

Please verify you are a human
Access to this page has been denied because we believe you are using automation tools to browse the website.
This may happen as a result of the following:
- Javascript is disabled or blocked by an extension (ad blockers for example)
- Your browser does not support cookies
Please make sure that Javascript and cookies are enabled on your browser and that you are not blocking them from loading.
Reference ID: 1df01899-158d-11ef-995a-f157faec83f0
Powered by PerimeterX , Inc.

Should You Use a Masthead Wind Indicator?
On a run with light and shifty wind, a masthead wind indicator is essential. The telltales on the shrouds are too affected by the sails to tell you what’s going on. Sailing Anarchy Forum
I do not like them because they really help your competition more than you. Sailing Anarchy Forum
Our coach, Dave Ullman, insisted that we get one and use it. Roble-Shea Sailing
A masthead wind indicator, sometimes called a masthead fly or a Windex (brand name), is a wind vane mounted at the top of the mast. Like shroud telltales, it tells you the direction of the apparent wind, which is a crucial cue for many aspects of sailing. See our post Ten Ways to Use Shroud Telltales for all the ways you can use shroud telltales (or a wind vane).
If you have shroud telltales, should you also use a masthead wind indicator? Sailors’ opinions vary, and a recent walk through the local boat park showed about 60% of boats with them (much higher % for the Flying Scots). Here we list the pros and cons.
Masthead wind indicator – Pros
#1. more precise than shroud telltales downwind.
When sailing downwind, a wind vane is a more precise indicator of apparent wind direction than shroud telltales, which are affected by flow off the sails. To see this, try a boat that has a wind vane. Sail downwind and adjust your heading so the wind vane points directly along the fore and aft axis of the mast. This indicates you are sailing dead downwind. At this heading, the difference in angle between shroud telltales and a wind vane can be as much as ten degrees. Knowing this allows you to sail dead downwind in breeze and thus sail less distance.
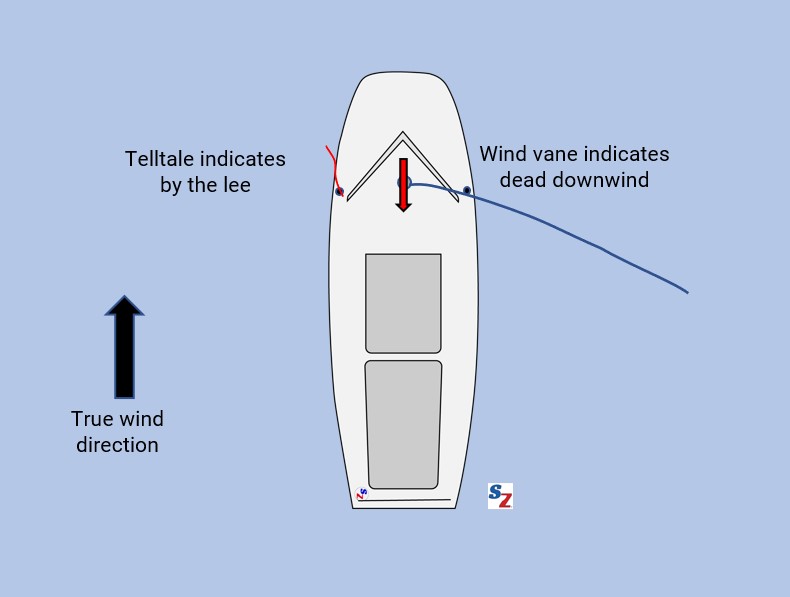
#2. Less Bouncy than Shroud Telltales
Being rigid, center mounted, and slightly heavier, a wind vane bounces around less than shroud telltales. In some cases, discussed below, it’s worth looking up to take advantage of this “noise reduction.”
#3. Better than Shroud Telltales for Some Situations
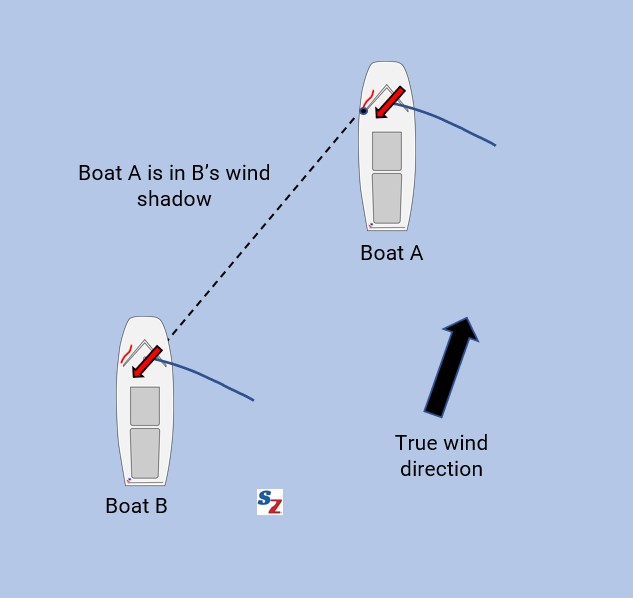
Attack and defend downwind.
It’s easier to use the wind vane here, due to its accuracy, stability, and unobstructed view. To attack, point the tail of the wind vane at competitors ahead. Defend by repositioning when the arrowhead of the wind vane is pointing at competitors behind you.
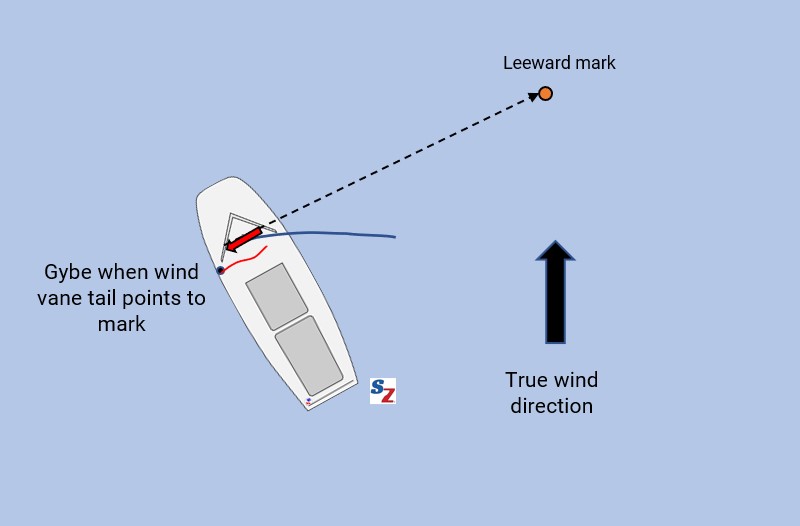
Identify layline downwind
The fastest way to the leeward mark is to keep sailing your best VMG angle until you reach the layline, then gybe and sail the same VMG angle to the mark. How do you identify the layline? Again the accuracy and unobstructed view make the wind vane more useful in this case. You reach the layline when the tail of your wind vane points to the leeward mark.
Identify true wind direction when sailing downwind
If you use a compass, you have to know the numbers. We all know how to identify the true wind direction by luffing head to wind. The accuracy of the wind vane allows you find the true wind direction when sailing downwind. Sail dead downwind, with the wind indicator lined up with the fore and aft axis. Check your compass heading and add or subtract 180 degrees to find the true wind direction.
This helps keep tabs on the “numbers” during the pre-race routine or on a downwind leg when you suspect the wind has shifted permanently.
Identify wind shear to aid sail trim
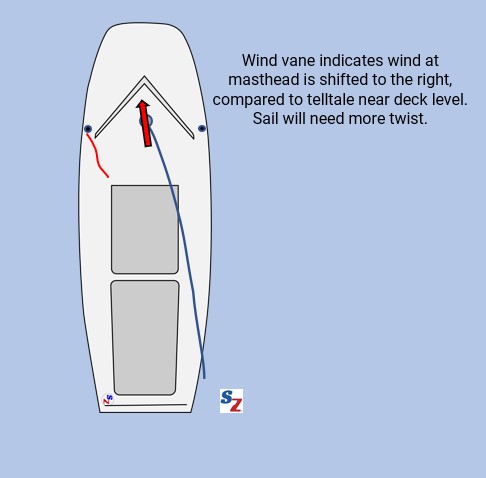
In very light air (no ripples), the wind true direction at the top of the mast may be different than near the bottom. This is important for upwind sail trim. Check your wind vane against the shroud telltales. If there’s shear or gradient, adjust your sail trim and twist as necessary. For more, see our post Wind Shear and Gradient Effects on Trim & Strategy.
Masthead wind indicator – Cons
#1. one more item to distract your focus.
Distractions take away your focus from the really important stuff, and many top sailors try to keep things simple. Wind vanes are another bright, shiny object to distract you, and worse, you must look way up to see them. Shroud telltales are in your line of sight and give you the same information. You can learn to compensate for their inaccuracies downwind.
#2. May give your competitor an advantage
Your masthead wind indicator is useful for competitors. They don’t need one – all they have to do is look at your indicator to determine if they are in your bad air or vice versa.
The Verdict?
Do the pros outweigh the cons? Your editor is always tempted to go for more indicators (shroud telltales, sail telltales, marks on control lines, etc.), but that approach has added lots of distractions and thus has not always served him well. Therefore, we decline to make a recommendation, except to say that used judiciously, we have found them helpful in the situations discussed above.
Related Content
Davis Windex 3120 – Amazon Downwind Strategy: Use Apparent Wind Cues
Related Posts

MC-Scow Midwinters – Aha! Insights from the Winners

Improve Your Average Score – One Race at a Time | Sailing World

Vincent Porter Shares Race Course Notes at ILYA Championship Regatta
2 thoughts on “should you use a masthead wind indicator”.
I firmly fall into the category of every boat (except mine) should have a masthead wind indicator. I love seeing the wind direction on my competitor’s boats!
Thanks, JP!
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Insert/edit link
Enter the destination URL
Or link to existing content
- New Sailboats
- Sailboats 21-30ft
- Sailboats 31-35ft
- Sailboats 36-40ft
- Sailboats Over 40ft
- Sailboats Under 21feet
- used_sailboats
- Apps and Computer Programs
- Communications
- Fishfinders
- Handheld Electronics
- Plotters MFDS Rradar
- Wind, Speed & Depth Instruments
- Anchoring Mooring
- Running Rigging
- Sails Canvas
- Standing Rigging
- Diesel Engines
- Off Grid Energy
- Cleaning Waxing
- DIY Projects
- Repair, Tools & Materials
- Spare Parts
- Tools & Gadgets
- Cabin Comfort
- Ventilation
- Footwear Apparel
- Foul Weather Gear
- Mailport & PS Advisor
- Inside Practical Sailor Blog
- Activate My Web Access
- Reset Password
- Customer Service

- Free Newsletter

Pearson Rhodes 41/Rhodes Bounty II Used Sailboat Review

Hallberg Rassy 42 Used Sailboat Review

How to Perform Your Own Pre-Buy Inspection

Beneteau 323 Used Boat Review

How Does the Gulf Stream Influence our Weather?

Can You Run a Marine Air-Conditioner on Battery Power?

Preparing Yourself for Solo Sailing

Your New Feature-Packed VHF Radio

Practical Sailor Classic: The Load on Your Rode

Anchor Rodes for Smaller Sailboats

Ground Tackle Inspection Tips

Shoe Goo II Excels for Quick Sail Repairs

What Oil Analysis Reveals About Your Engine

An Unusual Sailboat Shines a Light On A Sustainable Future

Is It Time to Get an Electric Dinghy Motor?

Bottom Paint 30-Month Update

Battle of the Teak Cleaners — Snappy Teak-Nu vs. Star Brite

New Seacocks for the Offshore Sailor

Bottom Paint Care

Are E-bikes Worth the Extra Weight and Cost?

How to Handle the Head

How to Select Crew for a Passage or Delivery

Preparing A Boat to Sail Solo

Re-sealing the Seams on Waterproof Fabrics

Waxing and Polishing Your Boat

Reducing Engine Room Noise

Tricks and Tips to Forming Do-it-yourself Rigging Terminals

Marine Toilet Maintenance Tips

Learning to Live with Plastic Boat Bits
- Sails, Rigging & Deck Gear
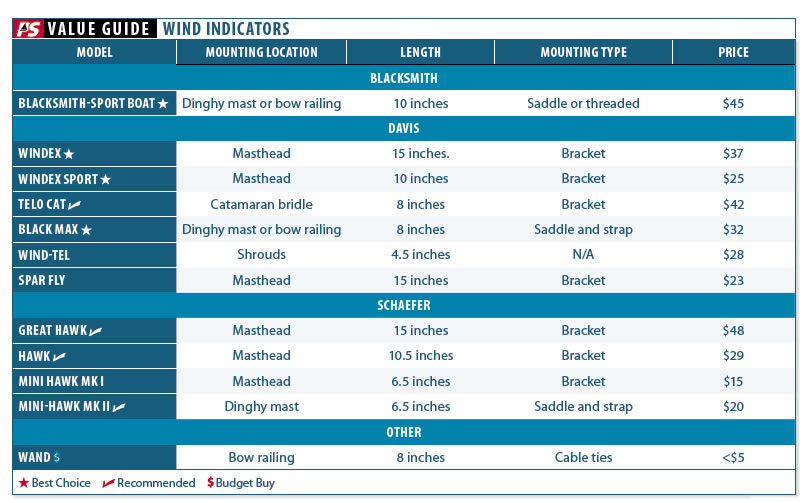
Top-notch Wind Indicators
In this torture test, we examine improvements over those silly bits of yarn (which work quite well, incidentally)..

That fragile plastic wind vane at the masthead looks like a child’s toy to a lubber. Its a nautical curiosity perched at the top of a yacht that is also equipped with a comprehensive electronics suite. While we can certainly sail without wind indicators and telltales, judging the strength and direction of the wind by its effect on the sails and the feel on our neck, those little bits of plastic and yarn are darn handy when trimming sail, or balancing the helm.
Information from fixed wind indicators is supplemented by telltales attached to the surface of the sails. These provide vital information about flow around the sails within the boundary layer. In this report, well look solely at the wind vanes.
WHAT WE TESTED
For this comparison, we looked at a variety of masthead and spar-mounted vanes from Blacksmith, Davis and Schaefer, two of the major players in this field. We also included a do-it-yourself (DIY) variation that we used for a decade. A few of these were new to us, but most we’ve used for decades, giving us a pretty good feel for their long-term durability and function.
HOW WE TESTED
First, we mounted all of the vanes on boards, three to four at a time, and observed responsiveness, sensitivity, and accuracy, both level and heeled at 30 degrees. Although there is no absolute reference for wind speed and direction, it was obvious when a single vane was consistently different from the group.
We then mounted vanes on the roof of our car and took them for a drive-first around the neighborhood at moderate speeds, and then for six hours at 50-65 miles per hour, simulating storm conditions.
Finally, we then put them all to work on our test boat. This was a fairly rigorous test that took place over several days (see adjacent article Wind Sensors Face-Off at Sea). Larger vanes were mounted in fishing rod holders along the transom. Although wind turbulence makes the aft vanes useless for windward courses, these worked when reaching, and the location was fine for durability testing and general observation.
OBSERVATIONS
A masthead mounting offers the cleanest air and greatest safety from damage (other than birds). Every sailboat should have one. The larger sizes make sense for larger boats, where visibility from a distance matters, but the smaller sizes seem quite suitable for masts less than 35 feet. Although a masthead indicator often has the cleanest air, it requires staring straight up, can spin crazily in rolly conditions in light air, and can be blocked from view by a Bimini top or sail (if the helm is to one side).
Although a masthead indicator is the norm, a deck-level indicator also offers advantages. Non-sailing crew appreciates them when asked to turn the boat into or away from the wind while hoisting or dousing the sail, for anchoring, or, in reality, any turn at the wheel when a steady course relative to the wind is required. Off the wind, a deck-level indicator is often more steady in rough conditions, less affected by pitching. It also remains in your line-of-sight, as you steer through either lumpy seas at high speed, or crab pots in failing light. The challenge is finding a location where it won’t be destroyed by sheets or sails, or disturbed by airflow.
Single-sail dinghies, such as Lasers or Optimus, can mount them on the mast, just below the sail. Two of the devices that we tested, the Davis Black Max and Schaefer Mini Hawk MK II come with elastic clamps that fit securely around the 1.5-inch aluminum spar.
These devices are quite rugged. During long-term testing, we inadvertently dropped snubber lines and dock lines on all of them, often deflecting them sharply downwards. However, the mounting strap stretched, and they popped right back up, undamaged. One vane was destroyed with a dock line, but that was no fault of the vane.
The bow is also popular on one-sail dinghies; with no headsails or sheets, there is little risk of damage. Beach cats can mount a Telocat just below the bridle. Even with a chute, the sensor is protected by the bowsprit. The straps on the Black Max and Mini Hawk fit -inch stainless railing, if the railing is wrapped with athletic or elastomeric self-bonding tape to reduce slippage (see Atomic Tape, PS December 2005). The occasional trip through a wave didn’t appear to shorten their lives.
A spinnaker complicates things-with sheets flying across the bow with every jibe, there is no sanctuary for a delicate instrument. We had a Davis Windex Sport on the starboard bow rail of our test boat for a while. It was fine with the working jib, the genoa bumped lightly a few times, rotating the mount but doing no harm. A chute, however, destroyed it on the first jibe. After a second vane was destroyed in roughly the same fashion, the solution was the DIY indicator (see adjacent article).
Wind indicators are by definition sensitive instruments, and even the best can be snapped or bent by a large bird. The Davis Windex has a bird spike that dissuades larger birds from sitting on the center support, but smaller birds still roost on the ends of the vane occasionally, spinning slowly. So far (we’ve had one installed for 20 years) they have done no harm, other than bend the indicator arms into a useless sculpture. The plastic indicator arms on the Shaefer wind indicator better resist bending. We presume a big bird could break them, but they survived the summer season test without harm-even after several birds roosted on them. Birds seem to ignore deck-level vanes.
All of the mounting brackets proved sufficiently durable and reasonably easy to fit.
Blacksmith Sport Boat Carbon
In its search for a lighter, more responsive vane, Blacksmith has used carbon fiber and aluminum to build the most responsive vane available. As a masthead fly, it is well balanced and reads the lightest zephyr true, even when heeled.
As a rail-mounted fly it has proven more durable than Windex and Hawk vanes, through we estimate it more fragile than the rugged Black Max/Telo Cat line. So far, it seems too oddly shaped for birds to perch on, and that is the primary mode of failure at the masthead. There is also a very similar Crazy Kids model for dinghies. The Blacksmith comes in both masthead and spar mount versions.
Bottom Line: Best Choice for sport boat masts.
Davis Windex
The most popular masthead wind indicator, these are the gold standard for detecting wind direction finding. Featuring perfect balance and a sapphire bearing, we’ve had these on boats for over 20 years without failure. They wear seemingly forever, the most common-and perhaps only-cause of death being a roosting osprey or eagle, and the bird spike seems to prevent that. The Windex Sport is a smaller version, perfect for smaller boats and some bow installations.
Bottom Line: Sensitivity and proven durability make the Windex our Best Choice for a masthead indicator for cruisers, and the Windex Sport for smaller boats.
We used one of these very regularly for eight years on a trailered beach catamaran, where it served very reliably, without receiving gentle treatment. Useful for estimating both windward and reaching angles. The bridle location is perfect for the high-speed antics of a beach catamaran, where the helmsmans eyes should not spend too much time peering aloft, distracted from the action and the waves. The Telo Cat is specifically designed to mount to the forestay turnbuckle of beach cats, hanging down below the bridle-the Black Max will be easier to fit to most boats.
Bottom Line: Best Choice for beach catamarans.
Sharing the same sturdy vane as the Telo Cat, the Black Max is stable, sturdy, and reliable. Secured by an adjustable elastic strap, the plastic mounting saddle can wrap around spars and poles from -inch to two inches in diameter,
Bottom line: Recommended for single-sail dinghies, gull strikers, and rail mounts.
Compared to other indicators in the group, the Spar Fly seemed to wander more in bouncy conditions and variable winds, taking longer to respond accurately to the true wind. Some will find the traditional design appealing.
Bottom line: This is a functional choice for the nostalgic sailor, but there are better vanes.
This device is little more than toy. Yarn is more durable and responsive, and less susceptible to damage from sheets and sails. The test samples all bent the first day. Additionally, the position near the dodger or cabin resulted in disturbed airflow and erratic readings.
Bottom line: Helpful on some small boats, Wind-Tels won’t be of much use to the cruising sailor.
Schaefer Hawk
Schaefers Hawk is very similar to the Windex, but with plastic indicator arms. The arms can be accurately positioned using a spacer kit and they are not bent when a bird lands on them. They seem nearly unbreakable under normal use, although we did not test for this. Using polyethylene bearings, it is both responsive and sensitive.
Bottom line: Recommended.
Mini-Hawk MKI
Sharing the same vane as the MKII, this is the smallest masthead vane of the group. It is light and very responsive, and is an excellent choice for the masthead of a sailing dinghy. We also tested it on the bow rail, simply attaching the wand with cable ties, and it did very well. If you break the vane, a replacement is $10.
The large tail made the Mini Hawk very responsive, even when wet or in light winds, reacting accurately and instantly to every shift. Although this resulted in a nervous flickering at times, it was always accurate, and its is bright and clearly visibility. The square vane was slightly more vulnerable to hooking a line, although all of the vanes (other than the DIY wand) can be destroyed by heavy contact with a sheet.
Bottom line: Great for dinghy masts and a nice fit for railings.
Mini-Hawk MKII
The spar mounting bracket for the Mini-Hawk II includes adjustability for horizontal or angled mounting on rails, which can be quite useful for bow mounting locations. The elastic mounting band is not adjustable, but it is secure on rails and spars from 1 to 2.5 inches.
Bottom line: This is the Best Choice for a railing or spar-mounted vane.
CONCLUSIONS
This was a strong group of products, and properly located, all provide excellent performance. We like the Windex 15 with the bird spike; it seems to help keep birds away from the masthead in general. The responsiveness of the Mini Hawk was impressive, and the durability of the Telo Cat and Black Max recommend them for use where some contact is possible. Our DIY wand remains a favorite where abuse is the rule.
- A Do-it-Yourself Wind Sensor

Our on-the-water testing revealed some advantages and vulnerabilities that were not apparent during controlled testing. The benefits of high-visibility colors became readily apparent.
The smaller vanes were mounted across the bow rail on our catamaran test boat for a summer, rotating location from time to time. We smashed through waves and occasionally battered them with sheets and docklines, although we avoided serious abuse for all but the unbreakable do-it-yourself vane.
- The DavisWind-Tels bent during a spinnaker gybe, but it was easy enough to straighten out so that it was still useful.
- The racey Davis Black Max faces off against the comparatively humble bit of yarn during testing.
- Dimensions varied greatly, from left: Schaefer Hawk, Mini-Hawk, and Blacksmith.
- The Blacksmith’s high visibility indicator was easy to read against a confused background.
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
The last three windex vanes I have used have decayed in the sun in less than a few weeks. any slight action like removing them to step the mast on the trailer sailer results in damage . brittle bits just flake off. I am averaging $50 a year AU in wind indicators. have ordered a stainless steel one. a bit big but may be UV stable.
How is your stainless wind indicator? I am working on designing a lightweight anodised aluminium wind indicator. I am a professional yachtsman and have seen lots of stories like yours in Oz particularly with cockatoos!
The indicator I am designing will be similar profile to the windex brand but a lot lighter than the available stainless ones also with jewel bearings for light air accuracy. Would you be interested in a solution like this? Any advice is appreciated.
Happy sailing
Hi Oliver, did you ever develop this?
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Log in to leave a comment
Latest Videos

What Is The Best Folding Bike For Your Sailboat?

The No Expense Spared Antigua 60 Cruising Sailboat Soolaimon

How To Buy Sails – With Joe Cooper

Bavaria C42: What You Should Know | Boat Tour
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell My Personal Information
- Online Account Activation
- Privacy Manager

Comments are closed.


Steering the dream
Hydrovane is your best crew member: an independent self-steering windvane and emergency rudder/steering system... ready to go!
Hydrovane will fit any cruising boat!
Off-center installations are the norm!

Doubles as Emergency Rudder/Steering!
True Stories

Golden Globe Update Day 113:
[GGR Leader Jean-Luc Van Den Heede sailing the Rustler 36 Matmut] was full of praise for his Hydrovane self-steering. “In a gale it has a big advantage because it is not steering the boat’s rudder, but has its own. This little rudder is far more efficient than the big rudder.”
– Jean Luc Van Den Heede on satellite phone call
“I am happy I did install the Hydrovane, especially that I saw on YouTube that at the same time 2 sailboats almost the same size as mine with the same problem. The crew had to abandon the the ships and left both boats in the middle of the Atlantic and lost everything … again thanks to the Hydrovane. It saved my boat.”
– Jacques Glaser, Amel Mango 52
“My wife and I have just completed a two month cruise with our new Hydrovane and it has performed beyond all expectations… If cruising I wouldn’t go to sea without one: strong, simple, reliable, an emergency helm and an extra crew member who never complains and doesn’t need a watch system.”
– Pete Goss, MBE, Frances 34
“So, I must tell you, and I mean this sincerely, the Hydrovane is simply a game changer for Quetzal. It’s just great and performs better than I expected… One other feature of the vane that I really appreciate is that it eases the load on the rudder and rudder bearings.”
– John Krestchmaer, Kaufman 47
“With just two of us on board, I wanted a system that was simple and effective to operate, and it has exceeded my most optimistic expectations by a considerable margin. It truly is our third crew member.”
– John Mennem, Jeanneau 45.2
“…it is still the most technically elegant solution i have ever seen for a wind vane… I was clawing off a lee shore on one side, and islands on another – winds were reported at 55 knots, and waves in the region were at least ‘boat length’ high and quite steep with the currents. This was an awful night and I was very afraid for myself, the boat and my equipment – I had new found respect, trust and comfort in the Hydrovane after that.”
– Steve De Maio, Contessa 26
In this recent Pacific crossing, the Hydrovane kept us on course (relative to the wind, of course) for several days at a time, requiring no tweaking or attention at all. If you can balance your boat and twist a dial, you can successfully operate a Hydrovane. Don’t leave home without one!
– Bill Ennis, Passport 40
“For the first time, we had to run downwind, under bare poles in gale force 8 conditions, with gusts to 50 knots – and don’t get me started on the sea conditions! Have you ever swallowed your tongue? Oh, and iVane, our wind-steering partner. What a gem! It steered 230 hard miles without even nut rations.”
– Brian Anderson, Hallberg Rassy 40
“The additional cash to purchase a windvane was almost too much… Just how good is this ‘Hydrovane’ anyway?”
After 29,000+ miles: “We’ve said to each many times that without doubt the most valuable piece of equipment on board was Casper – best purchase EVER. I will never own an offshore boat again that does not have this device.”
– Ryan Robertson, T 40
Swim Step / Sugar Scoop
External rudder, watt&sea bracket, other products.
Watt&Sea Hydrogenerator

Echo Tec Watermaker


Happy Halloween! This costume may have been for a different occasion but relevant nonetheless! 👻 “After seeing what Taurus [the Hydrovane] does for us [my friend] fell in love with him too. So much so that when the crew dressed up for the equator crossing, she dressed up as a Hydrovane!” - Norlin 37 owner 🙌🙌 ... See More See Less

- Comments: 2
2 Comments Comment on Facebook
Hi, can u reach me up via WhatsApp? My phone number is +56999728041 Txs
How times change just thought I’d send you this video that somebody sent me that bought a Hydrovane ❤️x
Well that was a fun night. 🎉 Thanks @cruisersawards Young Cruisers' Association for bringing together so many inspirational sailors and story tellers! Get out there and chase the wind ⛵️ #cruiserawards #youngcruisers #internationalcruiserawards #seapeople #annapolis #usboatshow #hydrovane ... See More See Less
- Comments: 0
0 Comments Comment on Facebook
#repost from @kirstenggr ⛵️ “Thinking back on the sailing, and missing it! Thanks to @ hydrovane for having serviced Minnehaha's hydrovane , which did about 45 000 nm before having any major overhaul - possibly more than any hydrovane has ever done before without a significant service. It saw Kirsten and Minnehaha all the way through the GGR and over the finish line! The unit is as good as new again, and it was smooth sailing all the way down to Madeira! Also, a big thanks to Eddie Arsenault, for having built such a solid mounting bracket for the hydrovane ! Without Eddie, Minnehaha would just not be the strong boat that she is today!” ... See More See Less
Wow, absolutely so proud my fathers invention and so glad everybody is so still going strong with this after so many years!! It is so lovely to see !❤️
Any photos of the mount Eddie made?
Thank you Kirsten Neuschäfer ! You are an inspiration. The Hydrovane loves sailing as much as you do 😀 Kudos to Eddie for the rock solid install! Thinking back on the sailing, and missing it! Thanks to Hydrovane International Marine for having serviced Minnehaha's hydrovane, which did about 45 000 nm before having any major overhaul - possibly more than any hydrovane has ever done before without a significant service. It saw Kirsten and Minnehaha all the way through the GGR and over the finish line! The unit is as good as new again, and it was smooth sailing all the way down to Madeira! Also, a big thanks to Eddie Arsenault, for having built such a solid mounting bracket for the hydrovane! Without Eddie, Minnehaha would just not be the strong boat that she is today! ... See More See Less

Hydrovane is my most trusted crewman.
Lee Colledge Shaun Colledge see what you have built 💪 👌
Once upon a time under spinnaker between Niue and Tonga 😍 ... See More See Less

- Comments: 1
1 Comment Comment on Facebook
This week we sailed from Lemvig Denmark to Vlieland Netherlands. 270nm and a tough journey for us and without the Hydrovane it really wouldn't have been possible for us. It gives us peace of mind while sailing and can no longer do without it. Boat is a Barbican 33.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Yacht Cruising Lifestyle
Everything fun you can do from your yacht
Why You Need a Wind Vane for Your Sailboat
September 24, 2021 by Travis Turgeon 1 Comment
Many of today’s offshore cruising sailboats utilize a type of autopilot equipment called a windvane. A sailboat wind vane is a mechanical self-steering system that requires no electricity, fuel, or manpower to operate. It’s the perfect addition to bluewater cruisers and offshore sailboats. While a mechanical self-steering wind vane can’t hold you on a compass course, they’re more accurate than human steering over long distances. By reducing the overall mileage of a passage, you’re able to save time and money on your journey. Alternatively, a windvane is essential for short-handed or single-handed sailing. It gives the skipper a much-needed break from the helm when conditions allow.
How Does a Wind Vane Work on a Sailboat?
Mechanical wind vane systems are relatively simple in concept. Once mounted at the boat’s transom or somewhere along the stern, wind prompts the elevated vane to adjust the rudder or wheel steering system, putting your sailboat back on a wind-based course dictated by the captain. The idea is that you won’t have to make constant adjustments in variable winds. Automatic adjustments reduce boat heeling and allow your vessel to remain trim in the water.
In other words, wind vanes use wind and water resistance to return a ship to course when wind chages direction.
Sailboat Windvane Gears Vs. Electronic Autopilot Systems
Two primary self-steering systems are standard for bluewater cruisers and offshore sailboats: wind vane steering gears and electronic autopilot systems. Both systems have advantages, and many sailors choose to install both systems on their boats.
Electronic Autopilot Systems
Electronic autopilot systems are the modern answer to self-steering. They’re easy to use, work without wind, and are an excellent option for near-shore cruising and short-term offshore sailing. Autopilots are also compatible with multi-hull vessels, unlike windvane systems.
The downfalls to these systems can be daunting, though. Electronic systems are complex and have numerous parts: displays, wiring, plotters, motors – the list goes on. To run an electric autopilot system, you’ll also need a generator. Most even have two generators, using one as a backup for reliability. As you’d expect, they also come with a higher price tag.
Self-Steering Wind Vane Systems
Windvane steering systems take a more traditional approach to self-steering. They rely on the wind to operate your boat on the desired course. Wind vane steering systems require no electricity, little maintenance, have few moving parts. They also come in several variations to fit your boat in the best way possible. Another massive benefit of a mechanical sailboat windvane is its robust build. This allows reliable and powerful performance in heavy weather conditions.
There are also several downfalls to a windvane system. They do not work in the absence of wind or under power, can add weight and stress to the boat stern, can be initially expensive to purchase, and won’t work on multi-hull vessels.
Types of Sailboat Wind Vane Systems
All wind vane systems direct a boat to a wind-based course, but they each do it differently.
Servo-Pendulum Wind Vane
Servo-pendulum windvane systems are the most common commercially available system, and they are a favorite among most sailors. The reliability for offshore sailing is a huge selling point. It re-affirms why these are the “classic” wind-driven autopilot systems.
Main steering servo-pendulum systems have control lines running from the primary steering quadrant to a wheel or tiller. As the wind pushes the pendulum, it directs the boat’s steering by way of the primary rudder. Because of this, the system is solely dependent on the power of the wind. The stronger the wind blows, the more force the system provides to push the boat back on the desired course.
Rudder steering servo-pendulum systems have the pendulum rudder connected to the primary boat rudder. It works almost the same as the “main steering system,” with a few minor differences. The wind pushes the pendulum rudder to the side, forcing water to pull the boat’s main rudder to change steering. The advantage of this system over the prior is that it involves fewer mechanical components, making it easier to check issues and fix any problems. The disadvantage is that it can be a bit trickier to set.
One of the biggest downfalls of either servo-pendulum system is that the pendulum rudder can not replace an auxiliary rudder. Unlike an auxiliary rudder, its one-dimensional operation makes it unable to run the system if the primary rudder fails. These systems can also create a cluttered cockpit due to the lines running from the steering quadrant. Lastly, servo-pendulum systems generally require more consistent maintenance and more common repairs.
Auxiliary-Rudder Wind Vane
Unlike servo-pendulum steering systems, auxiliary-rudder wind vanes are entirely independent of all other aspects of the boat. Instead, the main rudder is locked, and the auxiliary rudder steers the vessel after setting a powerful windvane to the desired angle. The main rudder is often locked to the left of center or slightly at an angle to balance the helm. One of the most significant advantages to these systems is that if the primary boat rudder fails, the auxiliary rudder can act as a replacement to steer the boat.
There are some important considerations to make when purchasing auxiliary-rudder wind vane steering gear. First, auxiliary-rudder windvanes put a significant amount of stress on the vane, making it vital that the model and components are well designed and made of quality materials. If you can source well-made parts, there is minimal risk while out at sea. There are very few moving parts and no critical lines attached to the system. Second, these systems are big, heavy, and bulky. Having such a massive piece of equipment at the stern of the boat isn’t always ideal in every scenario. Lastly, auxiliary rudders can be awkward to operate when the mizzen is in use on ketch-rigged vessels.
Trim-Tab Wind Vane
Trim-tab windvanes are less common than they used to be after the emergence of the steering technologies listed above. The system works by attaching a “tab” to the main rudder. The small surface of the trim tab makes it easy for the wind to move it from side to side, which then forces water over the primary rudder in the opposite direction to keep the boat on course. Those with the appropriate skills and know-how can even construct a trim-tab themselves, although we recommend that they do not rely entirely on a self-made system.
The major drawback to trim-tabs is that the ability to fine-tune the system is somewhat limited in heavy conditions.
How to Install a Sailboat Wind Vane System
Installing a wind vane on your boat is relatively easy, but it still takes a bit of planning.

Initial Considerations
All windvane models require installation at the center of the boat’s transom or as close to the center as possible. Depending on which system you choose to run, you may need to account for the steering lines that operate the system. Steering lines are approximately a quarter of an inch in diameter and need a clear path from the wind vane to the boat wheel. You may redirect the lines with steering blocks, but be aware that each block adds friction and lessens the overall efficiency of the steering system.
Balancing the Boat
Windvane gears adjust the course of a boat using the wind force at the surface. For this to happen efficiently, you’ll first need to ensure your boat is balanced and sailing as intended. Take your time to get the weight distributed evenly. You’ll also need to reef the sails appropriately so as not to be overpowered.
Adjusting the System for the Conditions
Regardless of the system, nearly all sailboat wind vanes have one or more adjustment features so that you can optimize performance in various conditions. When wind conditions are relatively light, you should expose the vane as much as possible so that the system receives the most force as possible. In heavy winds, however, you can lower the windvane to reduce the impact on the system. In some cases, the wind vanes have sensitivity adjustments where the vane meets the pivot, so you may not need to adjust the height as weather conditions change.
How to Engage a Sailboat Wind Vane System
Most wind vanes are relatively adaptable and can adjust to fit a variety of hull types. Some vanes are even customizable to bolt directly onto the boat. As with any other object you bolt to your hull, plan to through-bolt everything with the appropriate bedding and backplates for maximum security.
Operating a sailboat wind vane is far less complicated than you might expect. There are four standard steps to engaging a windvane:
- Deploy the Gear : To do this, attach the wind paddle and unfold the rudder to be placed in the water. Doing this should only take a few minutes at most.
- Connect the Control Lines : Control lines run from the windvane to the boat wheel and may have steering blocks included in the setup. The system may require you to make a few knots or use some hardware, but again, it’s a relatively easy process once you’ve completed it once or twice.
- Balance the Boat and Set a Course : With the wind vane deployed, balance your boat, set the course to the desired point of sail, and adjust the windvane to engage the steering.
- Evaluate the Course and Adjust as Needed : Adjust the vane to steer more accurately after evaluating your approach. Course adjustments are made by rotating and trimming the paddle to match your course.
Perfectly balancing your boat is one of the easiest ways to make your self-steering wind vane more efficient in the water. A vessel with poor balance or trim will not just sail inefficiently, but it will put unneeded stress on the wind vane system.
Have more questions about sailboat windvane systems and how you can best implement them on your boat? Reach out to the #Boatlife community on our forum with questions or comments!
If you found this article helpful, please leave a comment below, share it on social media, and subscribe to our email list.
For direct questions and comments, shoot me an email at [email protected]
Sharing is caring!
Reader Interactions
June 12, 2022 at 5:44 pm
Thanks for the useful information. However, you didn’t mention anything about the usefulness of wind vanes in light or downwind sailing. You mentioned the issue of a mizzen and auxiliary rudder, how do I understand that (as we sail a ketch and thinking about installing a Hydrovane.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
MB #20512 PO BOX 480 Sevenoaks Kent TN13 9JY
Tel: +44 56 0386 9163
Keep In Touch
Thank you for reading.
Join our online crew and find more about the #boatlife
- Account icon Log in

What Is A Sailing Wind Vane?
A sailing wind vane, also known as a wind indicator or wind arrow, is a device used in sailing to visually indicate the direction of the wind. It consists of a lightweight, arrow-shaped element that is mounted on top of a vertical mast or pole on the boat. The wind vane is designed to pivot and align itself with the direction from which the wind is blowing.

The wind vane is positioned at a height that allows it to catch the wind unobstructed by the boat's sails or other structures. As the wind blows, it exerts force on the arrow, causing it to rotate and align itself with the wind direction. This alignment provides a clear visual indication of the wind's flow, allowing the crew to quickly and easily determine the wind's direction.
Wind vanes come in various designs and sizes, ranging from simple and compact models for small sailboats to more sophisticated and larger ones for larger vessels. Some wind vanes incorporate additional features such as wind speed indicators or illumination for nighttime sailing.
How can I choose the best wind vane for my boat?
Choosing the best wind vane for your boat depends on various factors, including the size of your boat, your sailing preferences, and your budget. Here are a few considerations to help you make a decision:
Boat Size and Type
Sailboat wind vanes that can be mounted to the top or side of the mast are useful for boats of various sizes and types. Davis WindTrak 15 is ideal for large sailboats, while WindTrak 10 is designed for smaller boats.

Catamaran wind vanes often require unique attachments to the headstay bridle, such as those included with the Davis Telo-Cat .

Temporarily mounted wind vanes, such as Davis Black Max , are useful when transporting small Lasers and Sunfish boats. Black Max attaches to masts or booms with an elastic mounting band.

All-purpose wind vanes for use on a boat or at home, such as the Davis Spar-Fly , use a needle bearing wind vane that is unaffected by angle of heel and can be attached to the top or side of an object.

Determine your budget for a wind vane. Prices can vary significantly from a $60 non-electronic plastic wind vane, to a $10,000 electronic wind vane system with autopilot capabilities.
While most wind vanes are mounted at the top of a mast, others like the Davis Telo-Cat, can be mounted on the head stay bridle of a catamaran. Consider the mounting style that will be the most appropriate for you and your boat.

Davis instruments offers their "J-Base" which can be used to mount a wind vane on a vertical or horizontal surface. Davis Black Max includes a quick-release elastic band mount that attaches to masts and booms 1.5" to 2.5"
What good is a wind vane if you can't see where it is pointing? Get a model that includes reference arms with bright, easy to see reference tabs .

For easy viewing at night, Davis offers a light that can be installed on their Sport Wind, WindTrak 10, and WindTrak 15 indicators.
Functionality
Electronic vs. non-electronic wind vanes.
Electronic wind vane systems can cost up to $10,000 and often offer additional features beyond wind direction indication, such as wind speed measurement, data logging, autopilot systems, and integration with other onboard electronic systems.
Non-electronic wind vanes offer other advantages such as reliability, low maintenance requirements, independence from external power sources, simplicity of use, and cost-effectiveness. These factors make them a popular choice among sailors who value simplicity, durability, and a traditional approach to sailing.
Reliability
Non-electronic wind vanes are simpler in design and do not rely on electronic components pr sensors. This makes them less prone to technical malfunctions.
Low maintenance
Since non-electronic wind vanes have fewer components, they generally require less maintenance compared to their electronic counterparts. This can be particularly beneficial for long-distance sailors who may have limited access to repair facilities or power sources.
Independence
Non-electronic wind vanes do not require any external power source, such as batteries or electricity, to operate. This allows sailors to rely on the natural elements and reduces the need for additional equipment or power supply onboard.
Non-electronic wind vanes are often easier to understand and operate. They provide a clear visual indication of wind direction, allowing sailors to make quick and intuitive adjustments to their sails without the need for complex electronic displays or controls.
Cost-effective
Non-electronic wind vanes are inexpensive and usually cost under $100.
Wind sensitivity
Wind vanes such as Davis WindTrak utilize a sapphire jewel bearing suspension that is sensitive to very light breezes.
Definition of Marine Terms - Full List
Checkmark icon Added to your cart:
Wind and Weather Tools
The best sailboat wind direction indicators, wind speed meters & anemometers.

If you’re a sailing enthusiast you probably are no stranger to needing accurate wind speed and direction information. There are a slew of wind meters available today for just about every need: from handheld anemometers (wind speed meters), to sailboat mounted wind direction indicators and more. In this article, we’re going to do a roundup of the best wind meters for sailing, wind vanes for sailboats, the best anemometers for sailing, and more.
The best wind direction meters for sailing

WeatherHawk SM-18 SkyMate Hand-Held Wind Meter, Yellow
This floating anemometer is one of the best wind speed meters for sailing. It can measure wind speeds ranging from 0.5 miles per hour all the way up to 99MPH at user-selectable intervals of every five, ten, or 13 seconds (in addition to calculating the average wind speed and tracking peak speed for you). Plus it can also measure wind temperature and wind chill in both Fahrenheit and Celsius. One other nice feature about this sailboat anemometer is that it comes with a durable build and a bright yellow flip-shield. Naturally, it’s also water-resistant so if it falls into the water you’ll be able to easily spot it floating. Also comes with a loop for a lanyard or wrist strap if desired. A belt sheath is also available for this product.
For more handheld anemometers, see our full article: The Best Portable Anemometers & Portable Weather Meters .

Cape Cod Wind Speed Indicator for Sailboats
Cape Cod Wind & Weather instruments have been a staple of sailors since the company was founded in 1939. With an emphasis on quality American-made wind speed indicators, these gauges are built to last.
This wind speed indicator for sailing can mount on your sailboat either vertically or horizontally and it comes with a spinning cup wheel which can be mounted wherever you like (the supplied cable is 50 feet long and comes with a mounting bracket and screws). For wireless anemometers, see our related article: What is the Best Wireless Anemometer & Wireless Wind Speed Meter?
For decades Cape Cod Wind & Weather has supplied sailors with reliable real-time sailboat wind direction indicators, and this wind speed meter for sailing is no exception.
This unit measures wind speed from zero to 100 miles per hour and comes with a ten-year limited warranty. Pairs well with Cape Cod’s Wind Direction Indicator which matches with a lighted dial interface for wind direction metering.
Davis Instruments Windex 15 Suspension Bearing

This weather vane for sailboats mounts on your masthead through bolts or a tap and it provides an easy-to-read wind direction indicator. It’s one of the most popular sailing wind vanes on the market and this particular Davis Windex model is intended for medium to larger boats (the vane itself is 15 inches long; a smaller model exists for smaller boats). This model has what Davis calls a bird-proof spike to keep seagulls from trying to land on the instrument while you’re sailing. The vane itself features tabs that reflect in order to remain visible at night or in dark conditions.

Davis Instruments Spar-Fly Wind Indicator for Yachts and Dinghies
This compact sailboat wind direction indicator comes in a bright red color and has both a top and side mounting option. It measures 15 inches long, is highly visible, and weighs an astonishing 1.25oz for a highly responsive level of accuracy even in light wind conditions. The Spar Fly sailing wind vane is intended for sailing dinghies or small yachts and has great reviews.

Raymarine i60 Wind System with Masthead Instrument
The Raymarine i60 Wind System measures wind speed and direction as well as a slew of other readings with an easy-to-read digital-dial hybrid display and a masthead mounted instrument. It comes mounting gear and a 100 foot long (30 meters long) cable to connect the wind meter to the display. This is one of the best anemometers for sailing. Can measure wind speed/direction, maximum wind speed (peak), Beaufort scale, Tack and VMG. Plus it has a red backlight for dark conditions.
Frequently asked questions about windvanes for sailboats & the best anemometers for sailing
What features should I look for when shopping for a wind meter for sailing?
The best wind meters are often mounted anemometers made specifically for boating which have a display you can attach to your console. We have a few such wind speed meters for sailboats listed in this article, above.
Handheld anemometers for sailing usually float, are brightly colored, and are waterproof in case they fall into the water. They may also contain temperature gauges and loops for wriststraps or lanyards.
No matter the type of anemometer you choose, a large easy to read at a glance display is also especially useful for sailing anemometers.
What is an anemometer?
An anemometer is simply a wind speed meter. Some anemometers have digital displays, others have dial displays. The most sophisticated anemometers can also measure a variety of other metrics like temperature, dew point, humidity, barometric pressure, and so forth. Advanced anemometers can even give a personalized weather forecast for any location (especially useful if you’re using an anemometer in a spot where there isn’t a reliable weather forecast). Anemometers for sailing are useful because they give a clear and accurate reading of wind speed and direction. For more information about what anemometers are, read our related article: What is an Anemometer and What is it Used For?
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
- My Wish List
- Compare Products
- Create an Account
INTRODUCING RONSTAN ORBIT WINCHES™

- Remove This Item
Need some advice?
Official Sponsors of the Australian Sailing Team

Sailing With a Windvane
- By Alvah Simon
- Updated: December 9, 2019
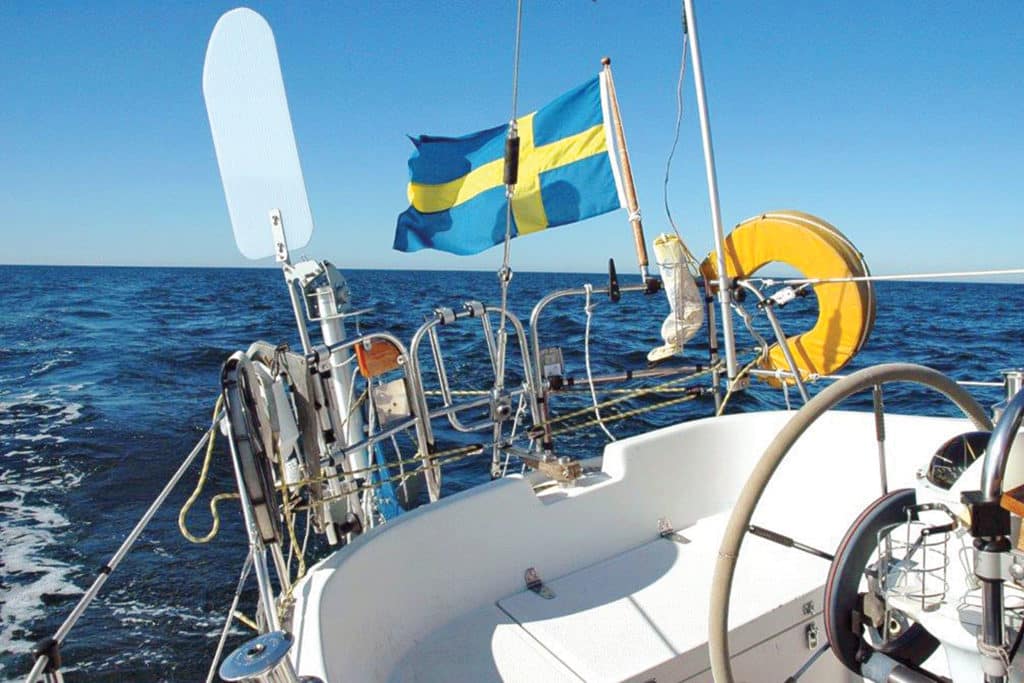

Once found only in the ascetic realm of single-handed sailing, self-steering gear has become ubiquitous on cruising boats, even fully crewed ones. That’s because a self-steering unit serves as an additional hand that possesses relentless concentration at the helm; subsists on only amps or lubricants; and, if properly trained, does what’s asked of it without question or complaint.
Reliable remote control of the helm relieves the fatigue and monotony of following a compass course at night. It allows time for sail changes and adjustments; horizon sweeps for ships; attentive navigation; and that quick dip below to check the bilges and grab a hot drink. Without question, self-steering makes for a more relaxed, enjoyable and safe voyage.
But the debate over which kind of self-steering is best for a sailboat — electric or windvane — rages on. I may be an old-fashioned belt-and-suspenders kind of sailor, but I believe both systems have their different strengths and weaknesses, and therefore complement each other. In other words, any vessel that is configured in a way that can accommodate both methods should do so.
In this scenario, the more robust mechanical sailboat windvane would be employed in heavier weather, while the electric autopilot would be used in light airs and under power, where directional corrections are provided not by the wind, but by a fluxgate compass. It is important to understand that while the electric autopilot maintains a steady compass course, a windvane is set to maintain a desired angle off the apparent wind, and therefore will follow any wind shifts or changes in wind velocity. While this does keep the sails perpetually in trim, the course must be monitored closely when in confined waterways.
That said, if forced to choose, I would go with the mechanical windvane, hands down. Vanes don’t rely on the ship’s electrical power supply, which serves as the last link in a long chain of delicate electrical components and breakable mechanical parts. Across the range of types and brands, mechanical windvanes generate amazing power in rough conditions (when needed most), coupled with notable durability. Almost 30 years ago I purchased an already well-used Aries windvane. It has faithfully followed me from boat to boat, and around the world, with clear indications that it will outlast me. On the other hand, I have an overflowing box of spare parts cannibalized from the many electric tiller-pilots I have chewed through in that same period.
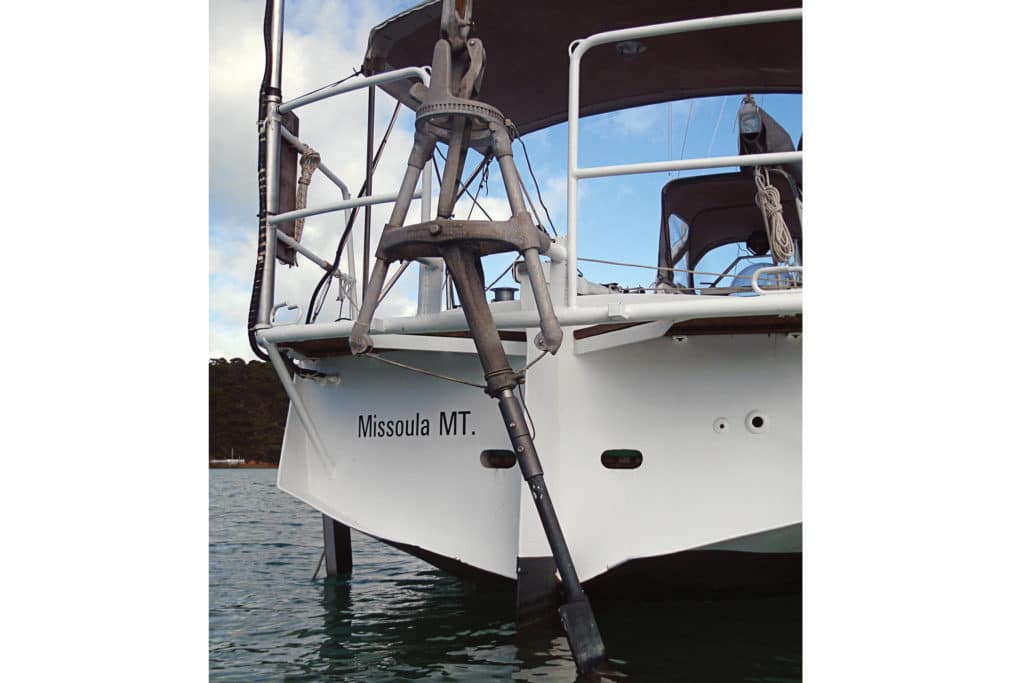

Types of Sailboat Windvanes
Introduced by the indomitable Blondie Hasler, founder of the OSTAR solo transatlantic race in 1960, the original sailboat windvane consisted of a direct coupling of a horizontally rotating (vertical axis) vane to a trim tab on the aft edge of a transom-hung rudder. Once the vane was fixed to the desired angle off the wind (using a round base plate with notches spaced at 5-degree intervals), any course change rotated the large vane like a weathercock. This in turn twisted the tab to one side of the main rudder, driving the rudder in the opposite direction, thus bringing the vessel back on course. The advantage to this system was its ease of construction and low cost, but it was best adapted to the waning style of transom-hung rudders. Also, a large vane was required to harness sufficient wind to power the trim tab. Therefore, especially in light airs, the tall, heavy vanes often reacted more to the yaw and roll of the vessel than to the wind, resulting in erratic meandering.
However, from this early and rudimentary concept, two sophisticated yet distinct types of vanes evolved: the servo-pendulum system (SPS) and the auxiliary rudder system (ARS). Both SPS and ARS systems employ a counterweighted horizontal- or vertical-axis wind vane to activate an appendage in the water, but the similarities end there. (To confuse the issue, there is now a hybrid system called the servo-driven auxiliary rudder, or SAR. But by first addressing the two basic concepts, a clearer understanding of this marriage of ideas will emerge.)
The SPS system — best represented by brands such as Aries , Cape Horn , Fleming, Monitor and Sailomat — uses the movement of the windvane to horizontally turn an independent servo-rudder (essentially a separate oar or paddle) that is deployed into the water. As the boat moves, the laminar flow of water presses against the positive lead on the servo-rudder, generating sufficient power to aggressively swing the servo-pendulum, or windvane, in one direction or the other.
While it is the power of the wind that directs the angle the servo-rudder presents to the passing water, it is boat speed through that water that exerts the considerable pounds of pull on the lines that run from the servo-rudder and through a series of turning blocks, ultimately connecting to the tiller (or, in the case of wheel steering, a drum in the center of the wheel). More simply, the servo-rudder does not turn the boat; it pulls on the tiller or rotates the wheel, which in turn moves the main rudder.
Perhaps the main drawback to this concept is the limited throw of the lines, as the distance of arc through which the pendulum swings is limited to the width of its supporting frame, an average of approximately 10 inches. This is no issue when connected to a tiller because one can fix the lines at the optimum point on the helm: high for more power, lower for a greater turning angle. But depending on the stop-to-stop ratio of a wheel steering system, the length of pull may not be sufficient to effectively control the vessel. This problem can be exacerbated by center-cockpit designs, as longer line lengths may stretch more, further limiting the effective length of pull.
The ARS system, best represented in the market by Hydrovane , employs an altogether separate appendage to steer the vessel. The boat’s main rudder is usually fixed amidship (or angled slightly to offset a lee or weather helm) and a second, auxiliary rudder, directed by a windvane, takes control of the steering. Thus, it is not only a self-steering device, but can also serve as an emergency rudder. Considering that all four of the Mayday calls I monitored on one of my Pacific crossings related to steering failure, this redundancy has considerable value. Because of the forces placed on this rudder it must be robust in construction, well fixed to the vessel, and of sufficient design and size to handily maneuver substantial tonnage.
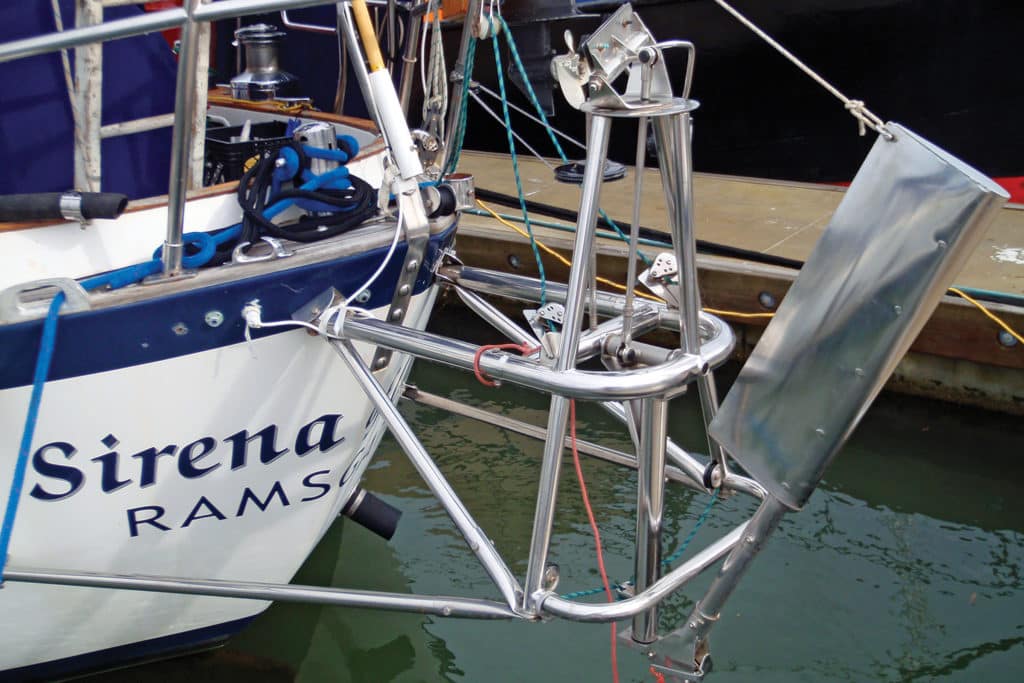

Pros and Cons of Sailboat Windvanes
There is a heated online debate among some of the manufacturers and distributors of the respective systems, each dismissing the supposed advantages of the other’s design concept while touting their own. I have sailed with both servo-pendulum designs and auxiliary rudders and found both to be practical and reliable; the final decision, to me, comes down to the type of vessel to which they will be attached, the steering system onboard, the conditions of sailing most likely to be experienced and the budget. In my opinion, the auxiliary rudder is more sensitive in light air, which is the average condition found in many recreational sailing areas. I’ve found the servo-pendulum model to be rock steady in conditions so rough that the average helmsperson would be exhausted within an hour.
But there are advantages and disadvantages to each approach. For example, the auxiliary rudder windvane has no provisions for being lifted out of the water to clear flotsam and seaweed; it can affect the backing characteristics of a vessel; and there’s no dedicated, engineered, breakaway “weak spot” when colliding with something like a submerged log. (In such instances, most servo-pendulum rudders simply flip up out of the way, and are popped back in place with the pull of a line.) On the other hand, auxiliary rudders don’t require lines that obstruct the decks and cockpit, a significant advantage depending on the placement of the helm.
To the latter point, perhaps too much is made of the difficulty in fixing, releasing and adjusting the tension of the lines on an SPS windvane. I corrected this problem with a $5 double jam cleat. Instead of using the typical link in a chain to connect to the tiller, I run my lines through an eye bolt on the tiller and back to the jam cleat. I can ease or tighten the lines balancing friction with precision; introduce infinite increments of bias to help balance the boat; and even when under tremendous pressure, immediately release the lines in an emergency situation.
A subtle but potentially important advantage of the SPS windvane is its natural aversion to broaching. As a steep wave slams into the quarter, the vessel can violently swing sideways. However, this same sudden sideways force pushes the servo-rudder in a direction that immediately tries to turn the boat back down the face of the wave. But even that point could be countered with the claim that by fixing the large main rudder in place, as in an ARS, substantial lateral stability is added to the vessel, thus minimizing any penchant to broach.
When mounting either system, the latest sailboat design trends — open, aft-entry cockpits and drop-down transoms — present new challenges. Hydrovane makes the unequivocal claim that its ARS windvane can be mounted off-center without affecting performance. Offsetting the vane opens access to the sugar scoop and/or the boarding and swim ladders. But as drop-down transoms, in particular, become ever beamier, there is less flat and fixed space available for robust windvane mounting. Depending on the stiffness of the vessel, one would not want to push the vane too far outboard for fear of lifting the auxiliary rudder clear out of the water on a heavy heel.
All SPS manufacturers stress the importance of meticulous centering during initial installation. Adapting to these new transoms, Monitor has introduced the SwingGate system to its windvanes. This is essentially a pivoting pushpit, much like a garden gate, with the vane attached. When the gate is open the boarding platform or swim ladder can be accessed, and when the gate is closed the vane sits firmly fixed amidship.
While completely appropriate for trimarans, windvane steering is not well suited for catamaran designs due to the dual rudders and high bridge-deck clearance.
As to pricing, there is no denying that the basic ARS units cost from 25 to 40 percent more than SPS models. Acting as the boat’s main rudder demands that the auxiliary rudder and mechanisms be constructed from heavy, high-quality materials. But if one chooses the swing-gate option, the additional cost of the gate structure must also be factored in.

Summing Up Self-Steering
When choosing a self-steering system for your sailboat, closely assess the design features of your boat and the conditions you will most often encounter. If you intend to make any kind of extended passages, consider a high-quality mechanical self-steering unit, possibly coupled with a lighter electrical system. Often, the two can be combined, offering the precision of fluxgate steering with the power and toughness of mechanical systems (see “ A Hybrid Self-Steering Solution “).
After the initial expense of purchase and installation, there will be no piece of equipment on your vessel more prized than your mechanical self-steering. I don’t know of a single long-distance sailor who has given a name to the roller-furling system, nor of one who has not named the windvane. Be it SPS or ARS, called Esther or Otto, trust me, out there on the Big Blue you will have many long and meaningful conversations with it.
But like all relationships, this one requires practice and patience. First and foremost, do not ask the windvane to make up for sloppy sailing. Balance your boat, starting with waterline trim. Keep the weight out of the ends and ensure that the sails are appropriately sized, set and trimmed to the conditions. Excessive heel is not only slow, but places the boat on lines that the designer never intended, resulting in poor tracking. Ensure that the windvane is not blanketed by superstructure or fed turbulent air via barbecues, solar panels or davits. Experiment with different settings, such as blade angle and line tension, to understand and optimize performance in various conditions.
Models that employ a mix of metals should be disassembled, cleaned and lubricated regularly to minimize electrolysis. When reassembling, use a high-grade barrier cream on all fasteners.
All models benefit from an occasional bath of scalding-hot fresh water to dissolve any buildup of salt, minerals and solidified grease.
And finally, for those concerned that these protruding, industrial-looking structures may ruin the lines of an otherwise lovely vessel, remember: “The rougher it gets, the better they look.”

Windvane Manufacturers
Aries Vane Gear ariesvane.com and ariesvanegear.com Cape Horn Marine Products Fleming Marine Hydrovane International Sailomat USA Scanmar International Voyager Self Steering Inc. Windpilot
Two-time circumnavigator Alvah Simon is a CW contributing editor. This article first appeared in the July 2014 issue of Cruising World as “A Vane to Steer Her By.”
- More: How To , installations , windvane
- More How To

Cruising with a Pet

Fatty Goodlander: Have Little, Want Less

How to Ride a Wave

How To Prioritize Your Sailboat’s Spring Checklist

A Big, New World

Cruising World On Board: Windelo 50

Into the Mystic: A Pacific Northwest Adventure

- Digital Edition
- Customer Service
- Privacy Policy
- Email Newsletters
- Cruising World
- Sailing World
- Salt Water Sportsman
- Sport Fishing
- Wakeboarding
Wind Vane Self Steering: The Ultimate Guide
by Emma Sullivan | Jul 20, 2023 | Sailboat Gear and Equipment

Short answer: wind vane self steering
Wind vane self steering is a mechanical device used on sailboats to maintain a desired course without the need for continuous manual adjustment. It utilizes the force of the wind and a vertical axis to steer the boat by adjusting the position of the rudder.
How Wind Vane Self Steering Works: A Comprehensive Guide
Title: How Wind Vane Self-Steering Works: A Comprehensive Guide to Sailboat Autonomy
Introduction: Sailing is the epitome of freedom, embracing the unpredictable elements as we navigate vast oceans. However, when embarking on long journeys or overnight trips, the need for reliable self-steering systems arises. Enter wind vane self-steering! In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into this ingenious system, explaining its principles and mechanics while highlighting its benefits for seafaring enthusiasts. So hoist your sails and embark on a journey of knowledge as we unravel the inner workings of wind vane self-steering.
Chapter 1: The Basics of Wind Vane Self-Steering 1.1 Understanding Sailboats’ Balancing Act: – Explaining the importance of maintaining equilibrium between the sail and rudder configurations. – Highlighting challenges faced when manually helming during long passages.
1.2 Introduction to Wind Vanes: – Defining the wind vane as an autonomous steering mechanism driven by apparent wind direction. – Detailing their various components such as vanes, sensors, gears, and linkages.
Chapter 2: Principles Behind Wind Vanes 2.1 Apparent vs True Wind: – Unveiling the distinction between apparent and true wind direction. – Describing how wind vanes utilize apparent wind to adjust course.
2.2 Weight vs Force Systems: – Distinguishing weight-driven systems (servo pendulum) from force-driven ones (auxiliary rudder). – Discussing pros and cons of each system in different sailing conditions.
Chapter 3: Mechanics of Wind Vane Self-Steering 3.1 Servo Pendulum System: – Unveiling the engineering marvels behind servo pendulum systems. – Analyzing their interaction with changing winds and seas.
3.2 Auxiliary Rudder Systems: – Detailing the mechanism of auxiliary rudder systems, their hydrodynamics, and adjustability. – Discussing how they maintain sailboat course while minimizing yaw.
Chapter 4: Installation and Utilization Tips 4.1 Installing Wind Vanes on Different Sailboats: – Providing step-by-step instructions for mounting wind vanes. – Highlighting considerations for various boat designs and sizes.
4.2 Calibration and Fine-Tuning: – Elaborating on the importance of accurate calibration to ensure precise steering. – Offering pro tips to optimize performance under different sailing conditions.
Chapter 5: Advantages and Limitations 5.1 Benefits of Wind Vane Self-Steering: – Presenting the advantages of autonomy, reduced energy consumption, and enhanced safety during long-haul sailing trips.
5.2 Considerations in Complex Sailing Conditions: – Identifying limitations related to challenging weather patterns or narrow channels, necessitating manual intervention.
Conclusion – Navigating the Open Seas with Confidence: Wind vane self-steering systems revolutionize long-distance sailing by providing sailors with a reliable automated alternative to constant helming. Understanding the principles, mechanics, and installation tips outlined in this comprehensive guide will empower seafarers to navigate vast oceans with confidence, leaving them more time to revel in the beauty of their surroundings. Embrace the freedom that wind vane self-steering offers–the transformative companion for every true sailor!
Wind Vane Self Steering Explained: Step by Step Process
When it comes to sailing, one of the most essential tools for achieving steady and reliable course keeping is a wind vane self-steering system. This mechanism harnesses the power of the wind to effectively steer the vessel autonomously, ensuring sailors can enjoy a smoother and more hands-free sailing experience. In this blog post, we will delve into the step-by-step process of how wind vane self-steering works, unraveling its inner workings and highlighting its benefits.
Step 1: Understanding the Basics
Before we dive into the intricacies, let’s start with the fundamentals. A wind vane self-steering system consists of three main components: a wind vane, a linkage mechanism, and auxiliary steering gear. The wind vane acts as a sensory organ that detects changes in wind direction while transmitting these signals to the linkage mechanism. The linkage mechanism then translates those signals into appropriate movements, which are eventually transmitted to auxiliary steering gear responsible for adjusting sail trim or rudder angle.
Step 2: Wind Vane Sensitivity Adjustment
Once you’ve set up your wind vane self-steering system on board your yacht or sailboat, it’s crucial to fine-tune its sensitivity for optimal performance. By adjusting the weight distribution or adding counterweights to your wind vane, you can achieve precise responsiveness according to prevailing weather conditions. This careful calibration ensures that even subtle nuances in wind direction are accurately detected by the wind vane.
Step 3: Setting Course
Now that your system is finely tuned, it’s time to set your desired course manually using traditional methods such as compass bearings or GPS coordinates. Aligning your vessel towards this designated course provides initial guidance for your wind vane self-steerer.
Step 4: Autonomy Engaged
As soon as you activate your wind vane self-steering gear, you enable an autonomous sailor’s best friend. Once the wind vane starts detecting any deviations from your initial course, it sends signals to the linkage mechanism, instructing it to make corrections. This process ensures that your vessel automatically adjusts its heading to maintain the desired course against external factors such as wind shifts or gusts.
Step 5: Continuous Monitoring
While wind vane self-steering handles most course corrections independently, it does require regular monitoring to avoid any potential issues and make minor adjustments as needed. It is crucial to stay vigilant and keep an eye on how your self-steering system performs with changing wind conditions and other environmental factors.
Benefits of Wind Vane Self-Steering
Now that we’ve dived into the step-by-step process of wind vane self-steering, let’s explore its advantages:
1. Hands-free Sailing: With a properly calibrated and functioning wind vane self-steering system, sailors can free themselves from continuously holding the helm, affording a more relaxed sailing experience.
2. Increased Safety: Wind vane self-steering reduces fatigue in long ocean crossings by maintaining a steady course, minimizing human error risk at times when crew members might be physically exhausted.
3. Energy Efficiency: By utilizing the power of nature (the wind), a wind vane self-steerer requires no fuel consumption or electricity input for operation, making it an environmentally friendly and cost-effective solution for long-distance voyages.
In conclusion, the step-by-step process behind a wind vane self-steering system involves understanding the basics of its components, adjusting sensitivity levels, setting an initial course manually while enabling autonomy through continuous monitoring. This technology not only enhances safety but also allows sailors to enjoy hands-free sailing while embracing Mother Nature’s forces to keep their vessels on track efficiently. So why not embrace this clever innovation and sail away into effortless adventure?
Frequently Asked Questions about Wind Vane Self Steering
Frequently Asked Questions about Wind Vane Self Steering: Unlocking the Secrets to Effortless Sailing
If you’ve ever been on a sailing adventure or have spent any time around seasoned sailors, you’ve likely heard of wind vane self steering devices. These ingenious contraptions have sparked curiosity and interest among many sailing enthusiasts, but like any new concept, questions tend to arise. In this blog post, we will dive deep into the frequently asked questions surrounding wind vane self steering systems and shed light on their working principles. Get ready to unravel the science behind these mechanical marvels!
Q1: What exactly is a wind vane self-steering system?
A wind vane self-steering system is a mechanism designed to keep a sailing vessel on course without manual intervention from the helmsman. This device utilizes the power of the wind to maintain a steady heading even in challenging weather conditions. By harnessing wind pressure and utilizing specially shaped vanes, wind vane self-steering systems elegantly counterbalance forces acting on sails and rudders.
Q2: How does a wind vane self-steering system work?
The operation of a wind vane self-steering system revolves around one fundamental principle—using apparent wind angles and force to steer the boat. Typically mounted at the stern of a vessel, these systems consist of an arrow-shaped vane that reacts to changes in apparent wind direction. As the breeze shifts or fluctuates in intensity, subtle movements in the vane are transmitted via lines or linkage mechanisms to adjust the position of an auxiliary rudder at the boat’s stern.
When the boat begins deviating from its intended course due to shifting winds, turbulence, or waves, this auxiliary rudder automatically adjusts itself according to variations in apparent wind angles detected by the main vane. Consequently, as long as there is sufficient breeze available for propulsion, these systems effectively maintain precise navigation even during extended periods at sea. It’s like having an invisible helmsman tirelessly steering your vessel, allowing you to relax and enjoy the journey.
Q3: Are wind vane self-steering systems compatible with all types of boats?
Wind vane self-steering systems are highly versatile and can be installed on a wide range of sailboats. Whether you have a small, single-handed cruiser or a larger ocean-going yacht, there is likely a system that suits your vessel. The main considerations when choosing the right wind vane self-steering system for your boat include size, weight, balance, and how well it integrates with the existing rigging setup. Manufacturers provide detailed guidelines and support to ensure compatibility with various boat designs.
Q4: Can wind vane self-steering systems handle different weather conditions?
Absolutely! Wind vane self-steering systems are designed to thrive in diverse weather conditions and adapt to changing environments. Whether you’re facing calm seas or rough waters with strong winds, these remarkable devices remain stable and steadfast in their coursekeeping abilities. However, it is essential to learn about any limitations specific to the model you choose based on sailing experience and intended use.
Q5: Are wind vane self-steering systems difficult to install?
While installing a wind vane self-steering system may require some technical know-how, most reputable manufacturers provide comprehensive manuals and guidance materials tailored for DIY installations. However, if you prefer professional assistance or lack the confidence in setting it up yourself, seeking help from expert marine technicians is always an option worth considering.
In conclusion, wind vane self-steering systems offer sailors an unprecedented level of autonomy on their voyages by effortlessly maintaining course while they sit back and take in the panoramic beauty around them. Their ingenious working principles elegantly leverage wind power to navigate through uncharted waters. Embracing one of these marvels on your own sailing adventure might just be the key to unlocking new levels of sailing satisfaction. So, batten down the hatches, set your sails, and let the wind vane self-steering system be your faithful navigator on this extraordinary journey!
Mastering the Art of Wind Vane Self Steering: Tips and Techniques
For sailors navigating the vast blue oceans, wind vane self-steering systems are an invaluable tool. These impressive devices not only alleviate the stress of manual helm control but also empower sailors to sail solo or in small crews with ease. However, mastering the art of wind vane self-steering requires more than just installing the equipment – it demands practice, knowledge, and a cunning understanding of its intricacies. In this blog post, we will delve into the depths of wind vane self-steering, providing you with tips and techniques that will have you sailing like a seasoned pro.
Understanding the Basics:
To begin our journey towards mastering wind vane self-steering, let’s start by unraveling its fundamentals. A wind vane self-steering system essentially functions based on an aerodynamic principle: it utilizes changing winds to adjust your boat’s course automatically. The device consists of a wind vane mounted atop your vessel’s stern along with various lines and connections to your ship’s wheel or tiller.
1. Sail Trim is Key:
Properly adjusting your sails plays a crucial role in maximizing the efficiency of your wind vane self-steering system. Ideally, before engaging the device, ensure that your sails are appropriately trimmed for optimal performance based on existing weather conditions. Fine-tuning this aspect will allow for smoother operation and minimize any unnecessary strain on both boat and gear.
2. Get Acquainted with Your System:
Understanding how every component in your wind vane self-steering system works is vital for seamless operation. Familiarize yourself with all cables, lines, blocks, attaching points, and mechanical adjustments within your setup through careful study of instructions provided by manufacturers. Additionally, consider practicing installation and removal procedures before setting sail to save time during maintenance or repairs at sea.
3. Devise Efficient Linkages:
Connecting your wind vane to the ship’s wheel or tiller requires creating a linkage mechanism that transmits the vane’s signals accurately. Carefully select and adjust mechanical linkages, ensuring that they offer proper responsiveness and minimal play. Remember, any slack in these connections will decrease accuracy and compromise performance.
4. Experiment with Tension:
Fine-tuning the tension on your wind vane’s lines is essential for achieving optimal response. Experiment by adjusting the tension – both tightness and looseness – of these lines based on prevailing conditions such as wave heights, wind strength, course changes, or boat speeds. This flexibility allows you to adapt your wind vane self-steering system according to real-time situations and enhance its efficiency.
5. Observe Nature’s Cues:
Nature can be an exceptional teacher when it comes to utilizing wind vane self-steering systems effectively. Observing how wind shifts affect your vessel’s course during different weather patterns will help you develop a keen sense of understanding impending changes in wind direction. By balancing this observation with data from meteorological sources or barometers, you can anticipate shifts ahead of time, allowing for precise adjustments even before they happen.
6. Make Incremental Adjustments:
Once your wind vane self-steering system is activated, it is essential not to make abrupt adjustments unless absolutely necessary. Instead, opt for small incremental changes when altering course or sail trim. Gradual adaptations ensure smoother transitions without overwhelming the device with sudden demands.
7. Continuously Monitor Performance:
Constant vigilance is key while learning to master your wind vane self-steering system completely. Continuously monitor its performance by observing your boat’s behavior relative to sea conditions (weather helm, leeway). Appropriate awareness combined with timely tweaks ensures efficient operation throughout extended voyages.
8. Seek Expert Advice:
When seeking mastery over any subject matter, there is no substitute for expertise gained through experience and shared wisdom. Engage with sailing communities, forums, or seek advice from seasoned sailors who have honed their skills in wind vane self-steering. Their firsthand experiences and clever tricks will provide invaluable insights to propel your learning curve forward.
In conclusion, mastering the art of wind vane self-steering is a journey that requires practice, experimentation, and understanding. By grasping the basics, fine-tuning sail trim, learning your system inside-out, observing nature’s cues, and making incremental adjustments while monitoring performance attentively, you can unlock the true potential of this remarkable piece of sailing technology. So hoist your sails high and let the wind vane guide you towards a new realm of solo or small crew sailing prowess!
Choosing the Right Wind Vane Self Steering System for Your Boat
When it comes to sailing, there’s nothing quite like the feeling of gliding through the open waters, with the wind in your hair and the sun on your face. However, navigating a boat can be a challenging task, especially when you’re all alone out on the vast ocean. That’s where wind vane self steering systems come into play.
A wind vane self steering system is an invaluable piece of equipment that allows sailors to maintain course without having to constantly adjust their sails or helm. This automated system harnesses the power of the wind to steer the boat, freeing up valuable time and energy for sailors to focus on other important tasks.
But with so many different options available on the market, how do you choose the right wind vane self-steering system for your boat? Here are some key factors to consider:
1. Boat Size and Weight: The first thing you need to take into account is the size and weight of your boat. Wind vane self-steering systems come in various sizes designed to accommodate different vessels. It’s important to choose a system that is specifically built for boats within your size range to ensure optimal performance and stability.
2. Ease of Installation: As a sailor, you want a wind vane self-steering system that can be easily installed without requiring extensive modifications or additional support structures. Look for systems that come with clear installation instructions and minimal hardware requirements.
3. Weather Conditions: Sailors know that weather conditions can change rapidly at sea. Therefore, it’s essential to select a wind vane self-steering system that can handle a wide range of weather conditions – from light breezes to heavy winds and high seas. Look for systems that are durable and capable of maintaining control even in challenging weather scenarios.
4. Sensitivity Adjustment: Every boat handles differently based on its design and load distribution. To ensure precise control, choose a wind vane self-steering system that allows you to adjust its sensitivity to match your boat’s characteristics. This flexibility will enable you to fine-tune the system for optimal performance and responsiveness.
5. Reliability and Durability: When you’re out on the open water, you rely heavily on your equipment. Therefore, selecting a wind vane self-steering system from reputable manufacturers known for their reliability and durability is crucial. Look for systems made from high-quality materials that can withstand the harsh marine environment for years to come.
6. Cost: While cost should never be the sole determining factor, it’s still an important consideration when choosing a wind vane self-steering system for your boat. Evaluate different options and compare their features, performance, and price tags to find the best value for your money.
Now, armed with these essential considerations, you can embark on finding the perfect wind vane self-steering system that suits your boat and sailing needs. Remember to carefully research different products and consult with fellow sailors or experts if needed. With the right wind vane self-steering system onboard your boat, you’ll experience smoother sailing adventures like never before!
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Wind Vane Self Steering
Introduction:
Wind vane self-steering systems are a remarkable solution for sailors aiming to harness the power of the wind to navigate their vessels. By allowing the wind to guide the boat’s rudder, these systems reduce manual effort and provide a more reliable means of steering. However, like any piece of equipment, wind vane self-steering systems can sometimes encounter common issues that require troubleshooting. In this blog post, we will delve into some possible problems and provide professional, witty, and clever explanations on how to overcome them.
1. Lack of responsiveness: One frustrating issue that sailors may encounter with wind vane self-steering is a lack of responsiveness. If your system seems sluggish or fails to react promptly to changes in the wind direction, there are a few potential causes.
Explanation: Just like us humans after an indulgent Thanksgiving dinner, wind vanes can become lethargic too! The most common culprit for unresponsiveness is excessive friction within the system caused by wear or improper lubrication. To tackle this issue, start by giving your system a good inspection. Look for any signs of wear on bearings and joints while applying lubrication generously where needed (Think spa day for your wind vane). If this fails to resolve the problem, it might be worth checking if any foreign objects or debris have made their way into critical components – just imagine trying to navigate gingerly during peak pollen season!
2. Oscillations and instability: Unwanted oscillations or instability in your self-steering system can make sailing feel like riding a bucking bronco! This issue can be concerning and potentially dangerous if left unresolved.
Explanation: Imagine you are attempting to steer straight but your trusty wind vane has gained an affinity for dancing instead – quite embarrassing! The primary reason behind oscillations and instability is often an imbalance between sensitivity settings and sail trim (imagine mismatched dance partners). Adjusting both variables can help find the sweet spot. Additionally, thicker or heavier sails may contribute to excessive oscillations, so it might be time to reassess your sail wardrobe and consider adopting a lighter ensemble for smoother sailing (we all deserve a wardrobe makeover now and then!).
3. Misalignment and wandering: Has your wind vane suddenly decided to become an explorer, sailing in any direction other than the one you intended? Misalignment and wandering can occur due to various factors.
Explanation: Picture this – you want your wind vane pointing north, but instead, it decides it wants to discover hidden treasures in the opposite direction – quite the rebellious spirit! Misalignment is commonly caused by incorrect installation or loose connections between the wind vane and the boat’s rudder. Ensure that all parts are securely fastened with the precision of a complicated jigsaw puzzle (but without the frustration). When resolving misalignment issues, imagine you are showing your wind vane some tough love – tighten those nuts and bolts until they can’t even think about misbehaving!
Conclusion: While wind vane self-steering systems generally offer efficient steering solutions for sailors, encountering common issues is not uncommon. By understanding these challenges and implementing our witty troubleshooting advice, your wind vane will be back in shape in no time. Remember, a witty approach combined with professional expertise ensures smooth sailing both on water and through blog posts!
Recent Posts

- Sailboat Gear and Equipment
- Sailboat Lifestyle
- Sailboat Maintenance
- Sailboat Racing
- Sailboat Tips and Tricks
- Sailboat Types
- Sailing Adventures
- Sailing Destinations
- Sailing Safety
- Sailing Techniques
United States
Netherlands

Save up to $3,000 on new electronics
Deals on FLIR M300 and M232 cameras
Wired Masthead Wind Transducer
Masthead wind speed and direction sensor for sailing vessels and powerboats
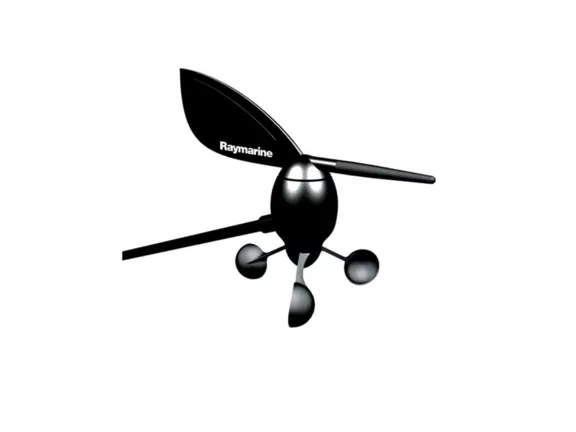

The wired masthead wind transducer provides accurate measurement of relative wind speed and direction.
When combined with other sensors like boat speed and compass, the masthead transducer provides the necessary wind information to calculate true wind speed, true direction and many other advanced data items.
Available in 2 different lengths, the 300mm short-arm version is the perfect choice for cruising sailboats or power boats. High performance sailing boats may prefer the 600mm long-arm version which moves the transducer farther away from the updraft of the boat's sails for enhanced accuracy.
- Durable anodized aluminum and UV-stabilized plastic construction
- Masthead mounting block and interconnect cable included
- Compatible with i60 Wind, iTC-5, ST60+ and ST60 series instruments
- Replaceable feather/pointer and speed cups (part number A28167)
Choose between standard short-arm or long-arm configurations.
Short Arm Wind Transducer supplied with 30m (97.5’) Cable

300mm length for cruising sailboats and powerboats
30-Meter (97.5-foot) interconnect cable included
Long Arm Wind Transducer supplied with 50m (162.5’) Cable

600mm length for high performance racing and cruising sailboats
50-Meter (162.5-foot) interconnect cable included
Wind Transducer Resources
- Specifications
What's in the box?
- Conformance

- Forums New posts Unanswered threads Register Top Posts Email
- What's new New posts New Posts (legacy) Latest activity New media
- Media New media New comments
- Boat Info Downloads Weekly Quiz Topic FAQ 10000boatnames.com
- Classifieds Sell Your Boat Used Gear for Sale
- Parts General Marine Parts Hunter Beneteau Catalina MacGregor Oday
- Help Terms of Use Monday Mail Subscribe Monday Mail Unsubscribe
Mounting a wind vane & mast float on 146
- Thread starter esterhazyinoz
- Start date Mar 10, 2010
- Hunter Owner Forums
- Day Sailers
esterhazyinoz
I don't have a mast float installed on mine and I just riveted the wind vane to the mast cap. I did install some of the noodles in the mast that to help the bouyance. I think Hunter modified the mast cap starting in 2004 and eliminted the hole that was causing the mast to fill with water in the event of a knock down.
esterhazyinoz said: I noticed some photos posted on this forum showing some owners (146/170) that have a mast float and a windex type wind vane (mounted off a bracket extending backwards from the mast). If anyone who has done this mod, would you please tell me if it was successful and how you did it? Always appreciate the advice of current owners. Cheers from Australia Click to expand
Good advice guys! I think I will put up a 'for sale' sign for the masthead float at one of the clubs here in Perth that has a large Hobie fleet. - On a slight tangent- what, do you think, is the most common reason for laying one of these boats down? - Mainsheet in cam cleat when a strong gust hits? HD
I got knocked down by a strong gust. The wind was blowing decent already and I should have rolled up the jib. You really don't know how far you can go until you get there. JerryA
I just re-read all the owners reviews of the 146 on this site. Some say the boat is stable and others say its very unstable. I guess it all come down to what you expect from a small boat with no ballast. Any boat that is over powered for the conditions will lay down, at least, and the small ones without mast flotation, turn turtle. In about 6 weeks, when my H15 lands in Fremantle, I'll get the chance to see for myself. Cheers, Hollis
On my Hunter 170 I find that any time wind starts blowing around 12 to 14 kts its time to reef the main. These boats are a lot of fun and I love the portability , but they do have their limits. First time I laid my 170 on its side it was super easy to get it right back up again. With sealed mast the tip of it will only sink about 1 foot underwater. I just swam out, grabed the end of a mast and threw it up in the air. Boat righted it self no problem. Unfortunately my main sheet got stuck and it didn't release properly so the second main caught air again boat took off on me like a rocket. Learnt few good lessons that day...lol cheers
Yep, I can just see that happening to me! Waving goodbye as my now righted boat takes off down the bay with my dog looking quizzically at me. Hollis
esterhazyinoz said: Yep, I can just see that happening to me! Waving goodbye as my now righted boat takes off down the bay with my dog looking quizzically at me. Hollis Click to expand
txjim said: That image keeps me very attentive to the wind when sailing solo! I used my 170 to teach the Boy Scout Sailing merit badge to my son's troop. Part of the lesson is capsize recovery and it takes a bit of effort in winds < 12 knots to knock the boat over. In addition to the standard recovery checklist, I tell them to ALWAYS have a dockline in hand before they right the boat! (I also tell them to make sure they recover my &^#@$ cushions, but that's another story....) Click to expand
Length of a rope with a small fender attached to it is exactly what I do now to avoid getting left behind...LOL I also carry a small Danforth anchor with me and here's why: H170 sits pretty high in the water, as a result boat offers a lot of hull side area for wind to push you around. Especially after a capsize its nice to be able to relax for a mintue and get your stuff back on board without having to fight the boat at the same time. This may seem like an overkill in a day sailor but I found an anchor to be very handy in the past. As I mentioned in my other post, this season I'll be trying the new configuration with a slightly lowered boom and a second reef point installed in the main. These two things should make a big difference in how the 170 handles. Cheers
Gee, if you need 2nd reef points you must have winds like we do here. Thay call it the Fremantle Doctor as it makes us feel better when it blow away the 100 degree plus heat at the height of summer. When I started sailing here I was amazed at the waves that were blown up by the winds on the river. Even though that boat had lead on her bottom there always were some hairy moments. I will certainly take your advice and have an extra set of reefing points cut into the mainsail when the boat arrives. BTW, As there is no dealership here on the westcoast, I will have to do the initial rigging myself. Any advice on tuning the rake of the mast? Cheers, H
I do most of my sailing on some sizeable lakes in the middle of Canadian prairies, wind is one thing we rarely lack around here. Weather can change quickly too, bringing with it some hefty winds and tall waves. I went with the second reef point more for safety sake than the sporting aspect of it. Unless I have a "heavy" and willing crew I will not be heading out if I have to start the day off with a second reef engaged. I'm not sure how similar the 140 setup is to the 170 but either way I would suggest going trough the Archive section of this website. There are literally tons of great posts dealing with the subject of rig tuning and other useful tricks on set up and sailing of these samll Hunters. When I first got my h170 I spent few days reading thru some of the older posts, a lot of it was of great help. One of the first and most helpful mods I did on my boat was getting rid of those cheap, crappy chain plates that Hunter supplies their standing rigging with and replacing them with some nice, adjustable Johnson quick-release shroud levers. As your rigging streches a bit over time those little things will make it a lot easier to keep it nice and tight. Apart from that I would just enjoy the boat for the first season and see which of the mods people talk about are suitable for your situation. Cheers,
esterhazyinoz said: ...what, do you think, is the most common reason for laying one of these boats down? - Mainsheet in cam cleat when a strong gust hits? HD Click to expand
I'm wondering how high up the sale a 2nd reef point should be?
- This site uses cookies to help personalise content, tailor your experience and to keep you logged in if you register. By continuing to use this site, you are consenting to our use of cookies. Accept Learn more…
- Shopping Cart 0
Marine Wind Indicators
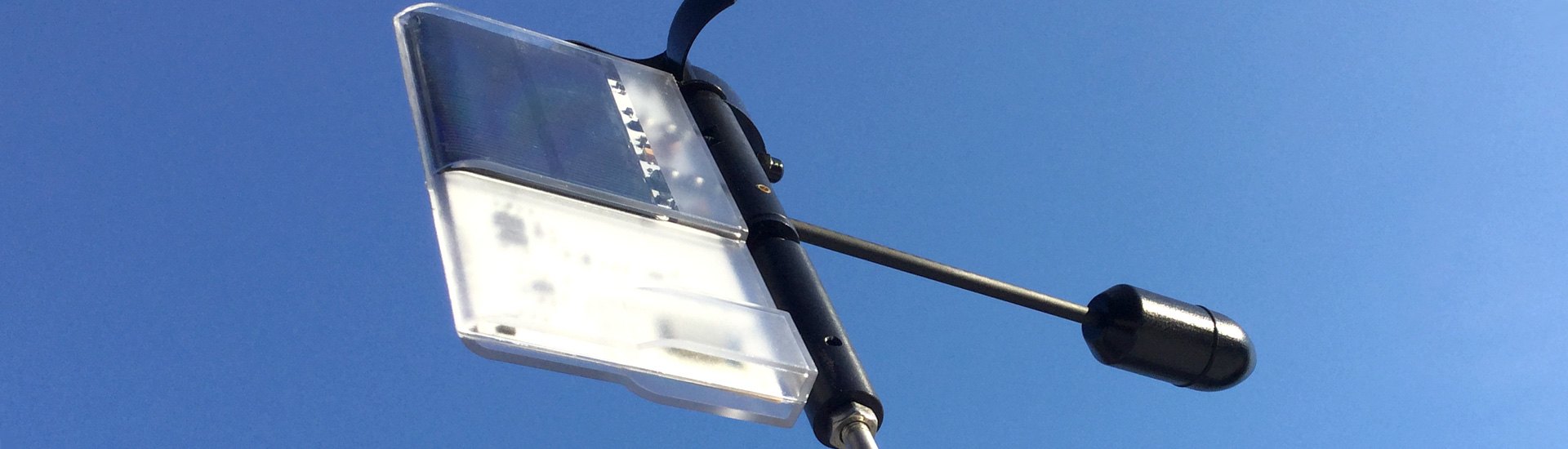

For boat junkies, thrill-seekers and everyone who eats, breathes and sleeps adventures, sailing is more than just a hobby; it’s a lifestyle. A sailboat is driven by the wind so make sure it has everything needed to let you sail off to the unknown destination with peace of mind. The weather offshore is unpredictable and can change rapidly so it’s essential to be aware of the current wind direction to take action when needed and keep your boat sailing in the right direction. And this is what a wind indicator does. It points out where the wind is blowing, assisting in vessel navigation and ensuring your safety. Knowing the current wind direction helps boatmen know when to raise the sails and where to direct them.
On our digital shelves, we handpick a comprehensive selection of premium wind indicators to help you get to your destination and back with confidence. We offer everything from wind wanes and spare wanes to airflow tels and mount hardware. The products provide the ultimate blend of quality, ease of installation and durability needed to help make your sailboat trip a safe, worry-free experience. Designed with style and functionality in mind, they come in a variety of designs and colors. You can opt for popular low-friction weather vanes with a strong, lightweight and balanced vane arm and durable support rod. You can also get top-notch tell tales and windsocks that will point you the airflow. So when sailing too slow or pinching, you'll be able to set the sails right and make your boat move faster.
Featured Brands


5 Best Wind Generators For Sailboats (2024)

Last Updated by
Daniel Wade
January 2, 2024
Wind generators, also known as micro turbines, have come a long way since their first appearance on the cruising scene back in the 1970's. Loud, relatively low output and large bladed, these forerunners of the modern day wind generators were both a mechanical marvel and a source of constant consternation. They were basically a small automotive alternator encased in an aluminum housing, with little thought into aesthetics or longevity. Cruisers equipped with an old Windbugger or K.I.S.S. wind generators come to mind as the loud boats in the anchorage no one wanted to be around.
As we all know, there are very few, if any, automotive products that last very long in a marine environment. A large stock of spare parts had to be stored in case of breakage, and daily maintenance consisted of checking the bearings, monitoring the voltage vs. wind speed for signs of decreased output, and rotating the blades into the wind when the boat position changed.
Today's best wind generators boast such features as CAD designed, self-feathering composite blades that are whisper quiet, brushless magnetic alternators, automatic braking and over-charge protection. Boxy aluminum housings have been replaced with sleek, carbon fiber and fiberglass nacelles.
While you may spend a small fortune on a wind generator that has all of these features and more, you can also opt for more budget friendly models, readily available from Amazon, Home Depot and other on-line retailers. The best wind generators are usually the most expensive, but when you are looking at the lower cost models, remember to add in the cost of wiring, mounting hardware, remote monitoring stations and installation, should you choose not to do the work yourself. Not all wind generators are purpose-built for the marine environment. Buyer beware: a turbine designed for the hobbyist on land will not stand up to the rigors of an offshore passage.
Table of contents
As with any mechanical device you are researching, it is a good idea to learn some of the terminology associated with the product. Not all of us know the meaning of 'swept area', 'power capture' or 'yaw error'. Likewise with the electrical side of the wind generator. Learning about output wattage, amps, and microprocessors can seem like a daunting task, but it is necessary to know these terms before you shell out hard earned cash for a quality wind generator.
Some features of wind generators, such as weather-proof coatings and low-noise operation, are common to all makes and models. The use of rare earth elements like Neodymium, (Nd2FE14B, used in magnetic rotors), can add hundreds of dollars to the price of some of these wind generators, but defiantly do add to the overall dependability of the unit.
Some of the more desirable things to look for in a wind generator are:
- Ease of Operation
Also known as plug-n-play, the simpler the set-up, the better. Choose a model that has built-in controllers, that ???makes for less complicated wiring runs. A remote monitor is handy to check on the status of the charging system without crawling into the battery room, or looking up to see if the blades are still turning. If you are ordering your generator and having it shipped, ask your salesman to be sure it has detailed assembly instructions and perhaps an owner's manual in either DVD or booklet form.
- Low Cut-In Speed
Wind generators work best when the blades are humming along in 20 knots of wind, but that's not always the case. Low cut-in speed means your batteries are getting a charge in the lightest of airs, if only a trickle charge.
If you happen to be ashore when the wind kicks up, you don't want your turbine to spin wildly out of control. Some generators feature a type of automatic speed governor that slows the blades down before they self destruct. Back in the day, you had to pull down on a cord to apply the brakes, then climb up the mast or mounting pole and manually tie off the blades.
- Over-Charge Protection
A 'brake' also kicks in when the batteries are nearing or at full capacity, to prevent overcharging. Some controllers slow the rotation of the blades, others 'dump' the excess power generated through a resistor and heat sink. Wiring an in line reset-able fuse can prevent damage to your batteries should a malfunction occur within the charging system.
- Portability
If you are one of those part-time sailors who cruises for a few months, then dry-docks your vessel for the off-season, choose a light-weight portable wind generator you can set up at home to off-set your electric bill. In case of a hurricane or other emergency when there is no power for days at a time, your wind generator can power cell phone chargers, laptops and rechargeable battery stations. Removing your wind generator and locking it away in the cabin also deters thieves. Portable wind generators that are light can be mounted on higher surfaces without worrying about upsetting the balance of your boat. The heavier the generator, the lower it should be mounted, allowing for safe passage under and around those spinning blades, of course!
It is also a good idea to know your boat's needs and desires before settling for a low cost, low output wind generator. Everything that runs off a battery, including the DC to AC inverter, should be listed, along with their amp/hour draw, to determine how much power you will need to generate. Compare your toys with your reserve amps of your house battery bank. Do you just have a few LED bulbs and a masthead light to run at anchor? Then you can get by with a low output generator. Are you keeping a keg cooler, stereo, disco ball and Netflix going all night? When underway, are you powering SSB, weatherfax, VHF and radar? Then you need a rack full of batteries, and a wind generator with the capacity to keep them topped off.
Speaking of batteries, make sure the wind generator you purchase can charge all the different batteries available. Even if you only have wet-cell lead/acid marine batteries now, you may upgrade to AGM, Gel or even LiFeMgPO4 (Lithium Iron Magnesium Phosphate) batteries in the future. Some wind generators and their controllers are not advanced enough to charge these newer power sources.
Unless you are well versed in the application of electrical theory and DC current, you probably don't know much about wire size and current loss. Even the best wind generator will not function as advertised if the power can not get from the blades to the battery. If you have a long run from your generator to the battery bank you intend to charge, make sure your wires are correctly sized to prevent line loss from resistance and over heating. Most installation manuals will have a wire chart included for DIY installations, and there is always a help line to the manufacturer.
Here are four out of the dozens of wind generators out there that have positive reviews and some of the most desirable features.
1.) Superwind 350, 353
This German manufactured turbine features their patented Auto-Feathering Overspeed-Avoidance System. This is basically the same method a helicopter uses to gain lift, and settle back down. As the wind speed reaches 25 knots, the blades 'feather', or dump air, making them less efficient, and slowing their speed. As the wind lessens, the blades re-pitch, becoming more efficient. This action delivers a steady flow of charging current to the batteries, without going into a shut-down mode to prevent overcharging, as some models do. The Superwind generators also can be combined with solar panels and conventional diesel generators. The Superwind generator family also uses a brushless A/C stator for maximum control of noise and radio interference while the unit is producing power. Two sets of bearings in the 350 make for smoother operation and overall longer bearing life. Available in 12v, 24v, or 48v outputs. At close to 30 lbs, these units are well built and dependable. With a price tag right around $2,700 for the Superwind 350 kit, you can expect German Engineering at it's finest. https://www.superwind.com/superwind-350-353/
2.) Automaxx
The Automaxx line of wind generators comes in 12v, 24v 48v models, in outputs from 400w up to 1500w. Survival wind speeds are listed at 110mph, but we hope you would never have to put that spec to the test. With very low cut-in speeds of less than 6mph, you will get charging amps on the slightest breeze. All their models come with auto-braking and manual braking system protection, over charge and over-speed protection. The 3600 rotation of the power head keeps the unit into the wind, even when you are docked or med-moored. Simple plug and play setup with an internal MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) charge controller makes the DB400 an easy to install unit, while their other models feature a remote charge controller. Works well when combined with solar chargers. At 16.75 lbs., it is lighter in weight than the Superwind, and it's seven times less expensive at around $400.00 for the DB400.
https://www.automaxxwindmill.com/
3.) MarineKinetix MK4
One look at this brand's marketing home page is like an advanced course in wind generator physics. The list of specs for it's models is truly impressive. Not only do they boast all the latest technologies featured in their product, they explain all the scientific jargon they use in terms us simple sailors can understand. They have been providing wind generators to the sailing community for 8 years now, and have a devoted following.
If you need to know the difference between $400.00 wind generators and $1,800 units, check out the product overview section of their website.
The MarineKinetix brand has the the industries best 3 year limited warranty, so they must be pretty sure about their product.
The 12v models of this brand are currently out of stock, due to parts supplier back-orders, but if you are in the market, there are plenty of 24v and 48v units in stock. https://store.marinebeam.com/marinekinetix-mk4-marine-wind-generator/
4.) Rutland 1200
One of the quieter wind generators out there, the U.K. made Rutland has a long track record of dependability and customer satisfaction. A manual switch is used to stop the blades when high wind is expected, there is no auto-brake. The Rutland can be combined with solar panels up to 20A, and can be also be used with deep cycle gel or AGM batteries, and there is a remote digital display available. One of the Rutland's best features is it's Tri-namic Blade profile design, which achieves low start-up speeds, silent operation in any wind, and maximum power transfer from wind to rotor. Overall good performance and features for the $1,600.00 price tag. https://www.emarineinc.com/Rutland-1200-Wind-Turbine
5.) DuoGen-3
Wind generators are a fairly common sight in most anchorages, and towable generating devices have been around for some time. The DuoGen-3 combines the two into one multi-use charging system. Underway, the high strength carbon fiber mast is lowered down to submerge the blades. At anchor, the unit functions like a typical wind generator. The results are impressive. In the water mode, the DuoGen-3 generates 200 Watts @ 16 amps cruising at 8 knots. Wind generators do not do well sailing downwind, so this may just be the answer. Available in 12v and 24v versions. Charging regulators are not included, so monitors and controllers have to be matched to the unit and sourced locally. https://eclectic-energy.co.uk/
Choosing the right wind generator for your vessel should be a pretty straightforward process, once you have an idea of your needs, the area you will be cruising in, and how long you expect to be 'off the grid'. If one generator is simply not enough because of the size of your battery banks and the load you put on them, you may need to purchase a pair of turbines. Customer support and availability of parts may be the determining factor in your purchase. Talk to other wind generator owners, and get a feel for what they have experienced with their current of former wind generators.
Related Articles
I've personally had thousands of questions about sailing and sailboats over the years. As I learn and experience sailing, and the community, I share the answers that work and make sense to me, here on Life of Sailing.
by this author
Sailboat Upgrades
Most Recent

What Does "Sailing By The Lee" Mean?
October 3, 2023

The Best Sailing Schools And Programs: Reviews & Ratings
September 26, 2023
Important Legal Info
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies.
Similar Posts

How To Choose The Right Sailing Instructor
August 16, 2023

Cost To Sail Around The World
May 16, 2023

Small Sailboat Sizes: A Complete Guide
October 30, 2022
Popular Posts

Best Liveaboard Catamaran Sailboats
December 28, 2023

Can a Novice Sail Around the World?
Elizabeth O'Malley
June 15, 2022

4 Best Electric Outboard Motors

How Long Did It Take The Vikings To Sail To England?

10 Best Sailboat Brands (And Why)
December 20, 2023

7 Best Places To Liveaboard A Sailboat
Get the best sailing content.
Top Rated Posts
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies. (866) 342-SAIL
© 2024 Life of Sailing Email: [email protected] Address: 11816 Inwood Rd #3024 Dallas, TX 75244 Disclaimer Privacy Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Improve sailing performance with a wind indicator for your sailboat. A sailboat's wind vane, also called a spar or masthead fly, shows in real-time the direction of the apparent wind, which you can use to trim your sails and sail most efficiently. ... While most wind vanes are mounted at the top of a mast, others like the Davis Instruments ...
THE WIND DIRECTION INDICATOR. The WINDEX Wind Direction Indicator is an indispensible tool for sailors of all levels since it allows instant and accurate wind information at all points of sail. The WINDEX is a Swedish invention from 1964 that is currently sold in more than 40 countries across five continents. In total more than 1,500,000 WINDEX ...
Bow Vanes. Single sail boats, such as Lasers and Optimus dinghies often clamp wind indicators on the forward side of the mast (see Practical Sailor, January 2018, Top Notch Wind Indicators). Without a jib to interfere with windflow or to luff at every wind shift (thus serving as a wind vane), they give a real-time estimate of wind direction.
When sailing downwind, a wind vane is a more precise indicator of apparent wind direction than shroud telltales, which are affected by flow off the sails. To see this, try a boat that has a wind vane. Sail downwind and adjust your heading so the wind vane points directly along the fore and aft axis of the mast.
That fragile plastic wind vane at the masthead looks like a child's toy to a lubber. Its a nautical curiosity perched at the top of a yacht that is also equipped with a comprehensive electronics suite. While we can certainly sail without wind indicators and telltales, judging the strength and direction of the wind by its effect on the sails ...
Windex offers a range of masthead wind indicators for sailboats from 15 to 100 feet. Windex vanes are sturdy, responsive, and easy to see at night with reflector tape and adjustable tacking tabs.
Golden Globe Update Day 113: [GGR Leader Jean-Luc Van Den Heede sailing the Rustler 36 Matmut] was full of praise for his Hydrovane self-steering. "In a gale it has a big advantage because it is not steering the boat's rudder, but has its own. This little rudder is far more efficient than the big rudder.". - Jean Luc Van Den Heede on ...
A sailboat wind vane is a mechanical self-steering system that requires no electricity, fuel, or manpower to operate. It's the perfect addition to bluewater cruisers and offshore sailboats. While a mechanical self-steering wind vane can't hold you on a compass course, they're more accurate than human steering over long distances.
A sailing wind vane, also known as a wind indicator or wind arrow, is a device used in sailing to visually indicate the direction of the wind. It consists of a lightweight, arrow-shaped element that is mounted on top of a vertical mast or pole on the boat. The wind vane is designed to pivot and align itself with the direction from which the ...
WINDEX 15 is the perfect choice for all family and racing boats from about 29 to 40 feet. The WINDEX Wind Indicator offers exceptionally good performance. The secret is the needle that rests in a sapphire layer, which means that Windex 15 finds the shifts even in extremely weak winds. Reflector tape on the vane and tacking tabs make Windex® 15 easy to see day and night. Windex® vanes are ...
This weather vane for sailboats mounts on your masthead through bolts or a tap and it provides an easy-to-read wind direction indicator. It's one of the most popular sailing wind vanes on the market and this particular Davis Windex model is intended for medium to larger boats (the vane itself is 15 inches long; a smaller model exists for smaller boats).
Step 1: Choose the Right Wind Vane. Before getting started, it's essential to invest in a quality wind vane that suits your sailboat's specific requirements. Look for one designed for offshore sailing as they are built to withstand harsh weather conditions. Step 2: Find the Ideal Mounting Location.
The WINDEX Dinghy Wind Indicator s designed for dinghies and smaller sailboats with quick attachment for the mast. Ideal for boats 10 to 20 feet in length. The quick fix allows easy removal of WINDEX Dinghy without using any tools. ... Davis Instruments introduces Blacksmith Wind Vanes, made from super lightweight 3D carbon fiber and ...
Keenso Sailboat Wind Vane, Marine Boat 304 Stainless Steel Weather Vane Wind Direction Indicator with Luminous Reflector for Yacht Sailboat Yard Boat/Yacht Spare Parts. 2.0 out of 5 stars 2. $45.62 $ 45. 62. Typical: $48.19 $48.19. FREE delivery Wed, Sep 20 . Or fastest delivery Tue, Sep 19 .
RFVANE-H Carbon Wind Vane Pro, Horizontal/ILCA. Carbon - Horizontal Wind Vane. $70.64. VIEW DETAILS. Add to Wish List Add to Compare. RFVANE-K Wind Vane Pro, Crazy Kids/Opti. Fibreglass - Crazy Kids. $29.95. VIEW DETAILS.
Updated: December 9, 2019. Manufactured in Sweden since 1976, Sailomat windvanes employ the servo-pendulum system (SPS) and are available in models to fit yachts from 26 to 55 feet LOA. Courtesy of Sailomat. Once found only in the ascetic realm of single-handed sailing, self-steering gear has become ubiquitous on cruising boats, even fully ...
Short answer: wind vane self steering Wind vane self steering is a mechanical device used on sailboats to maintain a desired course without the need for continuous manual adjustment. It utilizes the force of the wind and a vertical axis to steer the boat by adjusting the position of the rudder. How Wind Vane Self.
The operation of a windex weather vane on a sailboat. Mounted on a patented threaded attachment, the windex weather vane is fixed at the top of the mast of a sailboat in order to better capture the slightest change in wind direction. A real lookout for the boat, it is visible in all circumstances thanks to its reflective bands.
The 26M has a mast that rotates at the base, I'm guessing some 10 to 15 degrees. So, if the base of wind vane is fixed to the mast, then the base of the wind vane AND the tacking tabs would rotate with the mast. While this should not affect the vane itself which spins freely with wind direction or apparent wind, the "tacking tabs" moving with ...
When combined with other sensors like boat speed and compass, the masthead transducer provides the necessary wind information to calculate true wind speed, true direction and many other advanced data items. ... Boxed: 2.5 Kg (5.5 lbs), Wind vane assembly: 0.2 (0.4 lbs), Cable assembly: 1.2 Kg (2.6 lbs) Dimensions : Arm length: 300 mm (11.8 in ...
Jul 10, 2009. 32. Hunter 170 lake Manitoba. Mar 12, 2010. #3. esterhazyinoz said: I noticed some photos posted on this forum showing some owners (146/170) that have a mast float and a windex type wind vane (mounted off a bracket extending backwards from the mast). If anyone who has done this mod, would you please tell me if it was successful ...
Spar-Fly™ Wind Vane by Davis Instruments®. Spar-Fly combines needle bearing balance, high impact plastic, and marine grade metals for unsurpassed sensitivity and durability. ... Mast Pin Set for Optimist Pro™ Wind Vane by Davis Instruments®. If you're an avid sailboat enthusiast looking to enhance your experience on the water, then top ...
Automaxx. The Automaxx line of wind generators comes in 12v, 24v 48v models, in outputs from 400w up to 1500w. Survival wind speeds are listed at 110mph, but we hope you would never have to put that spec to the test. With very low cut-in speeds of less than 6mph, you will get charging amps on the slightest breeze.