the boat, the rudder responds, creating resistance against the water and redirecting the boat’s movement. By adjusting the angle of the rudder, the helmsperson can control the boat’s heading, making it possible to tack (change direction across the wind) or jibe (change direction with the wind from behind). The rudder is a fundamental component of sailboat control and is critical for maintaining stability and maneuverability.
In addition to steering, navigation instruments and equipment are essential for safe passage on the water. Here are a few key tools commonly found on sailboats:
- Compass: A compass is a navigational instrument that indicates the boat’s heading in relation to magnetic north. It provides a reliable reference point for maintaining a desired course and navigating with accuracy, even in the absence of electronic devices.
- GPS (Global Positioning System): GPS is a satellite-based navigation system that allows sailors to determine their precise location on the earth’s surface. GPS units on sailboats provide real-time positioning, speed, and course information, enhancing navigational accuracy and safety.
- Depth Sounder: A depth sounder, also known as a depth finder or echo sounder, measures the depth of the water beneath the sailboat. It helps sailors avoid shallow areas or underwater hazards, ensuring safe navigation.
- Charts: Nautical charts are maps specifically designed for navigation on the water. They provide important information about water depths, navigational aids, landmarks, and other details essential for planning and following a safe course. Charts are still a valuable tool, even with the advent of electronic navigation systems.
These are just a few examples of the many navigation instruments and equipment available to sailors. Depending on the complexity of the sailboat and the navigational requirements, additional tools such as radar, AIS ( Automatic Identification System ), wind instruments, and electronic chart plotters can also be found onboard.
Steering the sailboat and navigating the waters require a combination of traditional seamanship skills and modern technology. By mastering the steering system, understanding the role of the rudder, and utilizing navigation instruments effectively, sailors can confidently explore the seas, navigate challenging environments, and reach their destinations safely and efficiently.
Auxiliary Power and Safety Equipment
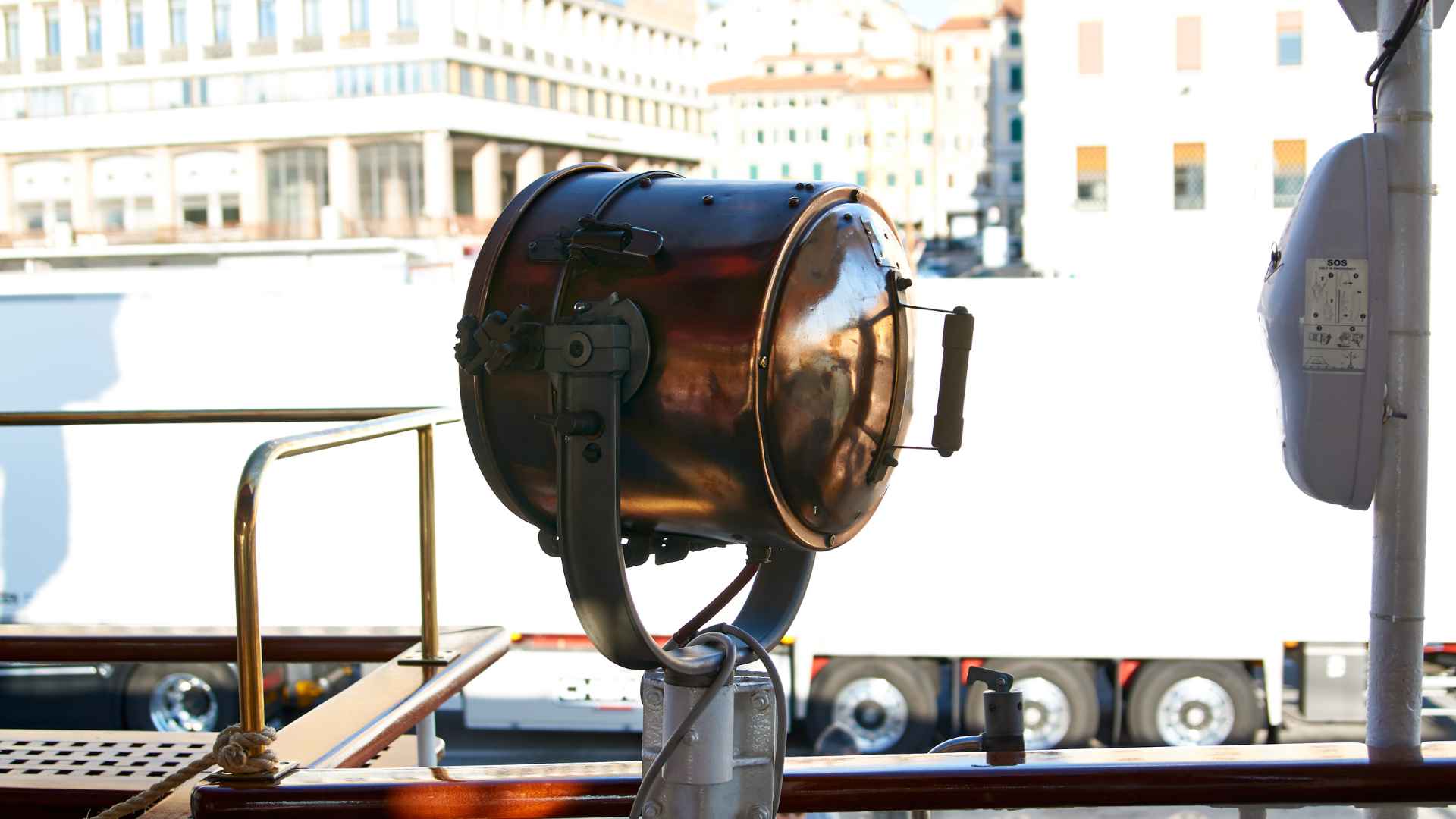

While sailboats primarily rely on the power of the wind to propel them, many sailboats are equipped with auxiliary power systems to provide additional maneuverability when needed. These auxiliary power systems typically consist of either an inboard or outboard engine.
An inboard engine is integrated into the hull of the sailboat and is positioned below deck. It offers advantages such as increased power, better fuel efficiency, and reduced noise compared to outboard engines. Inboard engines are typically larger and provide more torque, making them suitable for larger sailboats or those that frequently navigate in challenging conditions or against strong currents.
On the other hand, outboard engines are portable and mounted externally on the stern of the sailboat. They are versatile, lightweight, and easy to maintain. Outboard engines are popular among smaller sailboats or those that require occasional motorized propulsion.
The auxiliary power system, whether inboard or outboard, serves as a backup when wind conditions are light or during precise maneuvers in tight spaces, such as docking or maneuvering in crowded marinas. It provides sailors with increased control and helps ensure the safety of the vessel and its occupants in situations where sail power alone may be insufficient.
In addition to auxiliary power, ensuring the presence of proper safety equipment is crucial for any sailboat. Safety equipment helps to mitigate risks and ensure the well-being of everyone on board. Here are some essential safety items that should be present on a sailboat:
- Life jackets: Every person on board should have access to a properly fitting life jacket or personal flotation device (PFD). Life jackets are designed to keep individuals afloat and provide buoyancy in case of accidental falls overboard or emergencies.
- Fire extinguishers: Sailboats should be equipped with fire extinguishers suitable for extinguishing different types of fires. It’s important to have them readily accessible in case of a fire onboard.
- Distress signals: Distress signals, such as flares or electronic signaling devices, are crucial for attracting attention and signaling distress in emergency situations. These signals can aid in alerting nearby vessels or rescue services for assistance.
- Navigation lights: Sailboats must have properly functioning navigation lights, especially when operating during low visibility conditions or at night. Navigation lights allow other vessels to identify the sailboat’s position and determine the direction it is heading.
Complying with boating regulations regarding safety equipment is not only a legal requirement but also crucial for the well-being and security of everyone on board. It is essential to regularly inspect and maintain safety equipment to ensure it is in proper working condition and easily accessible in case of an emergency.
By understanding the role of auxiliary power systems and prioritizing the presence of essential safety equipment, sailors can navigate with confidence, knowing they have the necessary resources to handle various situations that may arise during their sailing adventures.
As we continue our journey through the anatomy of a sailboat, we uncover more elements that contribute to the joy and safety of sailing. Join us as we delve further into the intricacies of sailboat components and explore the secrets that make sailing a remarkable and secure experience.
Watch Parts of the boat and what they do | Video
Top 5 FAQs and answers related to What are the parts of a sailboat
What is the purpose of the mast on a sailboat .
The mast is the tall vertical structure on a sailboat that supports the sails. Its main purpose is to capture and harness the power of the wind, providing propulsion to the sailboat.
What are the different types of sails on a sailboat?
Sailboats have various types of sails, including the mainsail, headsail (jib/genoa), and specialty sails like spinnakers. The mainsail is the primary sail attached to the main mast, while the headsail is located at the front of the boat. Spinnakers are large, lightweight sails used for sailing downwind.
What are some important sail controls on a sailboat?
Sail controls play a crucial role in adjusting the shape and angle of the sails for optimal performance. Key sail controls include the boom, traveler, cunningham, outhaul, and reefing systems. The boom holds the foot of the mainsail, while the traveler allows sideways movement of the boom. The cunningham, outhaul, and reefing systems help control the tension and shape of the sails.
What is the purpose of the rudder on a sailboat?
The rudder is a vital component located beneath the waterline at the stern of the sailboat. Its primary purpose is to steer and maneuver the sailboat by redirecting the flow of water, allowing the helmsperson to control the direction of the boat.
What safety equipment should be on a sailboat?
Essential safety equipment on a sailboat includes life jackets or personal flotation devices (PFDs) for all passengers, fire extinguishers, distress signals such as flares or electronic signaling devices, and navigation lights. These items help ensure the safety of the crew and comply with boating regulations.

Understanding the various parts of a sailboat is fundamental to appreciating the art and science of sailing. From the sturdy hull and towering mast to the intricate rigging, sails, and navigation equipment, each component plays a vital role in the operation and performance of a sailboat.
We have explored the different types of hulls, the significance of the mast and rigging, and the versatility of sails and sail controls. We have also touched upon the importance of steering systems, the role of the rudder, and the essential safety equipment necessary for a safe and enjoyable sailing experience.
By recognizing the interconnectedness of these parts, we gain a deeper appreciation for the synergy between wind, water, and the intricate machinery of a sailboat. The thrill of harnessing the wind and propelling a vessel through the water becomes all the more captivating.
Whether you aspire to be a sailor, are already familiar with sailboats, or simply have a curiosity for the sea, there is always more to learn and discover. Dive into the world of sailing, explore the intricacies of sailboat design, and embrace the countless adventures that await on the open water.
So, hoist your sails, trim your sheets, and set a course for a lifetime of discovery. Let the wind guide you as you embark on your own sailing journey, where the beauty of nature and the art of sailing unite in a symphony of motion and tranquility.
Share What Are the Parts of a Sailboat and What They Do? Guide with your friends and Leave a comment below with your thoughts.
Read Is Boat Insurance Required in Michigan: Boat Owners Guide until we meet in the next article.
Similar Posts

New York Mills Lund Boats: “World’s Finest Fishing Boats”
Nestled in the heart of Minnesota lake country lies New York Mills, a small town with a big claim to fame: Lund Boats. For over 75 years, Lund has been synonymous with top-quality, innovative aluminum fishing boats, revered by anglers worldwide. A Legacy Built on Quality The story of Lund Boats begins in 1947 with…

Are Key West 239FS Boats Good & Reliable Enough to Own?
With their distinctive lines and reputation for versatility, Key West 239FS boats often tempt both seasoned captains and recreational boaters seeking fun and adventure on the water. But before casting off with a Key West, let’s navigate the choppy waters of reputation and reality, asking the crucial question: are Key West 239FS boats good and…

How to Fix Leaky Rivets in an Aluminium Boat: Stepwise Guide
Leaky rivets can be a frustrating issue for owners of Aluminium boats, affecting both the boating experience and safety on the water. It’s essential to address this problem promptly to prevent further damage and ensure a watertight vessel. In this comprehensive guide, we will provide you with the necessary steps and techniques to effectively fix…

20 Gallon Pontoon Gas Tank: All You Need to Know
Pontoon boats are beloved for their spacious decks, comfortable seating, and overall fun factor. But unlike their sleek cousins, center consoles and fishing boats, pontoons typically have limited built-in fuel storage. Here’s where the 20-gallon pontoon gas tank comes in. It offers a compact and efficient solution to extend your cruising range without sacrificing valuable…

Unveiling the Story of Terry Bass Boats: Guide
For bass fishing enthusiasts of a certain era, the name Terry Bass Boats evokes a sense of nostalgia and admiration. These meticulously crafted vessels carved their niche in the bass boat market during the mid-20th century, renowned for their innovative design, exceptional performance, and unwavering dedication to the angler’s experience. Today, we delve into the…

Used Boats for Sale Portland Oregon: Guide
Portland, Oregon, with its access to the Willamette River, Columbia River Gorge, and numerous lakes, is a haven for boating enthusiasts. If you’re dreaming of exploring the scenic waterways or enjoying a day of fishing or wakeboarding, buying a used boat can be a fantastic option. It allows you to experience the joys of boating…

Sailboats Explained
"...let us tell you the story of a sailing boat..."
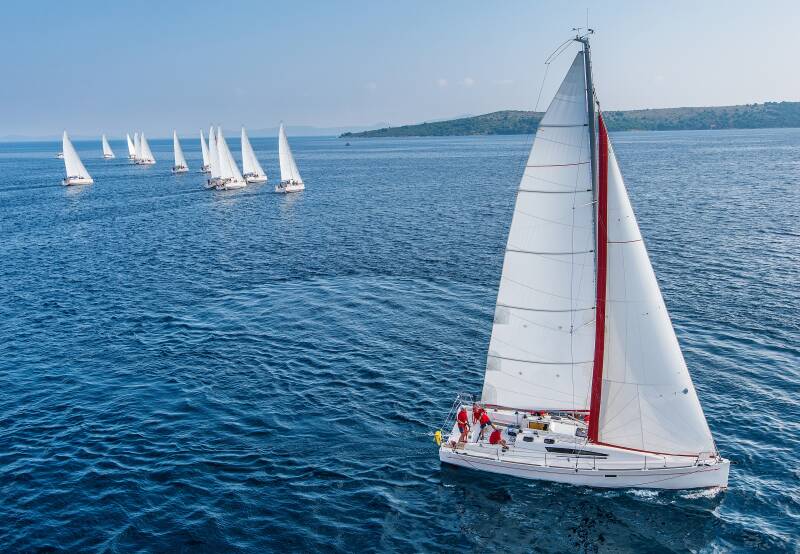

Stern, Helm, Bow and Sides of a Sailboat
When approaching a sailing yacht , you will notice its basic shapes and curves, front and back of a boat, a big pole in the middle, etc. So, let’s start with those basic parts of a sailboat. In Mediterranean countries, yachts will mostly be docked with their back part to the shore or peer. That back of a boat is called a stern . Yachts have a little bridge on the stern which helps you enter from the peer, and that bridge is called passarella in sailor slang.
On a sailing yacht, you will find one of its basic parts - the steering wheel on the stern of the yacht, and the correct sailing term for the wheel is the helm. Grab the helm and face forward toward the front of the sailing yacht. The front part of the sailing yacht is a bow , the right side is starboard side , and the left side is port side. The cockpit, located in the front, around and behind the helm, serves as a space for relaxation, dining, and recreational activities with the skipper, and is an important part of understanding parts of a sailboat and the front and back of a boat.
Cockpit and Mast of a Sailboat
While sailing, a cockpit area is the part of a sailboat that is turned into a workspace for sailors. The big pole that rises over the sailing yacht is a mast and the other pole that is connected under 90 degrees to the mast is a boom . It is called the boom since it can hit you in the head in some conditions, and at that point you will just hear a “boom”, so you need to always be careful while sailing as well as familiarize yourself with sailboat diagrams. While you are still at the helm, you can learn some more about boats. Right in front of you or on your sides you will find round devices around which ropes are wrapped. These devices are called winches and are used to lift sails and all kinds of heavy objects.
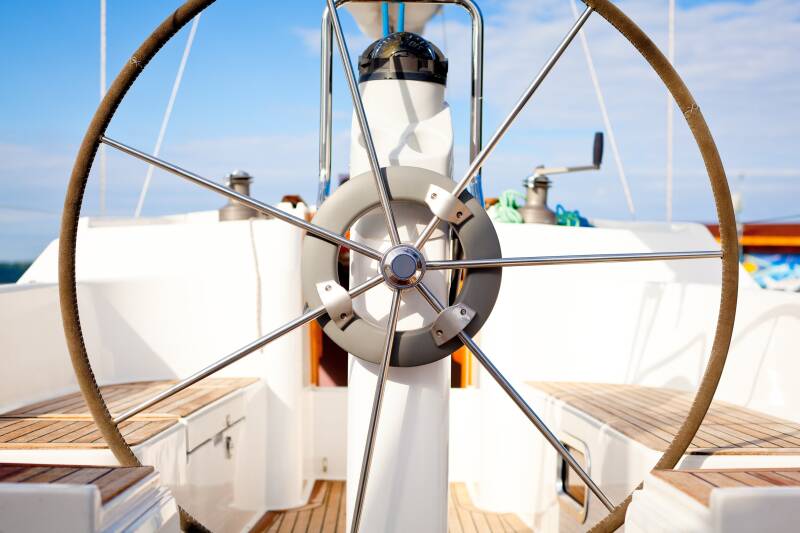

Find a sailboat in your dream destination

Discover sailboats in Croatia

Discover sailboats in Greece
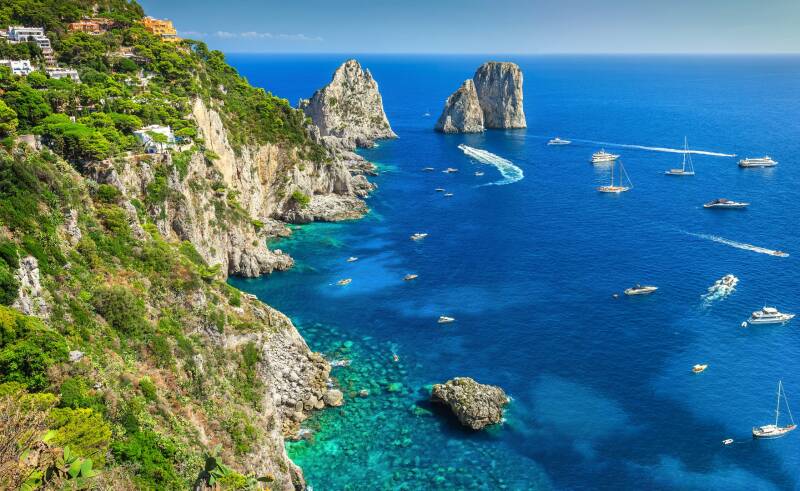

Discover sailboats in Italy

Discover sailboats in Spain

Discover sailboats in Turkey
The saloon area of a sailboat.
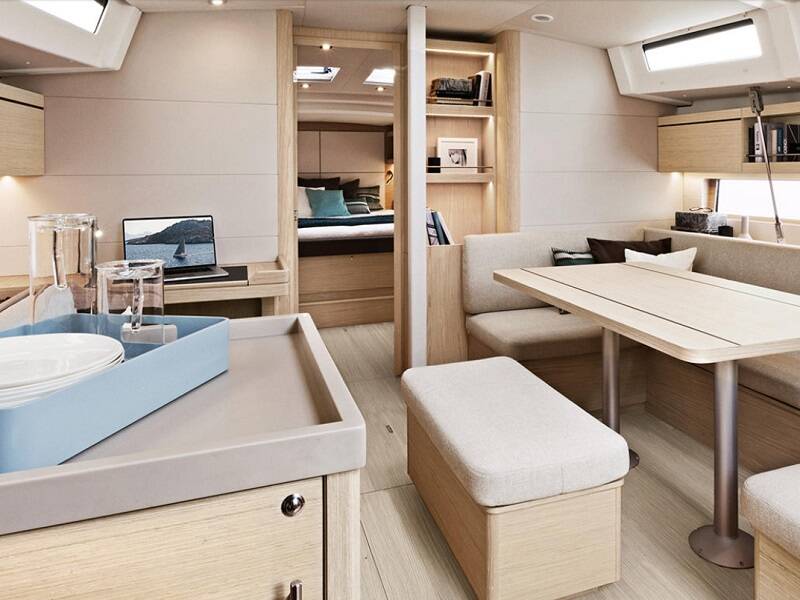

Once you enter the interior part of a sailboat, you will find yourself in the saloon area. This is a common gathering space for the crew. Within the saloon, you will find the galley or kitchen , which is equipped with all the necessary appliances for cooking. There is also a captain's desk that is equipped with navigation charts , electrical switches, tools , and safety equipment . These are all basic parts of a boat interior, used for sailing and navigation.
Further toward the bow, you have sofas for relaxation which can be used as a dining area. One thing about boats is that those sofas can be combined with a table and be converted into additional berths/beds for your guests.
Cabins in the Bow and Stern of a Sailboat
In the bow area of a sailboat, you will find one, two, or even three cabins , depending on the size of the yacht. These cabins are designed to provide a comfortable sleeping space for the crew. The cabins can have a double bed or bunk beds, so in each case, two people can fit comfortably per cabin. In the stern of the yacht, there are also one or two cabins, depending on the size and design of the sailboat. These cabins are also an important part of the sailboat, providing accommodation for crew members while sailing.
Halyards, Types of Sails, and Sheets of a Sailboat
Now when you know the basic parts of a sailboat, we can leave the port and sail out into freedom, which one can experience only while sailing the open seas. To lift the sails up, we will be using halyards , ropes which are connected to the sails on one side and to the winches on the other side, enabling us to lift the sails easily. There are two main types of sails on sailboats, a main sail (triangle shape) and a genoa sail (front sail). In addition to these two main types of sails, you can encounter a spinnaker sail for downwind sailing and a gennaker sail for upwind sailing.

The gennaker is used in conditions when the wind is shifting and starting to blow into the port or starboard side of the yacht. While sailing, the main sail is controlled with a main sheet , which is a rope connected to the main sail and with which we control the tension of the main sail. The front sail genoa is controlled with a jib sheet . When we exit the sail boat marina, we can sail into the wind - windward, or down the wind - downwind. One thing about sailboats is that they cannot sail directly into the wind by the laws of physics. Most commercial sailing yachts can sail the closest of 45 degrees towards the origin of the wind direction.

We use cookies to provide you with the best service on our website. If you stay on our website, you consent to our Cookies Policy .
Tell us about your dream holiday, and we'll make sure you get a personalised offer at the best price on the market.
Thank you for your message. We will get back to you as soon as possible.
We're looking forward to learn more about your dream holiday. The more info you send us, the more detailed and personalized offer we can provide.
You have succesfully submitted the details of your sailing trip. Your detailed and personalized offer is on its way.
- Inquire Now
- YACHT SEARCH
- Motor Yachts
- Sailing Yachts
- $1 – $25,000 Yachts
- $26,000 – $50,000 Yachts
- $50,000 – $100,000 Yachts
- $101,000 – $200,000 Yachts
- $200,000 – ∞ Yachts
- Virgin Islands
- Leeward Islands
- Turks and Caicos
- Spain & Balearic Islands
- New England
- Tahiti & South Pacific
- More destinations
- Charter Advice
Learning the Parts of a Sailboat
Teach yourself the definitions of the many different sailboat parts.
A sailboat is a boat that is propelled either partly or entirely by sails. Sailing is popular in many destinations around the world. For example, Bahamas catamaran charters are a time-honored tradition in the Caribbean, and in the Mediterranean, sailing is a way of life.
There are several different types of sailboats and what constitutes a sailboat varies by maritime culture and region. Most sailboats are classified based on their hull configuration, size, purpose, keel type, configuration and number of masts, and the sail plan. The different types of sailboats include cutters, catboats, dinghies, ketches, schooners, sloops, and yawls. There are many different parts that make up a sailboat. Continue reading to learn about the different parts of a sailboat.
- Backstay – A rod or cable that runs from the stern of the boat to the top of the mast.
- Block – This is the nautical term that means pulley.
- Boom – A pole that attached to the mast horizontally and is used for extending the foot of the mainsail.
- Boom Vang – A device used for holding down the boom.
- Bow – The front part of a boat.
- Centerboard – A plate that pivots and is used to lessen leeway and balance the boat.
- Cleat – A fastening where lines are able to be secured.
- Halyard – The line that is used to raise a sail; the main halyard raises the main sail.
- Hull – This is the body of the boat, not including masts, superstructure, or rigging.
- Jib – A foresail that fits within the foretriangle and the clew does not extend past the mast.
- Keel – The part of a boat that is fixed underwater and is used to provide stability and prevent drifting sideways.
- Line – Refers to any pieces of rope located on a boat.
- Mast – A vertical pole on a boat that is used for supporting sails.
- Outhaul – A sail control that allows tensioning of the foot and attaches to the clew.
- Painter – The line attached to a smaller boats bow that is used for tying it to another boat or a dock.
- Rudder – The movable underwater steering device of a boat.
- Shackle – A fitting composed of metal that is normally used to connect halyards and sails.
- Shrouds/Stays – Wires that help to hold the mast upright; the front wire is referred to as the forestay.
- Spreade r – Struts used to increase the power of the shrouds, they are attached to the mast.
- Stern – The afterpart of the boat.
- Tiller – A metal or wooden stick that is used to turn the rudder of the boat.
- Transom – The afterpart of the boat that is square to its centerline.
- Wheel – The apparatus used for steering.
- Winch – A drum shaped object made of metal which lines are wrapped around to make trimming easier.
There are many different parts of a sailboat that work together to help the boat move. Learning how to sail can be fun and the first step is becoming familiar with the parts of a sailboat and commonly used sailing terms. If you’re planning a yachting vacation – like a Bahamas yacht charter – this knowledge will come in handy, if you’d like a sailing lesson at sea. For more on sailboat parts and sailing terms, check out the pages below.
- In-Depth Page of Sailing Terminology
- The Basic Parts of a Sailboat
- Definitions and Mnemonics for Sailors and Powerboaters
- Learn the Parts of a Sailboat
- Sailing Terms Everyone Should Know
- Sailing Basics: Terms, Rules, and How to Sail
- Nautical Terms Related to Sails and Sailing
Written by Katja Kukovic
Go to Knowledgebase
Set your search criteria to find the perfect yacht
- Alaska Australia Bahamas BVI Caribbean Croatia Florida France Galapagos Greece Indonesia Italy Malaysia Maldives Mexico Mediterranean New England Norway Spain Thailand Tahiti Turkey
- Motor Yacht Catamaran Sailing Boats
- 2 4 6 8 10 12 12+
Search by yacht name
The Only 50 Sailing Terms You'll Need To Know (With Pictures)
Ever get confused by all those odd sailing terms? Starboard, tack, jib… Well, no worries. In this article, I'll go over the most important sailing terms for beginners.
This is a great resource for beginning sailors that need an overview of the most important sailing terms without drowning in it . For a comprehensive list, check out this Wikipedia glossary of nautical terms . There are A LOT of nautical terms there. But no one in his or her right mind will read through that entire page (it has 48.434 words!). There are a lot of obscure words listed that no one really uses anyways. So in this article, I've filtered out the most important ones to get you up to speed quickly. I've also added pictures so you'll know what we're talking about.
Let's jump straight in. For the sake of good manners, I have categorized them by topic. If you are looking for a specific term, just ctrl+f your way directly to it.
Here are the only 50 sailing terms you'll need to know:

Orientation
Parts of the boat, parts related to sails, other terms.
...because it isn't as easy as 'left', 'right', 'front' and 'back'. No, no.
Port is the left side of the boat. It's as simple as that. I'm not entirely sure why don't they just call it 'left' these days. The name came to existence because centuries ago, you always docked your big boat with the harbor (port) being on the left side. And the word stuck with us till today.

Starboard is the right side of the boat. If in a car, you say 'look to your right', on a boat, you say 'look to the starboard'. Again, you might as well just call it 'right'. Oh, wait… you wouldn't seem as cool if you did. Alright, let's keep calling it starboard.

The bow is the front of the boat. The word likely comes from the Middle Dutch 'boech' (nowadays spelled 'boeg'). If you call it 'front' instead, you will get your message across just as well. But it won't get you the admiring looks from those around you.
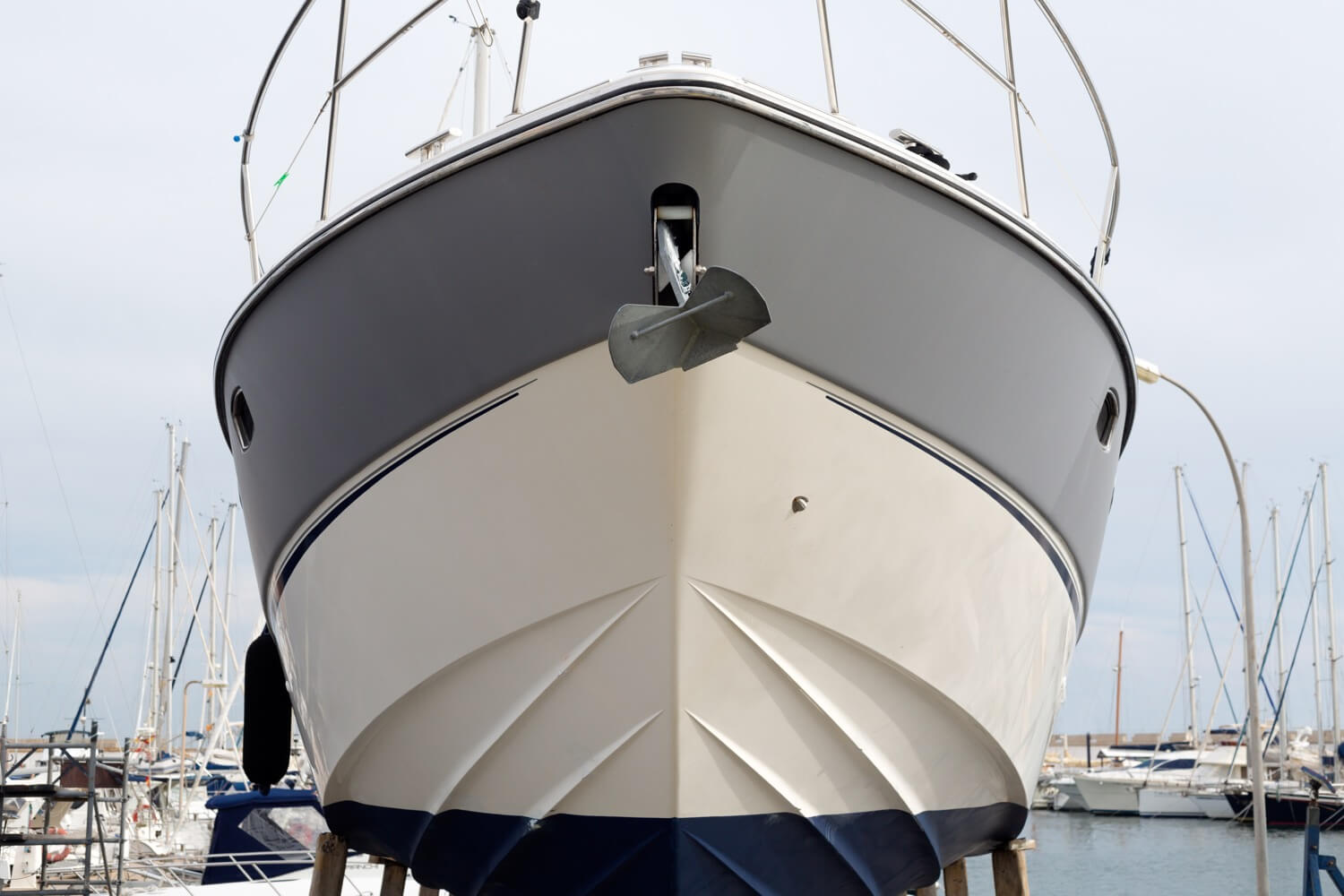

Stern is the back of the boat. That is where you, as a captain, will spend most of your time. Whether you will force your crew to call it 'stern' or let them use the word 'back', like the dry land creatures they are, is up to you. After all, you are the captain.

The windward side of the boat is the side facing into the wind. So if the wind is coming from the right side, the windward side is on the right. Unlike some of the previous ones, this term actually makes sense - at times you need to talk about a direction not fixed in relation to the boat, but rather relative to the direction of the wind.

Leeward side of the boat is the lee side. If the wind is coming from the right side, the leeward side is on the left. Note that neither windward nor leeward specify the angle of the wind. Thus even if the wind was coming 20 degrees right off of the direction of the boat, so almost from the front, left would still be considered the leeward side.

Since there are gadgets and parts on the boat that you won't see anywhere else, it only makes sense they all have their own special name. You want to know these because unlike the direction terms where you can do with 'left' and 'right', you don't want to call a tiller 'that stick thing back there'.
Helm is the boat's steering wheel. In this case, I forgive those who came up with this name, since it is shorter than 'steering wheel' and thus saves valuable time that we can spend on sailing. Though I doubt linguistic economy was the reason.
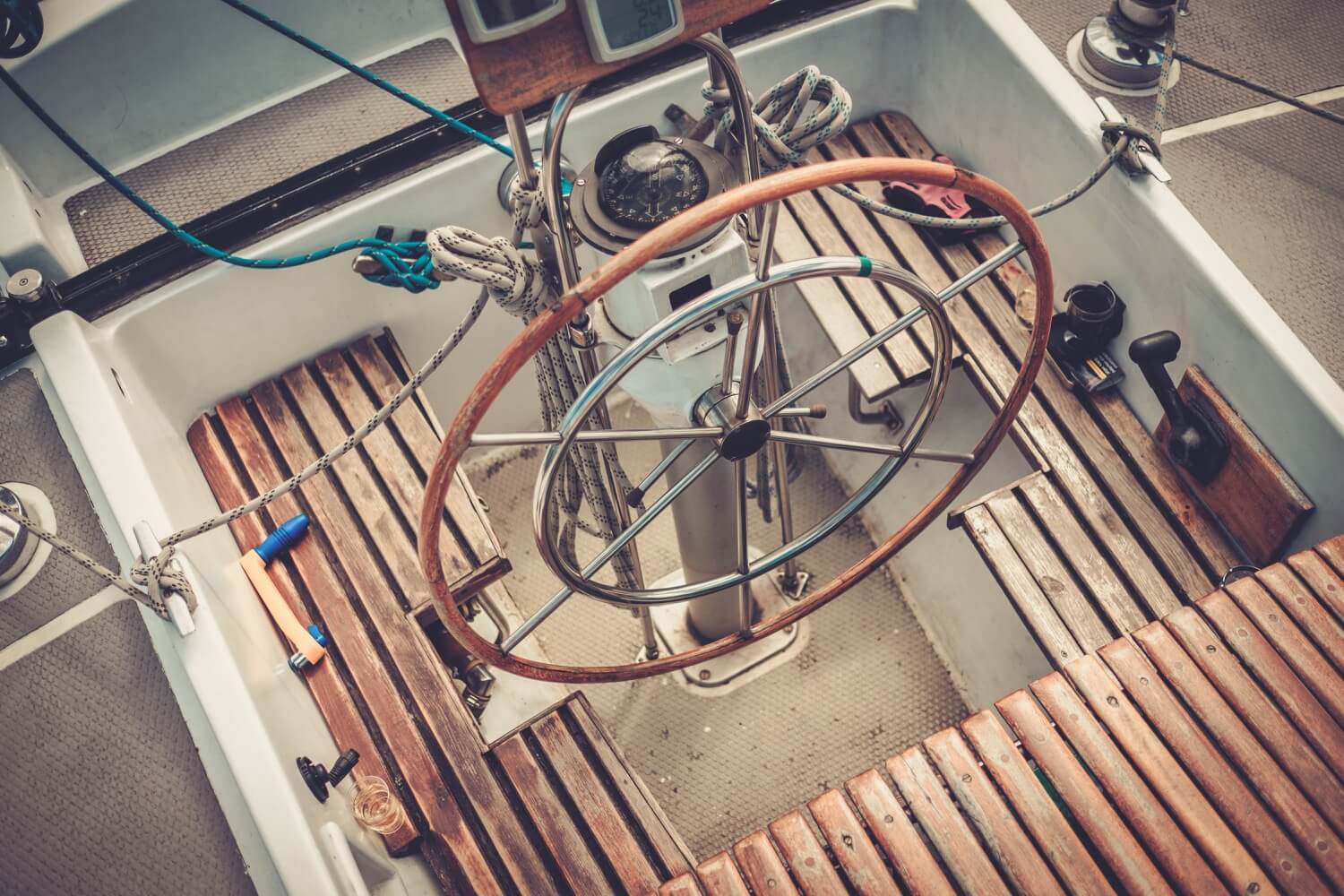

Tiller is the long stick that operates your boat's rudder. A steering stick, if you will. It has the same function as a helm does, but it is usually used on smaller boats, where a helm would take up too much space. Or by people who prefer it to a helm, since a tiller offers a bit more in terms of response.

The rudder is the long, flat piece of metal or wood that sits underwater below the back of your boat. Connected to a tiller or a helm, it is used to control the direction of your exciting voyage. By the way, since aerodynamics and hydrodynamics work in similar ways, a plane is also operated by a rudder. Though that one isn't underwater. Hopefully.

Hull is the boat's body. Whatever the shape or size, whether opened on top (like a dinghy) or closed by a deck, (like a traditional sailboat) it's all called a hull. Structures sitting on top of the deck, like a deck salon or cabins, aren't considered a part of the hull anymore.

The keel is an underwater fin below the boat's belly. The sizes and shapes vary, sometimes it is relatively short and goes deep, (fin keel) sometimes it runs from the front all the way to the back (full keel or ballast keel). It is there mainly for stability and to help maintain forward direction when sailing.
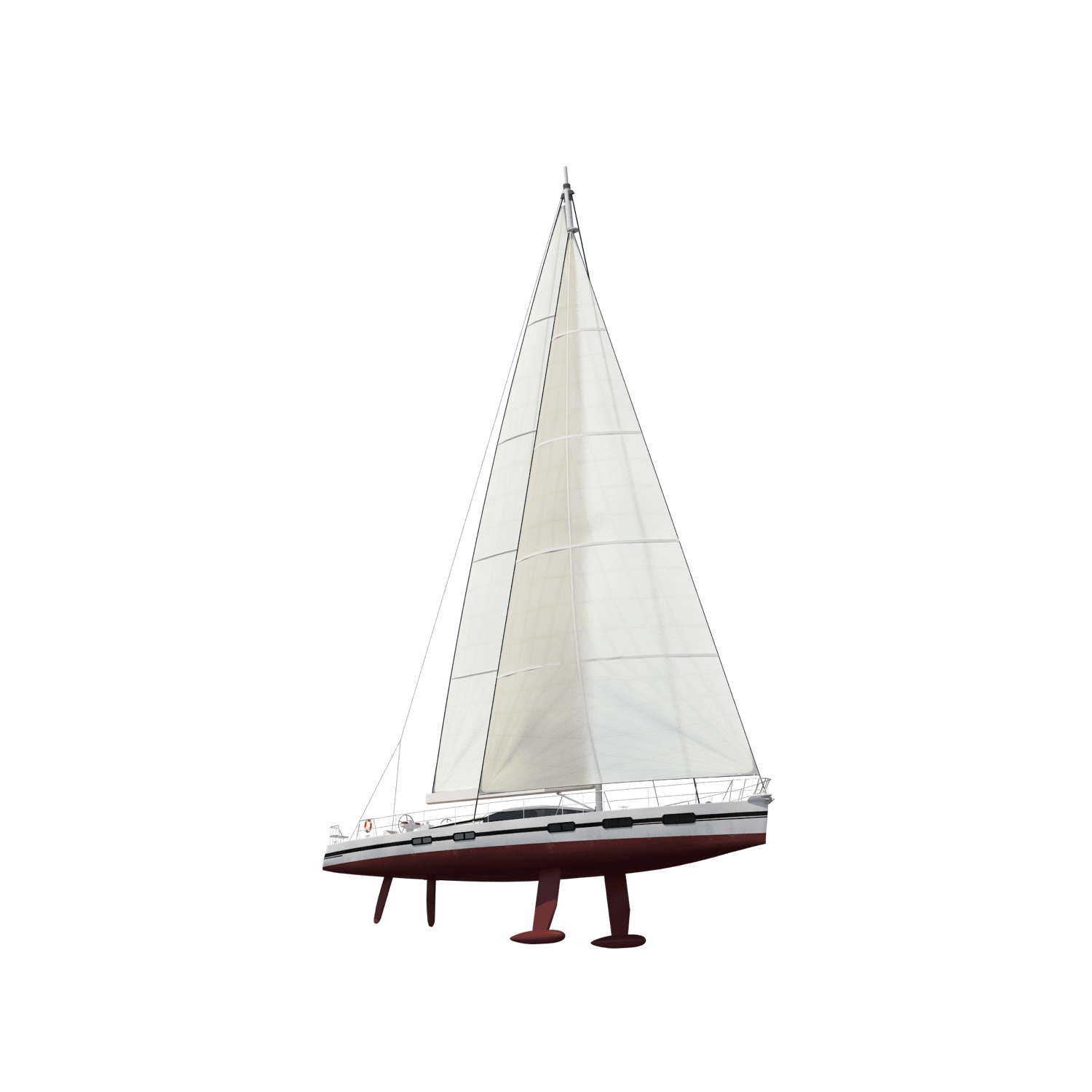

The cockpit is the area where a boat is operated from. On sailboats, it is usually in the back and it is an open area without a roof, though this varies. You will find the rudder control and winches there. In 'smaller' (below 70 ft or so) sailboats this area oftentimes doubles as a deck dining place with a table and seating.
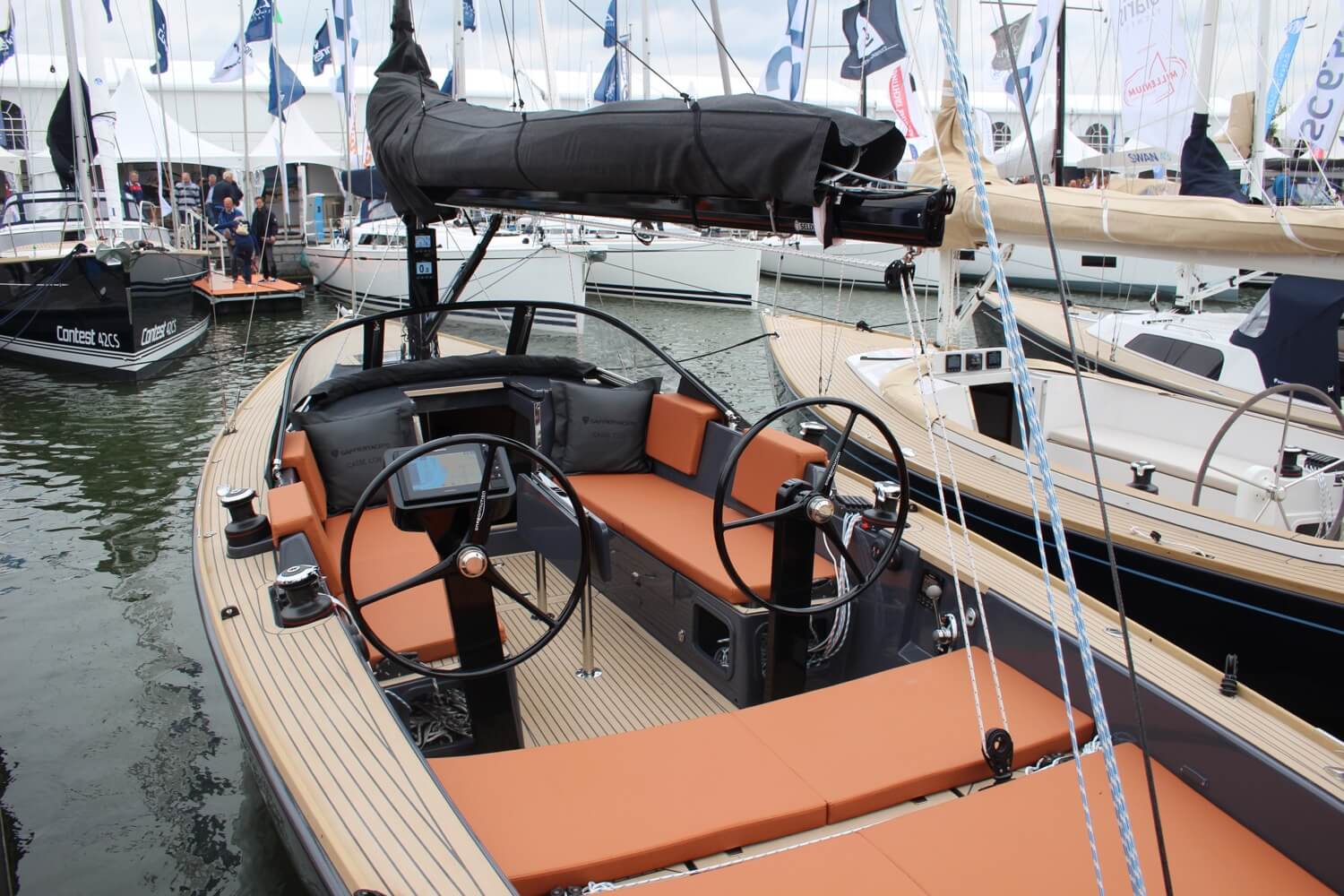

The bimini is a sun roof or shade that is covers the cockpit, and is generally attached to a steel frame which runs over the cockpit.
This is where things tend to get confusing. There are a whole lot of parts and a whole lot of names for them. It pays off for you and your crew to know them though, as during the stormier moments, you all want to be on the same boat (ha, ha) linguistically, as every second counts.
Lines are ropes. Not much more to add here. I suppose a 'line' sounds a bit fancier than a 'rope'. One thing this article will teach you is that if there is the slightest crack in the wall of your boat, linguistic elitism will leak its way in.
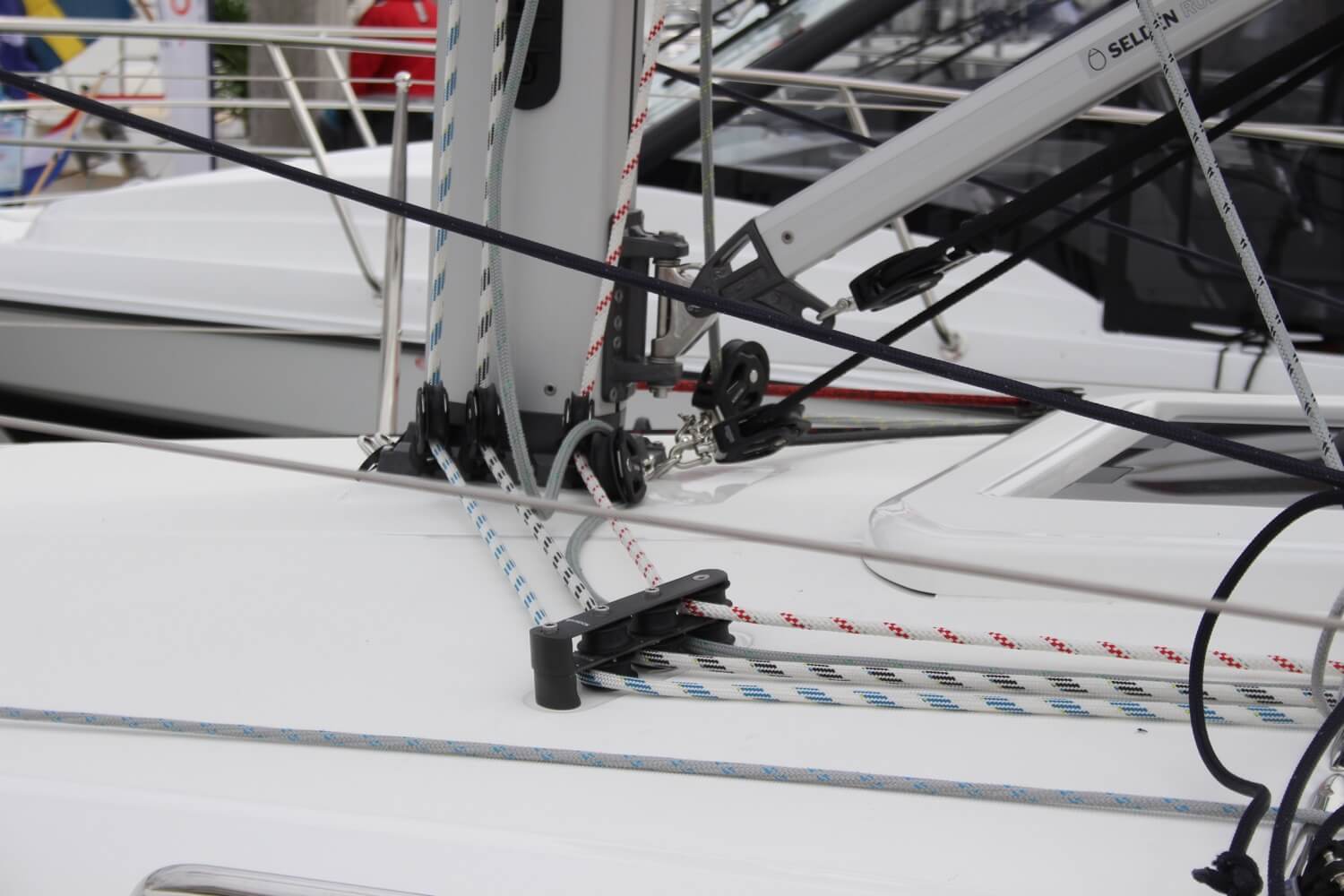

This one is quite self-explanatory. The mainsail is the main, largest sail of the boat, attached to the mast on the side and the boom at the bottom. It has a triangular shape and serves as the most important sail, the first one you should get acquainted with if you are just starting out.

The jib is the front sail of your boat, sometimes also called the genoa. That is as long as you are sailing on the traditional sloop - the classical two sail setup you see the most often. The jib is wrapped around the line that goes from the top of your mast to the boat's bow.
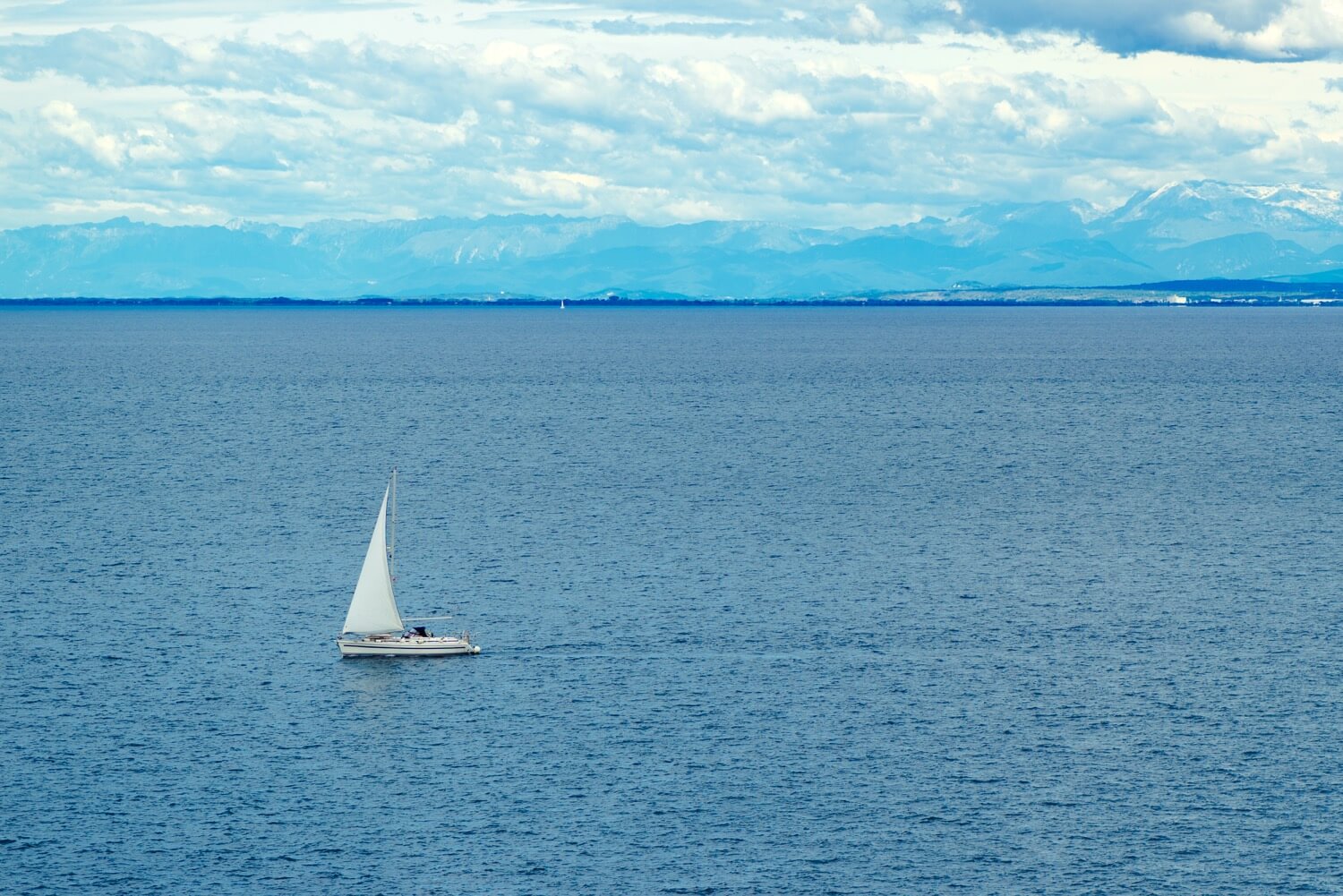

Spinnaker is the third type of sail you are the most likely to encounter on your travels. It goes in front of your boat and has a half balloon or kite-like shape. This is because it is constructed specifically for sailing downwind. Its purpose is to grab as much backwind as it can and drag your boat forward. It is not attached to the boat most of the time like the mainsail or the jib, instead, it is stored separately and used only when needed.
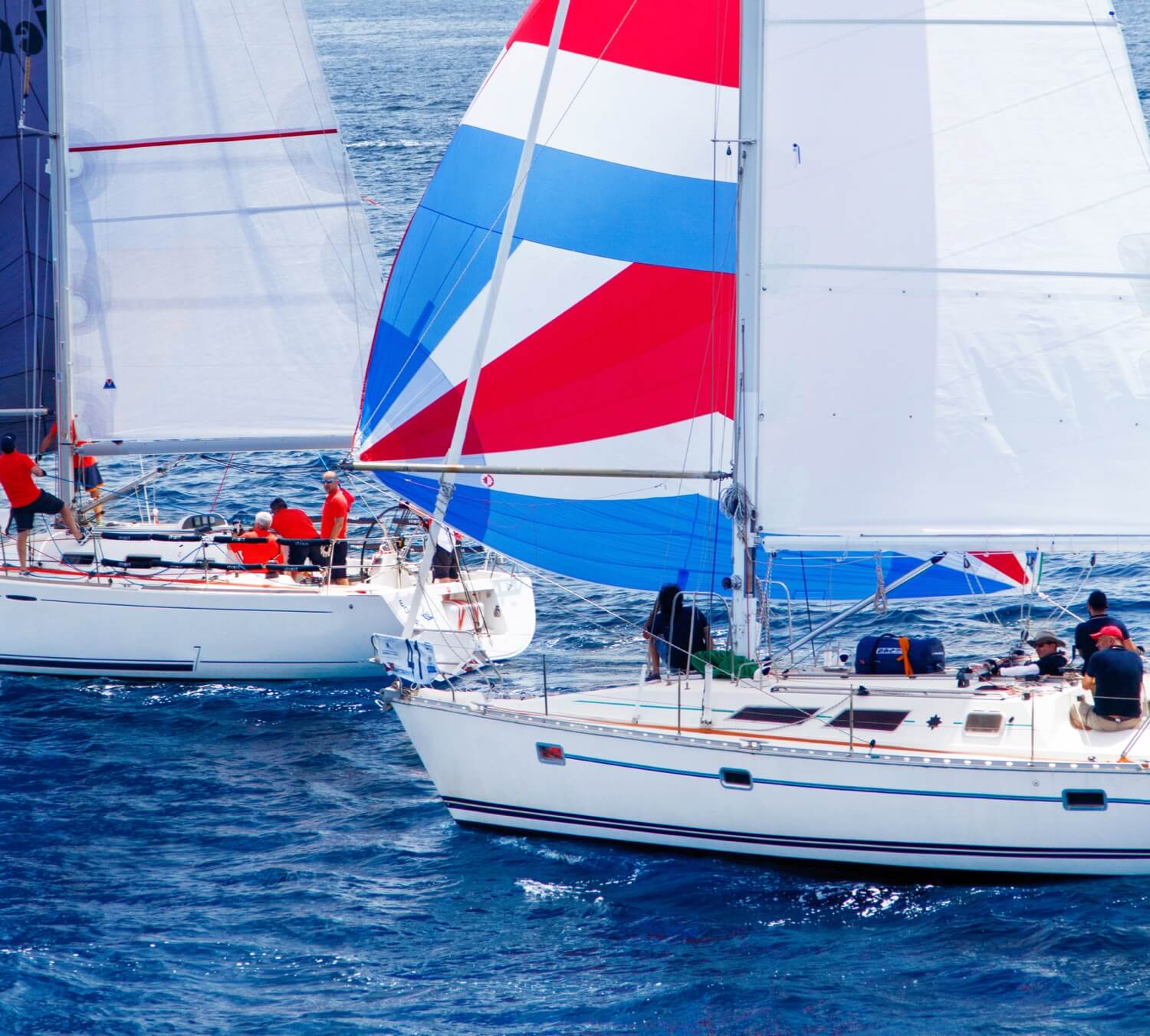

The mast is the tall, vertical pole that goes from the floor of your salon, through the deck, meters above your boat. All the sails are attached to it, also radars and lights, giving sailboats radio and visual visibility far greater than that of equally sized motorboats. Take that, ya noisy stinkies!
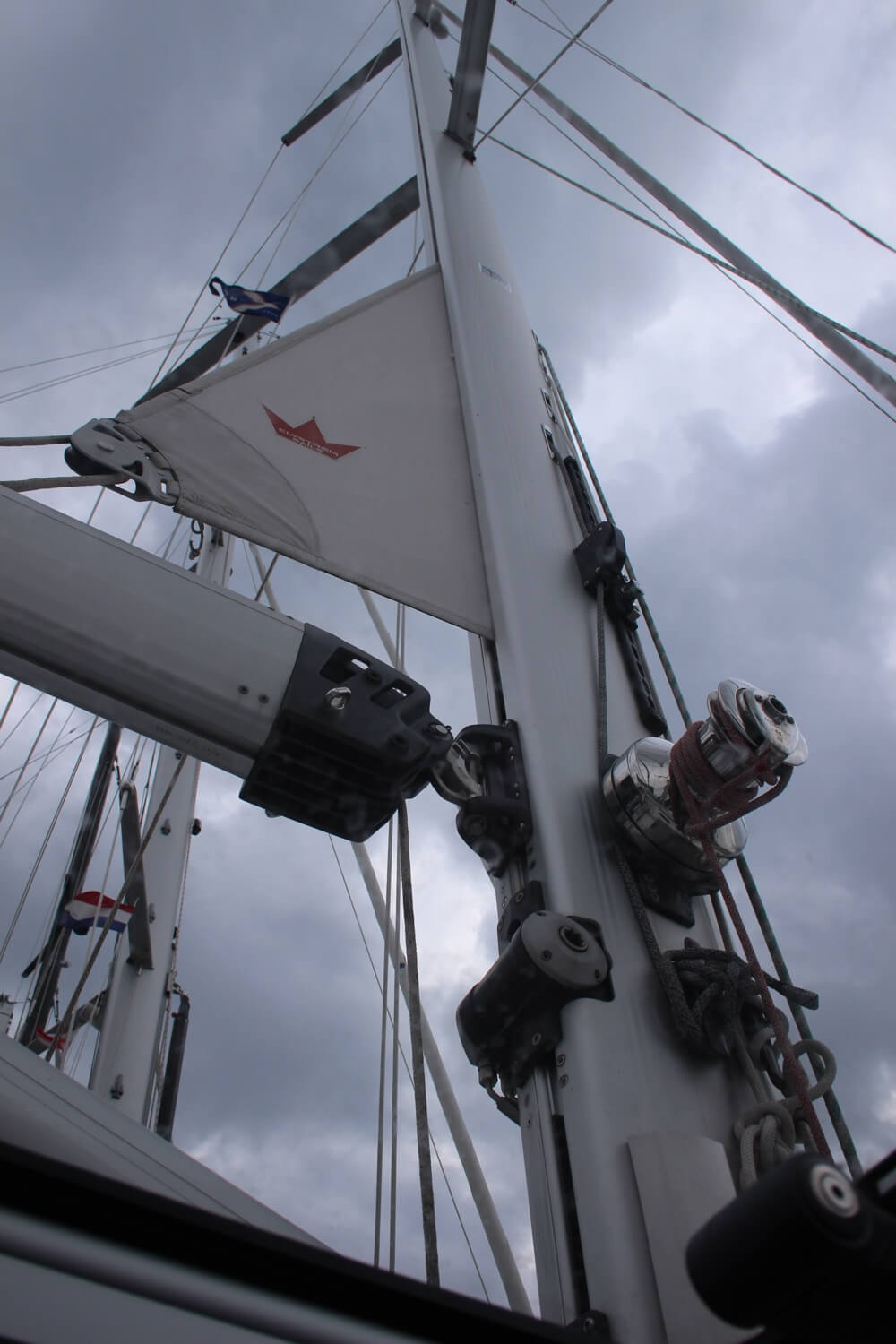

The boom is the horizontal pole right above the deck, attached to the mast at the right angle. The bottom of the mainsail is attached to it, it is used to determine its shape and direction. It is also where the mainsail is often stored, folded and covered with a protective sheet. The boom is also among the top causes of injuries on a sailboat, as in certain winds it tends to swing with force powerful enough to knock a few grown men overboard. Stay away from its reach at all times when under sail.
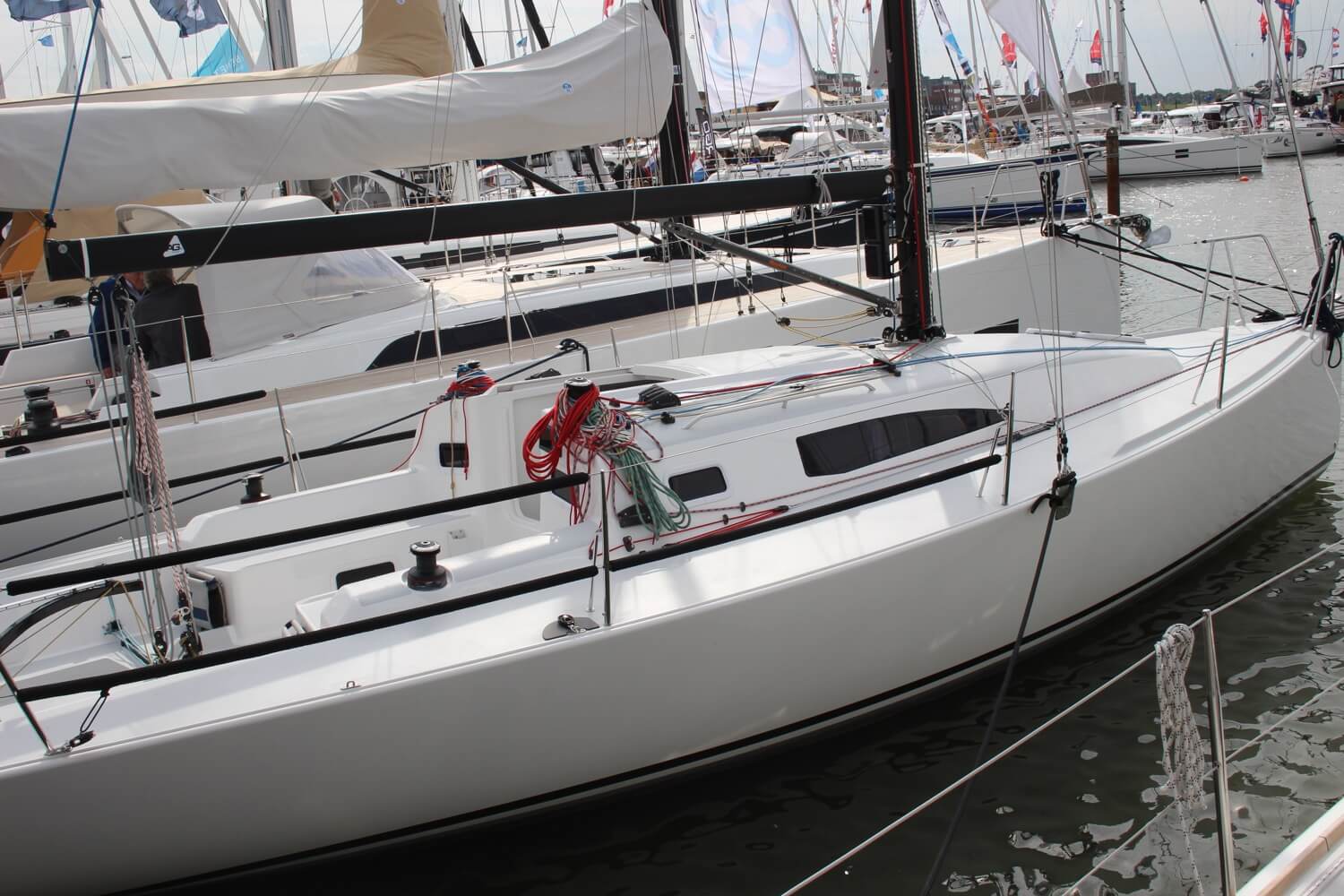

The forestay is the cable going from the top of the mast to the very front of the bow. It is there to hold the mast in place. Sometimes you will find people refer to it as the 'headstay'. It is often made of steel, so it is safe to hold on to it when you are pretending to be Jack on the bow of the Titanic's, the boat hits a wave and you lose your balance.
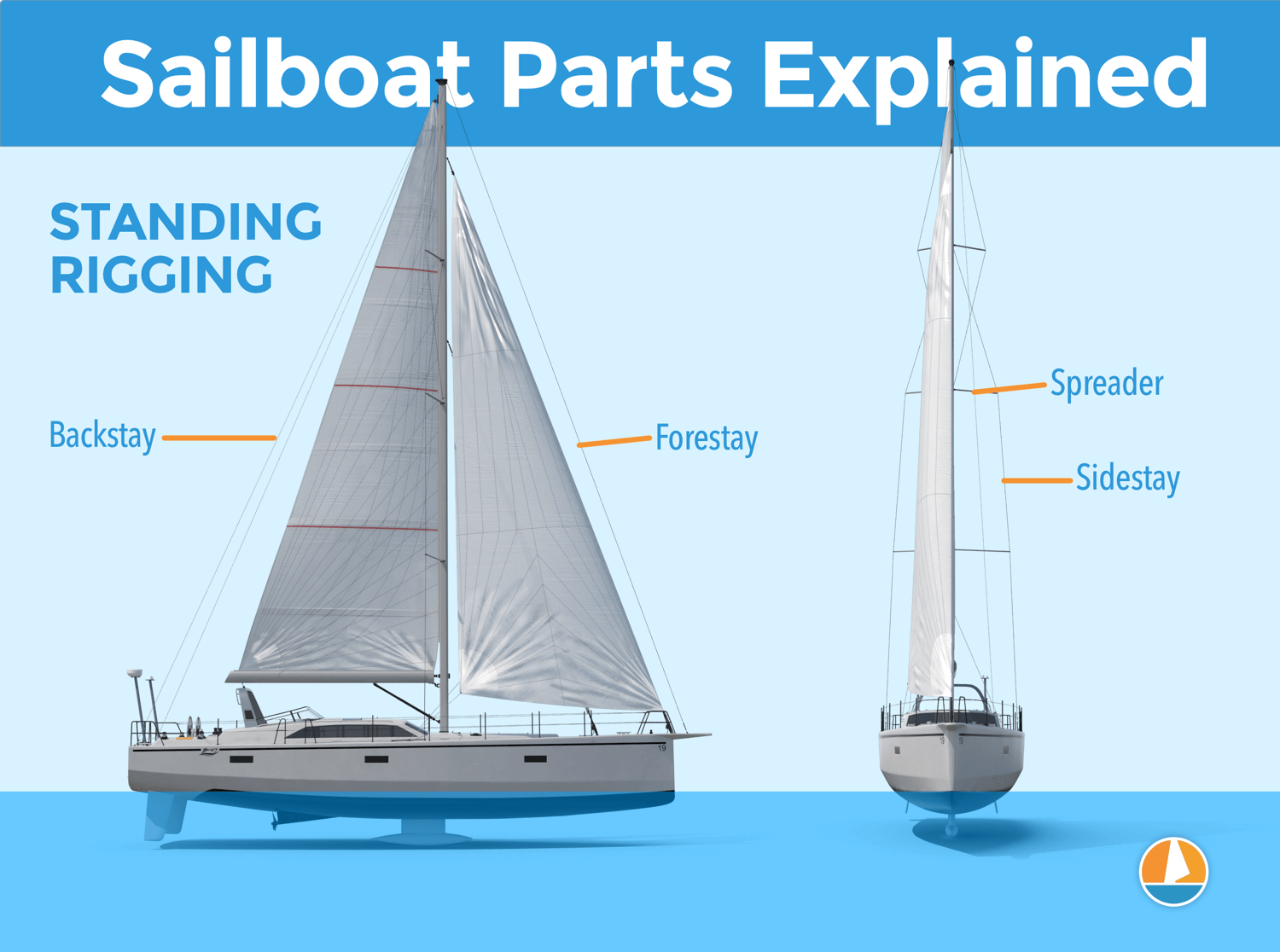
This diagram is from our guide on sailboat parts , which I really recommend for beginners. It walks you through all the most important sailboat parts in normal words.
The backstay is the cable going from the top of the mast to the very back of the boat. In many cases it is doubled at the bottom, each end attached to one corner of the back of the boat so that they don't interfere with space and provide more stability for the mast. Just as with forestay, these are made of steel.
Shrouds are the cables going from the top of the mast to the left and right side of the boat. Sometimes there are four, two on each side. Together with forestay and backstay, they make sure your mast withstands all the forces exerted on it when the wind pushes the sails.
The foot of a sail is its bottom edge. If you imagine a sail as a triangle, the base is called the foot. You probably won't use this term while sailing, but when researching proper sail trim, it is likely you will stumble upon it.
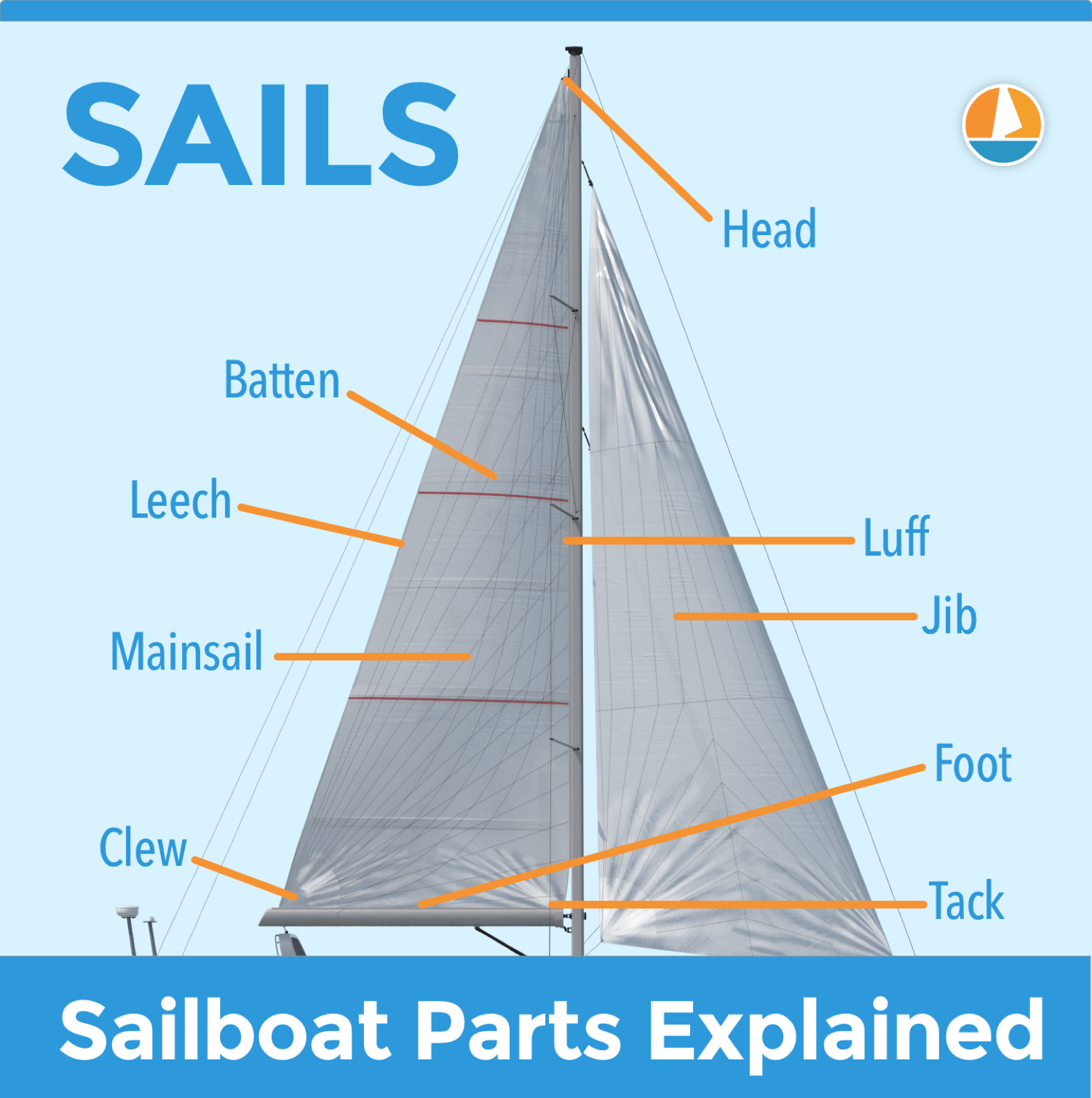
This diagram is again from our guide on sailboat parts , which I really recommend for beginners. If you're looking for a good starting point to learn your sailboat ins and outs, this article is perfect for you.
Leech of a sail is its back side edge. Thus it is the part closest to you when you are standing at the helm. Just as with the foot, this is a term quite often used when describing sail trimming techniques, since the shape of the leech determines the shape of the whole sail.
Luff of a sail is its front side edge. Thus the part the furthest from you when you are standing at the helm. For mainsail, it is the edge that is right next to the mast, for the foresail it is the edge right next to the forestay. Just as with foot and leech, the shape of these edges determines the overall shape of the sail so you will most likely encounter these terms in trimming lessons and tutorials.
The head of a sail is its top corner. On a traditional sloop, you will have the 'main head' and the 'jib head'. There is usually a reinforcing patch of some kind on these corners, as you will find a hole in them to which a line is attached.
It's also something else entirely, but more on that later ...
Halyard is the line attached to the sail head. On your boat, you will most likely have two. The 'main halyard' which is what you use to hoist your mainsail if it is folded on the boom, and the 'jib halyard' which holds the jib head up.
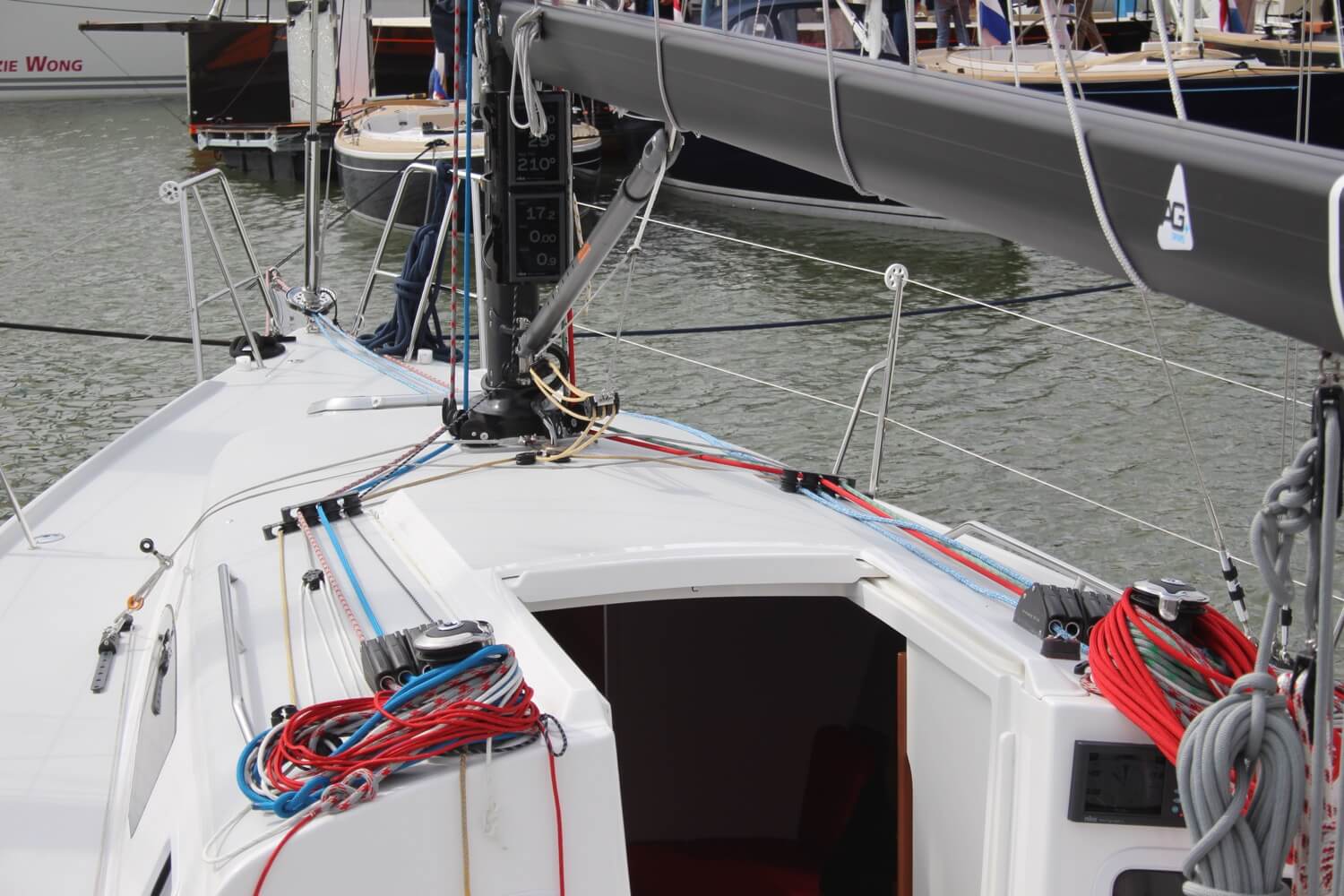

Clew of a sail is its back corner. The line attached to the 'main clew' will be used to hoist your mainsail if it is wrapped inside of the mast. The line attached to the 'jib clew' will be used to open the jib on most sailboats since jibs are most often wrapped around the luff.
Telltales are light, usually cotton or wool pieces of ropes attached to a sail, showing you the airflow around it. These are important because they help you determine if your trim is effective or not. Because of the material they are made of, you might sometimes encounter them being called 'woolies'.
Vang, or a 'boom vang' is a device pulling the boom down. This is important because it controls the tension of the mainsail, influencing its shape greatly. You won't find it on every boat though. Holiday cruisers often don't have it, as it is a piece of equipment focused on performance and thus not necessary for your average trip.
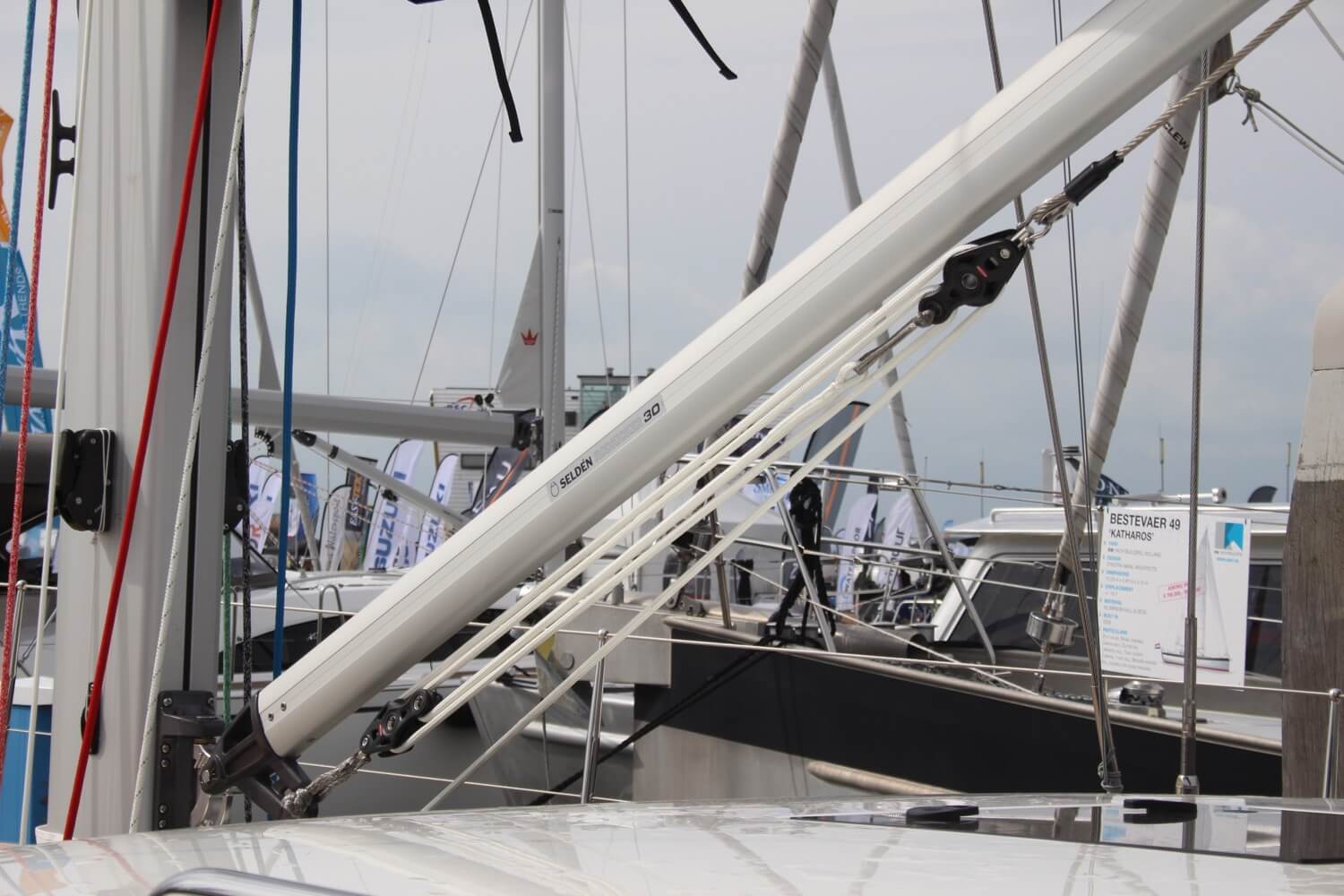

Topping Lift
The topping lift is a line that is attached to the aft (back) end of the boom and runs to the top of the mast. It supports the boom whenever you take down the mainsail.
Also referred to as a 'horse', the traveler is a side to side track to which the boom is attached, allowing the control of the extent to which the boom goes off the centerline. This is important especially if the wind is blowing from behind and you need to control the angle of the mainsheet.
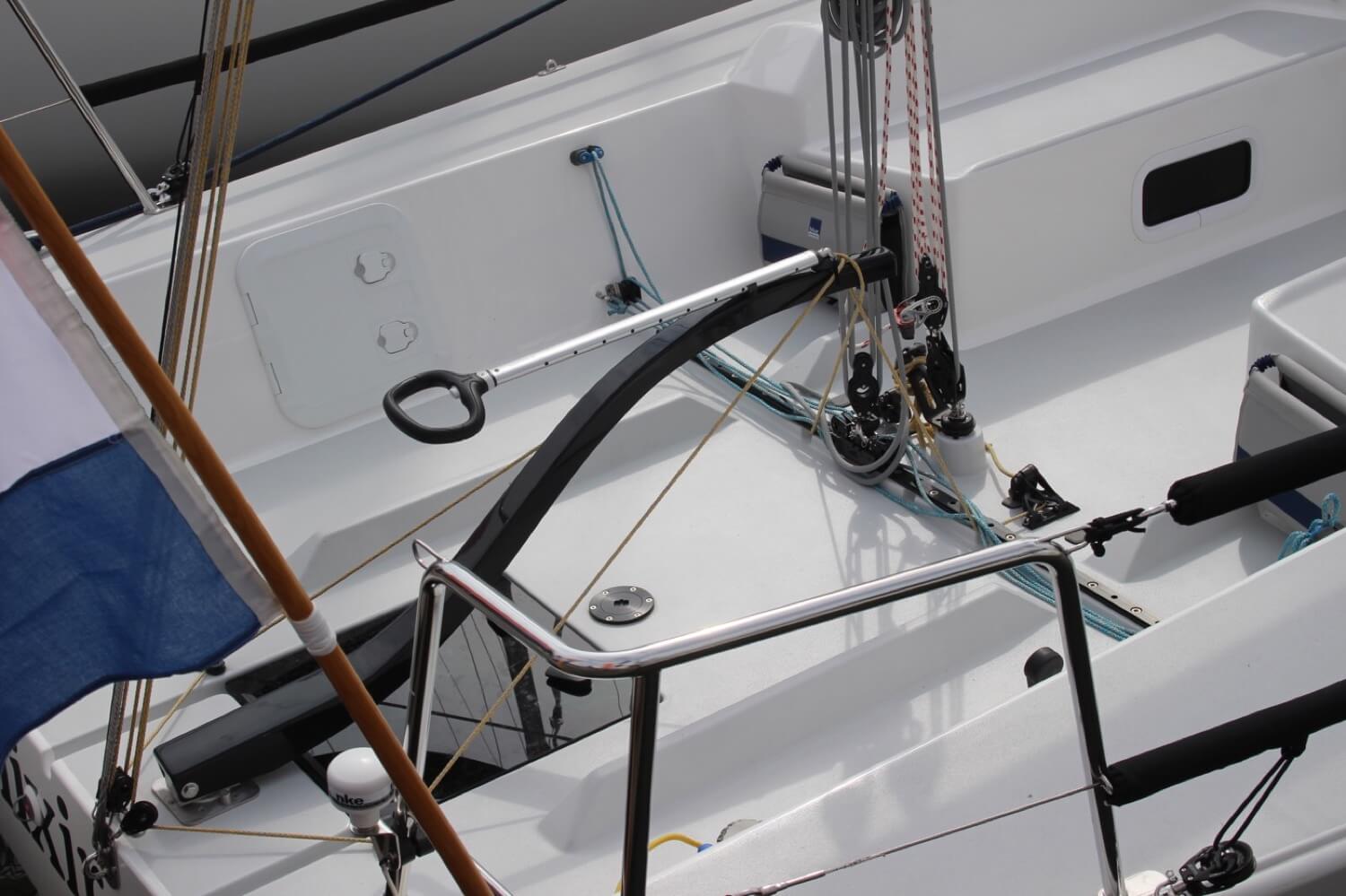

Outhaul is the line attached to the mainsail or the jib clew, allowing the control of the foot tension. This is important for determining the sail shape - for instance in stronger winds, you want the foot to be more tense to achieve a more effective airflow as opposed to slower winds where you can allow the foot to arch more.

Reefing is reducing the sail area to lessen the power exerted on it by the wind. You may want to reef if the wind is getting too strong for your boat, or if it is changing too rapidly, as an overpowered boat is difficult to control. Fun fact: they say that when you feel you need to reef because the wind got too strong, it is already too late to reef.

A batten is a slat placed horizontally in the body of the sail to support its shape. You will not find them on all sailboats, it is a performance-enhancing element that many cruisers lack. It helps tremendously as without it, sails tend to belly out and lose their shape under certain conditions.
The cleat is a piece of fitting where a line can be secured and immobilized, even if under great tension. It usually consists of two cogwheel-like pieces fastened close to each other, in the middle of which the rope is placed, unable to move thanks to friction. This type is great as it allows for a quick release. Sometimes though, it is a simple piece of metal or plastic where the rope is tied.
...and then there are all those things that just float around you when sailing, those little things that are the reason for you having to carry a dictionary in your pocket.
Fenders are bumpers allowing some contact with other boats or piers while docked, without scraping the paint. They are often balloon-shaped, made of rubber or some relatively soft material. They are usually attached to the boat's railing and you move them around as you need.

The beam is the width of the boat. Could be just called width, I know. The word comes from the fact that there are transverse reinforcing beams in the boat hull and deck. Next time you are choosing your charter boat for holidays, you will know what this attribute means.
True wind is the actual direction and speed of the wind. This is different than the apparent wind, which is wind direction and speed relative to the boat. Apparent wind is a combination of the true wind and the headwind, which is the wind the boat experiences solely by being in motion.
The berth is a sleeping space on a boat. Thus if a boat has eight berths, it means eight people can comfortably sleep on it. Note that this often includes the salon couches, so a berth is not necessarily a space in an actual bed for one person.

Boat's draft is the distance from the water surface to the deepest point of the boat. In other words, the draft is the minimum water depth you can go to and not scrape your hull or keel. Better double this number when sailing, just to be safe, as hitting the seabed can have disastrous consequences.
Tacking is zig-zagging towards your destination. It is necessary in case your destination is in the direction of the wind since sailboats can not go directly into it. Since the closest to the wind direction you can sail is around 45 degrees, you have to change direction left and right from your desired course.

This diagram is from our guide on sailing into the wind for beginners , which explains in 7 simple steps how to get good upwind sailing performance.
Bareboat is a boat without a skipper. You will encounter this term in boat charters and it means you rent the boat without any crew, thus you need to operate it yourself. It is the best way to sail unless you enjoy living in close proximity to a sea wolf who you also have to feed.
The chart is a nautical map. It differs from classical maps as it depicts information relevant for a sailor - water depth, navigational hazards, seabed material, anchorages and so on. Formerly made of paper, these days made of ones and zeros. As is everything in this digital world.
We have a guide that explains all the different chart types clearly for beginners - read it here .
Galley on a boat is its kitchen. Also a medieval warship, but if you find this term in a boat's description, war is not likely what they have in mind.

Heads on a boat is the bathroom. Though in all my years of sailing I have never ever heard anybody use this term instead of a 'bathroom'. I suppose saying that you are going to use the heads just sounds odd.
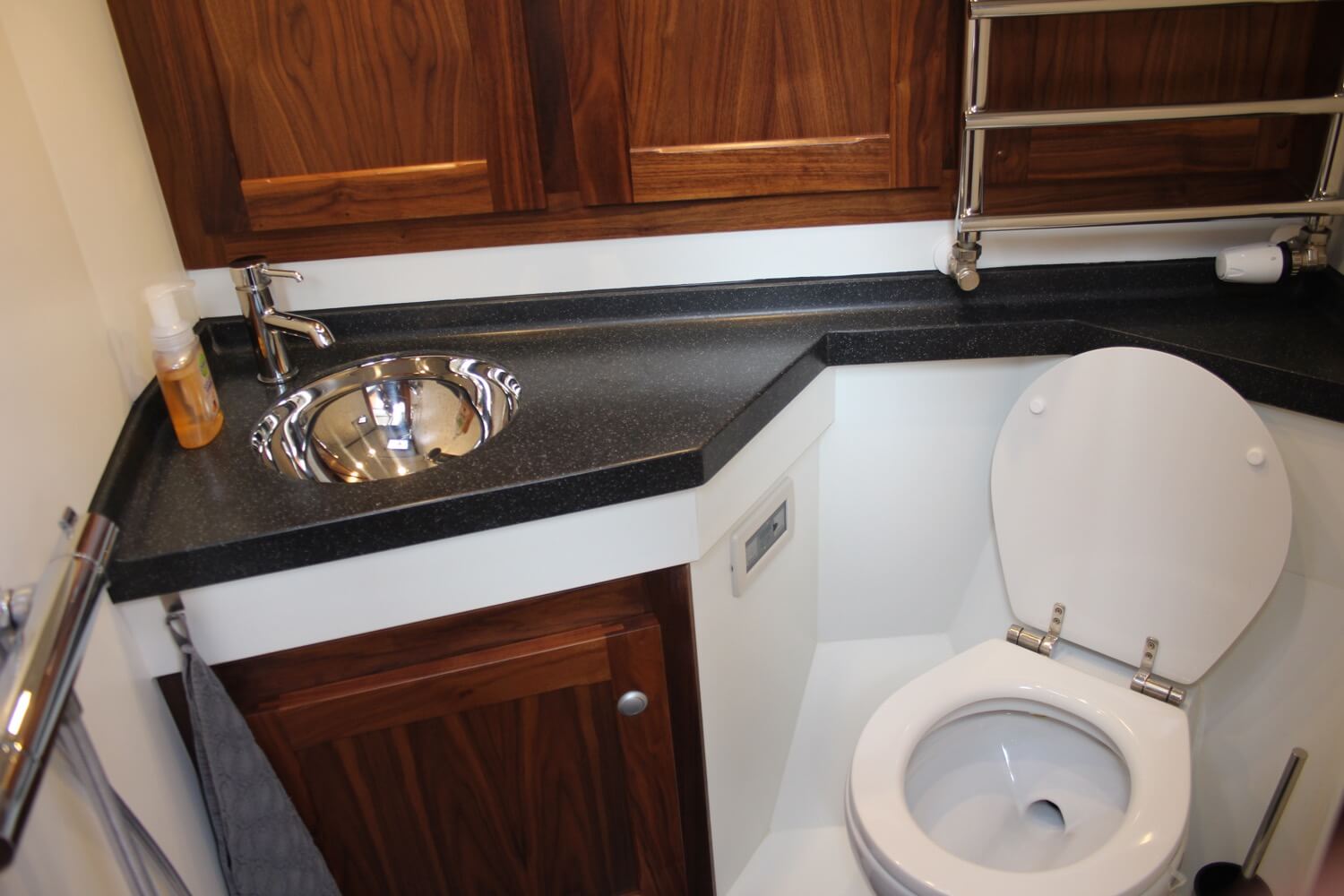

A knot is the unit of speed of boats. It is equal to one nautical mile per hour. That is 1.852 kilometers per hour or 1.5078 miles per hour. Though a bit confusing and annoying at times, you will have to get used to this, since most of your boat's instruments will use this unit. It dates all the way back to the seventeenth century when boat's speed was measured with a rope with knots tied on it.
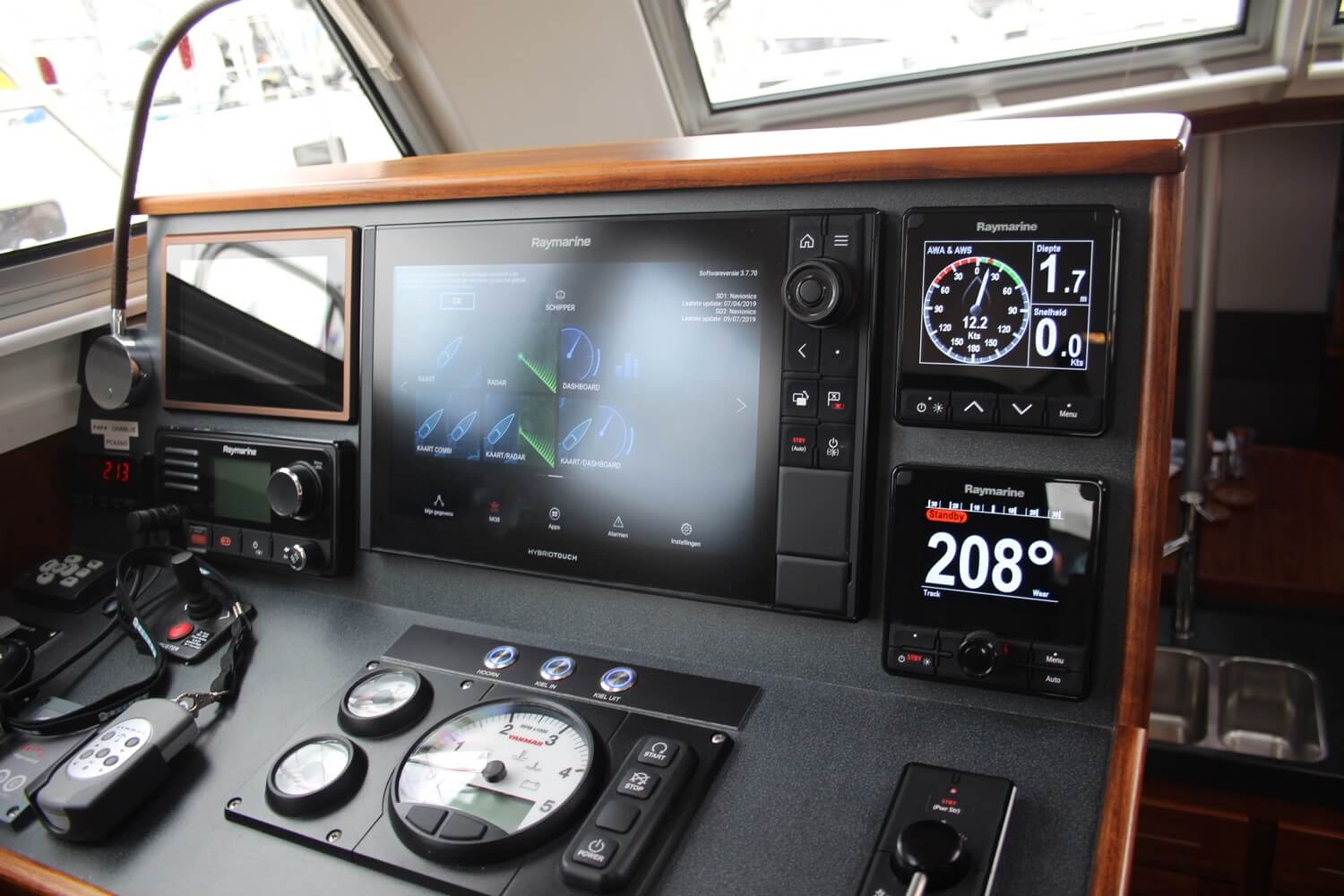

Mooring is attaching the boat to a buoy that is anchored to the seabed. This is usually a cheaper option to docking in a marina. It also means larger space between the boats anchored in the same area, thus more privacy. Though you will have to use your dinghy to get to shore instead of just stepping on the pier directly from your deck.

A salon on a boat is its living room. On smaller boats, it is usually in the same room as the boat's kitchen and the captain's corner with navigation instruments.
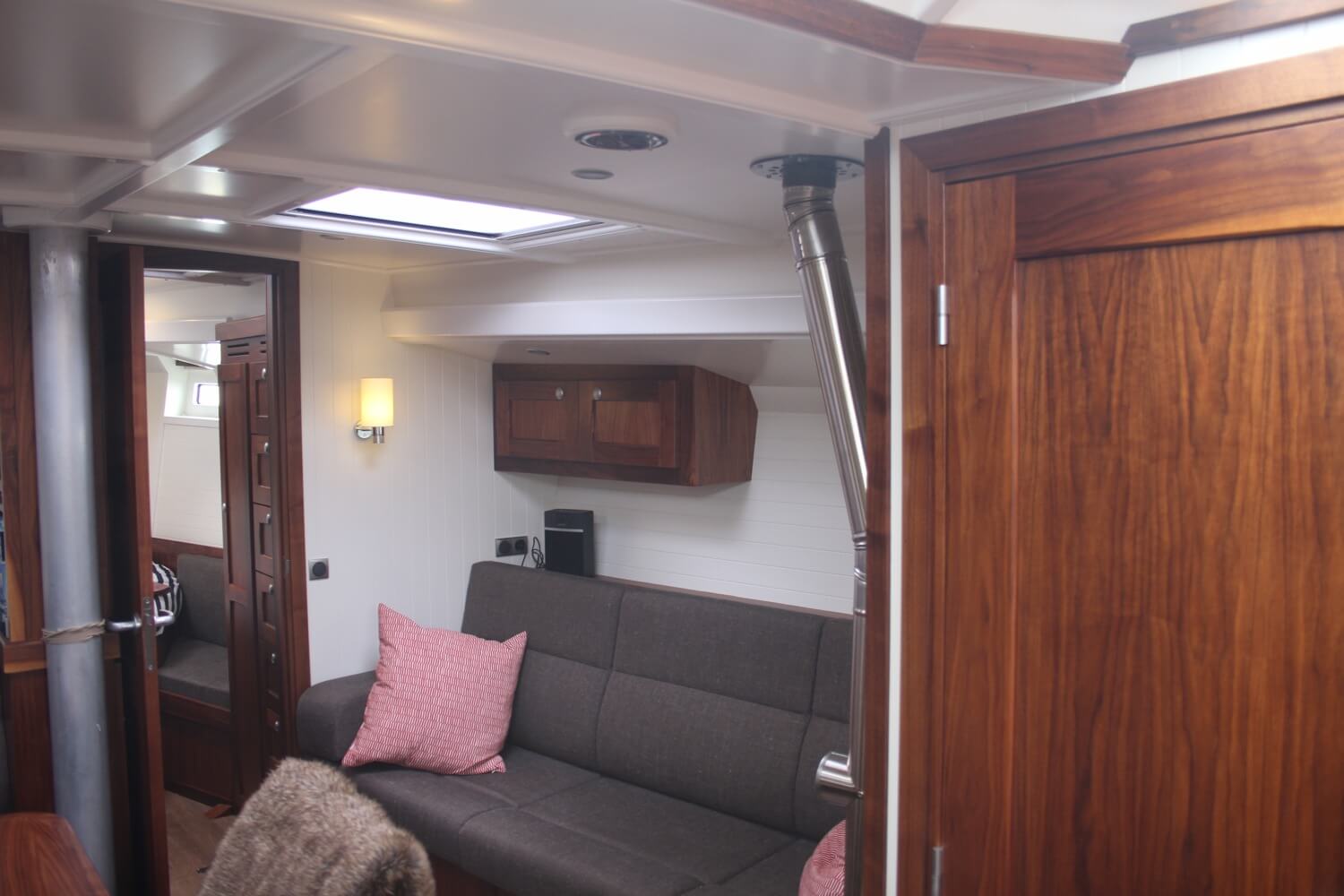

A skipper is the captain of a sailboat. If you ask me, the word 'captain' is much better than a skipper, which to me sounds like a small boy who sits on the shore the whole day, skipping stones. But hey, who am I to talk.
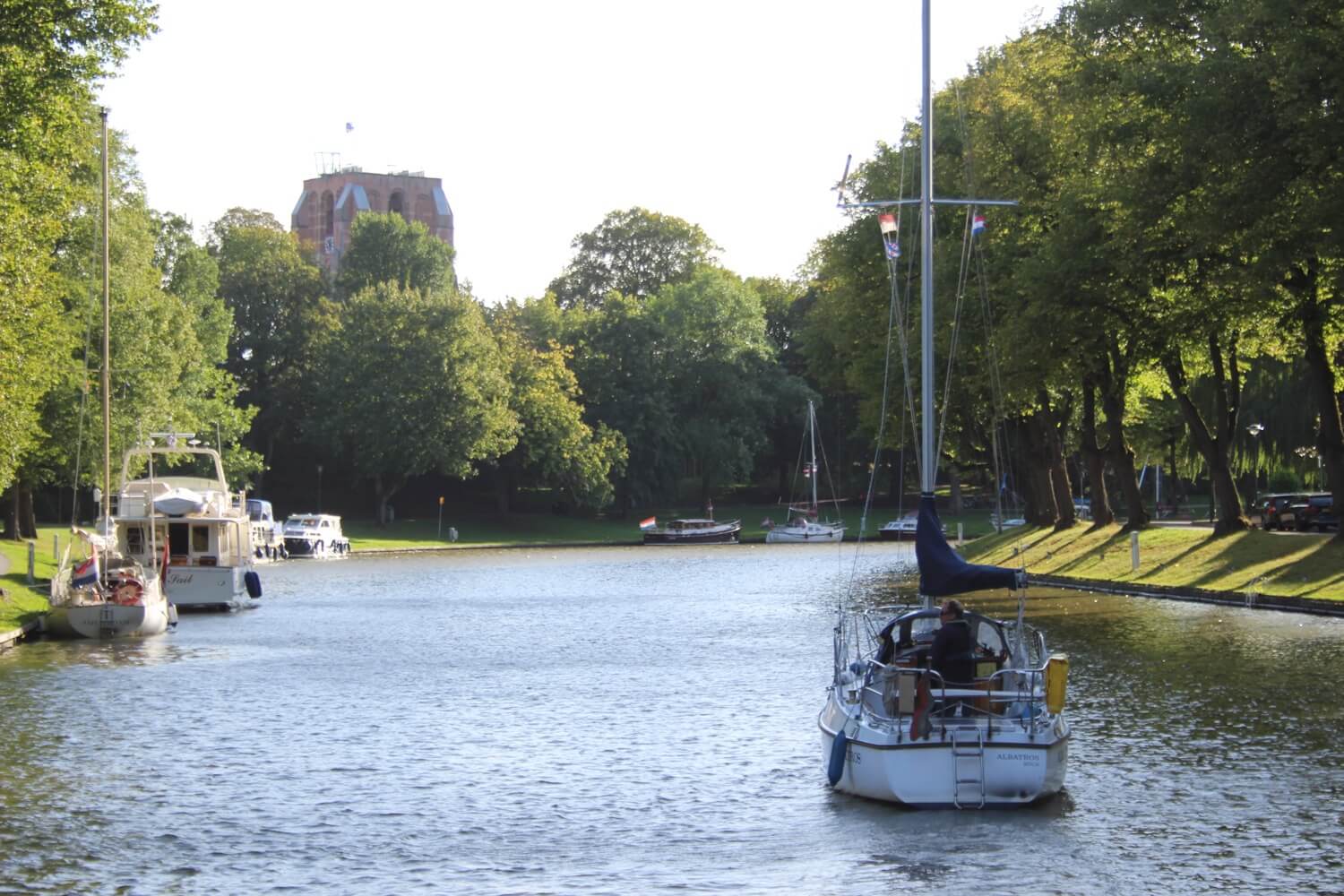

A monohull is a classical boat with a single hull. A boat with two hulls is called a catamaran, or a 'cat'. Although rare, there are also trimarans, boats with three hulls. Multihulls with four or more hulls do happen but they are an unnecessary freak of nature.
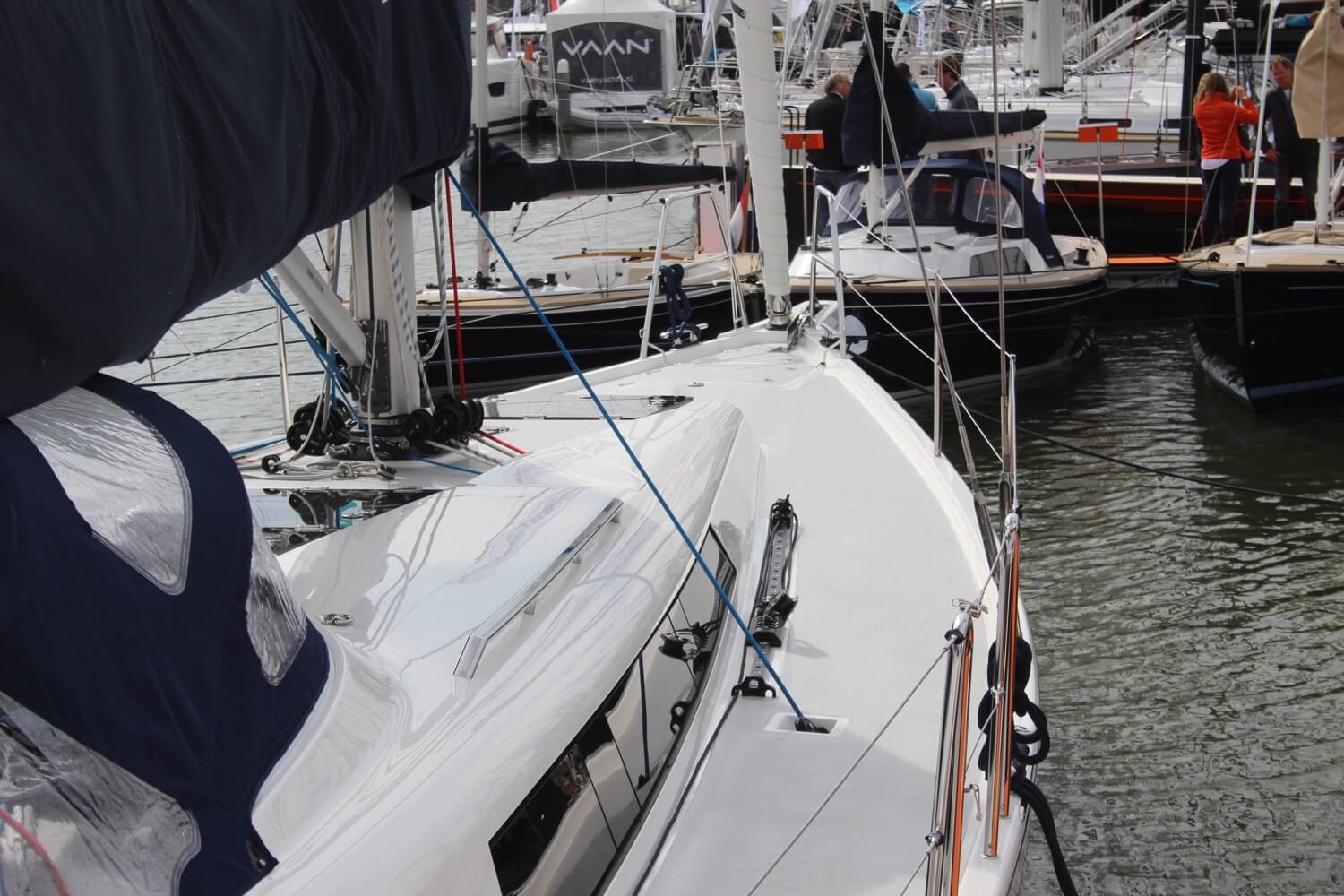

So there you have it. Fifty sailing terms you will encounter the most when traveling or learning. I know you might think some of them are a bit unnecessary since they have a perfectly fine 'real world' equivalent. I agree. But until the tradition changes, you might want to get some of these under your skin.
A boat's freeboard is the distance from the upper deck to the waterline. Classic yachts have low freeboards, so they appear to lay deeper in the water, as opposed to more modern yachts, which have a higher freeboard. It literally means 'free-board' : the amount of visible board.
The lunch hook is a light anchor setup that is used to moor small yachts temporarily. It typically uses a lightweight anchor on a short scope that takes little effort to set. The lunch hook is only used when the crew is on board and will be monitoring the anchor.
In naval architecture and ship design: “Head” = WC = Bathroom. A toilet is still a toilet. The toilet is in the head. In olden day, the toilet was a hole in the head.
Hi Rich, you’re absolutely right. I’ve corrected the error. Thanks for pointing it out.
A nautical mile is one minute of a degree, so if you travel 60 nautical miles that means you have gone 1 degree around the “globe”. (Note: arc length not actual length.) This is the original definition. As such the average was agreed upon and the lengths given a standardization. Which you mentioned.
As such 1 knot is to travel one nautical mile in an hour.
Also 1.5078. I think you made a mistake as it should be 1.1508 miles to a nautical mile.
Thanks for the information. Sorry about being a pedantic mathematics teacher.
So, where is the “nautical mile” calculated from, the equator or one of the tropic lines?
Just to clarify a nautical mile. If you draw an imaginary line from the North Pole or South Pole to the center of the Earth and draw another line from the center of the Earth to any point on the equator, it forms a right angle, which is 90 degrees. This equates to latitude. The equator is 0 degrees and the poles are 90 degrees. Your latitude is the angle that you are north or south of the equator. Each degree of latitude is divided into 60 minutes. A minute of latitude is the same distance matter where you are on Earth. It is 6,076 feet. This is the length of a nautical mile. A statute mile is 5,280 feet, so a nautical mile is 1.1508 statute miles.
Thank you very clear and well explained. Hopefully I’ll remember The Fifty
KöhnSharkösz
Really? No gunwale? No transom? Those or basic terms to the Washington State Boater Education Card required to operate watercraft here. Definitely more of a “need to know” than bimini.
Thank you, those definitions and explanations were clear, thorough, and helpful. I’m really glad I found my way (somehow) to your webpage.
Leave a comment
You may also like, 17 sailboat types explained: how to recognize them.
Ever wondered what type of sailboat you're looking at? Identifying sailboats isn't hard, you just have to know what to look for. In this article, I'll help you.

How Much Sailboats Cost On Average (380+ Prices Compared)

The Ultimate Guide to Sail Types and Rigs (with Pictures)

Sailboat Parts Explained: Illustrated Guide (with Diagrams)

How To Live On a Boat For Free: How I'd Do It

Parts of a ship explained

COVID 19: You can change your booking on most of our boats if your travel plans are affected by coronavirus. See here for more details
Let us help you plan the perfect sailing trip
Provide your travel details, receive free offer and enjoy your holiday!
What are the sides of a ship called?
THE FRONT of the ship is called the bow , and THE BACK of the ship is called the stern .
When looking towards the bow, THE LEFT SIDE is called the port side , and the right side is called the starboard .
But to really get to know the vessel you will spend your holidays on, you should learn a little something about the parts. Here is an alphabetical ”everything you have to know about ships” guide.
- ANCHOR – A chain with a hook on the end that falls to the bottom of the sea and prevents your yacht from sailing off without you. Used for parking your yacht in a bay.
- ANCHORAGE – A great spot for holding, anchoring and sheltering your vessel
- BACKSTAY – A steel wire attached to the back of the boat
- BEAM – The width of the vessel.
- BOW – Bow of a ship is the front of a vessel. A simpler term would be the pointy end of the boat.
- BOAT – A boat is a vessel small enough to be carried by another vessel. When a boat is no more possible to be transferred by another it is called a ship.
- BOAT HOOK – A pole with a hook. You use it to grab and pick up a rope, collect something that has fallen overboard, or push the vessel off the port.
- BOOM – A horizontally set pole that holds the bottom of the sail. Not a pleasant experience having this hit you in the head.
- BURGE – A distinguishing flag to identify a recreational organisation of the vessel.
- CABIN – A part of the vessel below the deck where you can sleep, spend time and relax.
- COCKPIT – A place in a boat from where you (or the captain) controls the boat. It is usually an open space outside the cabin.
- CLEAT – Metal fittings you use to fasten a rope.
- DECK – An area of the vessel that covers the hull. The part where you spend most of the time.
- DRAFT – The difference between the lowest point of the boat and the waterline.
- FENDERS – Cushions made out of rubber or plastic to prevent damage to the vessel.
- FORESTAY – A steel wire attached to the bow of the boat. The other side of the backstay.
- GALLEY – A vessel’s kitchen.
- GRAB RAILS – Rails you should grab when feeling like you might fall off.
- GUNNEL/ GUNWALE – The rail that goes along the edge of a vessel.
- HATCH – An opening in the vessel’s deck with a water-resistant cover.
- HELM – A wheel or a tiller that controls the vessel. One of the most important things on a vessel!
- HULL – The shell and the main part of a vessel, the floating part.
- IRON MIKE – A slang name for auto-pilot
- JACOB’S LADDER – The type of rope ladder that you’d use to climb up something. It can be lowered from the deck when passengers come on board.
- JIB – The triangular sail at the front of the vessel.

- KEEL – The structural base and the lowest point of the boat's hull, the backbone of a vessel.
- LINE – a general term for a rope on a vessel. It is a good thing to know how to tie knots when working with the lines (ropes).
- MAINSAIL – The sail behind the main mast of the vessel.
- MAST – The vertically set pole that supports the sail.
- MOORING – Mooring a vessel means fastening it so it can not go adrift. It also includes all sorts of locations a vessel can be moored on such as a pier, a wharf or something else.
- PORT – The left side of the vessel.
- PROW – A poetical term for the front of the boat.
- RIGGING – The ropes and wires that control the sails and support the masts.
- RUDDER – vertical plate or a board used to steer the vessel connected to the back.
- SAILS – An eco-friendly engine that converts wind power into boat speed. The most important part for sailing.
- SALOON – The living area in the vessel, you can go here to relax.
- SCUPPERS – The holes in the deck that let the water drain out and control the level of the vessel.
- SEA COCK – A faucet in the hull that can be turned off when not in use.
- SHIP – A vessel predominantly used for oceangoing travels.
- SKIPPER – The most important person on the vessel, the person in charge and responsible for the safety of all men aboard.
- SPRING LINE – This is a rope that stops a boat from moving forward or backward while being fastened to a dock.
- STARBOARD – Starboard is the right side of a vessel when looking towards the front/bow
- STEM – The front of the vessel. Also known as the bow.
- STERN – The back of the vessel. The stern of the ship is the opposite of the bow.
- STERN LINE – This is a rope leading from the stern (back) of the vessel.
- SUPERSTRUCTURE – Everything above the deck.
- TILLER – A tiller is a bar or handle that you use to turn a vessel’s rudder to change directions.
- TOPPING LIFT – A line (rope) used to hold the boom (a horizontal pole that holds the bottom of the sail) up when the sail is lowered.
- TRANSOM – The transom is a wall at the back of a vessel.
- UNDERSIDE – The area of the vessel that touches the sea. The bottom of the vessel.
- VESSEL – A craft made for traveling on water, usually a larger boat or a ship
- WINCH – A rotating drum powered either by electric motor or human motion

Vikings Season 6 Ending Explained: Ragnar's Sons & Kattegat's New Ruler
- The ending of Vikings closed the story of Ragnar Lothbrok and his sons with shocking developments and deaths.
- Ubbe fulfills Ragnar's dream by adventuring to the New World, while Ivar and Hvitserk face internal struggles and adopt new paths.
- Vikings ends with Ingrid as queen of Kattegat, bringing the show's core themes of faith and exploration full circle.
After 6 seasons, the Vikings ending brought the story of Ragnar Lothbrok and his sons to a close, though not without throwing in a few last-minute shocking developments (and, of course, deaths) The final season was split into two halves, and Vikings season 6b opened with the death of Ragnar's firstborn son, Bjorn Ironside, after leading the Norwegian army to victory against the invading Rus. Bjorn's half-brothers, Ivar the Boneless and Hvitserk, had fought on the side of the Rus during the invasion, and were left at a loose end after helping to secure a new leadership to the east.
While Ivar and Hvitserk left the Rus and went back to their old raiding ways before the end of Vikings , Ubbe sought to fulfill a different part of Ragnar Lothbrok's legacy by adventuring across the vast ocean to the west in search of a promised "Golden Land." Following a harsh journey, Ubbe finally reached the New World at the end of Vikings — and discovered that it was already inhabited. However, Ragnar's sons weren't the only characters in the show, and the Vikings ending spent just as much time showing what lay in store for Kattegat after the finale.
Vikings is available to stream on Amazon Prime Video and Hulu
All 6 Vikings Seasons, Ranked Worst To Best
Ubbe's settlement in north america, ragnar's most pragmatic son headed west at the end of vikings.
The ending of Vikings saw Ubbe finally fulfill his goal of traveling west and reaching the "Golden Land". Though Vikings viewers may think that the shot of a soaring eagle after Ubbe's arrival in the "New World" means he's reached the USA (or rather, the land that will eventually become the USA), he and his settlers actually arrive in Northeastern Canada. Ubbe's arrival in the west may not have happened in real life, but his story serves as both a fulfillment of Ragnar's dream of exploration, and as a foreshadowing of the colonization of the Americas by European explorers.
When asked by Othere what he sees when he looks at the new world at the end of Vikings , Ubbe replied excitedly that he sees farming land, minerals for mining, " rivers, ports, construction, abundance. Everything that Ragnar dreamed of. " Troubled by this, Othere points out the flaw in Ubbe's thinking:
" You discover a new land, but you behave in the same ways as you did before. And then it becomes just like the land you left behind ."
Sure enough, behaving in the old ways soon damages the relationship between Ubbe's settlers and the native Mi'kmaq tribe. After they receive a gift of a small lump of gold, a Norse settler called Naad grows greedy for more and searches the Mi'kmaq's camp for it — murdering the Sagamaw's son, Peminuit, when he's caught. Ubbe decides to punish Naad by executing him via a blood eagle, but in the end simply cuts his throat.
It wouldn't be surprising if he ultimately decided to adopt the Mi'kmaq's ways, rather than attempting to forcibly colonize his new world for the Norse.
Though he kills Ubbe quickly as an act of mercy, knowing that Naad would never be able to stay silent through the torture and earn his place in Valhalla , but can also be interpreted as Ubbe deciding to leave the old ways behind him. Ubbe has always been the most pragmatic and level-headed of Ragnar's sons, and previously converted to Christianity to secure a truce with King Alfred in England. It wouldn't be surprising if he ultimately decided to adopt the Mi'kmaq's ways, rather than attempting to forcibly colonize his new world for the Norse.
As far as historical records show, Norse explorers didn't reach North America until Leif Erikson's arrival in the 11th century . However, based on the presence of Mi'kmaq natives and the fact that Ubbe's boats travelled from Greenland, it can be assumed that they ended up in the area that would later be dubbed "Vinland" by Leif Erikson, and eventually dubbed Newfoundland by King Henry VII in the 15th century.
Vikings True Story: Did Ubbe Really Explore North America?
How (& why) floki came to the new world, the master boat-builder only found sadness in iceland.
To Ubbe's surprise, he found an old friend waiting for him in the new world: Floki, who returned for the Vikings ending. The last time viewers saw the giggling boat-builder, he was seemingly crushed in a cave-in after discovering to his maddening dismay that Christians had beaten him to Iceland, which he'd once believed to be Asgard — the home of the Norse gods.
Floki's own new world fell apart when the settlers he persuaded to come to Iceland descended into in-fighting and murder
Floki's own new world fell apart when the settlers he persuaded to come to Iceland descended into in-fighting and murder, culminating in the suicide of Kjetill's sweet-natured daughter, Aud. When asked why he left Iceland and travelled west, Floki simply replied that the sadness came to be too much for him. With his memories having become muddled in places, Floki doesn't offer many details about how exactly he made the epic journey, saying only that he " found a boat ."
As set-up for Floki's return prior to the ending of Vikings , it was mentioned earlier in season 6 that he was the greatest boat-builder of all the Vikings, and that his boats sailed smoothly through the waves. If he actually build the boat that he claims to have found, then Floki's journey may well have been easier than Ubbe's.
As he approaches death at the end of Vikings , Floki finally seems to have found peace.
The return of Floki reveals just how much he has changed from the man he was in Vikings season 1. Whereas he was once devoted to the Norse gods and very opinionated about how Ragnar should honor them, Floki's blind faith seems to have been shattered by his discovery of the Christian cross in a cave in Iceland. He shies away from giving advice, even when Ubbe directly asks for it. As he approaches death at the end of Vikings , Floki finally seems to have found peace.
As with Ubbe, Floki's journey to North America is fiction (though a real-life Viking called Floki was among the first of the Northmen to travel to Iceland).
Vikings: 10 Most Shocking Parts Of The Final Season
Ivar the boneless dies in battle, ragnar's youngest son embraced his end in the vikings finale.
Ragnar Lothbrok's youngest son, Ivar the Boneless, had perhaps the most interesting arc by the time Vikings ended. His legend started before he was even conceived, with his mother — Ragnar's second wife, Aslaug , who experienced visions of the future — warning her husband that he needed to wait three days before consummating their marriage, or their child would be monstrous. Ragnar ignored her, and a difficult pregnancy followed that culminated in a baby born with deformed legs.
Ivar was left to die in the woods by Ragnar, but after being rescued by Aslaug, he eventually grew up to be a favorite among Ragnar's sons, accompanying his father on his final journey to England. Ivar killed for the first time when he was still a child, hitting another boy in the head with his hatchet in a fit of anger. Later, he killed his own brother, Sigurd Snake-in-the-Eye, for mocking Ivar's apparent impotence.
Ivar declared that he was not simply descended from the gods, but an actual god himself.
If each of Ragnar's sons represents a different facet of his personality, Ivar embodies the part of Ragnar that hungers for violence and war. This came to a head when he became the king of Kattegat, and Ivar declared that he was not simply descended from the gods, but an actual god himself. In a short period of time, however, Ivar lost first his son, and then his rule over Kattegat, and his beloved wife Freydis, whom he strangled after learning that she'd betrayed him as revenge for the death of Baldur .
Though he attempted to take back Kattegat with Prince Oleg, Ivar's story in season 6 was largely one of introspection and even redemption. He became a father figure to Igor, fathered a biological child with Katia, and when conflict loomed on the horizon on Kattegat, he avoided a struggle for the throne by suggesting that he, Hvitserk, and Harald invade England instead.
Ultimately, like Ragnar, Ivar welcomes his death.
Ultimately, like Ragnar, Ivar welcomes his death. Despite the sclera of his eyes being very blue (a sign that he is in heightened danger of breaking his bones) he wades into the final battle against King Alfred's army and allows a soldier to fatally stab him in the stomach. In addition to securing an appropriate death for one of the greatest Vikings who ever lived, Ivar's decision to die also seems to be out of love for Hvitserk.
As he watches his brother ruthlessly kill people on the battlefield, Ivar experiences flashbacks to their life together. Perhaps he realized that as long as he lives, Hvitserk will always follow him into battle and will never know peace, and so Ivar chose to die so that the fight would end and Hvitserk would have a chance for a better life.
Vikings: 10 Things You Didn't Know About Ivar
Why hvitserk converted to christianity (& changed his name to athelstan), after a life being overshadowed, hvitserk found purpose away from kattegat.
If each of Ragnar's sons had an ending that pays tribute to their father — Ubbe fulfilling his dream of exploration, and Ivar his love of battle — then Hvitserk's ending in Vikings is a nod to Ragnar's love of Athelstan, and his curiosity about the Christian god. From the moment Athelstan's monastery was raided in Vikings season 1, and he was taken captive, the monk was an object of fascination for Ragnar, and eventually came to be his closest friend and adviser.
Even after Athelstan was murdered by Floki, he remained as a presence in the show
Even after Athelstan was murdered by Floki, he remained as a presence in the show — sometimes appearing to characters as a vision, and later manifesting spiritually in Othere, the wanderer who guided Ubbe to the "Golden Land," who claimed that he was once a Christian monk called Athelstan. Of course, Athelstan's most persistent presence in Vikings was through his son, King Alfred the Great, who faces Ivar and Hvitserk in season 6's final battle.
When Ivar is killed in battle, Alfred calls for a halt to the fighting so that Hvitserk can mourn his brother's death, and the invasion more or less fizzles out there. It's unclear whether Hvitserk was more of a guest or a prisoner in the days that followed (perhaps a bit of both), but when he's next seen his beard has grown out to indicate the passage of time. He converts to Christianity at the end of Vikings, and Alfred seals his conversion by changing his name from Hvitserk to Athelstan.
Hvitserk struggled more than his brothers in his search for greatness — never becoming a feared warrior like Bjorn, an adventurer like Ubbe, or the ruthless ruler that Ivar was.
Hvitserk struggled more than his brothers in his search for greatness — never becoming a feared warrior like Bjorn, an adventurer like Ubbe, or the ruthless ruler that Ivar was. By the end of Vikings , Hvitsekr/Athelstan had never married or had children, and both of the women he loved have died. He spent most of his life following after Ubbe or Ivar, and with both of them gone, he has nothing left to return to in Kattegat after Vikings finished. Hvitserk's expression is inscrutable during his baptism, but it's implied that some sort of deal was made when Alfred tells him:
" You entered here as a pagan, and you will leave here as a Christian Saxon prince ."
Vikings: 10 Things You Didn't Know About Hvitserk
Queen ingrid rules over kattegat, none of ragnar's offspring became the new leader.
Somewhat surprisingly, Vikings does not end with a son of Ragnar as the king of Kattegat.
The throne of Kattegat has held many different rulers, but somewhat surprisingly, Vikings does not end with a son of Ragnar as the king of Kattegat. Instead, Bjorn's second wife Ingrid — carrying a child that could be either Bjorn's or Harald's — declares herself the new queen after Harald is killed in the raid on Wessex (similar to how Aslaug became queen after Ragnar's death) . Some viewers expressed disappointment that a newer character ended up ruling Kattegat, but Vikings never had a fixation upon which character will "win" in the same way that, for example, Game of Thrones had.
A lesser-known character only related to Ragnar through marriage ending up on the throne of Kattegat can also be seen as another way of respecting Ragnar's memory.
A lesser-known character only related to Ragnar through marriage ending up on the throne of Kattegat can also be seen as another way of respecting Ragnar's memory. The legendary warrior was never very interested in being a king, and only became the ruler of Kattegat because his hand was forced by Earl Haraldson. Ragnar didn't want to be tied down to Kattegat, so it makes sense that his sons would also move on. E ven as she says " Long live the Queen ," Ingrid seems troubled — perhaps because she knows the rulers of Kattegat don't tend to live very long.
Was Ingrid A Witch? What Vikings' Real Life History Reveals
The real meaning of vikings' ending, the finale brings the show's core themes to a head.
The second half of Vikings season 6 brought the show's story full-circle, with Ubbe's storyline recalling Ragnar's desire to discover new land, while Ivar and Hvitserk once more returned to raid England. Though Vikings has frequently strayed from historical accuracy , the series has covered in broad strokes the first few decades of the Viking age in England, and the season 6 finale foreshadows the end of that age with the detail that a Danish king has converted to Christianity and forbidden worship of the Norse gods.
The final scene at the end of Vikings is Ubbe and Floki sitting on a beach in their new world, looking out over the waves towards the sunset. Floki says that he still sees Ragnar all the time:
" He keeps asking me to build him a new boat. And I say, 'What the hell do you need a new boat for, Ragnar? You're dead!' "
He then comments that Ubbe looks a lot like his father. Ubbe tells Floki that he loves him, symbolically healing the rift that was created between Floki and Ragnar many years ago.
A show that began with Ragnar Lothbrok and his burning curiosity ends, rather appropriately, on a question.
Amid all the bloodshed and battles, the idea of faith has persisted at the core of Vikings — with multiple characters finding themselves torn between faith in the Norse gods and faith in the Christian god, and the show's touches of magical realism implying that both could be real. But when Ubbe asks Floki whether death is the end, Floki offers no reply. And so Vikings , a show that began with Ragnar Lothbrok and his burning curiosity ends, rather appropriately, on a question.
Vikings is a historical drama series created for the History Channel by Michael Hirst. Based on stories passed down in Norse lore, the series focuses on the Lodbrok family and their lives during medieval Scandinavia. The family is formally established by the rise of Ragnar Lodbrok, a farmer turned Viking who rises to power as a Scandinavian King.
Cast Katheryn Winnick, Gustaf Skarsgrd, Travis Fimmel, Jessalyn Gilsig, George Blagden, Clive Standen
Release Date March 3, 2013
Streaming Service(s) Hulu, Amazon Prime Video
Showrunner Michael Hirst


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn the names and functions of all the sailboat parts, from hull to rigging, with clear diagrams and examples. This guide is a great reference for beginners and experienced sailors alike.
In this beginner's guide, we'll take a closer look at the different parts of a sailboat and how to orient ourselves onboard before we set sail!
Are you curious about sail mechanics and how they engage the wind? In this illustrated guide, we'll explain the various sail components and how they work together to propel a sailboat. From the head to the foot, the tack to the clew, we'll break down each part and give you a solid foundation to build on as you learn to trim sails and navigate the open sea.
Here's where to find a description of the essential parts of a sailboat and understand what each one does, and how it does it. And yes, there are a lot of them
If you're a beginner sailor, you want a quick and solid overview of the different sailboat parts. In this video, I go over the four main segments of the sailboat and the most important sailboat parts.
Sailboats are fascinating vessels that rely on the power of the wind to navigate the open waters. Understanding the parts of a sailboat are essential whether you're a seasoned sailor or someone who's just getting started. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the anatomy of a sailboat, exploring each component and its role in harnessing the wind and propelling your vessel forward ...
Parts of a Sailboat: Essential Components Explained Sailboats are fascinating vessels that have been used for centuries to explore and navigate the world's oceans.
Basic Sailing Terminology: Sailboat Parts Explained Sailing is a timeless activity that has captivated the hearts of adventurous souls for centuries. But, let's face it, for beginners, sailing can be as intimidating as trying to navigate through a dark, labyrinthine maze with a blindfold on. The vast array of sailing terminology, sailboat parts and jargon can seem like a foreign language ...
Short answer parts of sailboat: A sailboat consists of various essential components, including the hull, keel, rudder, mast, boom, sails, rigging, and cockpit. These parts work together to enable sailing and control the boat's movement and direction.
Illustrated Guide to Sailboat Parts [Updated 2023] Published September 5, 2022 By Matt C Categorized as Boat Parts. The lingo of sailing is baffling to many newcomers. While the actual sailing is pretty easy, it's hard to wrap your mind around the bookwork when it seems like every little thing on a boat goes by its own nautical term.
Sailboats share many parts with other boats, such as keels, decks, and sometimes engines. But parts like halyards, sheets, and blocks are unique to sailboats.
Main parts of a sailboat are explained for a Bermuda rigged sloop. This is the most widespread modern type of sailing boat and it is the boat type considered in this blog, as well as in Your First Sailing Handbook. For overview of other sailboat types and their classification see our post: Types of Sailboats.
When you rent a sailboat with Boatsetter, you will have the option to book a captained sailboat to enjoy your day out on the water or book bareboat to hone your sailing skills. Either way, you may be interested in the intricacies of a sailboat and its different parts. If this sounds like you, you have come to the right place. In this article, we go in-depth about the different parts of a ...
The main parts of a sailboat include the hull, wheel/tiller, rudder, keel, mainsail, jib/headsail, mast, and boom. While there are many other important parts of a sailboat, these are the main parts that serve specific purposes that are vital for successfully operating a sailboat. Learning about the main parts of a sailboat is going to allow you ...
Some Specific Parts of a Sailboat For this next part, I am going to talk about what is above the deck, the rigging. The rig includes the sails, the supporting cables, and everything that controls all of this. These are the parts of a sailboat that make it a sailboat and not just a mere boat.
From the bow to the stern and everything in between, read our descriptions of the different parts of a sailboat. A great guide for beginners, and a reference for experienced boaters.
Understanding the various parts of a sailboat is fundamental to appreciating the art and science of sailing. From the sturdy hull and towering mast to the intricate rigging, sails, and navigation equipment, each component plays a vital role in the operation and performance of a sailboat.
Sailboats Explained Sailboats have many parts and esoteric names, but when you break it down, it isn't all that complicated. Here, we'll make it simple for you by doing just that. Types Parts Sails Keels Sailboat types Sailboat parts Keels Sail types Rig types Hull types
Stern, Helm, Bow and Sides of a Sailboat When approaching a sailing yacht, you will notice its basic shapes and curves, front and back of a boat, a big pole in the middle, etc. So, let's start with those basic parts of a sailboat. In Mediterranean countries, yachts will mostly be docked with their back part to the shore or peer.
The different types of sailboats include cutters, catboats, dinghies, ketches, schooners, sloops, and yawls. There are many different parts that make up a sailboat. Continue reading to learn about the different parts of a sailboat.
The term sailboat includes many different sizes, shapes, and hull types. Here's how to identify most of the common ones.
Since there are gadgets and parts on the boat that you won't see anywhere else, it only makes sense they all have their own special name. You want to know these because unlike the direction terms where you can do with 'left' and 'right', you don't want to call a tiller 'that stick thing back there'.
Parts of a ship explained COVID 19: You can change your booking on most of our boats if your travel plans are affected by coronavirus. See here for more details
The sons of Ragnar Lothbrok fulfill their father's dreams in different ways in the Vikings series finale. Here's a breakdown of the emotional ending.