
Navigation Lights for Sailboats (And How To Read Them)

Last Updated by
Capt Chris German
June 15, 2022
Navigation lights on a sailboat can be confusing. If you understand the reason behind why they are the way they are however, they can make a lot more sense.
At their heart, sailboats are really just a power boat and as such must adhere to all power boat rules such as navigation lights. Other times however, a sailboat is classified in a special category. They have a set of additional lights they CAN show as an option, but are not always required to do so.
That’s about as clear as mud if you ask me and I contend that that is where the confusion about lighting a sailboat begins.
Just because you can show a light to identify yourself in times of low visibility, does not mean you have to and then we add in a little sibling rivalry between power and sail and things get downright adversarial when it comes to navigation and the night.
Table of contents

The USCG says You’re a Power Boat Whether You Like It or Not
Much to the consternation of many a sailor who has earned a commercial license to drive their sailboat, when you received your credential from the USCG it says you are a master of steam and power across the top with no mention of wind as a source of propulsion.
It is not until you read the back pages of your little red book that feels like a passport and looks like a US Sailing credential, that you will see the term “sail auxiliary”. That is because most of the time the U.S. Coast Guard knows that you are primarily reliant on your mechanical power to propel your vessel.
It's a sad thing, but the days of commercially viable sail boats are done and all but the most select few even have sails let alone use them as their primary power source. All sail boats by law are powerboats, but not all powerboats are sailboats.
Navigation Lights for a Power Boat
As a power boat, you are required to show certain lights and have been required to do so before power was even invented.
In the days of man powered vessels like the viking ships who relied on oars while in close quarters to power their vessels, they needed to show other boats, friend or foe, where they were by showing lanterns in the dark to identify themselves. As you know, it is a time honored rule among all the nations of the world both past and present, that you must avoid a collision at all costs while at sea and even the viking knew that you should not run into things.
By lighting the front and back of your boat, you could warn other boats of your presence as well as identify which way you were heading. As such there is a very specific rule in the Code of Federal Regulations Number 46 (CFR46 by common name) that spells out with detail how many, the color, the luminosity or brightness, the angle of visibility and the location of all of the lights required for navigation on every single boat, seaplane, submarine and other nondescript vessel conceived by man to date that they must show while underway in reduced visibility.
And there is no flexibility in the rules.
As such a power boat, and by extension all sailboats, MUST, without question show one green light on the starboard bow and one red light on the port bow and one all around white light or lights while operating in reduced visibility. These lights should shine at all 360 degrees of visibility with the bow lights shining at an angle of dead ahead to 22.5 degrees abaft the beam and the stern lights shining 225 degrees dead aft. A forward facing masthead light that is white in color shall shine forward to comply with the directive that all vessels must carry an all around white light. For more read here .
As you can see, there isn’t much wiggle room when it comes to lights that must be shown.
Sailboats get a little flexibility with lights
Sailboats however, are a little different when they are in fact sailboats, which is only when you are entirely reliant on the wind for power and in no way reliant on any mechanical or manual means of propulsion. And for good reason.
Back in the day when men were men and sailboats were wooden, fire was a major concern. Sails were coated with wax and other flammable substances and the wood on boats was saturated with oils and grease. Even the ropes were plant materials saturated with oils to keep them pliable and strong.
Add those highly flammable substances to a parching environment like the sea and you had what was essentially a giant floating tinderbox.
Then tell that giant floating tinderbox that they need to identify themselves to the world at large at night using oil lamps with flames because batteries and lights were not invented yet. It didn't take very long or very many ships burning to the water line for the Governments to say to the sailboats, you get to do things a little different.
As such, sailboats are given special dispensation when it comes to lights aloft. They don't have to show an all around white light in their rigging because no one wanted to set their rig on fire with oil lamps 60 feet up in their rig.
However, when a sailboat takes their sails down such as when they are powered or at anchor, they must resume the display of an all around white light or lights aloft. That became a real challenge with aluminum masts and the disappearance of rat lines on the shrouds because there was no easy way to climb the rig and check the bulbs up the mast on a regular basis.
Red over Green Sailing Machine
I have no idea where the history of this particular light comes from, but if you ever take a deck exam with the USCG, you better remember this mnemonic. An all around red light over an all around green may be displayed on a vessel during times of reduced visibility to indicate that a vessel is operating under sail power alone.
I won’t even speculate on how or why they came up with this particular light configuration, but if you want to use these lights as a sailing vessel, you can do so, but that means that you will need three all round lights at the top of your mast, an all around white, an all around red and an all around green, just in that order.
The red over green is to be displayed in addition to the running lights or the red and green bow lights with the 225 degree stern light. As always, when the motor comes on, so does the steaming light or the forward facing white light that is also usually about ¾ of the way up on your mast to complete the requirement of an all around white light that indicates a power vessel.
What is a “steaming light” and why are you mentioning it now?
Most sailboat electrical panels will have a switch that is labelled “steaming light” and it will only come on when your anchor light is off. This is probably the most confusing part of sailboat navigation lights so if you are confused about this, you're in good company as most people are.
A “steaming” light is named thusly, going back to the days of steam powered sailboats where when they fired up their boilers and doused the sails, they became a power boat once again. There aren’t too many steam powered boats, let alone steam powered sailboats, but the name stuck and it is a vestige of a bygone era.
Either way, when you fire up your motor, you turn on your “steaming light” and that locks out the all around white light which is used for anchoring to minimize the number of switches on your panel and reduce the number of wires in your mast. The fewer wires, the less chance of something not working or becoming disconnected.
The steaming light and the anchor light both go up the mast, but you can’t use an all around white light while using the 225 degree stern light at the deck level because to other boaters you would look like you have two white lights from the stern and that would be confusing.
The anchor light is used exclusively for anchoring while the steaming light is used to indicate you are a power vessel while underway.
As to why I am mentioning it now in the article, is because this would have blown your mind if I started with this subject cause it can be really confusing stuff.
Aspect Recognition with Lights
Remember when I said earlier that lights can help you tell others which way you are heading as well as tell you which way other boats are heading? That is called the aspect of the vessel and the USCG tests you on this for your deck exam as well.
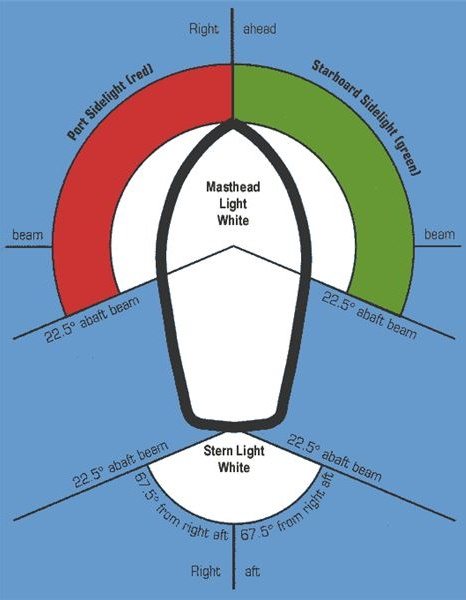
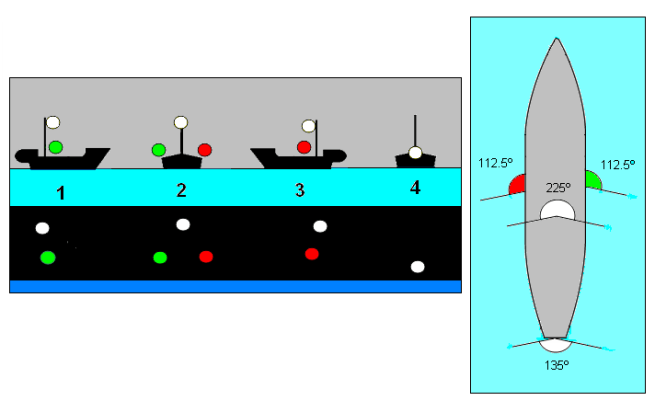
Knowing that the bow lights go 22.5 degrees abaft the beam on both sides or 112.5 degrees on each side, and the stern light faces 225 degrees aft for a total of 360 degrees of visibility, you can tell a lot about where a boat is heading and who has the right of way.
One thing that's easy to remember is red means stop and if you see a vessel's red light, it means stop as you are the give way vessel and approaching the other vessel from his port side. Conversely it works with green as well as that means you are approaching from the other vessel's starboard side and you are the standon vessel.
If you see a red and green light equally low on the horizon, that means your heading dead on into another vessel's path and conversely if all you see is a white light low on the horizon, it means you are overtaking another vessel power or sail, we don’t care because it is an overtaking situation. However, any time you do see a white light aloft in addition to the red and green bow lights, you know you are encountering a power boat.
Then there are angular approaches as well, where you see white and red or white and green light low on the horizon. You know in that case you are seeing a portion of the bow lights and stern lights from the side approaches of a vessel. Based on which direction those lights are heading, you can deduce which way that boat is going in relation to your boat.
So put it all together and you see a green light and a white light low on the horizon with a red over green light aloft, you know that you are approaching a sailboat that is traveling to your port and that might make you the standon vessel. That is of course, if we didn’t concern ourselves with windward and leeward and port tacks and starboard tacks, but that is a discussion for another article. So stay tuned when we talk about sailing rules and the right of way. But for now, do good, have fun and sail far.
Related Articles
Capt Chris German is a life long sailor and licensed captain who has taught thousands to sail over the last 20 years. In 2007, he founded a US Sailing-based community sailing school in Bridgeport, CT for inner city youth and families. When Hurricane Sandy forced him to abandon those efforts, he moved to North Carolina where he set out to share this love for broadcasting and sailing with a growing web-based television audience through The Charted Life Television Network.
by this author

Most Recent

What Does "Sailing By The Lee" Mean?
Daniel Wade
October 3, 2023

The Best Sailing Schools And Programs: Reviews & Ratings
September 26, 2023
Important Legal Info
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies.
Similar Posts

How To Choose The Right Sailing Instructor
August 16, 2023

Cost To Sail Around The World
May 16, 2023

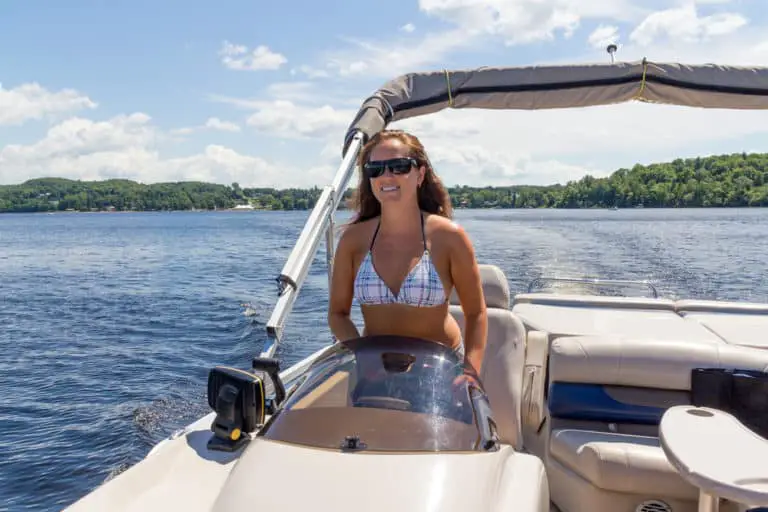
How To Drive A Pontoon Boat
Jacob Collier
December 19, 2022
Popular Posts

Best Liveaboard Catamaran Sailboats
December 28, 2023

Can a Novice Sail Around the World?
Elizabeth O'Malley

4 Best Electric Outboard Motors

How Long Did It Take The Vikings To Sail To England?

10 Best Sailboat Brands (And Why)
December 20, 2023

7 Best Places To Liveaboard A Sailboat
Get the best sailing content.
Top Rated Posts
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies. (866) 342-SAIL
© 2024 Life of Sailing Email: [email protected] Address: 11816 Inwood Rd #3024 Dallas, TX 75244 Disclaimer Privacy Policy
Boat Navigation Lights Rules: Illustrated Beginners Guide
When navigating at night, the lights on other boats are your first clue about the moving dangers around you. And your navigation lights are your first line of safety in avoiding collisions in the dark, and they tell others vessels what you are and what you are doing. The rules sound complex, but with a little understanding you can get the basics for any situation.
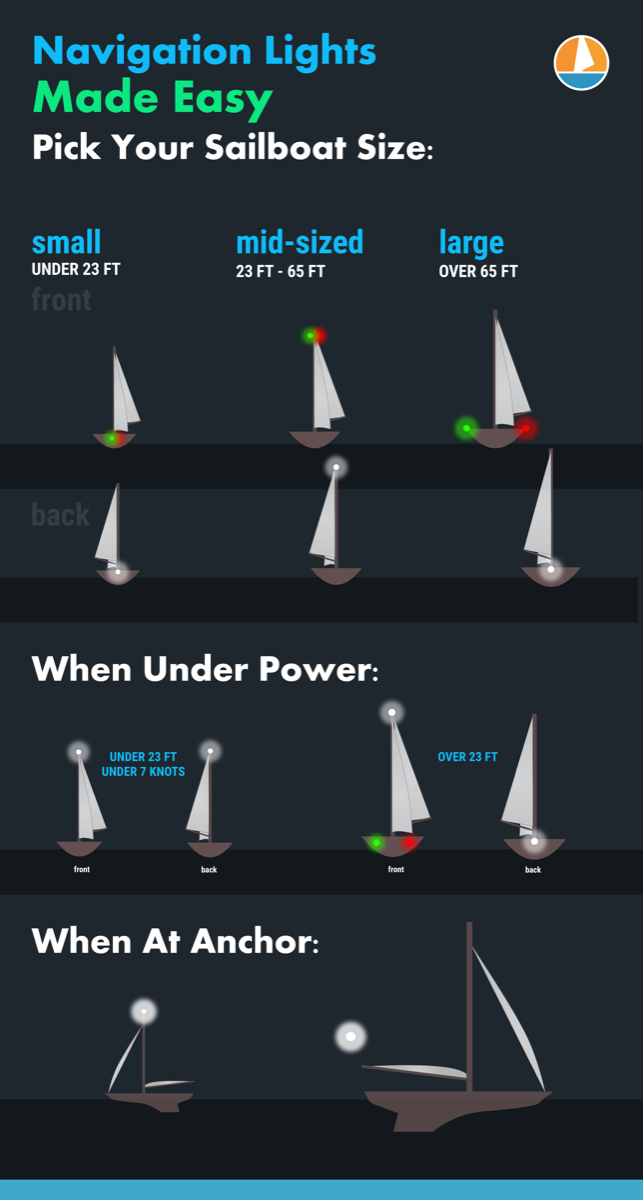
So what are the basic navigation light rules? For most small vessels, motoring requires red and green (port and starboard) lights, and a white light visible in all directions around the boat. This is almost always a stern light and a masthead light on sailboats. Boats under sail require port and starboard lights, and a white stern light. Sailboats below sixty-five feet may show a tricolor light at the masthead instead of side and stern lights when sailing.
That's it, in a nutshell. There's a little more to it, as the rules change with different sizes and there are some specifics about angles of display for the colors. Identifying other ships at sea requires more study, but the basics are the same. And it's not much trouble to make sure you've always got the proper lights on your vessel.
On this page:
What are the official colregs rules for your sailboat, what about the uscg (united states coast guard) rules, lighting at anchor, identifying the boats around you.
The International Regulations for the Prevention of Collision at Sea , abbreviated "COLREGS" is very specific about the lights required, their shapes and sizes, and the distance they must be visible. For the smaller boat, the following definitions apply.
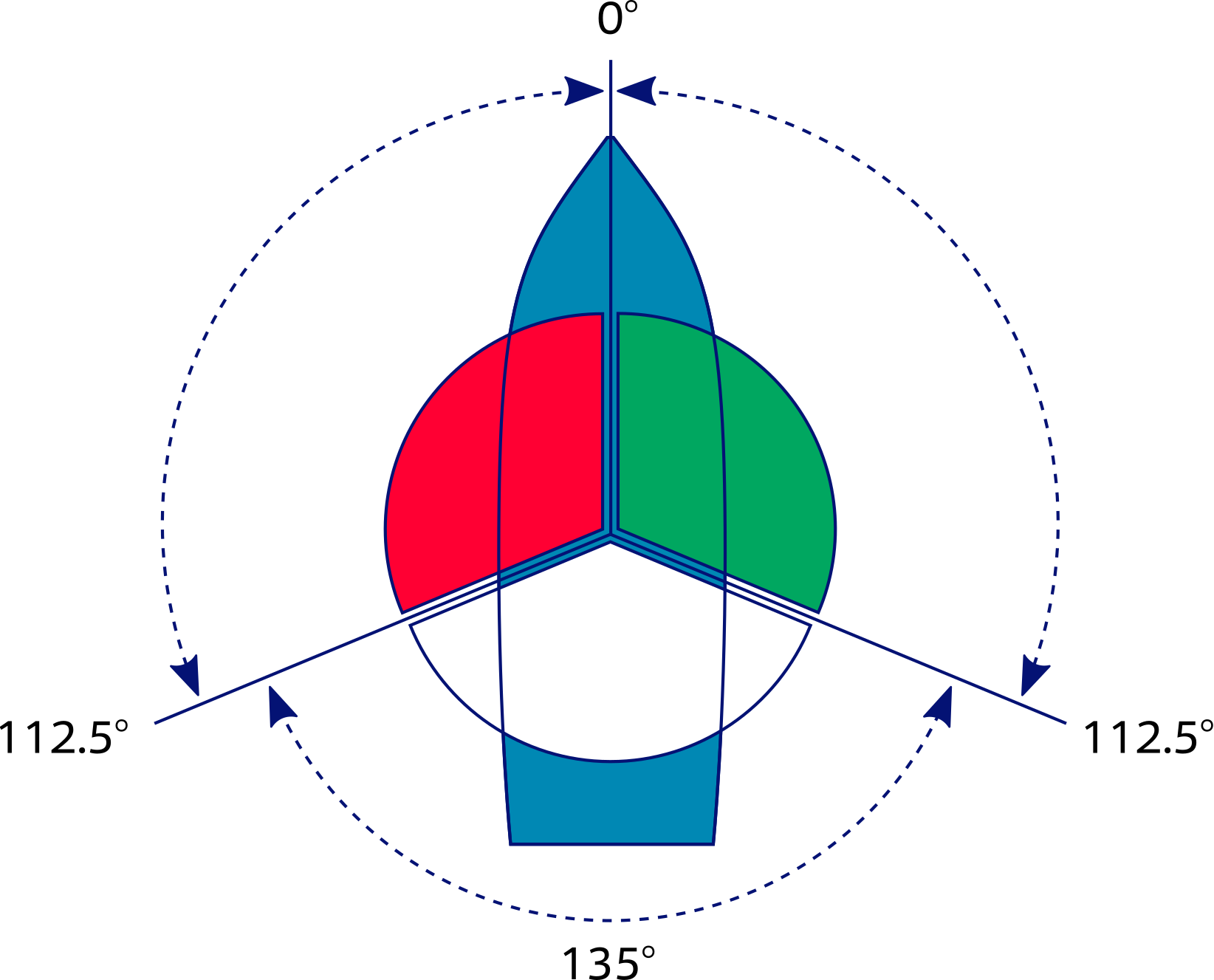
- Masthead Light - a white light placed centerline on the boat showing an arc of 225 degrees with 112.5 degrees either side of the front of the vessel.
- Sidelights - A red light on the port side and a green light on the starboard. They must show an arc of 112.5 degrees from centerline of the bow.
- Stern light - A white light on the stern of the boat showing an unbroken arc of 135 degrees from centerline of the vessel.
- All-round light - A light showing in an unbroken arc of 360 degrees.
The good news is you need not measure these angles. Any properly installed USCG or COLREGS approved light which will cover the correct arcs. If you have to replace the original light from your boat, make sure it's with an approved replacement.
Lights When Sailing
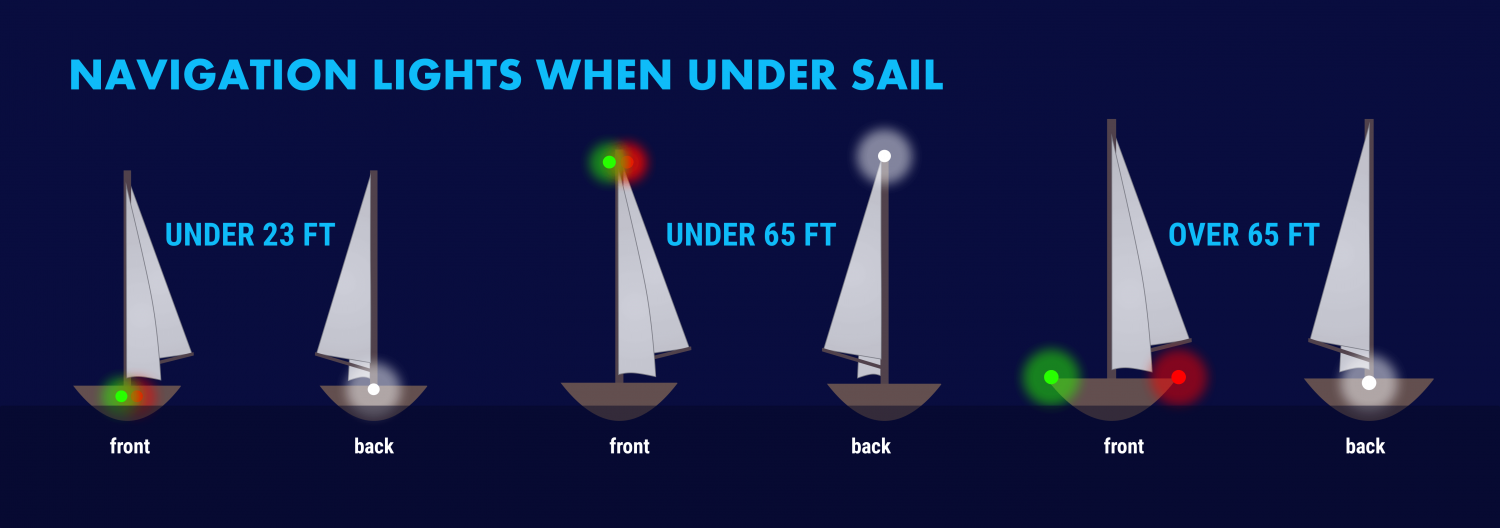
The specific rules for a sailboat under sail are in COLREGS Rule 25 and vary slightly with the size of the boat. A sailboat powering is considered a power boat and falls under in Rule 23.
- Under 23 feet (7 meters) - side lights and a stern light, possible. If these lights can not be displayed a light must be kept at hand to help avoid a collision. This can be a bright flashlight.
- Over 23 feet - Side lights visible to one nautical mile and stern light visible for two.
- Vessels under 65 feet may combine both sidelights into a single lantern on the bow.
- May show a tricolor light on the masthead instead of sidelights and a stern light. It's one or the other though, do not show these lights at the same time .
- Masthead light must be visible for three nautical miles, all other lights must have a two nautical mile visibility.
- Side lights must be separated.
- May not show a masthead tricolor light.
- Masthead light must have five nautical mile visibility, all other lights must be visible for two nautical miles.
- Optional masthead lights - any vessel under sail may display a red light over a green light at the masthead with sidelights and stern light. The red over green may NOT be displayed with a masthead tricolor light. It's one set or the other.
Lights When Motoring

For all navigational purposes a sailboat under power is considered a power boat. This includes motor sailing - if the engine is on and providing propulsion you are on a power boat, even if the sails are up . This applies to navigation lighting, sound signals in fog and limited visibility, and rights of way.
Sailboats under 50 meters under power need to show:
- A masthead light
- Stern light
A power-driven vessel under 23 feet (7 meters) that does not exceed seven knots of speed may display an all around white light, though sidelights should be used if available.

The USCG has published its own "Rules of the Road" that are based on the COLREGS. In addition, it has rules for the "Inland Waterways" for rivers, inland lakes and the Great Lakes.
The good news is this has no impact on what you have to do with your own boat.
They mostly relate to lighting changes on towed vessels like barges and tugs. For example, a vessel towing or pushing another vessel in the ocean under COLREGS shows two masthead lights, sidelights and a stern light, whereas in Inland Waterways the towing or pushing vessel displays two yellow towing lights instead of a white stern light.
If you sail on lakes, rivers or the Great Lakes where towed commercial traffic is common you should learn the inland lights, but coastal or ocean sailors will never see these.
When you anchor outside a designated mooring field, you should display an all around white light at the masthead or as high in the boat as practical.

If your boat is large and has a very tall mast, you may wish to display another light closer to the waterline. Boats approaching in the dark may not see a light on a mast sixty or seventy feet in the air when they are close to your boat.
We use a simple garden path light on our stern when we anchor, left in a rod holder or flag socket. It comes on automatically at dusk and is a cheap and easy way to be more visible. There is no specific rule stating you can not display more lights than required, or the nature of any lights beyond the required all around light.
The COLREGS also specify that a round black "daymark" should be displayed in the rigging of any vessel at anchor. Very few small vessels observe this, however it is the correct display for a vessel in an anchorage.
If you tie to a mooring in a marked mooring area you are not required to display anchor lights, but there is no harm in doing so.
The other important reason to know your lights is to figure out what's going on around you at night. The water may be ablaze with white, red, green and other lights at night and they are your first key to avoiding collisions and problems.
All combinations of lights for fishing boats, commercial vessels, and so on are outside this post‘s scope. The odds are small you will encounter a submarine, seaplane or hovercraft at night, but there are regulations regarding specific lighting for each of those vessels!
There are a few fundamentals to help you figure out what that is you see on the horizon, which way it is going, and whether it is a danger to you.
Port Wine is Red
The fundamental rule is that red sidelights will ALWAYS be on the port side of a vessel, and green lights will always be on starboard. However, some vessels can use all around red and green lights for other purposes, though those will be higher than sidelights.
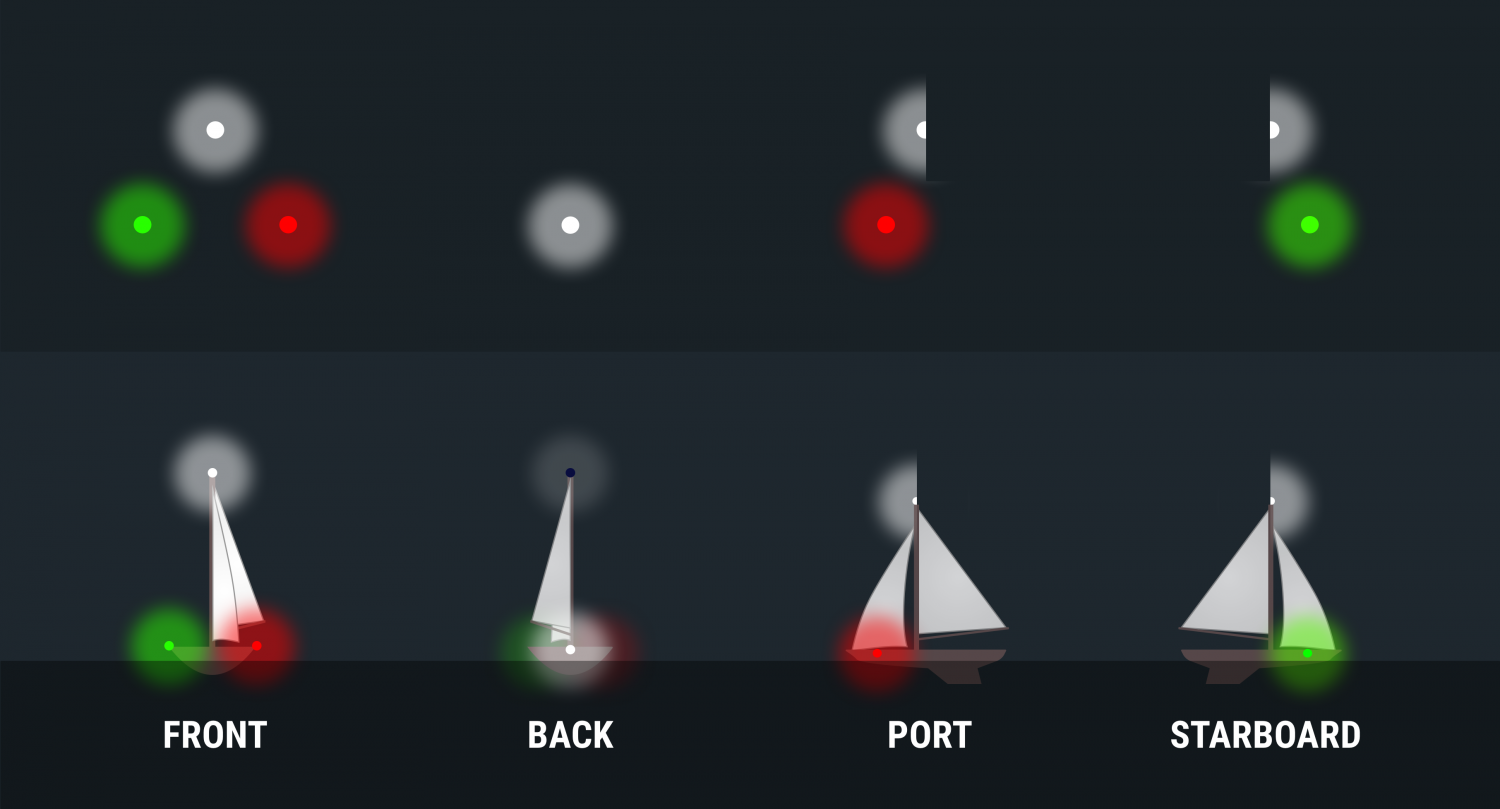
The light‘s on a ship is not important, some large tankers and freighters will have their sidelights far aft and put them on the superstructure for better visibility. It is not safe to assume that sidelights you can see are on the bow of large vessels .
When you can see the color, you know which way the bow is pointing. If it's red, it's pointing more or less to the left and will travel in that direction. A green light shows it is heading more or less to your right.
If you can see the red and green lights at the same time, you are looking directly at the bow of the vessel. When you are far away, this isn‘t as alarming as if you are close crossing. Seeing red and green lights together on a vessel is something you never want to see for long.
Be aware of red and green lights used in combination with other red, green and white lights. These may not be running lights and could have other significance.
Tankers, Freighters and Large Ships
Tankers, freighters and large ships will have side lights, a stern light and a masthead light. In addition, on vessels over 50 meters there will be a second masthead light further aft and higher than the forward light. The masthead light positions are a better tipoff to the bow direction and how far from the bow the sidelights might be. Remember - on a large vessel the sidelights may not be at the bow or even close to it.
USCG Inland Rules allow for a second all-around white light on large vessels on the Great Lakes instead of a second masthead light.
Fishing Boats
Fishing boats engaged in fishing will have more complex light displays. When they aren't fishing, they will show lights like any power vessel, but Rule 26 spells out light combinations that vary by the fishing activity being done. In general:
- Boats which are Trawling but not making headway will display a green all-around light over a white all-around light , and a masthead light aft of these lights. Boats making headway while trawling will show these lights, plus sidelights and a stern light.
- A vessel fishing other than trawling will show a red all-around light over a white all-around light . When making way they will also show sidelights and a stern light.
- If a vessel has gear more than 150 meters away from the boat, it will show a second all around light in the direction of the gear. The best rule is to give fishing boats as wide a berth as you can at night. They're easy to pick out if you check the top light configurations but their course may be difficult to predict.
Towing and Pushing
Towed vessels can be the most dangerous to cross, but they have the most lights to tell you what is happening. Refer to COLREGS or the USCG Rules of the Road Rule 24 for all combinations You can pick a tow/push vessel out with the following lights:
- Two or three masthead lights in a vertical line. Three masthead lights shows a tow over 200 meters. Additional masthead lights may show for larger tow vessels.
- A towing light (yellow light with the same characteristics as a stern light) directly above the stern light.
- The will also have side lights and a stern light.
- The towed vessel will show sidelights and a stern light. Lighting may vary under USCG inland rules, where towing lights may replace stern lights. Learn these differences if this is your regular cruising ground. If you think there is a tow ahead of you, always go well behind the aft most set of lights. Never go between a tow and avoid crossing ahead if possible as it may restrict their maneuverability.
Special Situations
There are several rare situations you may encounter. As a general rule, if there are a lot of lights and you don't understand them look for the sidelights on a moving vessel. If you can find them and figure out the direction it is moving, it makes the vessel easier to avoid. Stay well clear of lights you do not understand if you can avoid them without risk.
Most of these signals are used by larger, commercial vessels and you will not need them.
They use these light combinations with other light combinations. For example a towing vessel may also be restricted in maneuverability, and a vessel constrained by draft will show running lights if moving.
- Not Under Command - two all around red lights in a single line
- Restricted in Ability to Maneuver - red, white then red in a single line
- Constrained by draft - three all around red lights
Leave a comment
You may also like, 17 sailboat types explained: how to recognize them.
Ever wondered what type of sailboat you're looking at? Identifying sailboats isn't hard, you just have to know what to look for. In this article, I'll help you.

The Ultimate Guide to Sail Types and Rigs (with Pictures)
Own your first boat within a year on any budget.
A sailboat doesn't have to be expensive if you know what you're doing. If you want to learn how to make your sailing dream reality within a year, leave your email and I'll send you free updates . I don't like spam - I will only send helpful content.
Ready to Own Your First Boat?
Just tell us the best email address to send your tips to:

Boat Navigation Lights: Everything You NEED to Know (2024)
In many cases, boating at night requires the use of boat navigation lights, but boaters often have many questions about them.
They often wonder when they’re needed, what the requirements are for various locations and vessels, and more.
We’re going to do a deep dive into navigation lights for boat to see what you need on your boat, and when you need to use them.
Legal Requirements
Types of navigational lights, which navigation lights are required on my boat , operators responsibility , navigation lights .
On any vessel operating on or in US waters, there is a need for the operator to display navigation lights under certain circumstances. Their purpose is to make vessels aware of each other at night or in times of generally reduced visibility. This is incredibly important during times when you may not be able to see the craft itself.
Other than visibility, marine nav lights also help boat operators determine the size, direction of travel, and even the potential activity of another boat on the water. When an operator understands the type of information each light tells them, they will be better able to determine appropriate courses of action for potential situations.
Boat running lights are divided by location and color, and each of them has specific requirements with how they must be displayed and perceived. You are the one legally responsible for displaying proper nav lights on the boat, for displaying them at the proper times, and for understanding how to read them.
The US Coast Guard ’s legal navigation light requirements include guidelines for every aspect of light usage.
Their materials start by first defining the standard daily period during which they must be used, then they detail how many of each type of light is needed as well as where they are located. Each light also has constraints regarding its visible distance and the arc over which it can be seen.
In the US, the Coast Guard says that any powered vessel that is under 39.4ft., may operate with boat nav lights in as little as two positions, an all-round light at the stern, and a set of sidelights at the bow.
Vessels that are under 164ft. must have lights displayed in four positions, a stern light, a masthead light, and boat sidelights on both the port and starboard, near the bow.
The ship navigation lights also have minimum visibility distances, depending on the size of the craft. The minimum visibility for nav lights, even for small crafts, is one mile, with requirements that other lights on larger vessels be visible for up to 3 nautical miles.
Also read: Boating Rules and Etiquette On the Water
Boat lights come in 4 types, sidelights, stern light, masthead light, and all-round light. Lights only come in white, red, and green, and all have very specific jobs.
Masthead Light
The masthead light is the white light located about ⅔ of the way up the mast, rather than at the top as you’d think. This boat bow light is required when using motor power at night. To be acceptable, the light must have an arc of 225° and needs to be seen from 2 miles away.
Large boats can have up to 3 mast lights. If your boat is shorter than 39 ft., all 2-3 white mast lights can be combined, utilizing one larger white light at the top of the mast.
Color : White ARC : 225 degrees Position : Front of boat
Port Sidelight
The boating lights located on the port side of the watercraft are red and mounted so that boats can see as they approach either head-on or from the left. This light helps tell if a boat is coming towards you or if it is pointing away. The phrase “red, right, returning” means that if you see a boat with their red navigation light on the right, they are facing your boat. The only time it is not needed is when your boat is anchored for the night .
Color : Red ARC : 122.5 degrees Position : Forward, left side
Starboard Sidelight
If you are to approach a boat from the front or right, you will see the green starboard sidelight. With an ARC of 122.5 degrees, approaching boats will be able to see yours easily.
This light helps tell you whether or not you have the right of way, which is important when it comes to keeping both you and your passengers safe. These are some of the front boat lights.
This light will often be combined with the port light, in small boat navigation lights. When out in the water, if you see the green light, that means it is safe for you to go, as you have the right of way.
Color : Green ARC : 122.5 degrees Position : Forward, right side.
The rear boat light is called the stern light. It is used to mark the rear of the boat. The operator can infer from only setting a boat stern light, that they are directly behind the vessel.
The stern light is white and is visible for an arc of 112.5 degrees on both the port and starboard sides, making a full arc of 225. Being able to see the red starboard side light as well as the stern light, should indicate the other vessel is traveling to the right from the perspective of the observer.
Color : White ARC : 225 degrees Position : Stern
All-Around Light
One of the boat night lights that is required when on your boat between sunset and sunrise is the all-around light. This light is intended to be seen from any point and helps to tell what direction a boat is moving. This light is also used when a boat is stopped or anchored.
This anchor light is required to have an ARC of 360 degrees and should be visible for two miles. The all-around light is white and it is located at the top of your boat’s mast for maximum visibility.
Color : White ARC : 360 degrees Position : Top of mast
Tricolor Light
A tricolor light is a sailboat mast light that has your three types of bow light in one convenient piece of equipment. They are for sailboats that are smaller than 65.6 feet long. The point of this sailboat light is to increase your nighttime visibility. They are mounted at the top of the mast, allowing larger boats to see yours better. They are not permitted to be used by any boats with a motor. The only type of boat that can utilize a tricolor light is a sailboat.
Color : White, red, green ARC : 360 degrees Position : Top of mast
Towing Light
These yellow lights are important, as they indicate to other watercraft that, not only is there another boat nearby but that they are also towing someone as well. The light must be positioned at the back of the boat, as close to the stern as possible. The goal is to avoid having anyone run into the boat that is being towed, as there may be no lights showing where that boat is located. The boat lighting requirements when towing state that both sidelights, a stern light, and masthead lights should also be displayed.
Color : Yellow ARC : 135 degrees Position : Over fore and aft centerline of the boat
Law Enforcement Light
Lights used by law enforcement on the water are flashing blue lights that can flash 120 times per minute or more. They can be used nearly anywhere that is convenient for the operator, provided they do not interfere with the function of the other lights.
This light may be displayed by any type of local law enforcement that is engaged in the course of their duty. This can apply to local, state, or federal police, as well as officials from wildlife and conservation departments, the Coast Guard, and more.
Color : Flashing Blue ARC : 180-225 degrees Position : Anywhere not interfering with other lights
Find your boat type below for the lineup of nav lights that you will need to safely operate after sunset and in other times of limited visibility.
Be sure you know which lights you will need to have on while underway, as well as at anchor or while towing. If you’re sailing, don’t forget that you are considered power-driven when using your motor.
Powerboat under 23 feet (7m)
Powerboats under 23 feet are required to have the following navigation lights displayed:
- One white masthead light visible for 2 miles
- One red & green sidelight visible for 1 mile
- One stern light visible for 2 miles
- One white, red, green, or yellow all-round light visible for 2 miles
Powerboat Under 39,4 feet (12m)
Powerboats under 39,4 feet are required to follow these boat light rules:
- One all-round light visible for 2 miles
Powerboat Over 39,4 feet (12m)
Powerboats over 39,4 feet are required to have the following navigation lights displayed:
- One white masthead light visible for 5 miles, unless less than 20 meters, then 3 miles
- One red & green sidelight visible for 2 miles
Powerboat 39,4 feet (12m) to 164 feet (50m)
Powerboats between 39,4 feet and 164 feet are required to have the following marine running lights displayed:
- One white masthead light visible for 6 miles
- One red & green sidelight visible for 3 miles
- One stern light visible for 3 miles
- One all-round light visible for 3 miles
Sailboat Under 23 feet (7m)
Sailboats under 23 feet are required to have the following sailing navigation lights displayed:
- One white stern light
- One white mast lantern positioned at or near the top of the mast where it can be easily seen from a distance
Note: if it is not practicable for the vessel to display the prescribed lights, one all-round white light can be used or a hand torch, with enough time to prevent a collision.
Sailboat Under 65,6 feet (20m)
Sailboats under 65,6 feet are required to have the following sailing lights displayed:
Tug Boat With Tow Length Under 656 feet (200m)
Tug boats with tow lengths less than 656 feet are required to have the following navigation lights displayed:
- Two masthead lights in a vertical line
- Stern light
- Towing light in a vertical line above the stern light
Tug Boat With Tow Length Over 656 feet (200m)
Tug boats with tow lengths longer than 656 feet are required to have the following navigation lights displayed:
- Three masthead lights in a vertical line
- A towing light placed vertically above the stern light
- A diamond shape visibly displayed
Anchored Vessel
Vessels at anchor or aground are required to observe the following boat lighting rules:
- One white all-round in the fore
- One white all-round at a lower level than the fore, at the stern
If aground, the vessel should display two red all-round lights in a vertical line
Vessel Under Oars
Vessels under oar power have similar requirements to follow as small sailboat lighting:
- One stern light
Or, alternately, one white all-round light or hand torch to be used to manually signal to avoid collision
Vessel Engaged in Fishing
Vessels actively engaged in fishing are required to have the following marine navigation lights displayed:
- Two all-round lights oriented in a vertical line, red on top and white on the bottom
- One all-round white light for gear more than 150 meters from the vessel
- When making its way through the water, there shall also be sidelights and stern light
Vessel Engaged in Trawling
Vessels engaged in trawling are required to fulfill the following boat light requirements:
- Two all-round lights oriented in a vertical line, green on top and white on the bottom
- One masthead light abaft and higher than the all-round green
Kayakers and Canoers
Kayakers and canoers are required to have the following navigation lights displayed:
Alternatively, a hand torch or lantern which can be used to signal to avoid collisions
Personal Watercraft
There are no established rules for navigation lights on personal watercraft, even though many of them are classified as a boat by coast guard standards. Personal watercraft are often not permitted to operate outside of the sunrise-to-sunset period, and so most manufacturers do not install or make possible the installation of navigation lights.
Vessels Restricted in their Ability to Maneuver
Vessels restricted in their ability to maneuver are required to have the following navigation lights displayed:
- Three all-round lights displayed as high a possible in a vertical line, red at the top, and white in the middle
- One masthead light
The USCG as well as state authorities hold the operator of the vessel responsible for the correct use and understanding of nav lights.
This means they also must make sure all of the lights used meet the requirements set forth by the authorities.
This also extends to ensuring that the lights are all installed for optimal visibility while underway, so if your cruiser rides high, make sure your lights are still visible.
What navigation lights do I need on my boat?
Boat light regulations state boats must have a pair of red and green sidelights, and an all-around white light that can be seen from 360°.
Why are navigation lights red and green?
Navigation lights for boats indicate to others which direction a boat is facing. The red indicates the left side of the boat, green is on the right.
What lights need to be on a boat at night?
Per the navigation lighting rules, it is crucial that you have your red and green navigation lights, as well as the white 360° light.
Which three colors are used for navigational lights?
The boat light colors are going to be green, red, and white. If you see a blue light, this generally indicates a government vessel.
Do I need navigational lights on my boat?
Yes, all boats are legally required to have the minimum red, green, and white boat safety lights
when operating in the dark.
Why do boats have blue lights?
When you see a boat that has blue boat lights at night, that means that it is likely the coast guard or law enforcement.
Why is port red and starboard green?
The light on the starboard side of the boat is green because it is ‘safe’, as the steersman will be able to see other boats.
What does a single white light mean on a boat at night?
If you can only see a single white light on a boat at nighttime, you are likely seeing the stern light or the boat anchor light.

Robert Owens is the Chief of Content of Quicknav. Robert has been boating for over ten years and loves to share his experience on the water. His first boat was a dirt-cheap moderately beat up 2003 Bayliner 175, where he learned a tremendous amount about trailering, launching, docking, operating, and maintaining. He currently owns a Cruiser Yacht and is eyeing a sailboat.
Similar Posts
Glossary of GPS Terms in 2024 (The Definitive List)
Learning about global positioning systems or GPS can lead you down a rabbit hole of technical material, many dealing with…

How to Clean Boat Seats? (a Practical Guide)
So you’ve bought your first boat and while you think you can master most of it with ease, you keep…

Boating Statistics in 2024 (incl. Covid & Millennials)
It’s no secret that Americans love boating as boating and fishing are the largest outdoor recreation activities in the U.S….

Cabin Cruiser: The Ultimate Guide (2024)
Passengers: Maximum 10Length: 20-40 FeetTrailerable: YesBest for: Day Cruising & Overnight TripsPrice Range: $100,000-$500,000Propulsion: 2+ Outboard Engines Many boaters want…

8 Best Online Boating Safety Courses (2024)
Boating can be one of the most enjoyable pastimes, but it can also be deadly. Being familiar with all aspects…

How to Drive a Boat? (Step-by-Step Guide)
Now that you have a boat, or are close to picking up that new toy, one major hurdle you will…
Lights and shapes
Definitions
- Masthead light means a white light placed over the fore and aft centreline of the vessel showing an unbroken light over an arc of the horizon of 225° and so fixed as to show the light from right ahead to 22.5° abaft the beam on either side of the vessel.
- Sidelight means a green light on the starboard side and a red light on the port side each showing an unbroken light over an arc of the horizon of 112.5° and so fixed as to show the light from right ahead to 22.5° abaft the beam on its respective side. In a vessel of less than 20 metres in length the sidelights may be combined in one lantern carried on the fore and aft centreline of the vessel.
- Sternlight means a white light placed as nearly as practicable at the stern showing an unbroken light over an arc of the horizon of 135° and so fixed as to show the light 67.5° from right aft on each side of the vessel.
- Towing light means a yellow light having the same characteristics as the sternlight.
- All-round light means a light showing an unbroken light over an arc of the horizon of 360°.
- Flashing light means a light flashing at regular intervals at a frequency of 120 flashes or more per minute.
Colour legend
Power-driven vessel underway
A power-driven vessel underway shall exhibit:
- a masthead light forward;
- a second masthead light abaft of and higher than the forward one; except that a vessel of less than 50 metres in length shall not be obliged to exhibit such light but may do so;
- sidelights;
- a sternlight.
Sailing vessels underway and vessels under oars
A sailing vessel underway shall exhibit:
In a sailing vessel of less than 20 metres in length the lights may be combined in one lantern carried at or near the top of the mast where it can best be seen.
A sailing vessel underway may, in addition to the lights, exhibit at or near the top of the mast, where they can best be seen, two all-round lights in a vertical line, the upper being red and the lower green, but these lights shall not be exhibited in conjunction with the combined lantern.
4 lights configurations sailing
A sailing vessel of less than 7 metres in length shall, if practicable, exhibit the lights prescribed above, but if she does not, she shall have ready at hand an electric torch or lighted lantern showing a white light which shall be exhibited in sufficient time to prevent collision.
A vessel under oars may exhibit the lights prescribed in this Rule for sailing vessels, but if she does not, she shall have ready at hand an electric torch or lighted lantern showing a white light which shall be exhibited in sufficient time to prevent collision.
Sailing and Motoring
A vessel proceeding under sail which has her engine running shall exhibit, forward where it can best be seen, a conical shape, apex downwards. She shall exibit lights according to a power-driven vessel.
A vessel at anchor shall according to Rule 30 (a) (b) exhibit where it can best be seen:
- in the fore part, an all-round white light or one ball;
- at or near the stern and at a lower level than the light prescribed in Rule 30(a)(i), an all-round white light.
A vessel aground shall according to Rule 30 (d) exhibit the lights prescribed in Rule 30(a) or (b) and in addition, if practicable, where they can best be seen;
- two all-round red lights in a vertical line;
- three balls in a vertical line.
A power-driven vessel when towing shall exhibit:
- two masthead lights in a vertical line. When the length of the tow, measuring from the stern of the towing vessel to the after end of the tow exceeds 200 metres, three such lights in a vertical line; Rule 24 ;
- a sternlight;
- a towing light in a vertical line above the sternlight;
- when the length of the tow exceeds 200 metres, a diamond shape where it can best be seen.
Towing an inconspicuous, partly submerged object
An inconspicuous, partly submerged vessel or object, or combination of such vessels or objects being towed; Rule 24 (g) , shall exhibit:
- if it is less than 25 metres in breadth, one all-round white light at or near the forward end and one at or near the after end except that dracones need not exhibit a light at or near the forward end;
- if it is 25 metres or more in breadth, two additional all-round white lights at or near the extremities of its breadth;
- if it exceeds 100 metres in length, additional all-round white lights between these lights so that the distance between the lights shall not exceed 100 metres;
- a diamond shape at or near the aftermost extremity of the last vessel or object being towed and if the length of the tow exceeds 200 metres an additional diamond shape where it can best be seen and located as far forward as is practicable.
Pushing from ahead or towing alongside
When a pushing vessel and a vessel being pushed ahead are rigidly connected in a composite unit they shall be regarded as a power-driven vessel and exhibit the normal lights.
A power-driven vessel when pushing ahead or towing alongside, except in the case of a composite unit; Rule 24 (c) , shall exhibit:
- two masthead lights in a vertical line;
A vessel or object being towed shall exhibit:
- Provided that any number of vessels being towed alongside or pushed in a group shall be lighted as one vessel,
- a vessel being pushed ahead, not being part of a composite unit, shall exhibit at the forward end, sidelights;
- a vessel being towed alongside shall exhibit a sternlight and at the forward end, sidelights.
Fishing – Trawling
A vessel engaged in fishing, whether underway or at anchor, shall exhibit only the lights and shapes prescribed below; Rule 26
A vessel when engaged in trawling, by which is meant the dragging through the water of a dredge net or other apparatus used as a fishing appliance, shall exhibit:
- two all-round lights in a vertical line, the upper being green and the lower white, or a shape consisting of two cones with their apexes together in a vertical line one above the other;
- a masthead light abaft of and higher than the all-round green light; a vessel of less than 50 metres in length shall not be obliged to exhibit such a light but may do so;
- when making way through the water, in addition to the lights prescribed hereh, sidelights and a sternlight.
- when shooting nets, white light over white light (Flag Z by day);
- when hauling nets, white light over red light (Flag G by day);
- When nets are caught on the bottom, red light over red light (Flag P by day).
Trawling in span
When pair trawling, each vessel shows searchlights on water aiming forward ( Flag T by day); Rule 26 (f) (b)ǂ(2)
Fishing, other than trawling
A vessel engaged in fishing, other than trawling , according to Rule 26 (c) shall exhibit:
- two all-round lights in a vertical line, the upper being red and the lower white, or a shape consisting of two cones with apexes together in a vertical line one above the other;
- when there is outlying gear extending more than 150 metres horizontally from the vessel, an all-round white light or a cone apex upwards in the direction of the gear;
- when making way through the water, in addition to the lights prescribed here, sidelights and a sternlight.
Purse seining
Purse Seiners will exhibit two all-round yellow lights in a vertical line, flashing alternately; Rule 26 (f) 3ǂ(iii)
Constrained by draught
A vessel constrained by her draught / draft may, (and not “shall”!) in addition to the lights prescribed for power-driven vessels, exhibit where they can best be seen three all-round red lights in a vertical line, or as day sign a cylinder, Rule 28
Not under command
A vessel not under command, sometimes knows as a NUC N ot U nder C ommand." aria-label="Illumination" data-bs-original-title="NUC"> vessel, shall according to Rule 27(a) exhibit:
- two all-round red lights in a vertical line where they can best be seen;
- two spherical shapes in a vertical line where they can best be seen; and
- when making way through the water also normal sidelights and a sternlight (not shown in the examples below).
Restricted in her ability to manoeuvre
A vessel restricted in her ability to manoeuvre, sometimes knows as a RAM R estricted in her A bility to M anoeuvre." aria-label="Illumination" data-bs-original-title="RAM"> vessel, except a vessel engaged in mine clearance operations , shall according to Rule 27(b) exhibit:
- three all-round lights in a vertical line where they can best be seen. The highest and lowest of these lights shall be red and the middle light shall be white;
- three shapes in a vertical line where they can best be seen. The highest and lowest of these shapes shall be balls and the middle one a diamond;
- when making way through the water, also a masthead light or lights, sidelights and a sternlight
Dredging or underwater operations
A vessel engaged in dredging or underwater operations, when restricted in her ability to manoeuvre; Rule 27(d) , shall exibit
- two all-round red lights or two balls in a vertical line to indicate the side on which the obstruction exists;
- two all-round green lights or two diamonds in a vertical line to indicate the side on which another vessel may pass; and
- when at anchor (or not making way), the lights or shapes prescribed in this section instead of the lights or shapes prescribed in Rule 30
Small diving vessel
A vessel engaged on pilotage, according to Rule 29 , duty shall exhibit:
- at or near the masthead, two all-round lights in a vertical line, the upper being white and the lower red;
- when underway, in addition, sidelights and a sternlight; as shown in the example below.
Hovercraft, hydrofoil ferry
An air-cushion vessel when operating in non-displacement mode shall, besides a masthead light forward, (plus a masthead light abaft if longer than 50 m) sidelights and a sternlight, exhibit an all‑round flashing yellow light (faster than 2 flashes per second). Rule 23(b)
Also a hydrofoil ferry or high speed catamaran when acting as ferry is often allowed under local regulations to exhibit an all-round flashing yellow light.
Minesweeper
A vessel engaged in mine clearance operations shall in addition to the lights prescribed for a power-driven vessel, or to the lights or shape prescribed for a vessel at anchor, exhibit three all-round green lights or three balls. One of these lights or shapes shall be exhibited near the mast head and one at each end of the fore yard. These lights or shapes indicate that it is dangerous for another vessel to approach within 1000 metres of the mine clearance vessel. Rule 27(f)
See all chapters
Course overview Chapter 1 – Positions Chapter 2 – Nautical chart Chapter 3 – Compass Chapter 4 – Plotting and piloting Chapter 5 – Plotting and piloting – Advanced Chapter 6 – Tides Chapter 7 – Tide prediction Chapter 8 – Currents Chapter 9 – Navigation aids Chapter 10 – Lights and Shapes

Ultimate Guide To Marine Navigation Lighting

If you drive a car or even ride a bicycle, you might be well aware of the necessity of lighting systems (though in the second case the word ‘system’ doesn’t quite apply) for the safety of you and the people around you. The thing applies just as well for ships. But since they are much larger than a car, the lighting system or navigation lights on ships is a little bit more complicated as well. Marine navigation lighting is also one of the most critical aspects of nautical studies.
It is mandatory for boats of all sizes to have a navigation system . This is to make sure that the chances of any significant accident are minimized. The United States introduced the system in 1838, and the United Kingdom followed suit. Before being internationally adopted in 1897 suitable guidelines were established by the International Maritime Conference which was established in 1889. Three colors were chosen that were to be used for the light colors. They were red, green and white. This was based on a set of rules specified by the US and are followed around the world to this date.
This article discusses the different rules and regulations of using navigation lights, their importance, and also some basic marine navigation lighting systems along with their positions and ranges.
Marine Navigational Lights, Rules and Regulations
A standard pattern of marine navigation lighting is followed for the identification of both the vessel as well as the IALA buoyage system at night. If you are required to move from sea to a channel you need to have a list of all the IALA as well as the other fixed navigational lights that are visible on entering the channel. This includes distant lighthouses as well.
If you also make a note of the inland features like the radio and television transmitter masts it will benefit you because they act as good navigational aids due to their height and warning lights.
The helmsman should not be using any bright light source in the cockpit area and should rather take the aid of red lights and very dim white lights in the galley and navigation area. This is because he needs to preserve his night vision so that he can accurately interpret both the buoyage marine navigation lights as well as the boat navigation lights of other vessels.
The nautical almanacs contain the details of each and every visible maritime light signal coming from navigational markers that are both inside and outside the channel.
All the details about any particular light can be found in a published list or on a marine navigational lights chart: its color, period, and in some cases even the elevation and range of the beacon. Use the chart to keep a tag on the lights you are passing by putting a tick mark on the lights that you are about to pass and as the boat sails past, the tick is checked.
You will get two visual clues to figure out how far you are away from a buoy. The light will elevate from the horizon at 0.5 nm and at about 200m, the light will reflect on the surface.
Position of Boat Navigation Lights
Most of the variations that can be found in the different vessels can be read about in most almanacs. At the very basic level, a vessel needs to show a red light to port and green light to starboard. Depending on the size of the vessel, one or more colored or white lights are used as well.
For vessels that are 12 ft in length or shorter, the navigation lights must be visible from a range of one nautical mile and for the ones that are longer than 12 meters the required visibility range is 2 nautical miles. From 5 degrees above to 5 degrees below the horizontal happens to be the required minimum intensity in a vertical sector.
International Navigation Rules state that the boat navigation lights should be placed above the uppermost continuous deck. In case separate fixtures are used for the red and green sidelights, the masthead or all-round white light is placed as close as possible to the vessel’s fore and aft centerline. The masthead or all-around light needs to be positioned at least 1 m or 3.3 ft above the sidelights.
Following are the basic positions of navigational lights. We will discuss the same in greater detail ahead.
Also read: What Is A Marine Sextant?
Boat Navigation Light Regulations
Several rules and specifications are related to the type, size, layout, arc, and distance of visibility of boat navigation lights used by all vessel types which are collectively known as the International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea or COLREGs . The navigational lights used are known as ‘COLREG lights and shapes. A boat might be anchored or underway, under sail or power, or fishing or trawling. These various situations can be communicated through multiple combinations of boat navigational lights.
In addition to the primary navigation lights, vessels may also display one or more steaming lights. These lights are very useful for it gives details about the various aspects of the ship like whether it is in the sail or under power, the direction in which it is going and, in some cases, even the size of the vessel. If a ship is engaged in a specific task that might involve certain restrictions, that too can be indicated with some extra boat lights.
Always maintain the lighting system and display the correct navigation light combination to make other vessels in the vicinity aware of your course and state as to whether your vessel is under power or not. If you follow this a considerable amount lowers the chances of a collision. Here is a list that you might use to familiarise yourself with the basics of the lighting system.
- Basic Navigation Light White Light : Small dinghies that are 7m or less in size are required to carry a torch having a white light that can be flashed when needed.
- All-Round White Light: An all-round white light is expected to be displayed by a small boat, up to 7ft long that is under power and can go beyond 7 knots of speed. This light must be visible at an angle of 360 degrees and from two miles away. An all-around white light is also used when the boat or vessel is at anchor but not at a designated anchoring area. This is to make sure that the ship is visible to all the nearby ships to avoid any accidents.
- Stern and Combined Side Lights : A stern light is a white light that is installed at the end of a boat. A vessel that is over 7 m or 23 ft in length is expected to show red and green sidelights when sailing. Each of these lights needs to cover an arc of 112.5°. The sidelights may be combined in one lantern at the bow when below 25 m or 65 ft. The white stern light can be seen over an arc of 135°. These lights need to be visible from a distance of a mile and need to be placed 39 inches below all white lights for boats of lengths equal to or less than 12 ft.
- Masthead Light : A combination of sidelight and stern light in a tricolor combination may be used sailing yachts of heights 20 m or lower. A masthead light is required by vessels of lengths between 39.4 ft and 65.6 ft. It is placed in the masthead whose height provides excellent visibility. Still, stern lights and sidelights should be fitted separately in case of or use under power along with steaming light. This kind of light needs to be visible across an angle of 225 degrees and from a minimum distance of 2 miles.
- Separate Lights : The displaying of the tricolor masthead light is not allowed in the case of yachts that are longer than 20 m or 65 ft. Instead, they use them separately. Often on large sailing vessels, these all-around, red over green lights are present. These red and green sidelights need to be visible from a distance of one mile and across an angle of 112.5 degrees.
- Steaming Lights Combined Lights : A combination of the masthead and stern light are used in the case of power crafts that are less than 20 m or 65 ft in length. The arrangement is present at the bow.
- Single Steaming Light : Visible over a 225 degrees arc, a masthead steaming light is used by power-driven vessels that are up to 50 m or 160 ft long. Separate stern lights and sidelights are used in case of a length exceeding 20 m or 65 ft.
- Two Steaming Lights: Power-driven vessels that span over 50 m or 160 ft in length display two masthead steaming lights. The forward light placed lower than the aft light with both of them being visible over an arc of 225° with the sidelights and separate stern light.
The area of the nautical lighting system is a precise business and requires some amount of study and a good deal of responsibility. It is because its application forms a core element in safe marine navigation.
Similar Posts
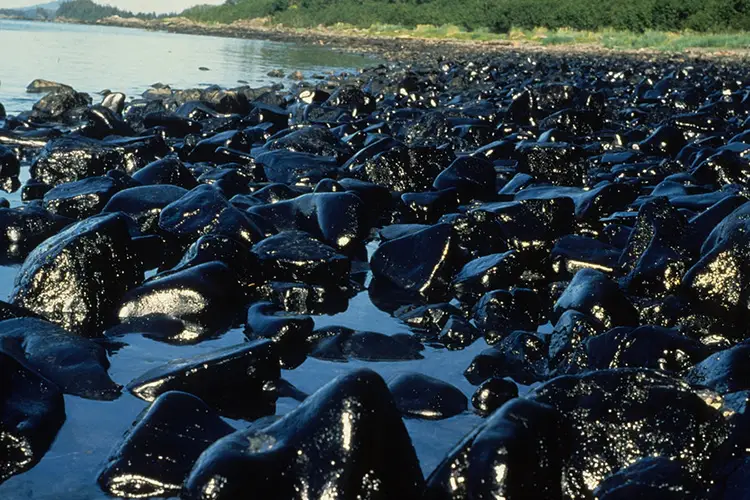

The Exxon Valdez Oil Spill Incident
Exxon Valdez oil spill was one of the worst accidents involving ocean oil spill. Today, we will uncover the true story behind it. The indispensability of oil in our day-to-day lives is unquestionable. The number of industries that are heavily reliant on oil as their source of fuel is vast. But what comes as a…
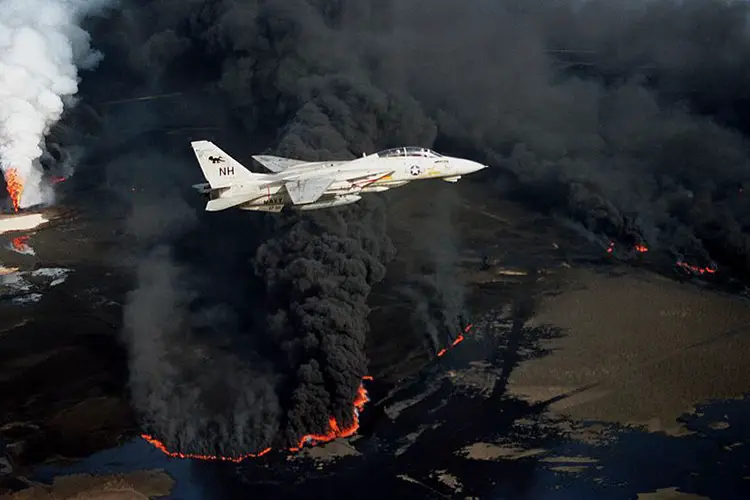

13 Major Oil Spills Of The Maritime World
An oil spill is the release of oil into the environment. Spilling of crude oil or any oil distilled product ( like gasoline, kerosene, diesel fuels, Stoddard solvent, hydraulic oils, lubricating oils) pollute the surface of the land, air, and water environment An oil spill is a kind of environmental pollution. Oil spill affects marine…
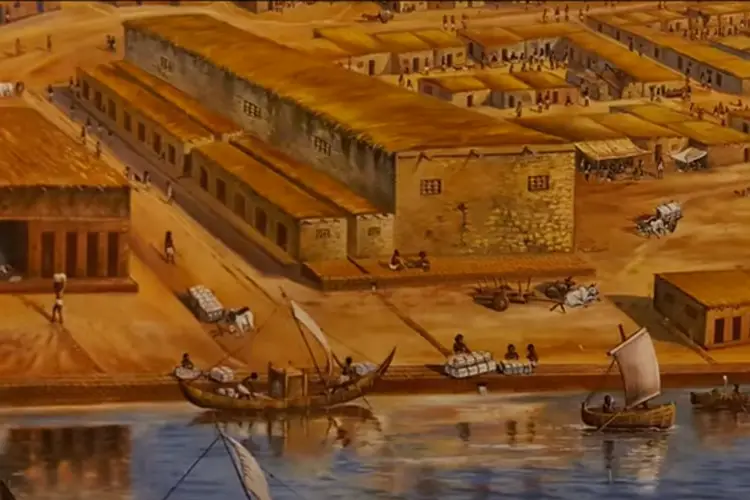

Ancient Seaports of India
It may come as a surprise to many people that India has a rich history of shipbuilding and Indians were quite accomplished seafarers. This obviously means that India also had many seaports in the past. Here is the list of ancient seaports of India. All of these ports were a hub of trade and commerce…

Automatic Identification System
Modern-day ships are equipped with several modern equipment and safety measures to ensure a smooth and successful voyage. These new techniques have emerged and evolved from years and years of study, research and experimenting. One such system is the Automatic Identification System or AIS. This article discusses the meaning of this term, the purpose and…
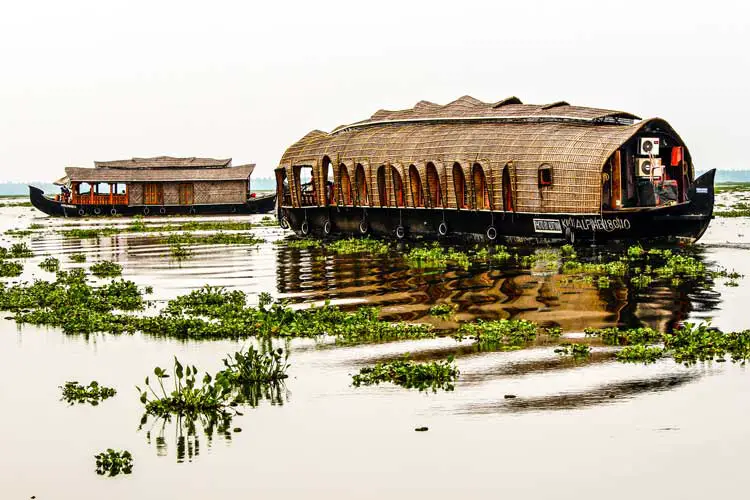

What Are Houseboats?
What Is A Houseboat? A houseboat as the name suggests is a boat that is constructed or modified to be used as a home. They are a result of a unique combination of housing and boating and are used for residential or recreational purposes. They are used as an alternate residency in many parts of…
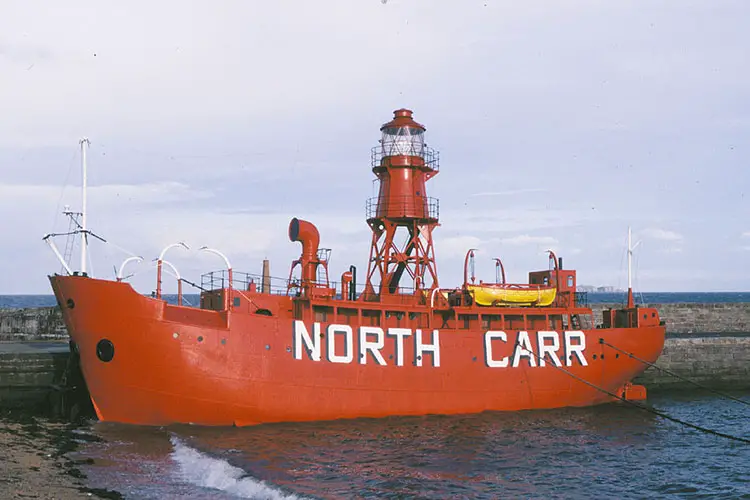

What Is A Lightship?
What is a Lightship? A lightship or a light vessel is a ship that can also operate as a lighthouse. These types of ships are used in waters that are too deep and where lighthouses cannot be constructed. Lightships play an important role in assisting other ships to navigate through waters. A lighthouse is a…
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This website uses cookies to improve your experience. We'll assume you're ok with this, but you can opt-out if you wish. Read More
- Upcoming Course Schedule
- Testimonials
- Get a Conservation ID
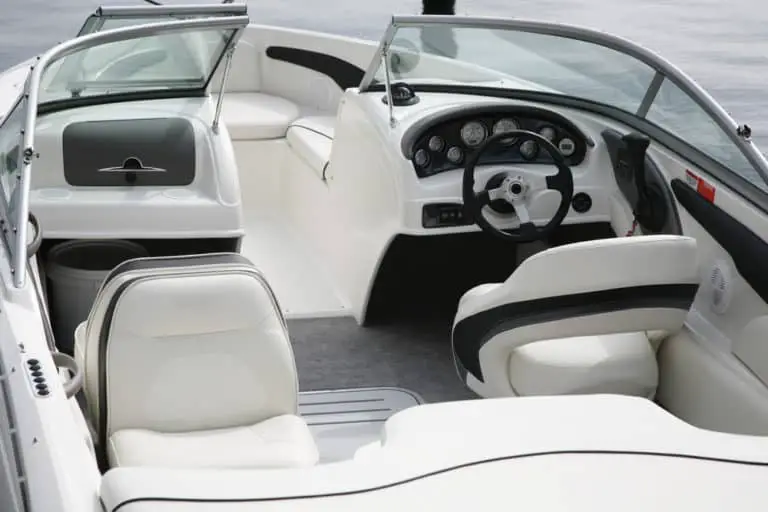
Sailboat Lights

Sailboat Lights can be confusing and usually need some explanation.
Common Questions:
Is the tri-color light all I need when under power? Are the red and green lights at the top of the mast all I need? Am I supposed to turn any of these off? How then do I let others know I am under power? If you are under power, you of course need your mast head light illuminated, correct? (As seen here on the left). What if there are no pulpit or stern lights on your vessel? Shouldn’t you always use your mast lights? This is confusing!
Let’s talk it through:
Mast head lights can also be seen on power boats. Take a look at this image shown in the rules. It shows a power-driven vessel longer than 50 meters using two mast head lights.

Here is the definition of a mast head light in the rules:
A “Masthead light” means a white light placed over the fore and aft centerline of the vessel showing an unbroken light over an arc of the horizon of 225 degrees and so fixed as to show the light from right ahead to 22.5 degrees abaft the beam on either side of the vessel.
Note: It does not say the light must be at the top of the mast.
What is the tricolored light for?
Well, it is at or near the top of the mast and is for sailing vessels less than 20 meters or 65.5 feet in length. It is an optional alternative to having the lights down on the hull or pulpits. The tri-color light at the top of the mast faces a white light to the aft 135 degrees plus red from directly forward around to port 112.5 degrees and a green light directly forward and around to starboard 112.5 degrees.
This makes up 360 degrees and meets the requirement for a sailboat sailing .
So, when the sailboat turns on its engines it must also, in addition to the tri-color light at the top of the mast , display a white light 225 degrees facing forward. You can call this light whatever you’d like but it must exist. Now these particular white lights that we preferably call mast head lights , shall be visible from 6 miles. Note: It does not mean they have to be at the top of the mast. On power vessels they are typically at the top of the mast because that is what the mast is for.
Here is a sailing vessel under sail using a tricolored light. There is no forward-facing white light, like in the upper picture, so we know it is under sail.

To clarify, on a sailboat less than 50 meters in length, a white under power mast head light can be just up the mast anywhere. That is to say that it’s not part of the tri color. It is white and faces forward 225 degrees and indicates a sailboat is under power.
Where the confusion lies:
You also might be confusing the term mast head light with the two all-around red and green lights at the top of the mast. These are not mast head lights. They can be used in addition to the hull or pulpit mounted red, green, and white. A sailing vessel cannot display a top of the mast tricolored light AND the two all-around red and green at the top of the mast. Above all, the mast head is white 225 deg forward facing to be used under power only.
Pictured, the Vessel on the left is utilizing the optional two all-around red and green lights. Subsequently, this states that it is under sail or underway and not under engine power.
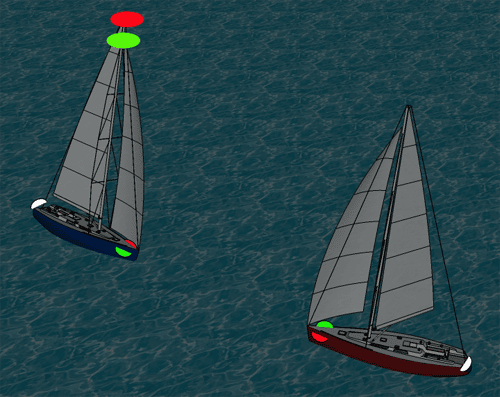
To further understand this picture, here are the rules as stated:
Rule 25 – Sailing Vessels Underway and Vessels Under Oars
(a) A sailing vessel underway shall exhibit:
(i) sidelights; (ii) a stern light
(c) A sailing vessel underway may, in addition to the lights prescribed in Rule 25(a), exhibit at or near the top of the mast, where they can best be seen, two all-round lights in a vertical line, the upper being red and the lower green, but these lights shall not be exhibited in conjunction with the combined lantern permitted by Rule 25(b).
In Conclusion:
You can further investigate using the United States Coast Guards book on Navigation Rules… NavRulesAmalgamatedwAnnexes.pdf (uscg.gov)
We are proud to discuss navigation lights in our Public Course please visit our Schedule any time. We teach all of our classes live in a virtual setting
NASBLA 2022 Accomplishments

Clean Drain and Dry

United States Coast Guard

Boating Tips for Beginners

Keeping a Lookout

2021 Boating Accident Report Notables

Sailing Signals: Nautical Lights, Shapes, & Sounds

You might be wondering what all those lights, shapes, and sounds that are either attached to a vessel or emanating from them.
While it might not be obvious what these mysterious modes of communication mean, they play a very important role in ensuring the safety and proper communication between vessels and non-vessels alike.
Sailing safety has a lot to do with proper preparedness, which means having the right gear , plan, experience, and mindset. However, sailing safety also requires knowledge in the various forms of communication between vessels and non-vessels. This is where lights, shapes, and sounds play a big role.
By using various lights, shapes, and sounds when out on the water, vessels and non-vessels are able to communicate whether there’s danger afoot, they need help, or simply telling you to get out of the way.
We’ll explore the most common and vitally important light, shape, and sound signals to make sure you’re able to pick up and recognize them when the time is right.
Vessel Lights
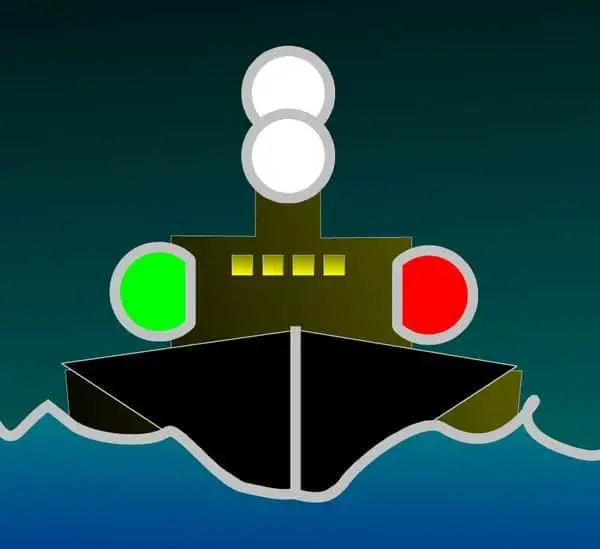

Whenever you see a vessel that has their lights on display, it’s most likely going to be during the evening when it matters most.
The combination of colors and how they’re oriented can mean a world of difference in terms of what they’re trying to communicate, so it’s important to keep an eye out.
The color of lights you’ll see when out on the water include white, red, green, and yellow. Again, you’ll see these on display at night when visual communication between vessels and non-vessels is crucial.
When you see lights on display, you’re essentially being told the vessel’s direction of movement, method of propulsion, and size.
Apart from the basic message of direction, propulsion method, and size, there are other light signals that are there to inform you of other situations. Some of those situations include when a vessel is
- Not under command
- Constrained by draft
- Unable to maneuver
The most important determination, when confronted with a vessel or non-vessel at night, is whether or not there’s a risk of collision.
Obviously, if there’s a risk of collision you need to attempt to communicate with the vessel immediately and to take proper action to avoid a collision. Ideally, you’ll be able to communicate with the other vessel so that you’re both in agreement about who does what to prevent a potential collision.
Basic Lights
As I mentioned previously, there are several basic colors that you’ll see on display from a vessel at night.
However, these lights can be displayed in different ways in terms of position on a vessel as well as how they’re displayed (e.g., blinking or static). Here are some basic definitions of lights that you should know.
Masthead Light
The masthead light is a static white light that sits partway up the main mast of a vessel and only displays to the front 225 degrees of the vessel.
This means that other vessels coming toward yours at an arc of 225 degrees will see an unbroken white light, which will inform them that you are possible head-on.
The sidelights are a pair of static lights that sit fore of the vessel at the bow with one being on the port side and the other on the starboard side.
The light on the port side is a static red light and the light on the starboard side is static green. The combination of both lights covers the same amount of arc as the masthead light, which is 225 degrees.
The sternlight is a static white light that sits as far back as possible aft the vessel at the stern and displays to the back 135 degrees of the vessel.
Other vessels who see this will know that they’re behind your vessel due to the light being lower than if they saw the masthead light and not being able to see the sidelights.
All-Round Light
The all-round light is a static white light that sits at the very top of a vessel’s mast and displays at a full 360-degree angle. You’ll see this light being displayed on a sailboat that’s either docked or at anchor.
Towing Light
The towing light is a static yellow light that sits at the same position as the sternlight and displays at an arc of 135 degrees aft the vessel. As the name suggests, this light indicates to other vessels that it’s currently towing an object.
Underway Vessels
When vessels are on the move and it’s dark out, there’s no doubt that being able to pick out fellow vessels is an important way to avoid any risk of collision .
In all likeliness, you’ll be able to pinpoint another vessel rather quickly at night be observing their lights and determine their position, direction of movement, and size.
Sailing Vessels
When spotting sailing vessels underway at night, you’ll be able to see at a bare minimum their sidelights and sternlight.
By observing which lights you can see and their orientation, you can quickly determine the position at which you’re viewing their vessel. However, depending on the size of the vessel, you’ll definitely see a different combination of lights.
If your vessel is less than 20 meters (65 feet) in length, then all you’ll need to display are the sidelights and sternlights when underway at night.
However, it’s also possible to display a similar set of lights in a different way indicating the same underway conditions, which is when you might see on the very top of the mast a 3-light combination — red, white, and green.
The 3-light combo displays at the same angles as the sidelights and sternlight. The only difference here is they’re situated at the top of the mast.
Sailing vessels underway that are larger than 20 meters will likely have a different set of lights on display, but the difference is huge.
With larger sailing vessels, you’ll still see the sidelights and sternlight with another pair of static lights near the top of the mast where the top light is red and the one below is green.
Power-Driven Vessels
Now, power-driven vessels are bit different when underway at night compared to sailing vessels. For one, a power-driven vessel can be as small or much larger than a sailing vessel, so the number of lights can vary quite a bit.
Also, a power-driven vessel is capable of much greater speeds than a sailing vessel, so ensuring other vessels are aware of their existence at night is very important.
Not unlike a sailing vessel, a power-driven vessel will also have a pair of sidelights and one sternlight. However, there’s an additional light that’s included in this combination and that being the white masthead light.
This 4-light combination will help other vessels like yours be aware that a 15 meter (50 feet) power-driven vessel is underway near them.
But what about the power-driven vessels that are well above the 15-meter size?
Well, the power-driven vessels that are much larger will have the same lights as the smaller power-driven vessel as well as a white static light at the bow that’s slightly lower in height than the masthead light.
This helps other vessels like yours get an idea of just how big this power-driven vessel really is.
Vessels At Anchor
Whenever you’re underway at night, there’s no doubt you want to be aware of other vessels underway to avoid a major collision .
But it’s also the case that you want to be able to spot those other vessels that are at anchor, especially if you’re moving around a marina or bay with other docked or anchored vessels.
Sailing vessels at anchor are very easy to pick out at night since all they need to have on display is their all-round light.
Remember that the all-round light is a static white light that provides a 360-degree view at the very top of a sailing vessels mast, so it’ll be quite difficult to miss. As a matter of fact, a power-driven vessel at anchor also has the same all-round light on display as long as it’s 50 meters (65 feet) or less in size.
For sailing and power-driven vessels that are greater than 50 meters in size, they have to put on display another all-round light.
However, this extra all-round light is placed near the stern of the vessel and is lower in height compared to the all-round light on the mast. This combination of all-round lights should tell you right away that you’re looking at a much larger vessel at anchor.
If you just so happen to see a vessel that’s greater than 100 meters (328 feet) in size and it’s also at anchor, you best believe you’ll see it lit up like a Christmas tree. When it comes to this size of a vessel, they’re required to put as many lights on display as possible.
Most of what we’ve covered up to this point has been under the conditions of being underway or at anchor during the evening.
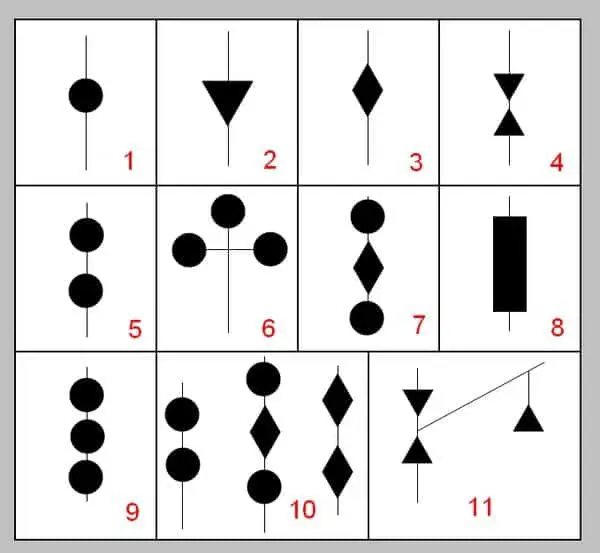
However, arguably more vessels will be out during the day than at night, so it’s important to be aware of other forms of visual communication such as day shapes.
During the day there’s little need for lights to communicate visually to other vessels, which is why we use shapes instead. There are a number of different shapes that take the form of circles, squares, triangles, and more that communicate different messages.
While there are a lot of different day shapes to consider, I want to cover the most common you’ll likely see while out on the water.
Being able to pinpoint a vessel, whether sailing or power-driven, that’s anchored during the day is rather straight forward as you should see a large black sphere hanging between the tip of the vessel’s mast to the fore of the vessel.
This single black sphere should be the size of a basketball and will be attached in the middle of a line.
Motoring and Sailing
If you’re out sailing and have your engine running to help boost your speed, you’ll need to ensure that you have a black, upside-down triangle attached to the middle of your forestay.
Just like the black sphere used to illustrate that your vessel is anchored, your sailboat should have the upside triangle in the same location. It’s important to note that this is only required for vessels that are 12 meters (39 feet) or greater in size.
Diving Operations
If you like to go freediving, scuba diving, or snorkeling, you’ll want to be sure to use the proper diving day shape.
Whether you’re on a small or medium sized vessel, make sure you put up the correct flag at the top of the mast. The most commonly used flag is blue and white while another flag is red with a white slash from one corner to another.
One of the worst situations you can find yourself or anyone else in while out sailing is ending up aground.
If this situation ever occurs, there should be three black spheres, just like the one you would use when anchored out, attached to the top of the mast in a vertical column. It’s important to note that this is only required for vessels that are 12 meters (39 feet) or greater in size.
Not Under Command
There will be times when vessels out on the water won’t be under command, which means you should be aware of this so you can make sure you can avoid them on your course.
Just like a vessel that’s run aground, you should see black spheres lined up vertically at the top of the mast, but instead of three spheres there should only be two. Again, this is only required for vessels that are 12 meters (39 feet) or greater in size.
Restricted Maneuverability
Some vessels can find themselves in situations that simply restrict their ability to maneuver, so being able to put that inability on full display to the rest of the vessels out on the water is rather important.
By putting a black, diamond-shaped object in between two black spheres in a vertical column at the top of the mast, this message is illustrated successfully. Similar to other day shapes, you’ll only find this on vessels that are 12 meters (or 39 feet) or greater in size.
Fishing and Trawling
Fishing is one of the oldest industries in the world and there’s no doubt that you’ll eventually find a vessel fishing and towing along a net.
Whenever a vessel is trawling, you should find two triangle shapes pointing at each other in a vertical column hoisted as high as possible.
There are also a few strange looking flags you’ll find being hoisted in the same location whenever a fishing vessel is either shooting nets, hauling nets, or their nets are caught on the seabed.
Buoys and Marks

Being able to safely navigate around other vessels out on the water is, of course, extremely important, but it’s also important to be observant of non-vessel objects that could get in your sailboat’s way.
Circumventing spots that are potentially dangerous comes first by being able to recognize the various buoys and marks on the water.
There are internationally agreed sets of buoys and marks that ensure safety for traveling vessels all over the world. Thanks to the International Association of Lighthouse Authorities (IALA), we have two major systems to abide by located in two different worldwide regions.
Fortunately, these two regions — Region A and B — have very few impactful differences. Region A (IALA A) covers all of Europe and pretty much the rest of the world while Region B (IALA B) covers the USA, Japan, The Philippines, and Korea.
Major Difference Between IALA A and IALA B
The major difference between the two regions is regarding the buoys which define which side of a channel the vessels should be traveling on.
For example, IALA B has red lights, marks, and/or buoys on the starboard (right) side of a channel when entering a place such as a harbor while under IALA A standards the red lights, marks, and/or buoys are on the port (left) side of a channel when entering.
These are known as lateral or channel marks and define the limits of the water that navigable across a channel.
Port and Starboard Marks
When it comes to buoys and marks that specify the port or starboard side of an object, the port side of an object is red and the starboard side of an object is green.
This is the same for when you’re sailing your boat when it comes to the foremost red and green lights on your vessel.
In regards to specific shapes of port and starboard marks, under the IALA B standards, port marks take the shape of a cone while the starboard marks take the shape of a can.
Safe Water Marks
A Safe Water Mark, also known as a Fairway buoy, is a red and white vertically striped object usually taking the shape of a sphere, pillar, or spar with a red ball on the top for the non-sphere shapes.
This mark usually indicates that you’re entering open and deep waters which should continue as you sail onwards.
Isolated Danger Marks
Having a mark named Isolated Danger Mark isn’t too comforting when you first read it, but it’s one of the most useful marks you’ll find. As the name implies, this mark indicates a location of potential hazard that should be avoided at all costs.
The Isolated Danger Mark should always be red and black horizontal bands with two black balls at the top. It should also have a flashing white light that comes in groups of two flashes.
Special Marks
A Special Mark can carry a number of different meanings, but it’s always displayed in the same way. Special Marks should be completely yellow and have an ‘X’ on the top of it.
A yellow flashing light is also found on the top of the Special Mark and can be seen quite distinctly at night. The reason you could find yourself near a Special Mark is due to it indicating
- Water skiing areas
- Anchorage areas
- Mooring areas
- Waiting areas
- Marine farms
- Historic wrecks
- Protected areas
- Sewerage pipes
- Submarine cables
Cardinal Buoyage System
Another useful set of buoys is based on the Cardinal Buoyage System, which was designed to indicate the safe passage around a potentially hazardous area.
These Cardinal Marks are signaling to vessels that there’s an area that’s shallow, contains sunken objects, reefs, rocks, or something else.
By observing the Cardinal Marks, you’ll be able to tell where not to go based on their explicit placement. For example, if you see a North Cardinal Mark, your vessel can safely pass the hazard by traveling North of that marker.
The same goes for South, East, and West Cardinal Marks. Cardinal Marks are always black and yellow horizontally striped pillars.
The North Cardinal Mark is black on the top, yellow on the bottom, has two vertical triangles pointing up, and has a continuously flashing white light on the top.
The South Cardinal Mark is yellow on the top, black on the bottom, has two vertical triangles pointing down, and has a flashing white light on the top that flashes in groups of six followed by one long flash.
The East Cardinal Mark is black with a yellow stripe in the middle, has two vertical triangles pointing outward, and has a flashing white light on the top that flashes in groups of three.
The West Cardinal Mark is yellow with a black stripe in the middle, has two vertical triangles pointing inward, and has a flashing white light on the top that flashes in groups of nine.
Sound Signals
There may be times when you’re out sailing and the visibility is just too poor to be able to point out any buoys, flags, or shapes of any kind. Thankfully, we have light signals that can help us out when it comes to navigation around other vessels and potentially hazardous areas.
However, there may be times when we need to communicate more direct messages much more quickly. If VHF is not an option under these conditions, the use of sound signals is your go-to solution.
“You Are Running into Danger”
There are plenty of useful sound signals to be able to send out as well as recognize when the moment’s right, but there’s one that everyone should be aware of.
When someone yells “heads up!”, it’s likely you’re going to cover your head as soon as possible. When out on the water, the “heads up” can come in the form of two distinct sounds.
When someone is attempting to warn you that “you are running into danger” or you need to inform another vessel of this, you’ll need to know the Morse code word for ‘U’.
The word ‘U’ is presented as a one-second horn blast followed by a 4-6 second horn blast. You can think of this as a short blast followed by a long blast.
In all likeliness, you’ll be the one hearing this sound signal as opposed to you sending it out. Most of the time when this sound signal is used, it’s coming from much larger vessels such as oil rigs, cruise ships, and other vessels of similar size.
Poor Visibility Sound Signals
There are a few sound signals that you should keep in mind when visibility becomes poor while out on the water. Some of the most important include:
- Power underway, making way: one 4-6 second blast and a 2-minute wait.
- Power underway, not making way: two 4-6 second blasts and a 2-minute wait.
- V essel sailing, fishing, not under command, towing, maneuverability restricted: one 4-6 second blast, two 1 second blasts, and a 2-minute wait.
- Last manned vessel of tow: one 4-6 second blast, three 1 second blasts, and a 2-minute wait.
- Warning from vessel at anchor: one 1 second blast, one 4-6 second blast, and one 1 second blast.
- Plot vessel on duty: four 1 second blasts.
- Vessel at anchor: 5 seconds of rapid bell ringing and a 1-minute wait.
- Vessel aground: 3 short bell rings, 5 seconds of rapid bell ringing, and 3 short bell rings.
Maneuvering and Warning Sound Signals
If you ever find yourself communicating with another vessel using sound signals, you’ll definitely need to confirm with one another who’s going to do what so as to avoid the risk of a collision.
Here are some of the most important sound signals you can use to communicate with other vessels.
- I’m altering course to starboard: one 1 second blast.
- I’m altering course to port: two 1 second blasts.
- I’m operating stern propulsion: three 1 second blasts.
- I don’t understand your intentions! I doubt you’re taking sufficient action to avoid collision: five or more 1-second blasts.
- I intend to overtake on your starboard side: two 4-6 second blasts and one 1 second blast.
- I intend to overtake on your port side: two 4-6 second blasts and two 1 second blasts.
- Agreement by overtaken vessel: one 4-6 second blast, one 1 second blast, one 4-6 second blast, and one 1 second blast.
- Approaching blind bend in channel: one 4-6 second blast.
- Reply from vessel on other side of bend: one 4-6 second blast.
Get the very best sailing stuff straight to your inbox
Nomadic sailing.
At Nomadic Sailing, we're all about helping the community learn all there is to know about sailing. From learning how to sail to popular and lesser-known destinations to essential sailing gear and more.
Quick Links
Business address.
1200 Fourth Street #1141 Key West, FL 33040 United States
Copyright © 2024 Nomadic Sailing. All rights reserved. Nomadic Sailing is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means to earn fees by linking to Amazon.com and affiliated sites.
- Navigating the High Seas: A Comprehensive Guide to Sailboat Masts
Sailboat masts are the unsung heroes of the sailing world, silently supporting the sails and ensuring a smooth journey across the open waters. Whether you're a seasoned sailor or a novice, understanding the intricacies of sailboat masts is essential for a safe and enjoyable voyage. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of sailboat masts, discussing their types, maintenance, and everything in between.
Types of Sailboat Masts
Sailboat masts come in various configurations, each with its advantages and drawbacks. The two primary types are keel-stepped and deck-stepped masts.
Keel-Stepped Masts
Keel-stepped masts are the most common type, extending through the deck and resting on the boat's keel. They provide excellent stability and are suitable for larger sailboats. However, they require careful maintenance to prevent water intrusion into the boat's cabin.
Deck-Stepped Masts
Deck-stepped masts rest on the deck of the boat, making them easier to install and remove. They are commonly found on smaller sailboats and are more forgiving in terms of maintenance. However, they may offer slightly less stability than keel-stepped masts.
Components of a Sailboat Mast
To understand mast maintenance better, it's essential to know the various components of a sailboat mast. The key parts include the masthead, spreaders, shrouds, and halyard sheaves.
The masthead is the topmost section of the mast, where the halyards are attached to raise and lower the sails. It also often houses instruments such as wind indicators and lights.
Spreaders and Shrouds
Spreaders are horizontal supports attached to the mast to help maintain the proper angle of the shrouds (cables or rods that provide lateral support to the mast). Properly adjusted spreaders and shrouds are crucial for mast stability and sail performance.
Mast Materials: Choosing the Right One
Sailboat masts are typically constructed from three primary materials: aluminum, wood, and carbon fiber. Each material has its unique characteristics and is suited to different sailing preferences.
Aluminum Masts
Aluminum masts are lightweight, durable, and relatively easy to maintain. They are commonly used in modern sailboats due to their cost-effectiveness and longevity.
Wooden Masts
Wooden masts, while classic and beautiful, require more maintenance than other materials. They are best suited for traditional or vintage sailboats, where aesthetics outweigh convenience.
Carbon Fiber Masts
Carbon fiber masts are the pinnacle of mast technology. They are incredibly lightweight and strong, enhancing a sailboat's performance. However, they come at a premium price.
Mast Maintenance
Proper mast maintenance is essential for safety and longevity. Regular cleaning, inspection, and addressing minor issues promptly can prevent costly repairs down the line.
Cleaning and Inspection
Regularly clean your mast to remove salt, dirt, and grime. Inspect it for signs of corrosion, wear, or damage, paying close attention to the masthead, spreaders, and shrouds.
Common Repairs and Their Costs
Common mast repairs include fixing corroded areas, replacing damaged spreaders, or repairing shrouds. The cost of repairs can vary widely, depending on the extent of the damage and the materials used.
Extending the Lifespan of Your Mast
Taking steps to prevent damage is essential. Avoid over-tightening halyards, protect your mast from UV radiation, and keep an eye on corrosion-prone areas.
Read our top notch articles on topics such as sailing , sailing tips and destinations in our Magazine .
Stepping and Unstepping a Mast
Stepping and unstepping a mast is a crucial skill for any sailboat owner. This process involves removing or installing the mast on your boat. Here's a step-by-step guide for safe mast handling.
Step-by-Step Guide for Safe Mast Handling
- Gather the necessary tools and equipment.
- Disconnect all electrical and rigging connections.
- Use a crane or mast-stepping system to safely lower or raise the mast.
- Secure the mast in its proper place.
- Reconnect all electrical and rigging connections.
When and Why to Unstep a Mast
You may need to unstep your mast for various reasons, such as transporting your sailboat or performing extensive maintenance. It's crucial to follow the manufacturer's recommendations and ensure a safe unstepping process.
Sailboat Mast Boot: Protecting Your Mast
A mast boot is a simple yet effective way to protect your mast from water intrusion and damage caused by the elements. Here's what you need to know.
The Purpose of a Mast Boot
A mast boot is a flexible material that wraps around the mast at the deck level. It prevents water from entering the cabin through the mast opening, keeping your boat dry and comfortable.
Installing and Maintaining a Mast Boot
Installing a mast boot is a straightforward DIY task. Regularly inspect and replace it if you notice any signs of wear or damage.

Replacing a Sailboat Mast
Despite your best efforts in maintenance, there may come a time when you need to replace your sailboat mast. Here's what you should consider.
Signs That Your Mast Needs Replacement
Common signs include severe corrosion, structural damage, or fatigue cracks. If your mast is beyond repair, it's essential to invest in a replacement promptly.
The Cost of Mast Replacement
The cost of mast replacement can vary significantly depending on the type of mast, materials, and additional rigging needed. It's advisable to obtain multiple quotes from reputable marine professionals.
Yacht Masts: Sailing in Style
For those looking to take their sailing experience to the next level, upgrading to a yacht mast can be a game-changer.
Differences Between Sailboat and Yacht Masts
Yacht masts are typically taller and offer enhanced sail performance. They are often equipped with advanced rigging systems and technology for a more luxurious sailing experience.
Upgrading to a Yacht Mast
Consult with a marine professional to determine if upgrading to a yacht mast is feasible for your sailboat. It can be a significant investment but can transform your sailing adventures.
Sailboat Mast Steps: Climbing to the Top
Mast steps are handy additions to your mast, allowing easier access to perform maintenance or enjoy panoramic views. Here's how to use them safely.
Using Mast Steps Safely
Always use proper safety equipment when climbing mast steps. Make sure they are securely attached to the mast and regularly inspect them for wear or damage.
The Advantages of Mast Steps
Mast steps provide convenience and accessibility, making sailboat maintenance tasks more manageable. They also offer an elevated vantage point for breathtaking views while at anchor.
Mast Maintenance Tips for Beginners
If you're new to sailboat ownership, these mast maintenance tips will help you get started on the right foot.
Essential Care for First-Time Sailboat Owners
- Establish a regular maintenance schedule.
- Seek advice from experienced sailors.
- Invest in quality cleaning and maintenance products.
Preventing Common Mistakes
Avoid common pitfalls, such as neglecting inspections or using harsh cleaning agents that can damage your mast's finish.
Sailing with a Mast in Top Condition
A well-maintained mast contributes to a safer and more enjoyable sailing experience. It enhances your boat's performance and ensures you can rely on it in various weather conditions.
How a Well-Maintained Mast Improves Performance
A properly maintained mast helps maintain sail shape, reducing drag and improving speed. It also ensures that your rigging remains strong and secure.
Safety Considerations
Never compromise on safety. Regularly inspect your mast, rigging, and all associated components to prevent accidents while at sea.
Sailboat masts are the backbone of any sailing adventure, and understanding their intricacies is crucial for a successful voyage. From choosing the right mast material to proper maintenance and upgrading options, this guide has covered it all. By following these guidelines, you can sail the high seas with confidence, knowing that your mast is in top condition.
So what are you waiting for ? Take a look at our range of charter boats and head to some of our favourite sailing destinations .
- Pontoon Boats
- Personal Watercraft
- nauticalknowhow
- Nautical Knots
- Tools and Calculators
Understanding Boat Navigation Lights
Boat navigation lights are essential when you’re out on the water. They’re essential, but it’s easy to misunderstand their uses and correct placements.
If you don’t know the correct placement for your stern lights or know what type of navigation light you need on your mast, don’t worry: we’re here to help. Below, we’ve got an overview of everything you need to know about boat navigation lights: what type of navigation lights you need, where to put them, and why you need to use them.
So without further ado, let’s learn more about boat navigation lights.
What navigation lights are required on a boat?
The U.S. Coast Guard Navigation Rules, International-Inland encompasses lighting requirements for every description of watercraft. The information provided there is intended for powerboats and sailing vessels less than 20 meters. The various options are illustrated.
The U.S. Inland Rules apply inside the demarcation lines at the entrances to inlets, bays, rivers, etc. The demarcation lines are shown on coastal charts as magenta dashed lines. Once outside of the demarcation lines, International Rules apply.
Powered Vessels
Power boats less than 20 meters shall exhibit navigation lights as shown in Figure 1. (Note: 2 masthead lights are optional for vessels under 50 meters. Vessels over 50 meters will display two masthead lights.)
Vessels of less than 12 meters in length, may show the lights in either Figure 1 or Figure 2.
Powerboats less than 7 meters whose maximum speed cannot exceed 7 knots may exhibit an all-round white light, and if practicable sidelights instead of the lights prescribed above, in international waters only.
Sailing Vessels and Vessels Under Oars
Sailing vessels less than 20 meters may exhibit the navigation lights shown in Figures 3 or 4.
Another option for sailboats is to use a single combination lamp at the top of the mast as shown in Figure 5.
Sailing vessels less than 7 meters may carry an electric torch or lit lantern showing a white light to be displayed in time to prevent collision (see Figure 6 – left picture).
If possible, the lights prescribed for sailing vessels less than 20 meters should be displayed.
Vessels under oars may display the lights prescribed for sailing vessels, but if not, must have ready at hand an electric torch or lighted lantern showing a white light to be displayed in time to prevent collision (see Figure 6 – right picture).
Small boats can benefit from using a temporary LED light with a suction cup attachment if permanent fixings aren’t possible.
Shapes and Lights
To alert other vessels of conditions that may be hazardous, there are requirements to display lights at night and shapes during the day.
Anchored Vessels
Powered vessels and sailing vessels at anchor must display anchor lights. An anchor light for a boat less than 50 meters in length is an all-around white light visible for 2 miles exhibited where it can best be seen (see Figure 7).
Vessels at anchor shall exhibit forward where best seen, a ball shape (see Figure 8).
Vessels less than 7 meters are not required to display anchor lights or day shapes unless anchored in or near a narrow channel, fairway or anchorage, or where other vessels normally navigate.
Anchor lights are not required on vessels less than 20 meters, anchored in special anchorages in inland waters designated by the Secretary of Transportation.
Sailing Vessels Under Power
Vessels under sail also being propelled by machinery, must exhibit forward where best seen, a conical shape with the apex pointing down (see Figure 9).
Vessels less than 12 meters are not required to exhibit the dayshape in inland waters.
Sailing vessels operating under machinery, or under sail and machinery are considered as powered boats and must display the lights prescribed for a power-driven vessel.
Restricted Maneuverability
The Navigation Rules require vessels restricted in their ability to maneuver to display appropriate day shapes or lights. To meet this requirement, recreational vessels engaged in diving activities may exhibit a rigid replica of the international code flag “A” not less than one meter in height or at night display the navigation lights shown in Figure 10.
This requirement does not affect the use of a red and white divers flag which may be required by state or local law to mark a diver’s location. The “A” flag is a navigation signal indicating the vessel’s restricted maneuverability and does not pertain to the diver.
Navigation lights should be checked prior to departing the dock and you should always carry spare bulbs. The USCG doesn’t care if they were working when you left, only that they are working when required.
Where do navigation lights go on a boat?
The current navigation light requirements are found in the Navigation Rules, International-Inland, and in Parts 81, 84, and 89 of Title 33, Code of Federal Regulations . They’re easy to find, but many sailors and boat manufacturers do not have a good understanding of the rules governing the proper installation of navigation lights. To help clear up any misunderstandings here’s all you need to know:
Sidelights that are installed in the contour of the bow without providing a mounting surface tooled to be parallel with the fore and aft centreline of the boat are not in compliance with the Inland or International Navigation Rules. Depending on the breadth of the boat near the bow and how far aft from the vessel’s stem the lights are mounted, this shift can be more than 20 degrees in some cases. Installing the fixtures too far aft of the vessel’s stem may result in the sidelights not being visible from a position dead ahead.
Another factor in the proper installation of sidelights is that they must maintain their required minimum intensity in a vertical sector from 5 degrees above to 5 degrees below the horizontal. They must also maintain at least 60 percent of their minimum required intensity from 7.5 degrees above to 7.5 degrees below the horizontal. Installing flush-mounted sidelights, designed to be mounted to a vertical surface in the hull contour, without providing a mounting surface tooled to be vertical, shifts the vertical coverage sector. This also results in non-compliance with the Inland or International Navigation Rules.
Additionally, most of these flush-mounted sidelights are installed below the vessel’s rub rail. International Navigation Rules require that sidelights be installed above the uppermost continuous deck. Therefore, this configuration would not be in compliance with International Navigation Rules.
When separate red and green sidelight fixtures are used, the masthead light or all-round white light, whichever configuration is installed, must be located as close as practical to the vessel’s fore and aft centerline. For vessels less than 12 meters in length, the masthead light or round lights may be displaced from the fore and aft centerline providing that the sidelights are contained within a common fixture and mounted on the vessel’s fore and aft centerline. The masthead or round lights must be installed at least one meter (3.3 ft.) above the sidelights.
Which navigation lights are you required to display when anchoring your boat for the night?
Boating at night (or in reduced visibility) can present some special challenges. Not only is your depth perception lessened, but bright lights on the shore can also cast misleading reflections on the water and if you wear glasses, or worse yet bifocals, you simply don’t see as well at night as you do during the day.
It is not only important that you be able to identify other vessels operating in your proximity, it is equally important that other vessels see you. Most recreational vessels are less than 30 feet in length and, according to the Rules of the Road, shall be equipped with navigation lights.
These lights not only have a certain arc through which they can be seen but must be seen from a minimum distance. The following lighting requirements are for recreational vessels less than 12 meters in length. (approximately 39.4′)
The arc of the lights and color allows you to determine the direction a boat is moving. How good are your boat’s lights? You should test them to check your nighttime visibility, or you might land yourself in hot water with the Coast Guard.
Whether on a trailer or at the marina, switch on your lights and see how well they can be seen. Walk away from the boat or row away, if you are at anchor or at a mooring, and see how visible the lights are as you move further away. How easy are they to see against the background of lights onshore?
Does your stern light shine dead astern over the required 135º arc or does it shine to one side or up or down? Can it be seen from the required 2 miles and why is that important? As an example, let’s say that your stern lights can only be seen for 1/2 mile. You are underway at 8 knots and a large ship is approaching at 15 knots. The ship is only 4 minutes away from a collision with you. By the time the ship “might” see you, identify the light, and decide on how to move, it is too late. A ship traveling at 15 knots may take miles to stop.
Look at the stern lights again, as you move from the stern toward the bow, does the stern light “disappear” as the sidelight “appears”? The stern light should disappear and sidelight appear at 22.5º abaft the beam. If you don’t see the green starboard sidelight or the red port side light when the stern light disappears there is a problem with the arc of one or all these lights. This means that if another boat were approaching you at the angle where no lights are seen there is an increased risk of collision.
If both the stern lights and side lights are seen brightly at the same time you still have a problem. A boat approaching won’t know whether they are overtaking or crossing and whether they should give-way or stand-on.
You should also check to make sure that your masthead light disappears at the same time each side lights disappear and they both disappear when the stern light appears.
Check your sidelights from dead ahead. You should see both red and green. However, by moving toward one side just 1-3º you should then see only one light. If you still see two lights, an approaching boat won’t be able to tell which direction you’re are going.
It is very important to be seen from a distance but also for an approaching boat to be able to determine your direction of travel.
When boating at night remember the following: “When two lights you see ahead, turn your helm and show your red”.
About Chris
Outdoors, I’m in my element, especially in the water. I know the importance of being geared up for anything. I do the deep digital dive, researching gear, boats and knowhow and love keeping my readership at the helm of their passions.
Categories : nauticalknowhow
Robert Hogward on September 12, 2021
Thanks for writing this post. I can either place them on the exterior or interior for decorations. Placing them on the exterior side is helpful when I go fishing and indulging in other night activities in the water.
Dalton Bourne on July 26, 2022
We love the lights! We put lights from Seaponer on my Jon boat right above the water line and use them for night fishing! The amount of brightness it offers is an assurance of my boat’s being seen clearly during the night. At the same time, the LED lights don’t consume too much energy, leading to a life span of up to 50,000 hours.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
More in nauticalknowhow

How to Tie a Boat to a Dock

How to Clean a Boat Cover

Everything You Need to Know About Your Boat’s Bilge Pump

4 Ways to Tie Your Boat Shoes

The People’s Poncho Review and Ratings

Oru Lake Kayak Review

What Is A Gunwale?

131 of the Best Hawaiian Boat Names

167 Patriotic Boat Names
About boatsafe.
Established in 1998, BoatSafe is your independent guide into the world of boating, fishing, and watersports. We provide expert insights and detailed guides to help you find products tailored to your needs and budget.
Contact Boatsafe
- Address: 4021 West Walnut Street. Rogers, AR 72756
- Phone: (479)339-4795
- Email: [email protected]
Site Navigation
- How We Test
- Corrections Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Editorial Policy
- Affiliate Disclosure
Our Reviews

All content is © Copyright 2024. All rights reserved.
- New Sailboats
- Sailboats 21-30ft
- Sailboats 31-35ft
- Sailboats 36-40ft
- Sailboats Over 40ft
- Sailboats Under 21feet
- used_sailboats
- Apps and Computer Programs
- Communications
- Fishfinders
- Handheld Electronics
- Plotters MFDS Rradar
- Wind, Speed & Depth Instruments
- Anchoring Mooring
- Running Rigging
- Sails Canvas
- Standing Rigging
- Diesel Engines
- Off Grid Energy
- Cleaning Waxing
- DIY Projects
- Repair, Tools & Materials
- Spare Parts
- Tools & Gadgets
- Cabin Comfort
- Ventilation
- Footwear Apparel
- Foul Weather Gear
- Mailport & PS Advisor
- Inside Practical Sailor Blog
- Activate My Web Access
- Reset Password
- Customer Service

- Free Newsletter

Ericson 34-2 Finds Sweet Spot

How to Sell Your Boat

Cal 2-46: A Venerable Lapworth Design Brought Up to Date

Rhumb Lines: Show Highlights from Annapolis

Solar Panels: Go Rigid If You have the Space…

Leaping Into Lithium

The Importance of Sea State in Weather Planning

Do-it-yourself Electrical System Survey and Inspection

When Should We Retire Dyneema Stays and Running Rigging?

Rethinking MOB Prevention

Top-notch Wind Indicators

The Everlasting Multihull Trampoline

What Your Boat and the Baltimore Super Container Ship May Have…

Check Your Shorepower System for Hidden Dangers

DIY survey of boat solar and wind turbine systems

What’s Involved in Setting Up a Lithium Battery System?

The Scraper-only Approach to Bottom Paint Removal

Can You Recoat Dyneema?

How to Handle the Head

The Day Sailor’s First-Aid Kit

Choosing and Securing Seat Cushions

Cockpit Drains on Race Boats

Re-sealing the Seams on Waterproof Fabrics

Safer Sailing: Add Leg Loops to Your Harness

Waxing and Polishing Your Boat

Reducing Engine Room Noise

Tricks and Tips to Forming Do-it-yourself Rigging Terminals

Marine Toilet Maintenance Tips

Learning to Live with Plastic Boat Bits
- Safety & Seamanship
- Sails, Rigging & Deck Gear
Navigation Lights: Hella and Aqua Signal Shine Brightest
Three of the four major light manufacturers serve up superlative lights-many lights even satisfied coast guard requirements at our engine-off test voltage. still, a variation of the golden rule applies: shine unto others as you would have them shine unto you..

Most boats, new or used, come with navigation lights installed-and that’s about all that we care about them until one of them fails. Sometimes the failure is in the light itself, sometimes in the wiring leading to it. The fix is usually simple enough to perform mechanically or electrically, but there’s an inconvenience factor that varies from minor to major, depending on where the failure occurs. If a light goes out on the bow pulpit or cabinside, it’s no big deal. If it goes out at the top of the mast, it’s a royal pain. After the first of these pains, you begin to pay more attention to how the lights are mounted and sealed against the elements, and how the wiring is led and protected from chafe and crimping. And you begin to consider the design, construction, and materials of the lights themselves.
The other occasional concern we have with these lights is how they actually perform. Again, most of the time we take them for granted-the waters are less crowded at night, tense crossing situations are relatively infrequent, and there’s usually plenty of time to study a developing situation and make a course change if necessary. In times like that, you might feel that you have your lights on just to obey the law, nothing more.
However, when you find yourself negotiating a busy harbor or channel at night, or the visibility isn’t what it could be, or you’re traveling along a shore twinkling with houselights and floodlights and car headlights and all sorts of other distractions, you instantly appreciate running lights that are clear and bright and that stand out against the background-and you wonder just how visible yours are to others.
There are minimal visibility requirements set by the US Coast Guard-see the sidebar on pages 8-9 for the basics. But note that there’s no rule prohibiting a boat from carrying bigger, better lights than those that satisfy the minimum, as long as they don’t shine so brightly or cause so much glare that they interfere with the helmsman’s vision.
Obviously, navigation lights exist to help prevent collisions. As such, they’re important pieces of safety gear. If you suspect the ones aboard your boat are feeble, either in form or function, consider replacing them. It’s to help with your decisions on that score that we’ve done this evaluation.
Light Basics The point of navigation lights underway is to show a 360-degree circle of light at all times, including red and green sidelights, each visible through 112.5 degrees, and a stern light, visible through 135 degrees to complete the circle. On boats under 20 meters, sidelights can be combined in one unit (a bi-color light).
Powerboats underway are required to show sidelights and 360 degrees of white light. The usual configuration is sidelights, a sternlight, and a masthead light. If the boat is under 12 meters in length, an all-round white light can be substituted. The all-round white light also serves as an anchor light, required from sunset to sunrise in areas that are not designated anchorages.
On a sailboat under 20 meters, all three lights can be combined in a tri-color light at the masthead, but only when sailing; under power, a sailboat must show a 360-degree circle of white light, either in an all-around light at the masthead, or in a combination of stern light plus a 225-degree masthead light. (The masthead light is confusingly named, since it’s rarely located at the top of the mast. Usually it’s about three-quarters of the way up. On powerboats it’s usually mounted on a short pole.)
We’re referring here to boats between 7 and 20 meters in length. There are variations on the rules outside that range, but we don’t have enough paper to cover them all.
What Was Tested The last time we tested navigation lights was in 1993-the results were published in the July 1 issue of that year. We evaluated 70 lights then, and as it turns out we looked at 70 lights this time around, too, although there were some variations-missing were lights from Wilcox-Crittenden, which no longer makes them, and Forespar’s ML2 combination masthead/deck light, recommended in ’93 and still on the market (which we forgot). Otherwise we collected all the lights in the major catalogs and chandleries, including individual and bi-color sidelights, tri-color lights, sternlights, masthead lights, and all-round white lights. The lights were represented by four manufacturers-Aqua Signal, Attwood, Hella Marine, and Perko.
How We Tested Our evaluations were simple: All the lights were mounted on pine planks and properly bedded and sealed. On a chilly October night with virtually unlimited visibility, we took the planks to a local beach parking lot with little ambient light around, and set them on sawhorses. With our observer (the keenest-eyed among us) anchored offshore at one nautical mile, we powered each light individually, and the observer called in his impressions via cell phone.

We had noted that the American Boat and Yacht Council (ABYC), in their specs for the Intensity/Nominal Voltage Test for nav lights, says that the test fixture “shall be tested for its ability to meet minimum required luminous intensity… when operated at its intended nominal system voltage. This shall be a single reading at a point selected by the fixture manufacturer.”
That leaves the manufacturers quite a bit of wiggle room to balance bulb characteristics against input voltages in order to achieve their visibility requirements.
We decided to see how the lights would do in less forgiving circumstances. For power we used a truck-mounted 4-D deep-cycle marine battery monitored throughout the test at 12.4 volts-a standing voltage that would approximate power to the lights with the boat’s engine off and the supply battery in reasonably good shape, but with one or two other power demands being made on it at the same time-nav instruments and an interior light or two.
Obviously, with the engine running and an alternator output of 13 volts or more, the lights will shine brighter-so the ratings in our chart should be seen as pessimistic across the board.
After looking at all 70 lights and communicating his ratings at 1 nm, the observer moved out to 2 nm and the whole procedure was repeated. The planks were adjusted as necessary to give the observer the full proper view of each type of light. Occasionally it appeared to the testers on shore that the powered light was mounted close enough to its neighbor that it was picking up an extra reflection. In those cases they inserted a brown clipboard between the lights. It didn’t seem to make much difference.
After the visibility tests, all the lights were sprayed forcefully with a gardenhose and left to sit for two weeks. Then they were sprayed again and checked for continued function. All lights functioned fine after both inundations.
Finally, we studied the lights for quality of construction, mounting methods, and ease of maintenance. Comments on these topics are included in the main chart (see bottom).
We didn’t measure each lens for its required cuto-off angle (e.g. 112.5), reasoning that even if we were persnickety enough to find lights that were a degree or two off either way, such minor anomalies would be of little consequence on the water.
What We Found The chart provides specifics about the lights and our visibility tests. In general, we found that lights met the minimum visibility requirements at 1 mile, with the exception of two red sidelights-the Aqua Signal 22300-1 and the Attwood 3150R7.
Twenty-two lights, nine of which were rated at 2 nautical miles, were invisible at that distance and at our unforgiving voltage. Again, all lights must meet their Coast Guard requirements when powered at the test voltages allowed their manufacturers.
We should note that Hella Marine’s Model 62149 red sidelight, a 3-nm light, is rated to burn a 29-watt bulb at 13 volts, so it was unfairly underpowered in the test. Maybe it’s just for powerboats.
The fit and finish of the lights varied quite a bit, and those variations are often reflected in the price. Only one light, Perko’s Model 170BMD masthead/decklight combination arrived with an obvious flaw-a 4-mm separation in one side of the plastic housing.
A few lights were quite a bit brighter and more visible than the rest of the pack. Only five lights rated good at 2 nm: Aqua Signal’s 40100-1 bi-color light and 40400-1 masthead; Hella Marine’s 62208 stern light, 62206 masthead, and 6225 tri-color. (This tricolor was actually the most visible of all the lights in the test, scoring “excellent” at 1 nm and “good” at 2 nm.)
Some sidelights that were rated for only one nautical mile were still visible at two, even if they were only dimly seen at both distances. Those two achievements-overall brightness and staying power, were, to our minds, the top rating criteria.
See the big chart for further comments. See the recommendations box on page 5 for our picks by light type.
Navigation lights are easy to take for granted, but like so many other bits of safety and navigation gear on a boat, there may eventually come a time when they really need to shine.
Contacts- Attwood, 1016 N. Monroe St., Lowell, MI 49331; 616/897-9241. Hella Marine, 201 Kelly Dr., Peachtree City, GA 30269; 877/224-3552; www.hellana.com . Aqua Signal, 1125 Alexander Court, Cary IL, 60013; 847/639-6412. Perko, Inc., 16490 NW 13th Ave., Miami, FL 33169; 305/621-7525; www.perko.com/ .
Also With This Article Click here to view “Most Visible Lights.” Click here to view “Value Guide: Navigation Lights.” Click here to view “Light Rules.”
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
What your boat and the baltimore super container ship may have in common.
These best boat navigation lights are what most boaters have on their marine vessels for safer and convenient boating trips. I use these bow lights for boat for secured and easy navigation during extreme weather conditions or poor visibility.
Unfortuntately, the links to additional information at the bottom of this article are broken. (Error 404 – not found) Any way to get them fixed?
This may not be the correct location to ask this question about Nav Light placement so please forgive me and direct me if need be. I am mounting a Tri-color light on top of my 26 ft mast. I presently have an under power, “steaming” light on the mast at 11 feet. COLREGS require this forward facing 225 degree white light to be at least 3′ 3″ ABOVE the forward “side markers/lights”. Where do I, or anyone else, mount the steaming light?
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Log in to leave a comment
Latest Videos

40-Footer Boat Tours – With Some Big Surprises! | Boat Tour

Electrical Do’s and Don’ts

Bahamas Travel Advisory: Cause for Concern?

Island Packet 370: What You Should Know | Boat Review
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell My Personal Information
- Online Account Activation
- Privacy Manager

Please verify you are a human
Access to this page has been denied because we believe you are using automation tools to browse the website.
This may happen as a result of the following:
- Javascript is disabled or blocked by an extension (ad blockers for example)
- Your browser does not support cookies
Please make sure that Javascript and cookies are enabled on your browser and that you are not blocking them from loading.
Reference ID: 5df7b2dc-ee35-11ee-b658-7aa38e964ae2
Powered by PerimeterX , Inc.
Sign up now for our WhatsApp newsletter and receive a FREE SVB set of playing cards!
- Spare parts
- SVB@Youtube
- Saved Guides
- My Skipper profile
- My boat on Portmaps.com
- General settings:
- Newsletter and messages
- NEW WhatsApp & SMS
- Compare list
Are you missing items that you have already placed in your shopping cart? Log in to see your saved items.
- Boat Safety Equipment
Navigation Lights on Sailing Yachts and Motor Boats

Navigation lights ensure the safety of everyone at sea. The Convention on the International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea (IMO COLREG 72) precisely sets out the guidelines for navigation lights, i.e., displaying lights, their range (distance from which the light is visible), as well as how they should be constructed and assembled. Our guide is of interest to sailors and sports boats enthusiasts with boats up to 20 m in length.
Regulations and official certifications:
When must navigation lights be displayed, what are the regulations concerning the use of navigation lights at sea, how do i know that my lights are eu-compliant, what is a ce mark, how are navigation lights defined, minimum range of navigation lights:.
- From what distance must lights be visible?
- What lights are required for my boat?
What lights must be displayed on a sailboat or rowing boat with a motor?
What lights should i exhibit when at anchor, what lights should be displayed to show that a vessel is unable to manoeuvre.
- How do I indicate that my vessel has run aground?
Navigation lights – Conventional and LED:
What distinguishes led from conventional navigation lights.
- Replacement bulbs for conventional & LED lights
What are the advantages of LED navigation lights?
Switching from conventional to led navigation lights.
According to COLREGs part C, rule 20), navigation lights must always be used on board from sunset to sunrise or during the day if visibility is poor.
Please refer to the German Traffic Regulations for Navigable Maritime Waterways , §8 -10 and Preventing Collisions at Sea. Part C - Lights and Shapes. rules 20 - 31, and annexes I 1. - 14 for the exact wording.
NOTE: Vessels that are authorised to fly the German flag are generally only permitted to use approved navigation lights and sound signalling devices.
EU approval can be identified via the wheel mark symbol and the notified body number. BSH approved navigation lights (previously DHI) are marked with a model number (e.g., BSH/00/01/90).
However, even older lights with DHI approval that have already been installed maintain their approval, despite the changes made by the BSH.
In addition to the wheel mark symbol and German BSH approval, some lights are also approved by other countries, such as RINA (Registro Italiano Navale), MCA (Maritime and Coastguard Agency) and the USCG (United States Coast Guard). These are now recognised, provided the approval comes from the national approval body recognised in the country of origin.
National bodies whose accreditation is currently recognised in Germany:
The wheel mark symbol indicates approval of the Marine Equipment Directive (MED). This approval is valid for all EU member states, both for commercial vessels and recreational shipping.
0098 = Notified Body number (here 0098 = Germanischer Lloyd in Hamburg) 18 = year in which the mark is affixed, here 2018

- A CE mark is a symbol that must be affixed to a product by the manufacturer before it is sold on the European market. It indicates that the manufacturer is aware of the specific requirements for the product in question and that it fulfils the requirements of relevant European product directives. A CE mark does not supersede approval according to collision prevention regulations.
- Navigation lights are defined in detail by the International Maritime Organization (IMO), according to the International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea, 1972 (COLREGs) Convention on the International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea, 1972), in sections C and D. The following rules apply:
Which navigation lights are required on board according to IMO COL REG?
Definitions according to the 1972 International Regulations for Prevention of Collisions at Sea (COL REG 72):

1. Side lights for starboard and port
A green light on the starboard side and a red light on the port side, which shine from dead ahead in an arc of 112.5° aft to a point 22.5° abaft the beam (behind the beam) on either side of the vessel. On ships of less than 20 metres in length, the two individual sidelights may be replaced by a dual-colour combined light. This must be centrally located on the bow and stern axis.

2. Stern light
A white light mounted as close to the stern as possible and shines dead ahead in an arc of 135° (67.5° to each side). The mounting height should be aligned to the height of the side lights and should never be higher.

3. Three-colour light for sailing vessels (sailing lights)
On sail boats up to a length of 20 m, the side light and stern light can be combined into one three-colour light mounted on top of the mast. However, as soon as the sail boat's motor is engaged, the use of a three-colour light is no longer permitted. The rules for motor-powered vessels then apply.

4. Mast-head light
A white light placed over the centre line of the vessel and shines dead ahead in an arc of 225° (from straight ahead up to 22.5° more aft than crosswise to each side). The mounting height should be at least 1 m higher than the side lights. In the past, the mast-head light was also referred to as a steam boat light or steamer light, as it is only seen on ships that operate under engine power.

5. Signal light or all-round light
A light that shines in a complete circle of 360°. It may emit white, red or green light, depending on use. Examples of use: All sailboats and motorboats at anchor must exhibit a white anchor light . Ships over 12m in length must, if necessary, display vessel-in-distress lights (two red signal lights) placed at a vertical distance of at least 12 m. The distance between such lights must not exceed 1 m.
From what distance must navigation lights be visible?
The range indicates the distance from which the light can be seen. The minimum ranges of navigation lights are defined according to ship size as follows::
Best-seller Hella marine

Note: When sailing boats are powered by a motor, the rules for motorboats apply and not for sailboats. The tricolour light may then no longer be displayed.

Displaying lights for sailboats up to 20 m
1 x red port side light
1 x green starboard light
1 x stern light
Also allowed:
1 x red all-round light on or near the mast top
1 x green all-round light on or near the mast top

1 x 3-colour light

Sailing vessels under 7 m (dinghies or small sports boats)
If, due to their design, no modern lights can be fitted, sailing vessels under 7 m in length and vessels being rowed must always carry an electric torch or lantern showing a white light, ready to exhibit in sufficient time to prevent a collision.
1 x Electric light or a torch with white light

Motorised vessels over 12 m
Lights used must be either / or:
1 x white masthead light fore

1 x dual colour light

Motorised vessels under 12 m
Alternatively, motorised vessels under 12 m can exhibit the following lights:
1 x white all-round light

Motorised vessels under 7 m and 7 knots maximum speed (small motor boats, dinghies or inflatables):
Motorised vehicles under 7 metres and with a maximum speed of no more than 7 knots can display the following navigation lights: all-round lights, portside and starboard lights.
The following applies in accordance with German Traffic Regulations for Navigable Maritime Waterways (SeeSchStrO): If, due to their design, no lights can be displayed (e.g., dinghies), sailing vessels under 7 m in length and 7 knots maximum speed must carry an electric hand-held spotlight or a torch to prevent collisions in the dark.
Left: 1 x white all-round light, 1 x red port side light, 1 x green starboard light
Right: 1 x hand-held spotlight or torch
Best-seller Aqua Signal Conventional

Best-seller Aqua Signal LED

Provided no engine power is used, the rules for sailboats apply. Motor-sailing vessels must display a large black cone pointing downwards when sailing during the day or at good light.
For vessels travelling under sail or at rudder during darkness or at reduced visibility, the rules for carrying lights for motorised boats automatically apply. This then depends on the length of the boat.
By day with a black cone, tip pointing downwards.
Visual signalling equipment

Torches & Spotlights

How must navigation lights be mounted on board?
Navigation lights must be securely mounted perpendicular to the waterline. Mast-head lights and stern lights should both be placed above the keel line.
At anchor during daylight? This must be displayed with a black anchor ball.
If the vessel is anchored outside of an area of water known by the River and Shipping Police Authority as an anchorage and berth for small vessels, this must be indicated as follows:
A black ball by day, 1 x white all-round light at night

Marker Lights

If your boat is unable to manoeuvre*, this should be indicated as follows:
Stationary: 2 x red all-round light, 2 x black ball, one below the other (during the day)
Moving: 1 x red port side light, 1 x green starboard light, 1 x white stern light
* A vessel is described as if, due to exceptional circumstances (e.g., rudder failure or engine malfunction), it cannot manoeuvre as prescribed and therefore cannot avoid another vessel.

How do I indicate correctly that my sailboat or motorboat has run aground?
If your boat has run aground, this should be indicated as follows:
2 x red all-round light, 1 x white all-round light, 3 x black ball, one below the other (during the day)
Manufacturers that specialise in navigation lights such as Aqua Signal or Hella Marine supply a wide range of internationally approved navigation lights which work with conventional (with BSH bulb) or with permanently installed light-emitting semiconductor components (LEDs). The bulbs required for operation are an integral part of the approval. Replacement bulbs must also be certified so that approval / your insurance protection is guaranteed. Ships under 20 m: Stern and anchor lights require BSH-approved light bulbs with 10 watts, all other navigation lights 25 watts.
All series listed above with BAY15d sockets could alternatively be operated with a high-Power LED . The big advantage in doing so is that the LED is suitable for multiple voltages (10-30 V) and consumes just 3 watts during operation. Since the light colour, range of light or beam angle can vary depending on the housing, this light is NOT yet internationally approved.
Spare Bulbs - Conventional & LED

Energy consumption on sailing ships is, as ever, a topic of significant interest. This is especially true for blue-water sailors who like to sail longer distances at a stretch. The arguments for converting to LED technology are as follows:
- High energy savings due to the low power consumption
- Long lifespan (over 10,000 hours)
- MultivoltTM technology (10-30V) with greater tolerance to voltage peaks
- Compact and light housing constructions
- Waterproofed, hermetically sealed housings
- Maintenance free
When switching completely from conventional navigation lights to LED lights, lights with the BSH seal of approval / EU wheel mark meet all the requirements in terms of light colour (no risk of blue tint), range of light and beam angle, and that you are travelling in accordance with KVR.
Navigation lights with LED technology

Replacing your navigation lights is often easy to do as manufacturers usually use the same mounting points for LED lights or have an adapter plate for further use of existing drill holes:

Adapter plate

Share our guide on social media

Written by our SVB (technical) experts
Our SVB safety experts regularly carry out maintenance checks and tests on our safety products, such as life jackets, life rafts etc. They test products and base their recommendations on many years of experience and their own know-how.
Steaming Light on Sailboat: A Guide to Proper Usage
by Emma Sullivan | Aug 11, 2023 | Sailboat Maintenance

== Short answer: Steaming light on sailboat == A steaming light is a white navigation light fitted on the mast of a sailboat to provide visibility during low-visibility conditions. It is typically placed near the front side of the mast and angled downwards to indicate that the vessel is under power and moving forward. This light helps other boats identify and avoid collisions, ensuring safe navigation at night or in limited visibility situations.
Understanding the Purpose of a Steaming Light on a Sailboat: What You Need to Know
Have you ever been out on a sailboat and noticed a small light at the top of the mast? You might have wondered what its purpose is or why it’s necessary. Well, that little light is called a steaming light, and it plays a crucial role in ensuring safety and navigation on a sailboat . In this blog post, we will dive into the details of understanding the purpose of a steaming light on a sailboat.
To begin with, let’s clarify what exactly a steaming light is. A steaming light is a white-colored navigation light located on the front of the mast or near the bow of a sailboat. Its main function is to provide visibility to other vessels during low-light conditions or at night. This means that whether you’re sailing in foggy weather, dim lighting, or after sunset when natural visibility decreases, the steaming light will maximize your boat’s presence to prevent collisions with other boats.
So why is it specifically called a “steaming” light? The term “steaming” refers to sailing when using an engine rather than relying solely on wind power. When you are using your boat’s engine for propulsion instead of sailing with just your sails, it is known as “motoring” or “steaming.” The steaming light got its name because it primarily signifies that the vessel has powered propulsion engaged rather than utilizing only wind power.
Now that we know what a steaming light does and where it gets its name from let’s discuss more about its importance. One major reason for having this navigation aid onboard is compliance with international boating regulations and standards set by organizations like COLREGs (Convention on the International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea). These regulations ensure safe navigation practices globally and require boats to display certain lights for visibility purposes both to avoid accidents and allow other captains to understand their intentions.
When operating under engine power, displaying only proper red (port) and green (starboard) sidelights can confuse other boaters, as these lights typically indicate the presence of a vessel under sail. To avoid such confusion, the use of a steaming light in conjunction with the appropriate sidelights clarifies that the boat is motoring and not just relying on its sails for propulsion.
Another important aspect to note about steaming lights is their distinct positioning on a sailboat . Typically, they are mounted at least one meter above the deck level to ensure maximum visibility. This height allows for unobstructed illumination, making it easier for other boaters to see your vessel from afar. It’s crucial to maintain this specific positioning to comply with regulations and maximize safety on the water.
In summary, understanding the purpose of a steaming light on a sailboat is essential for any sailor or boat owner. Its primary function is to provide visibility during low-light conditions or at night when using engine power instead of relying solely on wind power. By complying with international regulations and properly displaying navigation lights like a steaming light , you enhance safety by avoiding confusion between sailing and motoring vessels. So next time you’re out on the water after dusk or in foggy weather, remember the importance of that little but mighty steaming light atop your sailboat’s mast!
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Install a Steaming Light on Your Sailboat
Installing a steaming light on your sailboat might seem like a daunting task, but with the right guidance and a bit of patience, you’ll have it up and running in no time. In this step-by-step guide, we’ll walk you through the process of installing a steaming light on your sailboat, ensuring that you have a safe and well-lit vessel on your next sailing adventure.
Step 1: Gather the necessary tools and materials Before diving into the installation process, make sure you have all the tools and materials required. You’ll need a steaming light fixture, wires (preferably marine-grade), heat shrink tubing, electrical connectors, wire cutters/strippers, crimping tool, electrical tape, screwdrivers (flathead and Phillips-head), mounting brackets or screws if needed, and a drill with appropriate bits.
Step 2: Identify the ideal location for installation Finding the right spot for your steaming light is crucial as it needs to be clearly visible from all angles while ensuring it won’t interfere with other equipment or rigging. Typically, sailors prefer placing it at the masthead or near where the mast meets the deck.
Step 3: Prepare for installation Ensure that all power sources are disconnected before beginning any work. Next, carefully remove any existing fixtures or wiring from the chosen location (if applicable). If there’s already an ample power supply nearby (e.g., an existing navigation light circuit), tap into it to minimize additional wire routing.
Step 4: Mount the steaming light fixture If your chosen spot requires mounting brackets or screws for support, position them accordingly using suitable hardware. Ensure they are firmly secured to prevent any movement due to vibrations caused by sailing conditions. Attach the steaming light fixture securely to these brackets using screws provided with the fixture.
Step 5: Connect wires and ensure proper wiring configuration Strip off some insulation from both ends of each wire to be connected. Using heat shrink tubing, slide it over one end of each wire to ensure a clean finish once the connections are made. Connect the appropriate wires from the steaming light fixture to the power supply or existing wiring and secure them using electrical connectors. It’s crucial to follow a proper wiring configuration, so refer to the manufacturer’s instructions or consult a professional if needed.
Step 6: Test functionality and safety Once all connections are securely made, reconnect the power source and turn on your sailboat’s battery. Switch on your steaming light and verify that it’s functioning correctly. Check for any loose connections, flickering lights, or signs of overheating during this testing phase. If everything looks good, proceed to finalize the installation.
Step 7: Secure and protect the wires Using zip ties or cable clamps, neatly bundle and secure all wires along their path towards the power source or existing wiring nearby. This step is especially important as it prevents any accidental snagging or damage caused by movement while sailing.
Step 8: Add finishing touches To ensure long-lasting durability and protection against environmental factors (moisture, saltwater), add an extra layer of weather-resistant insulation tape around exposed wiring connections. This additional safeguard will help shield your newly installed steaming light from any potential issues that may arise due to harsh maritime conditions.
By following these step-by-step instructions carefully, you can install a steaming light on your sailboat like a pro! Not only will you be adding an essential safety feature to illuminate your vessel in low visibility situations but also enhancing its overall aesthetics for impressive nighttime sailing adventures. So don’t let darkness dampen your enthusiasm – take charge of your boat’s illumination and enjoy safe sailing every time!
Common FAQs About Steaming Lights on Sailboats: Answered!
Introduction: When it comes to sailboats, there are often many questions that arise about various aspects of their features and functionalities. One such area of curiosity is the steaming lights on these vessels . To shed some light on this topic, we have put together a list of common frequently asked questions (FAQs) regarding steaming lights on sailboats, along with their detailed answers. So without further ado, let’s dive into these queries and unravel the mysteries surrounding steaming lights!
Question 1: What are steaming lights? Answer: Steaming lights refer to a specific type of navigation light installed on sailboats . These lights are commonly found on the front or aft of a vessel and emit a white light that extends over a defined arc.
Question 2: Why are steaming lights necessary for sailboats ? Answer: The main purpose of steaming lights is to ensure the safety and visibility of sailboats while navigating in low visibility conditions or at night. By illuminating the boat from forward or aft, they help other vessels identify its position, direction, and whether it is underway.
Question 3: Are steaming lights always required to be displayed ? Answer: Yes, according to international maritime regulations (COLREGS), all mechanically propelled vessels (including sailboats) exceeding a certain length must display proper navigation lights during nighttime navigation or in times of restricted visibility. Steaming lights are an essential component of these required navigational signaling devices.
Question 4: Where should steaming lights be positioned on a sailboat ? Answer: Typically, steaming lights are mounted on either the front masthead or closer to the bow (foremost part) of the vessel . The exact positioning depends on the boat’s design and requirements outlined by local boating regulations.
Question 5: Can other colored lights be used instead of white for sailing at night? Answer: No, according to international standards, specifically Rule 23 of COLREGS, steaming lights on sailboats must emit a white color to maintain consistency and avoid confusion with other types of vessels. White lights also have the advantage of visibility at greater distances.
Question 6: Are there any rules regarding the brightness or intensity of steaming lights ? Answer: Yes, regulations exist concerning the luminous intensity required from steaming lights . However, these requirements differ depending on the length of the vessel and are specified in international maritime regulations or local boating guidelines. Sailors must ensure their steaming lights meet these specifications.
Question 7: Can steaming lights be used while at anchor or in port? Answer: No, steaming lights should not be used while a sailboat is at anchor or docked in a port. These lights are specifically designed to indicate that a vessel is underway. When anchored or moored, different lighting configurations, such as an anchor light or deck-level navigation lights, should be used instead.
Conclusion: Understanding the significance and proper usage of steaming lights on sailboats is crucial for both experienced sailors and newcomers to ensure boating safety. In this blog post, we have addressed some common questions about these navigation lights and provided detailed explanations for each query. By following international regulations and local guidelines regarding the positioning, color, brightness, and usage of these essential lighting devices, sailors can navigate their vessels confidently even in reduced visibility conditions. Remember, responsible sailing includes being knowledgeable about every aspect of your boat’s equipment – including its illuminating features!
Choosing the Right Steaming Light for Your Sailboat: Factors to Consider
Picture this: you’re sailing gracefully through the open waters, harnessing the power of the wind, when suddenly darkness descends upon you. The sun has set, and it’s time to rely on your trusty steaming light to guide your way. But wait! How do you choose the right one? Fear not, fellow sailors, for we are here to shed some light (pun intended) on this important decision. Here are some factors you should consider before picking out the perfect steaming light.
1. Regulations and Safety Standards: First and foremost, always adhere to regulations and safety standards set by maritime authorities. Different jurisdictions might have specific requirements regarding visibility range, color specifications, mounting heights, and more. Familiarize yourself with these guidelines to avoid unnecessary fines or safety hazards.
2. Visibility: Ahoy there! One of the primary purposes of a steaming light is to ensure that other vessels can see you while underway. Consider both the intensity of the light and its range. Opt for a light that boasts exceptional brightness without blinding nearby captains (we don’t want any sailors rubbing their eyes in confusion!).
3. Energy Efficiency: As responsible stewards of our oceans, sustainability should always be on our minds – even when it comes to choosing a simple steaming light. Look for LED lights as they consume significantly less power compared to traditional incandescent bulbs while providing excellent illumination throughout your journey.
4. Durability: When it comes to marine equipment, durability is essential since it may face harsh weather conditions such as intense sun exposure and heavy rainstorms – not to mention saltwater corrosion! Seek a steaming light specifically designed for marine environments; preferably made from strong materials like stainless steel or robust plastics.
5. Ease of Installation: Unless you’re an adept sailor who thrives on complex wiring tasks reminiscent of navigating through treacherous waters, selecting a steaming light that is easy to install and maintain is paramount. Look for lights that come with simple mounting options and clear instructions – nobody wants to be left in the dark (literally) while fumbling around with confusing installation manuals.
6. Compatibility: Your sailboat’s existing electrical system should be considered when choosing a steaming light. Ensure that the voltage requirements of your chosen light match those of your marine battery system. Additionally, check if the wiring connections are compatible for seamless integration.
7. Aesthetics: Ah, sailors are known for their keen sense of style! While aesthetics may not directly impact the functionality of a steaming light, many sailors take pride in outfitting their vessels with accessories that enhance its overall design. Consider opting for a sleek and modern design that complements the aesthetics of your sailboat while providing superior performance.
8. Value for Money: As much as we hate to admit it, costs play an important role in decision-making processes. Research different brands and models to find out which ones offer excellent value for money without compromising on quality or reliability. Remember, skimping on safety equipment isn’t just unwise; it could also turn into an expensive mistake down the line.
By considering these factors and conducting thorough research, you can confidently choose the right steaming light for your sailboat – ensuring safer navigation during both day and night expeditions. May your voyages always be illuminated by the perfect beacon, guiding you towards memorable adventures on the high seas !
Troubleshooting Tips for Maintaining your Steaming Light on a Sailboat
Maintaining the steaming light on a sailboat is essential for safe navigation, especially during low visibility conditions. This small but mighty light not only helps you see ahead but also signals your presence to other vessels on the water. However, as with any electrical equipment, issues can arise that require troubleshooting and maintenance. In this blog post, we will provide you with professional, witty, and clever tips to ensure your steaming light stays in top-notch condition.
1. Check the Basics: First things first – let’s start with the basics! Before diving into complex troubleshooting techniques, make sure to inspect the obvious factors that could lead to a malfunctioning steaming light. Check if it’s properly connected and securely fastened to avoid loose or faulty wiring connections—an easy fix that might save you hours of troubleshooting later!
2. Don’t Underestimate Corrosion: Ahoy there Captain! When it comes to maritime environments, corrosion is your worst enemy. The combination of saltwater spray and constant exposure can wreak havoc on electrical systems onboard; your steaming light is no exception! Regularly inspect the contacts and terminals for signs of corrosion or rust buildup. Use a brush or a fine-grit sandpaper to remove any unwanted visitors from these surfaces. Remember, a clean connection ensures optimal performance !
3. Fuse in Time Saves Nine: Some sailors tend to forget about fuses while troubleshooting their boat’s lighting system—don’t be one of them! The humble fuse protects your electrical system from potential overloads, shorts, and fire hazards caused by an unexpected surge in current flow . If your steaming light fails to illuminate even after checking wiring connections and corrosion issues, don’t overlook this vital component! Replace any blown fuses promptly according to their specifications.
4. Shine Bright Like a Pro: “A dim steaming light? Oh buoy!” Dim lights can affect visibility for both yourself and other mariners around you—so don’t compromise on this important safety feature! If your steaming light seems less luminous than usual, check for bulb degradation. Even a slightly loose bulb can significantly reduce its brightness. Tighten it up carefully or, better yet, replace it with a fresh and bright LED bulb that offers increased energy efficiency and longevity.
5. Put the Voltmeter to Work: When all else fails, put your trust in technology! The trusty voltmeter can help you diagnose electrical issues like a true sailor troubleshooter. Connect the meter to the terminals of your steaming light and measure the voltage supply when turned on. An insufficient voltage reading indicates wiring problems or potential battery drain issues that need further inspection.
6. Beware of Murphy’s Law: Ahoy there Landlubber! When troubleshooting any onboard issue, always keep Murphy’s Law in mind: “Anything that can go wrong will go wrong.” That’s why having spare parts like bulbs, fuses, and even extra wire connectors is essential for sailboat maintenance. Preparation is key when cruising on the open water !
7. Seek Help from Fellow Sea Dogs: Remember, you’re not sailing alone in this boat—a vast community of seasoned sea dogs is out there ready to lend a helping hand! Don’t hesitate to consult online forums or reach out to fellow sailors who might have encountered similar issues before. They may share their witty anecdotes and clever solutions that could solve your steaming light troubles faster than you think!
At the end of the day, maintaining your steaming light is not just about complying with maritime regulations; it’s about ensuring safe passage for both yourself and others on the waterways. By following these troubleshooting tips – from checking connections and addressing corrosion to involving technology like voltmeters – you’ll be able to maintain an illuminated path amidst challenging maritime conditions.
So set sail confidently knowing that even if darkness falls upon you (figuratively or literally), you’ll be well-prepared to troubleshoot and maintain your steaming light like a true professional sailor.
Don’t Set Sail Without It: The Importance of a Functional Steaming Light
When embarking on a sailing adventure, it’s crucial to ensure that every aspect of your vessel is in impeccable condition. From the sails to the rudder and everything in between, one essential component that often goes unnoticed is the steaming light. This small yet mighty fixture plays a significant role in ensuring both your safety and that of other sailors out on the water. In this blog post, we will explore why having a functional steaming light should never be overlooked when setting sail.
Firstly, let’s understand what a steaming light actually is. Mounted on top of the mast or at its front, the steaming light serves as an all-around white navigation light for boats under power. Its primary purpose is to help you stay visible to other vessels nearby by indicating your direction of travel at night or during periods of diminished visibility such as fog or heavy rain.
Now, you may be wondering why this seemingly inconspicuous light deserves so much attention. Well, think about it – imagine sailing through dense fog without a working steaming light! Without this beacon guiding your path, not only are you jeopardizing your own safety but also putting fellow seafarers at risk by refusing to comply with maritime regulations.
Additionally, navigating harbors and congested waterways becomes an even greater challenge without an operational steaming light. Picture yourself approaching a bustling marina late into the evening; by illuminating your boat’s foredeck with its bright white glow, the steaming light acts as a signal for others around you to be cautious and respect your right of way. This simple yet effective communication tool prevents accidental collisions and fosters harmony among boaters sharing busy waters.
But if safety isn’t reason enough to prioritize a fully functioning steaming light before each voyage, consider this: Mariners have an inherent responsibility to adhere to international maritime regulations set forth by bodies such as the International Maritime Organization (IMO). These regulations explicitly state that every vessel under power must display a white steaming light while underway during hours of darkness or limited visibility. By neglecting this requirement, you not only risk severe penalties but also jeopardize your reputation as a responsible boater.
Now that we understand the importance of a functional steaming light, it’s essential to keep it well-maintained and regularly inspected. After all, there’s nothing worse than setting sail only to have your navigation light fail at the most inopportune moment. Inspecting the wiring, replacing any worn-out bulbs, and ensuring proper alignment are simple steps that should form part of your pre-departure routine.
Remember, when it comes to sailing, “Don’t Set Sail Without It: The Importance of a Functional Steaming Light.” This unassuming yet crucial piece of equipment acts as both an indispensable safety feature and a responsible adherence to maritime regulations. So, before you embark on your next voyage, take the time to ensure that your steaming light is functioning optimally – after all, smooth seas start with being visible and considerate towards fellow sailors!
Recent Posts

- Sailboat Gear and Equipment
- Sailboat Lifestyle
- Sailboat Maintenance
- Sailboat Racing
- Sailboat Tips and Tricks
- Sailboat Types
- Sailing Adventures
- Sailing Destinations
- Sailing Safety
- Sailing Techniques

Mast head light confusion
Here is a question from a Student who posted it on Disqus. I felt it was important enough to post out here for public. Displaying correct lights on boats is important.
Could you please provide more of an explanation for the following: Although ‘steaming light’ is used extensively, this does not have a definition within the IRPCS [International Regulations for Prevention of Collisions at Sea], the correct definition being a masthead light.
If the tri-colour light can replace the stern and red/green pulpit light on a sailboat how can it be unacceptable to use the tri-colour light with mast head light? If you are under power you of course need your steaming light/ mast head light illuminated. So if you don’t have pulpit or stern lights aboard as you are using a tri colour light how can you do this?
Agreed – lights can be confusing at the onset. In this particular topic, sailors tend to get confused because they think a mast is only on a sailboat. But, a mast head light is also used (and defined for use) on power boats. Take a look at this image shown in the rules. It shows a power driven vessel longer than 50 meters using two mast head lights.

A large Power vessel displaying two mast head lights.
Here is the definition of a mast head light in the rules:
(a) “Masthead light” means a white light placed over the fore and aft centerline of the vessel showing an unbroken light over an arc of the horizon of 225 degrees and so fixed as to show the light from right ahead to 22.5 degrees abaft the beam on either side of the vessel.
Note also that is does not say the light must be at the top of the mast.
For sailboats, a tricolored light is a light described by rule 25(b) in USCG Nav Rules. It is at or near the top of the mast and is for sailing vessels less than 20 meters in length. It is an optional alternative to having the lights down on the hull or pulpits. It faces a white light to the aft 135 degrees plus red from directly forward around to port 112.5 degrees and a green light directly forward and around to starboard 112.5 degrees. This makes up 360 degrees and meets the requirement for a sailboat sailing. When the sailboat turns on it’s engines it must also in addition to the white, red and green above, display a white light 225 degrees facing forward. You can name this light what ever you like but it must exist. These white “mast head” lights are also defined by the distance they must be seen by – it does not mean they have to be at the top of the mast. On power vessels they are typically at the top of the mast because that is what the mast is for.
Here is a sailing vessel under sail only with a tricolored light

Tri-colored lights on a sailboat
On a sailboat less than 50 meters in length, a mast head light (white under power light) can be just “up the mast” anywhere. It’s not part of the tri color. It is white and faces forward 225 degrees and is to be used when the sailboat is under power. You also might be confusing the term mast head light with the two all around red and green lights at the top of the mast. These are not mast head lights. They can be used in addition to the hull or pulpit mounted red green and white. The rules prevent a top of the mast tricolored light AND the two all around red and green at the top of the mast. This would create confusion and may be your source of confusion. i.e it is unacceptable to use the tricolored and two all around red and green lights. Again the mast head is white 225 deg forward facing to be used under power only.
Here is a vessel with the two all around red and green lights.

The Vessel sailing “on starboard” is utilizing the optional two all around red and green lights.
Here are the rules as stated: Rule 25 – Sailing Vessels Underway and Vessels Under Oars
(a) A sailing vessel underway shall exhibit:
(i) sidelights; (ii) a stern light
(b) In a sailing vessel of less than 20 meters in length, the lights prescribed in Rule 25(a) may be combined in one lantern carried at or near the top of the mast where it can best be seen. [note this is the tricolored light]
(c) A sailing vessel underway may, in addition to the lights prescribed in Rule 25(a), exhibit at or near the top of the mast, where they can best be seen, two all-round lights in a vertical line, the upper being red and the lower green, but these lights shall not be exhibited in conjunction with the combined lantern permitted by Rule 25(b).
I hope that helps.
I highly recommend that you complete our Navigation Rules Course . It is free for everyone.

International Rules for Prevention of Collision at Sea FREE Sailing Course
We also have a Paper Book that you should order and keep on your boat for reference.
The book is a stand alone excellent explanation of the Rules of the Nautical road and is a good and quick easy read. It has additional really cool features. Through out the book you will see QR Codes. When you scan any QR code with your mobile device, the book element comes alive and shows you animations and videos.
To get a QR Reader –
For Android
Order the International Rules of Prevention of Collision at Sea Book from Amazon.
- Recent Posts
- NauticEd uses the SailTies GPS Tracking App - March 29, 2024
- Sea of Cortez Flotilla – February 2025 - March 8, 2024
- British Virgin Islands Flotilla – March 2025 - March 2, 2024
You might also like
TWEET ABOUT

FIGHT CHILDHOOD CANCER
NauticEd is a fully recognized education and certification platform for sailing students combining online and on-the-water real instruction ( and now VR ). NauticEd offers +24 online courses , a free sailor's toolkit that includes 2 free courses, and six ranks of certification – all integrated into NauticEd’s proprietary platform. The USCG and NASBLA recognize NauticEd as having met the established American National Standards. Learn more at www.nauticed.org .

The NauticEd Vacations team are Expert Global Yacht Charter Agents – when you book a sailing vacation or bareboat charter through NauticEd, we don’t charge you a fee – we often save you money since we can compare prices from all yacht charter companies. PLUS, we can give you advice on which destination or charter company will suit your needs best. Inquire about a Sailing Vacation or Charter .
Online Sailing Courses Sailing Vacations | Charters Practical Sailing Courses Sailing Certification | License
Sign up for 2 FREE Sailing Courses Try sailing in Virtual Reality! Gift a Friend a Sailing Course Sailing Events | Opportunities
About NauticEd Contact Us NauticEd Support Privacy Policy
- Gift Certificate
- --> Login or Sign Up

Shop by Category
- All LED Replacement Bulbs
- BA15S/BA15D Bayonets (1141/1142/1156)
- BAY15D Indexed Bayonet (1157)
- BA9S Miniature Bayonet
- Edison - Screw-Type
- Festoon (SV8.5)
- Fluorescent Style
- MR11 & MR16
- PAR 36 Sealed-Beams
- Socket Adapters
- Boat Specific LEDs
- All LED Fixtures
- Interior LED Fixtures
- Exterior LED Fixtures
- All Navigation Lights
- Nav Lights By Function
- Economy Series LED Navigation Lights
- USCG Certified Navigation Lights
- LED Retrofit Bulbs for Nav Lights
- Portable LEDs & Flashlights
- All Cruising Necessities
- Comfortable Cruising Accessories
- Wireless Headset Communicators
- Chemicals and Compounds
- All Marine Wind Generators
- MarineKinetix MK4+ Wind Generator
- Wind Generator Installation Accessories
- Spare & Replacement Parts
- Marine Energy Products
- All Wiring & Electrical
- Marine Wire & Accessories
- Power Supplies & Voltage Converters
- LED Dimmers & Switches
- Wireless Remote Controls
- Dusk-to-Dawn Photocells
- 12VDC Device Chargers
- All Cristec / Scheiber OEM
- Cristec Products
- Scheiber Products
- Mantus Anchors
Shop by Brand
- MarineKinetix
- Cruising Solutions
- Sirius Signal
- View all Brands
- Navigation Lights
All-Around LED Anchor Light for Sailboat Mast - Series 40 Type <20M

- Create New Wish List
- Similar Products
Product Description
An economical 2NM LED All-Around Anchor Light fixture navigation light intended to be mounted on the top of the mast on larger sailboats. It replaces the Aqua Signal Series 40 type anchor lights, as it is of similar size and height.
Prefitted with a user-replaceable Marinebeam constant-current 10-30VDC BAY15d high-output LED bulb and 8" of marine tinned wire - ready to mount. The wiring connection can be made inside the fixture via the internal spade terminal connections, or by connecting to the included external wire pigtails.
The height is 4-3/8" and the base diameter is 3". Mounted with 4 screws or bolts (not included) to any flat surface.
You won't find a brighter LED fixture with a longer life for this price.
Made of UV resistant plastic with brass internals. O-ring sealed cover.
- Draws 0.18A at 12VDC
- Constant-Current LED driver
- Replaceable 30,000 hour LED bulb
- Cool White high-intensity LED output (>2nm visibility)
- Candela output exceeds COLREG 72 requirements for boats up to 20M
- 360 degree visibility
- Tinned marine wiring and o-ring sealed cover
- 2 year warranty
Product Videos
Custom field, product reviews, write a review.

1 Review Hide Reviews Show Reviews
Posted by Molly Mullins on 14th Sep 2023
Works well, easy installation.
Recommended

sku: N1-360-CLR
Led all-around anchor light, sku: n2-360-fld, folding all-round anchor light for boats < 20m.

sku: N4-TRI-124
Led tri-color and all-around anchor navigation stack light.

Stainless Steel PAR36 LED Spreader Light for sailboats
- Shopping Cart 0

Boat Masthead Lights

Whether you use your craft for water sports, fishing, or leisure cruising, it should be equipped with proper navigation lights to make sure it is safe and legal. Even if taking a boat out on the water after the dark is not your cup of tea, sometimes your afternoon water trip may turn into a night adventure. Besides, if you are a regular boater you will inevitably get caught in a rain or fog at some point. Obviously, inclement weather reduces visibility putting you at risk of having an accident with another vessel. That is why every craft is required to have navigation lights. The size of a boat determines what type of them should be used. To wit, masthead lights are required by all motorized boats that are longer than 39.4 feet.
They are white and installed at the front of a vessel. The arc of illumination is 225 degrees. They are combined with stern lights which are visible across 135 degrees to provide 360 degrees of visibility. When it comes to boats that are greater than 39.4 feet but less than 65.6 feet, they should be visible from at least three nautical miles away. For vessels which are less than 39.4 feet, the visibility range is two nautical miles. Keep in mind that they can be also equipped with an all-round light instead of a set of stern and masthead lights. Whatever size of your vessel, we have the right product for it in our selection. Our offerings are made by reliable brands including Sea Dog , Attwood , and many others.
Featured Brands

Related Categories

- Forum Listing
- Marketplace
- Advanced Search
- All Topics Sailing
- Skills & Seamanship
- Learning to Sail
- SailNet is a forum community dedicated to Sailing enthusiasts. Come join the discussion about sailing, modifications, classifieds, troubleshooting, repairs, reviews, maintenance, and more!
When use mast strobe light?
- Add to quote
Realized that I do not understand the proper use of a strobe as part of a masthead light. I thought the strobe was an ''emergency only'' device, used much like flares only to indicate distress. But now I''ve seen two references to single-handers leaving the strobe on at night to supplement their radar deflectors as warning or "see me" devices for passing ships. So what is the proper use and intention of a masthead stobe light? Thanks!
Isn''t the exception that one may use a strobe or any other means to attract attention in an emergency?
Not a challenge Gordon, but how come folks like Aqua Signal offer it as a standard option/upgrade for their series 40 tri-color nav lights? They even charge an extra like $150 for it added to their generic tri-color/anchor light setup.
Manufacturers sell Strobe Lights because we will buy them. They are expensive because they cost a lot to make. We buy them because we think (rightfully) that we may want the brightest, most obvious signal possible, in extreme situations - rules be dammed. See the COLREGS (Rules 20, 21, & 36) http://www.boatsafe.com/nauticalknowhow/boating/colregs.html - Rule 36 Signals to Attract Attention If necessary to attract the attention of another vessel, any vessel may make light or sound signals that cannot be mistaken for any signal authorized elsewhere in these Rules, or may direct the beam of her searchlight in the direction of the danger, in such a way as not to embarrass any vessel. Any light to attract the attention of another vessel shall be such that it cannot be mistaken for any aid to navigation. For the purpose of this Rule the use of high intensity intermittent or revolving lights, such as strobe lights, shall be avoided. Regards, Gord
Honestly. If I was going to cary a strobe for this kind of emergency signalling, I would carry a completely seperate unit, with independent battery power, that could be hoisted up the mast at will. That way, if I need it because my other powersources have died and I do not have other lights, or my masthead light has been blown off the mast (has been known to happen) or any number of other nasty things have come to pass....well, the strobe can still function, for what that''s worth. We have a $40 unit that I have attached two hose clamps and rings to. It takes less then 30 seconds to activate and hoist up the mast on its stick in the practice run we have done. It makes much more sense to me then paying an extra $150 in order to put more weight permanently at the top of your mast, with all the potential for blown bulbs and fried wires that this implies) Sasha
ASHA said (about portable strobes):"... It takes less then 30 seconds to activate and hoist up the mast on its stick in the practice run we have done..." That would be 30 sec. after you locate it, and get it & yourself to the halyard. Not a bad "back-up" - but I prefer an instantaneous "See-Me" light. OMO Gord
Sorry Sasha, I can''t get this site to accept my updates & edit.
I guess I have less boat to lose stuff in. I can always find it the strobe (The peronal strobes and the emergency strobe are all in clamps near the companionway). For the instant "oh dear" emergency wheer you want to be seen...there is a lot to be said for the white "see me" flares in the locker next to the helm. Way brighter then a strobe and covered by the col regs with no ambiguity. If I could afford white parachute flares for the emergency kit (in addition to the reds) I probably would have two of those as well. Sasha
Not to put too fine a point on it - but flares are unambiguously DISTRESS signals (not "hey there, watch out"). You could definately get into trouble misusing flares as a "see me" signal. OMO Gord
You are incorrect. Read your colregs. Red flares (both parachute and heand held) are distress. Orange daylight smoke is distress. white is a signalling/alert device used by yachts, shipping (including pilot boats). Green flares are used by search and rescue craft (especially aircraft) to acknowledge that they have seen your distress signal and have relayed information to crews that are better placed to get to you. In daylight, an aircraft will usually waggle its wings instead. White flares are also occassionaly used as a locater device by search and rescue services during inland searches. A white flare will be fired to signal that a rescuer is watching and the people that are in distress respond by firing one of their red flares, knowing that someone is actually looking out for it. White flares are GOOD! Sasha
I do not understand where we disagree. I stated that the use of a white flare in a "I need to be seen right NOW, but this is not (yet) and emergency" situation was a good and acceptable thing. You responded by saying that fares were for distress only and I would gt into trouble for setting one off when not in direct distress. I pointed out that white flares are not the same as red ones and that they were an acceptable GOOD THING for becoming instantly visible without signaling distress. and would not confuse the usage. I gave examples. You gave examples of the exact same thing... I am sorry, but I do not see where we disagree. By the way. My base on this comes from the Yachtmaster course (in which I hold my coastal skipper and competet offshore crew certificate as well as a few other earlier courses). I have no experience with courses taught by the US coast gaurd (nor an interest in them, seeing as how I am in Australia). I do not have my colregs near to hand, so cannot quote chapter and verse on usage of green nd white flares. It is even possible that it comes form the big-blue-book-of-fun (International yacht racing rules) which has a section on emergency procedures. Sasha
Sasha: I think we disagree on the “Legal & Proper” usage of White & Green Flares, and Strobe Lights. We seem to agree more on their “effective” use. Speaking of White Flares, you indicated that they were “...covered by the col regs with no ambiguity ...” The COLREGS specify the use of Red Flares & Orange Smoke, but are silent on the subject of White Flares. I can find no internationally recognized standards on the use of White Flares. As I previously posted (but failed to attribute) Pains-Wessex states: “...there is no standard for white flares”. As I also posted previously, The COLREGS (Rule 36) specifically admonish against the use of Strobe Lights - “... the use of high intensity intermittent or revolving lights, such as strobe lights, shall be avoided.” It seems to me, that the use of either Strobes or White Flares is not “legal”, or (at least) not recognized by the treaties, & regulations. Under certain circumstance we may not really care as much about conventions & treaties, as we do about effectiveness. A Strobe Light will be VERY visible over a distance of several miles (limited by DIP to horizon), whereas a Flare might be visible over many MORE miles. If our intent is to alert a relatively nearby vessel to our presence, a Strobe may be effective. If we want to alert the larger world to our presence, a Flare may be more effective. We deploy either at our own hazard and liability for any unintended consequences. I’m using (wasting) up bandwidth arguing over semantics, in an effort to answer Jonathan’s original question regarding the “PROPER” use of a masthead Strobe (there is none). Thanks for taking the time to intelligently engage the debate. Gord
The only thing I could find in what Gordon quoted which might permit/justify a strobe was the line: "(d) a signal made by radiotelegraphy or by any other signaling method consisting of the group . . .- - -. . . (SOS) in the Morse Code;" Which hardly seems to make a strobe become ''valueable'' on the masthead; although I -did- come across a mention of one boat in distress which did exactly that (used the strobe to flash an SOS). Aside from that one mention and two hearing of strobe used by single-handers as a nighttime ''see me'', that''s all I''ve been able to find about it -- accept that Aqua Signal offers it as an option for their tri-colors. Just for grins I will send Aqua Signal a message and ask them why they offer it and what its -approved- use would be (smile). I''ll report back when/if they reply. Jonathan
I spoke too soon. There apparently -are- valid uses for the masthead strobe. First, West Marine says it is approved for use as a distress light on inland waters; but illegal offshore. Next, the rules for the ''Singlehanded Transpacific Yacht Race'' actually -requires- masthead stobe lights on participating vessels. (Page 5, 7.24) at: http://www.sfbaysss.org/transpac2004/transpac_nor.pdf The Port of Charleston mentions them (and white flares) as visibility tools -- but says the strobe is for ''distress only''. http://www.port-of-charleston.com/community/keep.asp Same is repeated for Chesapeake Bay at: http://www.mdsg.umd.edu/CB/keepclear.html Seems to be prohibted in Austraila: http://www.austlii.edu.au/au/other/dfat/treaties/1983/34.html Basically same said at: http://www.boatingsafety.com/colregs.htm And the definatibve answer seems to be at: http://www.offsoundings.com/22STROBLIGHTS.pdf Which references the -approved- use of strobe likes described by the USCG Navigation Center. I''l take their word for it (smile). So there are approved uses of a masthead strobe, but mainly on inland waterways. How the Transpac avoids the clear international prohibition of the lights is confusing to me. Jonathan
Has anything changed that I could not locate regarding Strobes. I had a tri color, anchor, strobe mast light but I am in need of replacing it and will go with LED... and NO strobe light. While on the subject of mast head lighting.,, there is a pretty wide range of LED Tri Color/Anchor lights on the market. I could really careless as long as they meet USCG Regs... unless I'm missing something I will probably go with ones around $250
I recently installed one of these: Ultra Light LED Navigation Light Fixture | Products | Lunasea Lighting Nice little unit and incorporates a strobe if you want it. It is probably 10% of the size of my last tricolor/anchor light combo and uses a lot less power.
I like this one from Marine Beam: Smart Switching LED Tri-Color / Anchor / SOS Strobe Light LED - Tricolor, Anchor AND Strobe! $100!!
- ?
- 173.9K members
Top Contributors this Month
- International
March 26, 2024 - Baltimore Key Bridge collapses after ship collision
By Helen Regan , Kathleen Magramo , Antoinette Radford, Alisha Ebrahimji , Maureen Chowdhury , Rachel Ramirez , Elise Hammond , Aditi Sangal , Tori B. Powell , Piper Hudspeth Blackburn and Kathleen Magramo , CNN
Ship lights flickered and veered off course shortly before Baltimore bridge hit, CNN analysis shows
From CNN’s Allegra Goodwin in London

The Singaporean-flagged cargo ship that struck the Francis Scott Key Bridge in Baltimore Tuesday altered course and veered toward a pillar shortly before impact, a CNN analysis of MarineTraffic ship-tracking data confirms.
It’s unclear what caused the ship to crash into the bridge or why its lights were flickering. CNN has reached out to the National Transportation Safety Board to inquire about a possible power failure.
The container ship DALI, which was en route to Colombo, Sri Lanka, begins to change course toward the bridge’s pillar at 1:26 a.m. local time, striking the bridge at 1:28 a.m. ET, according to MarineTraffic data and video from the scene. Video from 1:25 a.m. ET shows a plume of dark smoke billowing from the ship. DALI's lights flicker at least twice before the incident.
In video, as it navigates down the Patapsco River, the ship’s lights can be seen going out at 1:24 a.m. ET, before turning back on, and then flickering off and on again between 1:26 a.m. ET and 1.27 a.m. ET, just before it hits the bridge.
Maryland transportation secretary says contractors were working on bridge at time of collapse
From CNN's Antoinette Radford
Maryland State Transportation Secretary Paul Wiedefeld told reporters there were workers on the Francis Scott Key Bridge at the time of its collapse.
"We know there were individuals on the bridge at the time of the collapse, working on the bridge, contractors for us," he said at a news conference Tuesday morning.
Wiedefeld said the workers were "basically doing some concrete deck repair," but said they did not know how many vehicles were involved.
He added that the transport authority has set up a facility for family members of those who were believed to be on the bridge at the time of its collapse.
Baltimore fire chief: Sonar has detected the presence of vehicles submerged in the water
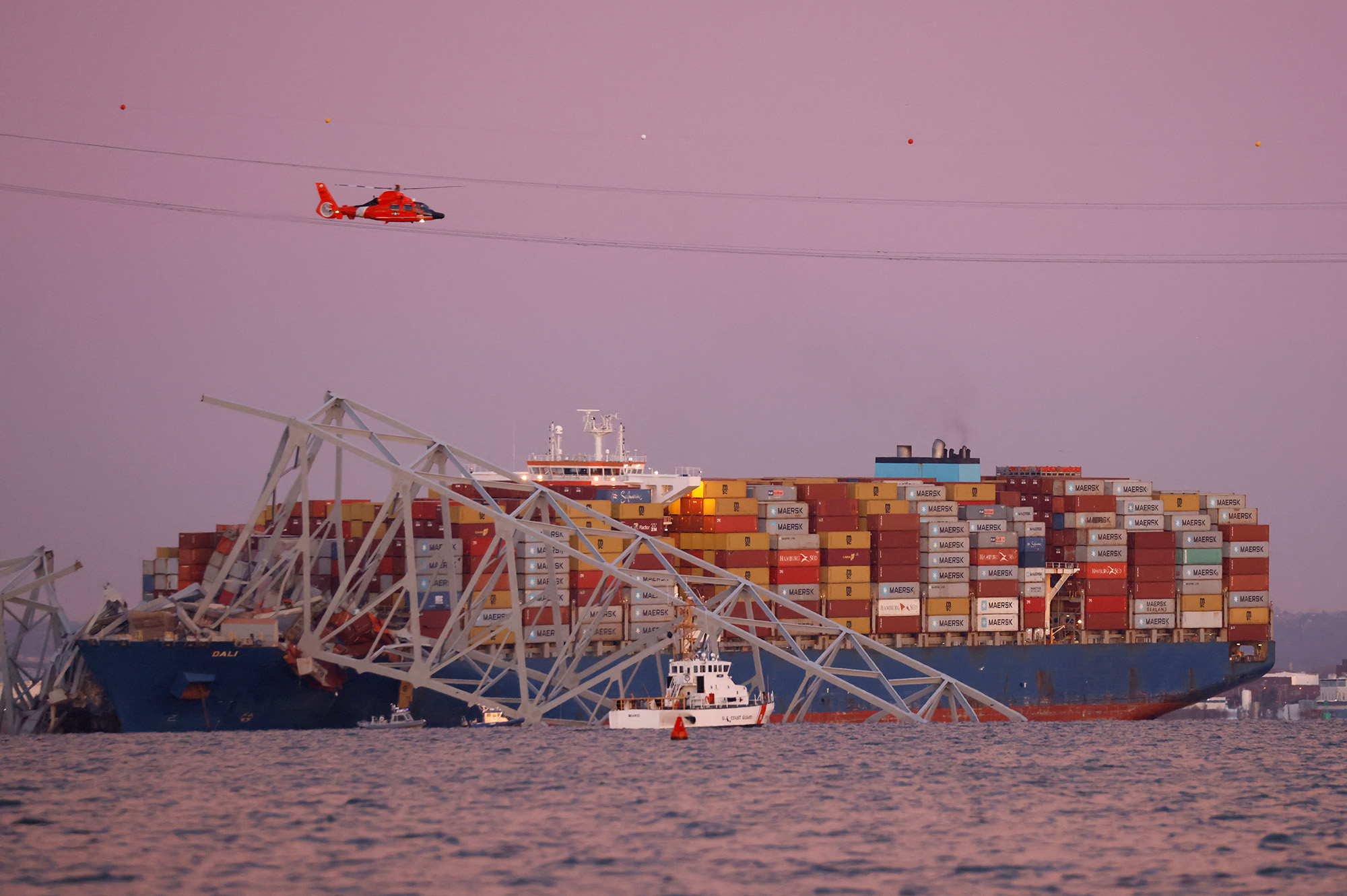

Baltimore Fire Chief James Wallace says authorities have detected vehicles submerged in the water.
“Our sonar has detected the presence of vehicles submerged in the water,” said Wallace at a news conference on the collapse of Francis Scott Key Bridge. “I don't have a count of that yet.”
He said emergency services are using sonar, drones and infrared technology as a part of their search for people and vehicles who may have fallen from the Key Bridge into the Patapsco River.
No indication of "terrorism" or intent in Baltimore bridge collapse, police chief says
From CNN’s Andy Rose

Baltimore Police said there was no evidence that the ship collision that caused the collapse of the Francis Scott Key Bridge was intentional.
“There is absolutely no indication that there's any terrorism, that this was done on purpose,” Chief Richard Worley said at a news conference.
The FBI said that it was joining the investigation into the cause of the collision.
Rescue crews have determined there are vehicles in the Patapsco River following the bridge collapse.
“Our sonar has detected the presence of vehicles submerged in the water,” said Fire Chief James Wallace. “I don't have a count of that yet.”
Wallace said they are waiting to make sure that the ship is secure and stable before investigators board it.
“Never would you think that you would see, physically see, the Key Bridge tumble down like that,” Mayor Brandon M. Scott said.
Cruises, cars and commodities: What to know about the Port of Baltimore
From CNN's Mark Thompson and Hanna Ziady

The collapse of the Francis Scott Key Bridge over the Patapsco River outside the Port of Baltimore threatens to disrupt shipping operations at a major US trade hub for autos, container traffic and commodities. Baltimore also has a cruise terminal.
Closer to the Midwest than any other port on the East Coast, Baltimore ranks first in the United States for autos and light trucks, handling a record 850,000 vehicles last year. It was also the leading port for farming and construction machinery, as well as imported sugar and gypsum. It was second in the country for exporting coal.
Overall, Baltimore ranks as the 9th biggest US port for international cargo, handling a record 52.3 million tons, valued at $80.8 billion in 2023.
“The immediate focus is the rescue operation, but there will clearly be a highly-complex recovery phase and investigation to follow and we don't know what impact this will have on operations at the Port of Baltimore," said Emily Stausbøll, market analyst at Norway-based shipping analytics company Xeneta.
“While Baltimore is not one of the largest US East Coast ports, it still imports and exports more than one million containers each year so there is the potential for this to cause significant disruption to supply chains," she added.
Baltimore's cruise terminal serves ships operated by Royal Caribbean, Carnival and Norwegian. Cruises carrying more than 444,000 passengers departed from the port last year.
According to the Maryland state government, the port supports 15,330 direct jobs and 139,180 jobs in related services.
Rescue crews looking for at least seven people in Baltimore bridge collapse
Rescue operations are underway near the wreckage of the Francis Scott Key Bridge in Baltimore, as crews look for people who fell into the Patapsco River.
“We are still very much in an active search and rescue posture at this point, and we will continue to be for some time,” Wallace added.
Baltimore Fire says two people have been rescued from the river – one who was uninjured, and another in hospitalized “very serious condition.”
“This is an unthinkable tragedy,” Mayor Brandon Scott said. “We have to first and foremost pray for all of those impacted.”
Ship that collided with Baltimore bridge was chartered by Danish shipping company Maersk
From CNN's Alex Stambaugh in Hong Kong
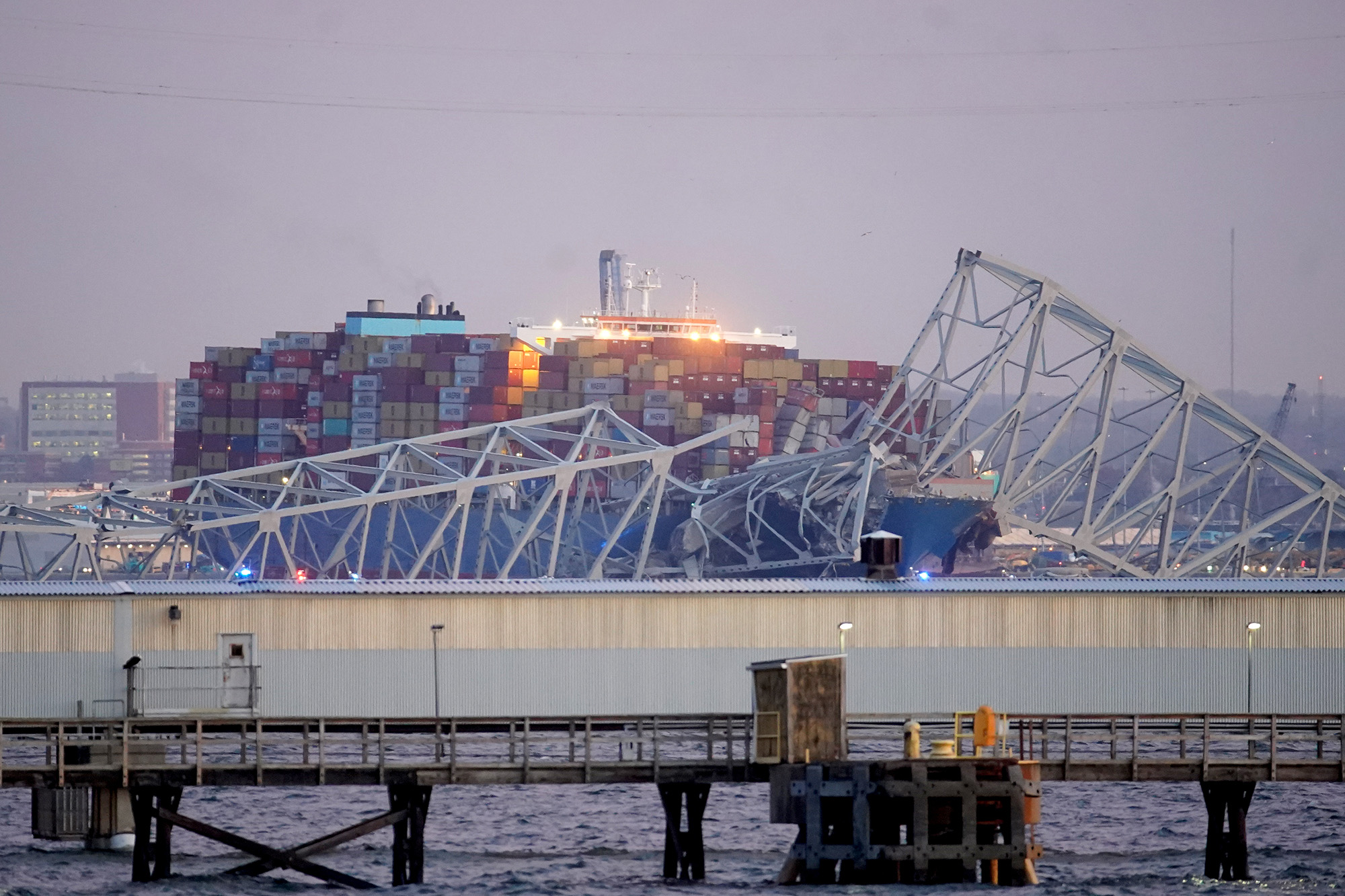

The container ship that collided with the Francis Scott Key Bridge in Baltimore on Tuesday was chartered by Maersk and carrying their customers' cargo, the Danish shipping company told CNN.
"We are horrified by what has happened in Baltimore, and our thoughts are with all of those affected," The company said in its statement.
The company, which has a full name of A.P. Moller - Maersk, said no company crew and personnel were onboard the vessel. It said the ship, DALI, is operated by charter vessel company Synergy Group.
"We are closely following the investigations conducted by authorities and Synergy, and we will do our utmost to keep our customers informed," the statement said.
CNN is attempting to contact the owner and managers of the ship, including Synergy.
FBI Baltimore on the scene at the Key Bridge
FBI Baltimore personnel are on the scene at the Francis Scott Key Bridge, they have said in a post on X.
The agency said it was working "side by side with our local, state and federal partners."
Baltimore fire emergency chief says 2 people saved from water after Key Bridge collapse
The Baltimore Fire Department Chief James Wallace says authorities rescued two people from the water this morning, one without injury and the other who has been transferred to hospital in a serious condition.
Authorities are continuing their search for upwards of seven people, Wallace says. But, he says that number could change as it is a "very large incident." Earlier on Tuesday, an official said as many as 20 people could be in the water.
Wallace added that the crew remains on board the ship, and are communicating with the US Coast Guard. He added that emergency services are looking into reports that there were workers on the bridge at the time of the incident.
Speaking at the press conference, Baltimore Mayor Brandon Scott also described the incident as an “unthinkable tragedy,” and offered his prayers for all those affected, as well as his thanks to first responders.
Please enable JavaScript for a better experience.
Six presumed dead after cargo ship crash levels Baltimore bridge
BALTIMORE — A major Baltimore bridge collapsed like a house of cards early Tuesday after it was struck by a container ship, sending six people to their deaths in the dark waters below, and closing one of the country’s busiest ports.
By nightfall, the desperate search for six people who were working on the bridge and vanished when it fell apart had become a grim search for bodies.
“We do not believe that we’re going to find any of these individuals still alive,” Coast Guard Rear Admiral Shannon N. Gilreath said.
Jeffrey Pritzker, executive vice president of Brawner Builders, said earlier that one of his workers had survived. He did not release their names.
Up until then, Maryland Gov. Wes Moore had held out hope that the missing people might be found even as law enforcement warned that the frigid water and the fact that there had been no sign of them since 1:30 a.m. when the ship struck Francis Scott Key Bridge.
Moore expressed heartbreak after officials suspended the search for survivors.
"Our heart goes out to the families," he said. "I can’t imagine how painful today has been for these families, how painful these hours have been have been for these families."
It was a crushing blow to the loved ones of the missing men, who had waited for hours at a Royal Farms convenience store near the entrance of the bridge for word of their fate.
Follow live updates on the Baltimore bridge collapse
The tragic chain of events began early Tuesday when the cargo ship Dali notified authorities that it had lost power and issued a mayday moments before the 984-foot vessel slammed into a bridge support at a speed of 8 knots, which is about 9 mph.
Moore declared a state of emergency while rescue crews using sonar detected at least five vehicles in the frigid 50-foot-deep water: three passenger cars, a cement truck and another vehicle of some kind. Authorities do not believe anyone was inside the vehicles.
Investigators quickly concluded that it was an accident and not an act of terrorism.
Ship was involved in another collision
Earlier, two people were rescued from the water, Baltimore Fire Chief James Wallace said. One was in good condition and refused treatment, he said. The other was seriously injured and was being treated in a trauma center.
Moore said other drivers might have been in the water had it not been for those who, upon hearing the mayday, blocked off the bridge and kept other vehicles from crossing.
“These people are heroes,” Moore said. “They saved lives.”
Nearly eight years ago, the Dali was involved in an accident. In July 2016, it struck a quay at the Port of Antwerp-Bruges in Belgium, damaging the quay.
The nautical commission investigated the accident, but the details of the inquiry were not immediately clear Tuesday.
The Dali is operated and managed by Synergy Group. In a statement, the company said that two port pilots were at the helm during Tuesday's crash and that all 22 crew members onboard were accounted for.
The Dali was chartered by the Danish shipping giant Maersk, which said it would have no choice but to send its ships to other nearby ports with the Port of Baltimore closed.
The bridge, which is about a mile and a half long and carries Interstate 695 over the Patapsco River southeast of Baltimore, was "fully up to code," Moore said.
National Transportation Safety Board Chairwoman Jennifer Homendy said that her agency will lead the investigation and that a data recorder on the ship could provide more information.
"But right now we're focusing on the people, on the families," she said. "The rest can wait."
President Joe Biden vowed to rebuild the bridge and send federal funds.
"This is going to take some time," the president warned. "The people of Baltimore can count on us though to stick with them, at every step of the way, till the port is reopened and the bridge is rebuilt."
Speaking in Baltimore, Transportation Secretary Pete Buttigieg echoed the president's promise.
"This is no ordinary bridge," he said. "This is one of the cathedrals of American infrastructure."
But Buttigieg warned that replacing the bridge and reopening the port will take time and money and that it could affect supply chains.
The Port of Baltimore, the 11th largest in the U.S., is the busiest port for car imports and exports, handling more than 750,000 vehicles in 2023 alone, according to data from the Maryland Port Administration.
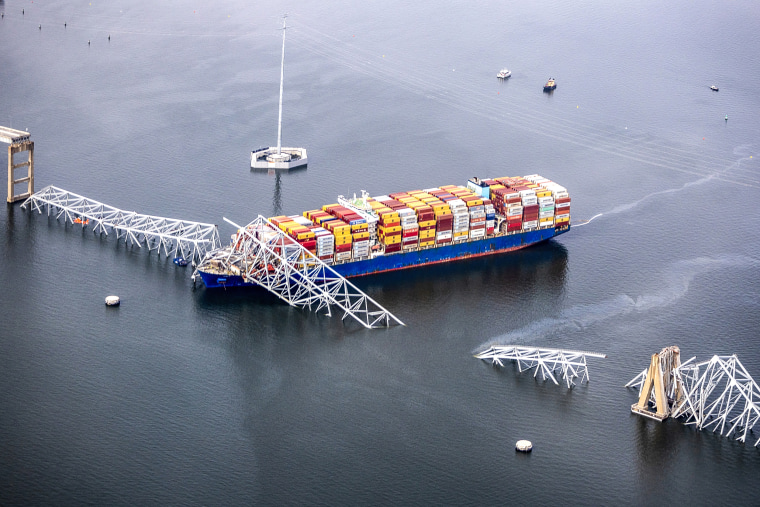

Writer David Simon, a champion of Baltimore who set his TV crime drama "The Wire" on the streets of the city he once covered as a reporter, warned online that the people who will suffer the most are those whose livelihoods depend on the port.
"Thinking first of the people on the bridge," Simon posted on X . "But the mind wanders to a port city strangling. All the people who rely on ships in and out."
Timeline of crash
Dramatic video captured the moment at 1:28 a.m. Tuesday when the Dali struck a support and sent the bridge tumbling into the water. A livestream showed cars and trucks on the bridge just before the strike. The ship did not sink, and its lights remained on.
Investigators said in a timeline that the Dali's lights suddenly shut off four minutes earlier before they came back on and that then, at 1:25 a.m. dark black smoke began billowing from the ship's chimney.
A minute later, at 1:26 a.m., the ship appeared to turn. And in the minutes before it slammed into the support, the lights flickered again.
Maryland Transportation Secretary Paul Wiedefeld said the workers on the bridge were repairing concrete ducts when the ship crashed into the structure.
At least seven workers were pouring concrete to fix potholes on the roadway on the bridge directly above where the ship hit, said James Krutzfeldt, a foreman.
Earlier, the Coast Guard said it had received a report that a “motor vessel made impact with the bridge” and confirmed it was the Dali, a containership sailing under a Singaporean flag that was heading for Sri Lanka.

Bobby Haines, who lives in Dundalk in Baltimore County, said he felt the impact of the bridge collapse from his house nearby.
"I woke up at 1:30 this morning and my house shook, and I was freaking out," he said. "I thought it was an earthquake, and to find out it was a bridge is really, really scary."
Families of bridge workers wait for updates
Earlier in the day, relatives of the construction crew waited for updates on their loved ones.
Marian Del Carmen Castellon told Telemundo her husband, Miguel Luna, 49, was working on the bridge.
“They only tell us that we have to wait and that they can’t give us information,” she said.
Castellon said she was "devastated, devastated because our heart is broken, because we don’t know how they have been rescued yet. We are just waiting for the news."
Luna's co-worker Jesús Campos said he felt crushed, too.
“It hurts my heart to see what is happening. We are human beings, and they are my folks,” he said.
Campos told The Baltimore Banner that the missing men are from El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras and Mexico.
Active search and rescue ends
The Coast Guard said it was suspending the active search-and-rescue effort at 7:30 p.m. Tuesday.
"Coast Guard’s not going away, none of our partners are going away, but we’re just going to transition into a different phase," Gilreath said at a news conference.
Maryland State Police Superintendent Roland L. Butler, Jr., said it was moving to a recovery operation. Changing conditions have made it dangerous for divers, he said.
Butler pledged to "do our very best to recover those six missing people," but the conditions are difficult.
"If we look at how challenging it is at a simple motor vehicle crash to extract an individual, I'm sure we can all imagine how much harder it is to do it in inclement weather, when it's cold, under the water, with very limited to no visibility," he said.
"There's a tremendous amount of debris in the water," which can include sharp metal and other hazards, and that could take time, Butler said.
'A long road in front of us'
Built in 1977 and referred to locally as the Key Bridge, the structure was later named after the author of the American national anthem.
The bridge is more than 8,500 feet long, or 1.6 miles. Its main section spans 1,200 feet, and it was one of the longest continuous truss bridges in the world upon its completion, according to the National Steel Bridge Alliance .
About 31,000 vehicles a day use the bridge, which equals 11.3 million vehicles per year, according to the Maryland Transportation Authority.
The river and the Port of Baltimore are both key to the shipping industry on the East Coast, generating more than $3.3 billion a year and directly employing more than 15,000 people.
Asked what people in Baltimore can expect going forward, the state's transportation secretary said it is too early to tell.
"Obviously we reached out to a number of engineering companies, so obviously we have a long road in front of us," Wiedefeld said.
Julia Jester reported from Baltimore, Patrick Smith from London, Corky Siemaszko from New York and Phil Helsel from Los Angeles.
Julia Jester is a producer for NBC News based in Washington, D.C.
Patrick Smith is a London-based editor and reporter for NBC News Digital.
Phil Helsel is a reporter for NBC News.
Corky Siemaszko is a senior reporter for NBC News Digital.
Advertisement
The Dali was just starting a 27-day voyage.
The ship had spent two days in Baltimore’s port before setting off.
- Share full article

By Claire Moses and Jenny Gross
- Published March 26, 2024 Updated March 27, 2024
The Dali was less than 30 minutes into its planned 27-day journey when the ship ran into the Francis Scott Key Bridge on Tuesday.
The ship, which was sailing under the Singaporean flag, was on its way to Sri Lanka and was supposed to arrive there on April 22, according to VesselFinder, a ship tracking website.
The Dali, which is nearly 1,000 feet long, left the Baltimore port around 1 a.m. Eastern on Tuesday. The ship had two pilots onboard, according to a statement by its owners, Grace Ocean Investment. There were 22 crew members on board, the Maritime & Port Authority of Singapore said in a statement. There were no reports of any injuries, Grace Ocean said.
Before heading off on its voyage, the Dali had returned to the United States from Panama on March 19, harboring in New York. It then arrived on Saturday in Baltimore, where it spent two days in the port.
Maersk, the shipping giant, said in a statement on Tuesday that it had chartered the vessel, which was carrying Maersk cargo. No Maersk crew and personnel were onboard, the statement said, adding that the company was monitoring the investigations being carried out by the authorities and by Synergy Group, the company that was operating the vessel.
“We are horrified by what has happened in Baltimore, and our thoughts are with all of those affected,” the Maersk statement said.
The Dali was built in 2015 by the South Korea-based Hyundai Heavy Industries. The following year, the ship was involved in a minor incident when it hit a stone wall at the port of Antwerp . The Dali sustained damage at the time, but no one was injured.
Claire Moses is a reporter for the Express desk in London. More about Claire Moses
Jenny Gross is a reporter for The Times in London covering breaking news and other topics. More about Jenny Gross

- Forums New posts Unanswered threads Register Top Posts Email
- What's new New posts New Posts (legacy) Latest activity New media
- Media New media New comments
- Boat Info Downloads Weekly Quiz Topic FAQ 10000boatnames.com
- Classifieds Sell Your Boat Used Gear for Sale
- Parts General Marine Parts Hunter Beneteau Catalina MacGregor Oday
- Help Terms of Use Monday Mail Subscribe Monday Mail Unsubscribe
Mast Wiring for Dummies ...
- Thread starter Scott
- Start date Feb 18, 2007
- Forums for All Owners
- Ask All Sailors
I have to admit that electrical wiring is not my strong suit (by far) and since I am installing new lights, a new wind instrument and new coax for the VHF antenna on the mast for my winter re-fit project, I bought Dan Casey's Sailboat Electrics Simplified for guidance. A few things leave me with unanswered questions. I am planning on using a four-way plug connection to join the wiring at the mast base. I will have an anchor light drawing .83 amps (10 W) with a total round trip length from the terminal box to the top of the mast of 100', a steamer light, also .83 amps but the length is 65', and the deck light drawing 1.67 amps (20 W)with a length of 65'. Using the wire size formula for 3% voltage drop I find that the steamer and the anchor lights can be 16 guage and the deck light can be 14 guage. I assume that even though there is a break in the wiring where the deck plug is located (my mast is 33') I have calculated the round trip length as if the wire runs were continuous and independant. I thought about using primary wire to run positives up the mast to the lights and primary wire to daisy chain the negatives for the 3 lights down the mast. I reconsidered and figured I would rather use duplex safety wire because of the added insulation to the wire. I assume that for the 4-way plug to work, I would pigtail the 3 negatives into the plug and run one negative primary wire from the mast base to the terminal box. So to summarize the wiring, I will have 3 primary positive wires from the terminal box to the plug at the base of the mast, 3 duplex wires inside the mast serving the 3 lights, and one negative primary wire from the plug back to the box (about 15' one-way). So now, sizing the primary ground is my first question. If I assume the run is only 15', for 3.33 total amps it appears that a 16 guage wire is sufficient. That doesn't seem logical to me so I assumed that the formula should be used assuming the combined amps for the longest run of 100'. This leads me to a 10 guage wire. Is my logic faulty? I am assuming that ALL lights can be on at the same time (by mistake) even though it isn't logical for the anchor and the steamer to be on at the same time. Also, I thought I read that it is not a good idea to have a coax cable and an instrument cable in close proximity. I planned on putting them both inside the 1-1/4" pvc conduit that will be used to run all the wiring. Is this something that should be avoided? I figure that if the wind instument is disrupted during a vhf transmission it would be no big deal. Any comments about this?
Don S/V ILLusion
sounds correct to me Scott Wire size you plan sounds right but not sure without checking voltage drop tables which it sounds like you already did. Coax is shielded cable and, with a properly tuned antenna, you should have no RF on the outside braid to interfere with any instrument wiring, regardless of how close they are.
Dan Johnson
Scott... If the 4 wire connector you are contemplating using is one of the small Perko-like screw-on plug units as found in the WM catalog, you might want to reconsider. I found the clearances extremely tight inside the plug for even 16 AWG wire, causing shorts when closed up. Consider a trailer wiring plug/socket assembly inside the mast to make for an easy mast removal the next time.
Almost there I'll concur that running coaxial next to power is fine; that's the beauty of the coaxial design, with the ground surrounding the signal. You need to account for 30' (15' X 2) on the final run to power and ground. Round-trip. Maybe 14AWG. But no need for 10AWG. Good luck. Paul
Thanks! That is what I thought about coax so I was surprised by something I thought I read. I couldn't find the reference again when I was looking last night so I probably was mistaken. My main concern was having the right size for the common ground back to the ground bus at the box when the three grounds from the lights are connected at the plug.
Mast Wiring Coax cable has no electric field outside of its shield. The field is between he conductors only - even if the antenna is not tuned properly. As far as the gauge of the wire used - 14 AGW is plenty for the grounds of all of your lights even if all of them are on at the same time. Think of the wiring in your car lights. The lights on your car are brighter and draw more current, yet you do not see any wire larger that 14 for any of the running lights. The hear light that draw 10 Amps have larger wire. The mast is already grounded to the negative side of the battery by the manufacturer, but I would still run a separate ground for all the lights on the mast. To keep the plug pins from corroding and causing bad contacts - go to an aouto store and buy the kind of dielctric paste used to water proof the spark plug caps on your card. It looks like vaseline.
Expensive grease! Joe- "go to an aouto store and buy the kind of dielctric paste used to water proof the spark plug caps on your card. It looks like vaseline. " The grease sold specifically for plugs and points is often Krytox grease, about $5 for a 1/2 ounce tube. It's great stuff, but for wiring all you need is silicone grease, aka "High temperature brake grease" "vacuum dielectric grease" and a couple of other names. In the auto stores, $3 for a single ounce tube or $5 for the big six ounce tube, I bought the big one and can afford to be generous about using it.<G> In fact I won't make any connection in the boat or car with it, I've been so impressed at the way a little bit of it keeps corrosion out of crimps and bulb sockets and battery terminals so many other things. Scott- Running all those duplex cables up the mast is a bit redundant. overkill and excess weight aloft. If you really want to splurge, there are some comapnies that sell 4-up and 5-up wiring (i.e. quadplex and quintplex, not just duplex) in one jacket. Even marine grade tinned stranded. It might take some looking to find it, but that gives you just the wires you need, in the extra jacket. Remember that the splices you make at the mast base, at the lights, and the through-deck are all subject to failure, you need to make top-quality splices and then seal them, i.e. wrap them in butyl tape to keep the water out, even if you've used grease on the pins or crimps. A little extra time and money here really pays off long term.
sand sailor
simple is the way to go i have this same project going myself the wire im using is 16awg 4plex the kind used for direct bury its rated for 600 volt i would recommend two of these up the mast with a pair to each lite make sure you grease and shrink wrap each connection(i use high temp wheel bearing grease and heat shrink tubing) the whole idea is to keep water and air from the exposed wire so oxidation wont take place good for battery terminals also ive rewired semi trucks & trailers for years and i grease all my connections and heat shrink when possible because these things see contaminates you couldnt imagine out there on the road that your boat will never encounter and ive never had to redo them a second time
Why run 4-plex ? I have no need for 4 or more wires running to the top of the mast for one anchor light. The steamer and the deck light are midway up the mast and where I could use a 3-plex for them (2 positive, one common negative), they have different minimum guage requirements so it made more sense to me to run separate duplex cables. Although it may make sense to run the 3-plex with the larger (14 guage) wire. I considered that the bare minimum in wiring could be three primaries with the minimum guage requirement running up the mast to the respective lights and one negative primary daisy chained to the three lights down the mast, but I think the duplex wiring makes life easiest. Gregs diagram pretty much sums it up. I appreciate the comments about the size of the plug at the base of the mast. I will look at this with a more critical eye. Thanks!
Ross in Tampa
I am gonna sound stupid... I got the diagram of the mast, thank you it's awesome just what I need. I was working on my mast lights this weekend, and found out I had more of a problem than I first thought. My lights are as follows. I have a steaming light, a mast head anchor light and a spreader light on my port spreader. I was hoping that my issues were bulb related that I couldn't get my steaming light to come on with my nav lights. My anchor light has always been hit and miss, some days it's on, others not so much. I took off my steaming light and only one wire was connected. Great, found the problem, but, can't find the other end. I want to rewire the whole mast, just so I know what is what. The wiring drawing makes perfect sense to me and looks like a relatively easy weekend project. But, here is where I might sound stupid. Since the anchor light and the steaming light will never be on at the same time, but the spreader light and the steaming light could be, and the anchor light and the spreader light could be. So, obviously, they all need their own switch. Does the switch go on the postive or negative wire. (I am no electrician) Help!!! Ross in Tampa
Scott On Eagles Wings
Always break the positive Always break the positive side of a circiut with the switch. Your ground should be uninterupded. Fair Winds Scott On Eagles Wings.
Thanks Scott... That's what I thought. Thanks for the response. RE
- This site uses cookies to help personalise content, tailor your experience and to keep you logged in if you register. By continuing to use this site, you are consenting to our use of cookies. Accept Learn more…
Boat tragedy victim Alan Bottrill remembered as 'adventurer' after 'megawave' claims three lives
Family members of one of the men who died after a boat capsized near Port Lincoln late on Monday have paid tribute to the "adventurer who loved fishing".
Alan Leslie Bottrill, 71, was among three people who died when their boat was swamped by a wave off South Australia's Eyre Peninsula around 4pm on Monday .
His body and the bodies of the two other victims, Paul Eckert and his son Tom, were retrieved from the water on Tuesday.
Another of Paul's sons, Flinders University sleep expert Professor Danny Eckert, and Danny's 12-year-old son survived by clinging to a reef off Spilsby Island, 45 kilometres east of Port Lincoln, where they were found about 2am on Tuesday.
In a statement released on Wednesday, Mr Bottrill's wife Pamela and children Rónán and Amélie expressed their grief.
"Alan was 71 years old and still very much an adventurer who loved fishing, golfing and travelling with friends and family," they said in the statement.
"He leaves behind a wife, two children and two grandchildren who will miss him very much."
The family extended a "heartfelt thanks" to everyone involved in the search efforts including police, who "did a wonderful job", and the "community that has gathered around to support and care for our family".
"Our most heartfelt thoughts are with the families of everybody affected by this tragedy," Mr Bottrill's family said.
Ms Bottrill told ABC News she understood a "megawave" had struck the 6.2-metre fishing boat, and that there had been no time to activate new safety gear which had recently been installed.
She said her husband was an experienced fisher who had twice battled cancer and "never" thought he would have been killed fishing.
Survivors battled 'daunting' seas
Police began searching for the missing boat after family members raised the alarm about 8:30pm on Monday when the vessel failed to return from a fishing trip.
A police helicopter located the upturned fishing boat about 2am on Tuesday.
It was brought back to shore aboard commercial fishing vessel Delamere.
SA Police's Superintendent Paul Bahr told ABC Eyre Peninsula the duo who survived had to contend with a 1.5-metre swell as they clung to the reef.
"Because they were at a reef, they would have had the odd breaker breaking onto that reef so I think it would have been pretty daunting," he said.
"I think they are incredibly lucky and it speaks a lot about their own resilience that they managed to hang on."
He said the search – which included "selfless" efforts from local fishing vessels, the P&O cruise ship Pacific Explorer and a cargo ship – was assisted by teams on land.
"A lot of the search is guided by people remote from the actual search area who are running algorithms across drift patterns and swell patterns and tides to determine where debris and individuals may float and drift as the days go on," he said.
"There's a lot of work goes into ensuring that we put a bit of intelligence into this and make sure that our searches are concentrating in the right areas and that's where we get this sort of result."
Superintendent Bahr said the involvement of local fishing vessels in the search had been "critical".
"Port Lincoln is remote from the rest of the state and so we are very self-reliant. We are reliant on the good will of volunteers to help us and we are fortunate that we have such a large fishing fleet here," he said.
"The crews like the Delamere were pretty selfless in the support they gave us."
He urged anyone planning a fishing trip to ensure they have working and up-to-date safety equipment, and ensure everyone aboard knows how to use it.
He said a report would be prepared for the coroner.
- X (formerly Twitter)
Related Stories
Three people found dead after fishing boat capsizes near port lincoln.
One person found dead, search continues for two missing after fishing boat capsizes in South Australian waters
- Accidents and Emergency Incidents
- Death and Dying
- Maritime Accidents and Incidents
- Port Lincoln
- Recreational Fishing
- Torrens Park

Pulling together: how Cambridge came to dominate the Boat Race – a photo essay
The race along the River Thames between England’s two greatest universities spans 195 years of rivalry and is now one of the world’s oldest and most famous amateur sporting events. Our photographer has been spending time with the Cambridge University Boat Club over the past few months as they prepare for 2024’s races
T he idea of a Boat Race between the two universities dates back to 1829, sparked into life by a conversation between Old Harrovian schoolfriends Charles Merivale, a student at the time at St John’s College Cambridge, and Charles Wordsworth who was at Christ Church Oxford. On 12 March that year, following a meeting of the newly formed Cambridge University Boat Club, a letter was sent to Oxford.
The University of Cambridge hereby challenge the University of Oxford to row a match at or near London each in an eight-oar boat during the Easter vacation.
From then, the Cambridge University Boat Club has existed to win just one race against just one opponent, something Cambridge has got very good at recently. Last year the Light Blues won every race: the open-weight men’s and women’s races, both reserve races, plus both lightweight races – six victories, no losses, an unprecedented clean sweep. Cambridge women’s open-weight boat, or blue boat, has won the last six Boat Races while the men’s equivalent have won five out of the last seven. In such an unpredictable race, where external factors can play a large part, this dominance is startling.

Thames trials
Rough water as the two women’s boats make their way along the River Thames near Putney Embankment during the Cambridge University Boat Race trials.
It’s a mid-December day by the River Thames. The sky and water merge together in a uniform battleship grey and the bitter north wind whips the tops off the waves. Outside a Putney boathouse two groups of tense-looking women dressed in duck-egg blue tops and black leggings with festive antlers in their hair are huddling together, perhaps for warmth, maybe for solidarity. The odd nervous bout of laughter breaks out. For some of them this is about to be their first experience of rowing on the Tideway, a baptism of fire on the famous stretch of London water where the Boat Race takes place. “Perfect conditions,” remarks Paddy Ryan, the head coach for Cambridge University women, for this is trial eights day, when friends in different boats duel for coveted spots in the top boat.
A couple of hours later these women along with their male equivalents will have pushed themselves to the absolute limit, so much so that several of the men are seen trying to throw up over the side of their boats at the finish under Chiswick Bridge. This may be brutal but it’s just the start. For these students the next few months are going to be incredibly tough, balancing academic work with training like a professional athlete. Through the harshest months of the year they will be focused on preparing for the end of March and a very simple goal: beating Oxford in the Boat Race.

Agony for one of the men’s boats after the finish of the race near Chiswick Bridge during the Cambridge University Boat Race trials.

Ely early mornings
Two of the women’s boats head out in the early morning for a training session on the Great Ouse.
Early winter mornings on the banks of the Great Ouse, well before the sun has risen, can be pretty bleak. In the pitch black a batch of light blue minivans drop off the men and women rowers together at the sleek Ely boathouse that was opened in 2016 at the cost of £4.9m – it’s here that all Cambridge’s on-water training takes place. Very soon a fleet of boats carrying all the teams takes to the water for a training session that may last a couple of hours. Then it’s a quick change, a lift to the train station and back to Cambridge for morning lectures.

The women’s squad head into the Ely boathouse after a 6am drop-off.
As a rower descends the stairs to the bays where the boats are stored, there is a clear indication of why it was built and why they are there. “This is where we prepare to win Boat Races,” a sign says. Since this boathouse was built, Cambridge have won 30 of the 37 races across all categories.

Top: The men’s squad stretch in the boathouse before an early morning training session and a member of the men’s blue boat descends the stairs into where the boats are kept. Below: One of the men’s teams set off for early morning training and the women’s blue boat rows past the women’s lightweight crew during a training session.
It’s a far cry from the old tin sheds with barely any heating and no showers. These current facilities are impressive, enabling the entire men’s and women’s squads to be there at the same time and get boats out.

Top: The men’s blue boat prepare to derig their boat at their Ely training site. Above: The women’s blue boat put their vessel back in the boathouse after a training session on the Great Ouse.
But it’s not just the boathouse that has contributed so much, it’s also the stretch of water they train on. In a year when floods have affected so many parts of the country it has really come into its own. Paddy Ryan, the chief women’s coach, explains: “Along this stretch the river is actually higher than the surrounding land. The water levels are carefully managed by dikes and pumps. As a result we haven’t lost a single session to flooding. That’s not the case for Oxford. I believe their boathouse has been flooded multiple times this year, unable to get to their boats. We’ve had multiple storms but we’ve been able to row through them all.”

The men’s third boat practises on the Great Ouse.
It’s a flat, unforgiving landscape, especially in midwinter, definitely not the prettiest stretch of water, but Cambridge don’t care. Ryan says: “It might be a little dull on the viewing perspective but we could row on for 27km before needing to turn round. We have a 5km stretch that is marked out every 250m. We are lucky to have it.”

The men’s blue boat practise their starts on the long straight on the Great Ouse.

The sweat box
Members of the men’s squad check on their technique with the use of a mirror at the Goldie boathouse.
The old-fashioned Goldie boathouse is right in the centre of Cambridge perched on the banks of the River Cam. Built in 1873, its delicate exterior belies what goes on inside. This is the boat club’s pain cave, where the rowers sweat buckets, pushing themselves over and over again; it’s a good job the floor is rubberised and easy to wipe clean.

A wreath to Charles Merivale, the founder of the Boat Race, and wood panelling in the upstairs room at the Goldie boathouse which commemorates Cambridge crews that have competed in the Boat Race from 1829.

(Top) Seb Benzecry, men’s president of the Cambridge University Boat Club, and (above) Martin Amethier, a member of the reserve Goldie crew, sweat during sessions on ergo machines.
Iris Powell of the women’s blue boat (above) performs pull-ups during a training session.

Above left: Hannah Murphy, the cox of the women’s blue boat, urges on four of her crew (left to right) Gemma King, Megan Lee, Jenna Armstrong and Clare Hole, as they undertake a long session on the ergo machines. Above right: Kenny Coplan, a member of the men’s blue boat crew, looks exhausted then writes in his times after his session on an ergo machine (below).

Brutal sessions on the various ergo machines, where thousands of metres are clocked and recorded, are a staple of the training regime set in place. If there is any slacking off the students just need to look up at one of the walls where a map of the Boat Race course hangs. The “S” shape of the Thames has been carefully coloured in the correct shade of blue and record timings for various key points on the course have been written in for both men and women. All but one record, and that one is shared, is held by Cambridge.

Paddy Ryan, the women’s chief coach, talks to the women’s blue boat during a training session on the River Great Ouse in February.
A key ingredient in any successful team is the coaching. Cambridge’s setup is stable and well established. Paddy Ryan is the chief women’s coach, a genial, tall Australian, he has been part of the women’s coaching team since 2013. The care and devotion to his squad is perfectly clear. “I have my notebook next to my bed so I can jot things down. I wake up in the middle of the night going: am I making the right decisions? I care about them as people and I need to manage them … We joke as coaches that we are teaching some of the smartest people on the planet how to pull on a stick.”
Rob Baker, the chief men’s coach, has Cambridge rowing in the blood. Born and bred in the city, his father was a university boatman for 25 years. He even married into the sport – his wife, Hayley, rowed for Cambridge as a lightweight – so it was no surprise that he became part of the coaching setup way back in 2001. He was the first full-time women’s coach in 2015 then moved to take over the men in 2018.

Rob Baker, the men’s chief coach, talks to his blue boat at their Ely training site.
Apart from an obvious role in the development of rowing skills, a key part of their job is making sure there is a balance for their student athletes. They understand they have to juggle training needs. “Every week we have a general plan,” says Baker, “but then someone might have an extra class or supervision they’ve got to do so we have to move around it. They are studying at one of the most competitive universities in the world with the highest standards so you’ve got to give them space to do that properly.” He goes on: “But when they get on the start line for their race, they’ll be just as competitive as if they were professionals.”

The presidents
Jenna Armstrong and Seb Benzecry discuss their plans in the Great Hall at Jesus College.
Every year one man and one woman are elected presidents to represent Cambridge University Boat Club. They are the captains and leaders, not only responsible for helping design the training programme in conjunction with the coaches but also making budgetary and tactical decisions along the way. This year both of them, Jenna Armstrong and Seb Benzecry, are from the same college, Jesus, which helps the communication between the two of them. They share ideas and knowledge, thoughts and worries. Their lives, for these intense few months, are a juggling act.
Armstrong is a 30-year-old from New Jersey, and doing a PhD in physiology. Once a very keen competitive junior skier she was forced to abandon her hopes of a career on the slopes after a number of serious knee injuries. She only started rowing in 2011 and only became aware of the Boat Race when she saw it on TV a couple of years later.

Jenna Armstrong, cycling down the Chimney, the grand entrance to Jesus College, to go to the other side of the city to carry out more of her PhD research at the department of physiology, development and neuroscience.
The research she carries out at the university labs could be turn out to be life-saving. “I study mitochondrial function in placentas from women from all over the world to learn how genetic and environmental factors during pregnancy can influence placental metabolism and impact the health of both mother and baby. I’m particularly interested in growth restriction which affects about 10% of babies worldwide. That can have lifelong implications for these babies and currently we don’t have any treatment for this.”
Benzecry, 27, is studying for a PhD in film and screen studies, and comes from a completely different rowing background. He grew up just a stone’s throw from the Boat Race course and went to a school on the banks of the Thames. This will be his 14th year of competitive rowing but his fourth and last Boat Race.
“ I remember one year my birthday fell on race day and we watched after my birthday party. Because we live fairly close to the course, I’ve always felt connected to the race.”

Seb Benzecry stands next to an Antony Gormley statue in the Quincentenary Library at Jesus College as he conducts research for his dissertation which forms part of his PhD in film and screen studies.
Talking about how hard it is to get the right balance between academic student life and rowing, Benzecry says: “I guess you have to accept there are many, many things you can’t do, you just don’t have time for during the season. You have to put the blinkers on.”
Armstrong says: “I have to be very prepared, very strategic and organised. I pack everything the night before, and then once I leave my room in the morning, I don’t go back. That allows me to go to training, go to the lab, go to training again. It’s surreal actually, to come to a place like Cambridge, have one of the best educations in the world on top of the most incredible rowing experiences in the world. We have a thing now in the boat, when we are doing something incredibly hard, I say this is my ideal Saturday, I wouldn’t want to be anywhere else. I would rather be here than in bed or on a date. And I make everyone else say it with me too. I’d rather be nowhere else.”
Benzecry states: “When it’s really bad, when training is so hard, we say Oxford aren’t doing this, they could never do this. It’s an incredibly powerful thing to be thinking we work harder than them, our culture is better than them. They don’t want to go hard as we do – they might think they do but they don’t, they just don’t have it.”

Integration
The men’s and women’s blue boats during a training session on the River Great Ouse in February.
Until 1 August 2020, there were three separate university boat clubs in Cambridge: one for open-weight men, one for lightweight men, and one for open-weight and lightweight women. Since they merged to become one club, it has undoubtedly helped with everyone sharing the same resources and motivating and inspiring one another. No one is more important and everyone has a key part to play in the result. This year, Oxford have followed suit.
Baker says: “I definitely feel, for the athletes themselves, it makes a big difference. They all feel like they’re contributing to one common goal. Every cog in the wheel has to do its job but for sure it feels like one big team on a mission.”
Benzecry explains: “We’re seeing each other train, we’re all out on the water at the same time, we’re supporting each other throughout the season, building a sense of momentum for the whole club towards the races. Everyone’s just inspiring each other all the time and I think that’s been such a sort of cultural shift for Cambridge.”

The men’s blue boat pack their craft on to a trailer at their Ely training site ready for the trip down to London for the Boat Race.
Siobhan Cassidy, the chair of the Boat Race, knows from first-hand how the integration has helped. She rowed for the Light Blues in 1995 and had a key role in the transition. “We could see the advantages of working together, collaborating as a bigger team, the positive impact we felt that could have on performance. But not just the output, actually the whole experience for the young people taking part.”

Siobhan Cassidy, the chair of the Boat Race, pictured at the Thames Rowing Club at Putney Embankment.
This Saturday, if the weather holds, an estimated 250,000 people, the vast majority of whom have no allegiance to one shade of blue or the other, will pack the banks of the Thames to see these races. It’s one of the largest free events in Britain. Broadcast live on BBC One, the race is also beamed to 200 countries across the world.

The starting stone for the University Boat Race and pavement inscription: “The best leveller is the river we have in common” at Putney Embankment.
A map of the Boat Race course at the Goldie boathouse, with the Thames coloured in Cambridge blue and record timings written in for men and women showing almost total Cambridge dominance.
A sporting pinnacle being contested on a fast-flowing, unpredictable river by two teams of university students – it’s pretty bizarre. But maybe it’s that quirkiness that keeps the race, after almost two hundred years, still going strong. And even more bizarre to think that Cambridge, the current dominant force in the Boat Race, a sporting event that can’t shrug off its elitist stereotype, owes so much of that success to such egalitarian principles.
- The Guardian picture essay
- The Boat Race
- University of Cambridge
- Photography
Most viewed

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
As such a power boat, and by extension all sailboats, MUST, without question show one green light on the starboard bow and one red light on the port bow and one all around white light or lights while operating in reduced visibility. These lights should shine at all 360 degrees of visibility with the bow lights shining at an angle of dead ahead ...
For most small vessels, motoring requires red and green (port and starboard) lights, and a white light visible in all directions around the boat. This is almost always a stern light and a masthead light on sailboats. Boats under sail require port and starboard lights, and a white stern light. Sailboats below sixty-five feet may show a tricolor ...
The all-around light is white and it is located at the top of your boat's mast for maximum visibility. Color: White ARC: 360 degrees Position: Top of mast. Tricolor Light. A tricolor light is a sailboat mast light that has your three types of bow light in one convenient piece of equipment. They are for sailboats that are smaller than 65.6 ...
Rule 29, duty shall exhibit: at or near the masthead, two all-round lights in a vertical line, the upper being white and the lower red; when underway, in addition, sidelights and a sternlight; as shown in the example below. Pilot boat, shorter than 50 m. Abeam, starboard side.
Boat Navigation Light Regulations. Several rules and specifications are related to the type, size, layout, arc, and distance of visibility of boat navigation lights used by all vessel types which are collectively known as the International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea or COLREGs.The navigational lights used are known as 'COLREG lights and shapes.
A "Masthead light" means a white light placed over the fore and aft centerline of the vessel showing an unbroken light over an arc of the horizon of 225 degrees and so fixed as to show the light from right ahead to 22.5 degrees abaft the beam on either side of the vessel. Note: It does not say the light must be at the top of the mast.
Remember that the all-round light is a static white light that provides a 360-degree view at the very top of a sailing vessels mast, so it'll be quite difficult to miss. As a matter of fact, a power-driven vessel at anchor also has the same all-round light on display as long as it's 50 meters (65 feet) or less in size.
Explore sailboat mast types, maintenance tips, and upgrading options. Learn how to keep your sailboat mast in top condition for a safe and enjoyable sailing experience. +49 211 54 69 22 23. 0. FormResult. ... It also often houses instruments such as wind indicators and lights.
Phone: (479)339-4795. Email: [email protected]. Boat navigation lights are essential when you're out on the water. They're essential, but it's easy to misunderstand their uses and correct placements. If you don't know the correct placement for your stern lights or know what type of navigation light you need on your mast, don't ...
Only five lights rated good at 2 nm: Aqua Signal's 40100-1 bi-color light and 40400-1 masthead; Hella Marine's 62208 stern light, 62206 masthead, and 6225 tri-color. (This tricolor was actually the most visible of all the lights in the test, scoring "excellent" at 1 nm and "good" at 2 nm.) Some sidelights that were rated for only ...
Boats less than 12m (39.4'), sidelights must be visible for at least 1nm. All other lights must be visible for at least 2nm. Boats less than 20m (65.7'), a masthead light must be visible for 3nm. All other lights must be visible for 2nm. Boat over 20m (65.7') and less than 50m (164') must display a masthead light visible for 5nm.
Mast-head light A white light placed over the centre line of the vessel and shines dead ahead in an arc of 225° (from straight ahead up to 22.5° more aft than crosswise to each side). ... Displaying lights for sailboats up to 20 m 1 x red port side light. 1 x green starboard light. 1 x stern light. Also allowed: 1 x red all-round light on or ...
A steaming light is a white navigation light fitted on the mast of a sailboat to provide visibility during low-visibility conditions. It is typically placed near the front side of the mast and angled downwards to indicate that the vessel is under power and moving forward. This light helps other boats identify and avoid collisions, ensuring safe ...
For sailboats, a tricolored light is a light described by rule 25 (b) in USCG Nav Rules. It is at or near the top of the mast and is for sailing vessels less than 20 meters in length. It is an optional alternative to having the lights down on the hull or pulpits. It faces a white light to the aft 135 degrees plus red from directly forward ...
Red and green sidelights, one sternlight, and two all-round lights in a vertical line (upper red, lower green) also meet the navigation lights requirement for sailboats that are not operating under engine power (Rule 25). One combination red, green, and white light exhibited near the top of the mast meets the navigation lights requirement for ...
Change to an LED that draws less than 1 an and you can go with the less expensive and lighter 16ga. 30 feet from the base of the mast to the panel seems a bit long on a 27' boat. You can also cheat a bit and run 12 ga to the mast and 16 or 14 up the mast. Just be sure to fuse for the smaller wire. J.
An economical 2NM LED All-Around Anchor Light fixture navigation light intended to be mounted on the top of the mast on larger sailboats. It replaces the Aqua Signal Series 40 type anchor lights, as it is of similar size and height. Prefitted with a user-replaceable Marinebeam constant-current 10-30VDC BAY15d high-output LED bulb and 8" of ...
1. $182.41 - $182.57. Perko® 225° Lens for Masthead Lights (0281DPAWHT) 0. $8.69. Attwood® 12" L Horizontal Mount Fold Down Anchor/Masthead LED Light with Base (7812-S-7) 0. $131.81. Attwood® 12" L Horizontal Mount Fold Down Anchor/Masthead Light with Rail Adaptor (7201-P-7)
There apparently -are- valid uses for the masthead strobe. First, West Marine says it is approved for use as a distress light on inland waters; but illegal offshore. Next, the rules for the ''Singlehanded Transpacific Yacht Race'' actually -requires- masthead stobe lights on participating vessels. (Page 5, 7.24) at:
In video, as it navigates down the Patapsco River, the ship's lights can be seen going out at 1:24 a.m. ET, before turning back on, and then flickering off and on again between 1:26 a.m. ET and ...
According to the navigation rules the steaming light/mast light should be 1 meter above sidelights. In reality, I have seen mast lights a few feet above the spreaders and a few feet below the spreaders. My mast is 28 ft long . I have already installed the anchor light on top of the mast. Now, I only have to install the steaming light/mast light ...
Shortly after, the emergency generator kicked on-emergency lighting, steering, and navigation equipment, which is when the lights on the ship flickered back on. However, the ship's engines never ...
Investigators said in a timeline that the Dali's lights suddenly shut off four minutes earlier before they came back on and that then, at 1:25 a.m. dark black smoke began billowing from the ship's ...
The Dali was less than 30 minutes into its planned 27-day journey when the ship ran into the Francis Scott Key Bridge on Tuesday.. The ship, which was sailing under the Singaporean flag, was on ...
Feb 25, 2007. #6. Mast Wiring. Coax cable has no electric field outside of its shield. The field is between he conductors only - even if the antenna is not tuned properly. As far as the gauge of the wire used - 14 AGW is plenty for the grounds of all of your lights even if all of them are on at the same time.
The wife and children of Alan Bottrill, who was one of three men who died in a boat tragedy near Port Lincoln, has remembered the 71-year-old father and grandfather as an "adventurer" who loved ...
The men's blue boat pack their craft on to a trailer at their Ely training site ready for the trip down to London for the Boat Race. Siobhan Cassidy, the chair of the Boat Race, knows from first ...